3.3.3 Economies and diseconomies of scale
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
economies of scale
cost advantages of production on a large scale as a result firms will exrience increasing returns to scale
diseconomies of scale
average costs rise with increaisng outut the firm exeriences decreasing returnes to scale
increasing retunrs to scale
occurs when an increase in inuts leads to a larger than proportional increase in output
%change in output > % change in input
decreasing returns to scale
occurs when an increase in the quantity of inputs leads to a less than proportional increase in the quantity of output
%change in output < % change in input
internal economies of scale
when unit costs of one firms falls as outut increases
tyes of internal economes of scale 6
purchasing
risk bearing
financial
technical
managerial
marketing
Financial economies of scale
Large firms often receive lower interest rates on loans than smaller firms as they are perceived as less risky
Managerial economies of scale
Large firms will be able to employ specialist manager who are more efficient at certain tasks and make better decisions.
number of managers isnt depended on production scale so reduces management cost per unit
marketing economies of scale
large firms spread the cost of advertising over a large number of sales reducing ac
reuse marketing materials in different geographical regions
cost per product of advertising several products may be also lower than cost of advertising just one as can advertise several products at once
benefit from brand awareness so less advertising needed
purchasing economies of scale
buy raw materials in greater volumes and receive a bulk purchase discount
Technical economies of scale
production line methods can be used by large firms to make a lot of things at a low cost
invest in more specialist and expensive machinery increasing production
workers can specialise
get bigger warehouse cheaper per m²
risk bearing econoies of scale
large firms can diversify into different prodcut areas and marjet so more predictable oevrall demand more able to take risks as if product is unsuccesful other sales will absorb cost of failure
external economies of scale definition
cost benefits for members because they are members of an industry or because of their location
tyes of external economies of scale
ancillary firms move closer to major manafacturers to cut costs and generate more bsiness
improved transport links develo around growing industries
increase in skilled labour can lower cost larger the geograhic cluster the larger pool of skilled labour colleges teach skills required
favourable legislation
examle of georgahic cluster
car manufacters in sunderland rely on the service of 2500 ancillary firms
silicon valley california large pool of highly skilles technology workers creates a network that benefits firms by attracting talent and sharing ideas
example of transport links
transport links around the M4 corridor tech area between reading and bracknell have experienced significant improvement
example of favourable legislation
animation cluster in bristol and bath is growing due to tax incentives offered to the industry by the government
internal diseconomies of scale
wastage and loss can increase as materials seem in plentiful supply and large warehouses can lead to mroe things being lost and mislaid
communication more difficult affecting staff morale
managers less able to control wat goes on
harder to coordinate activities between different fivisions and deparrments
workers might put their departments interests before the companies leading to less cooperation and lower efficienc
external diseconomies of scale
as a whole industry increase price of raw materials increases as higher demand
buying large amounts may not make the cheaper per unit
returns of scale grah
when returns to scal are increasing lrac will fall
when returns to scal are constant lrac will stay the same
when returns to scale are decreasing lrac will rise
lrac are minimises at the minimum efficient scale of rosuction
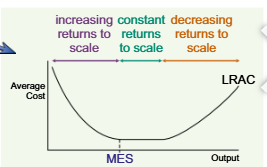
minimum efficient scale
lowest cost point on a long run average total cost curve lowest possible cost er unit that a firm can achieve in the long run
constant returns to scale
where firms increase inuts and receive an increas ein outut by same %