Viruses and Prokaryotes: Diversity and Impact
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Virus
Infectious particle needing host for replication.
Capsid
Protein coat enclosing viral nucleic acid.
Glycoprotein spikes
Mutating proteins aiding virus in evading immune system.
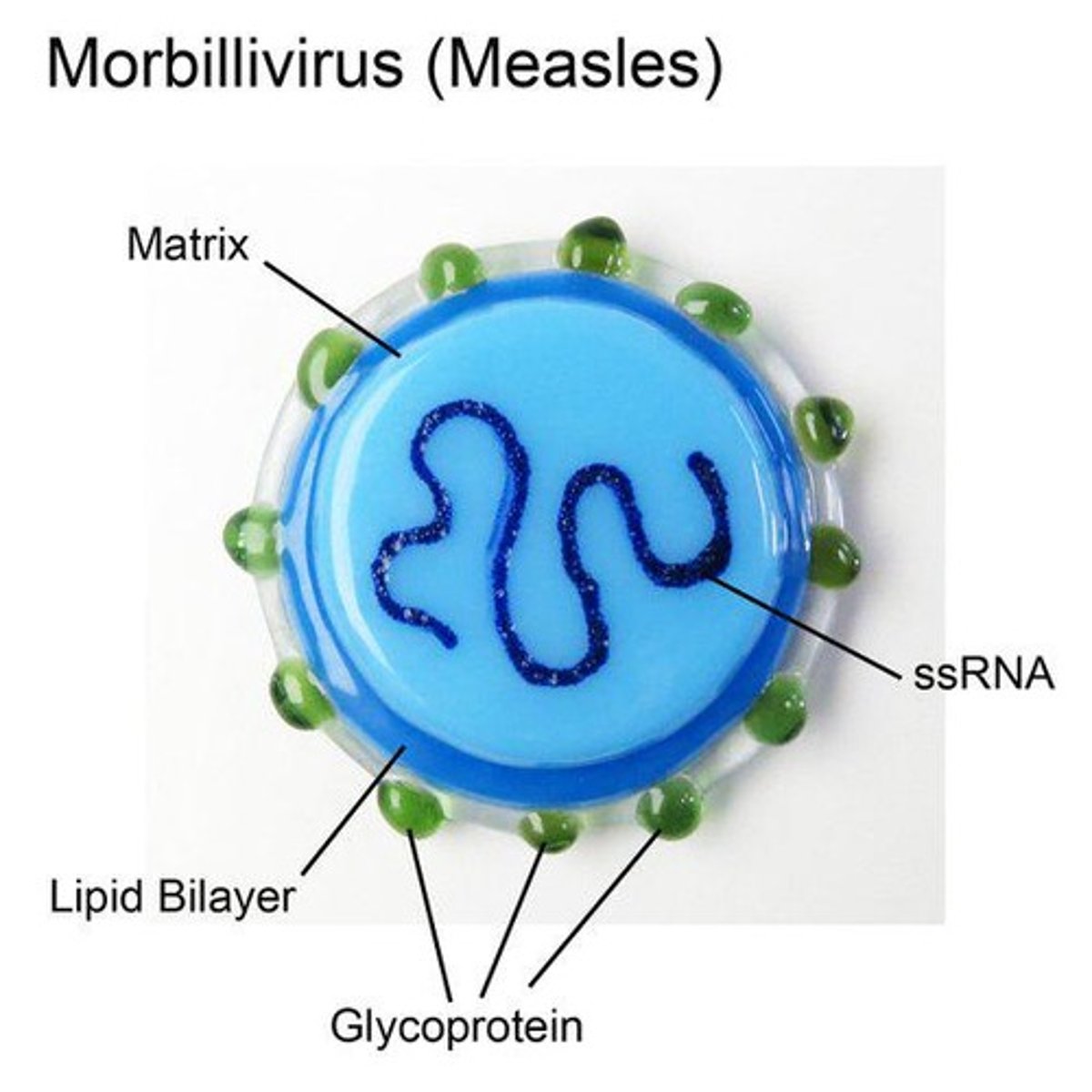
Sea Star Wasting Disease
Weakens starfish, increasing bacterial infection risk.
Influenza Virus
RNA virus causing respiratory illness, H1N1 subtype.
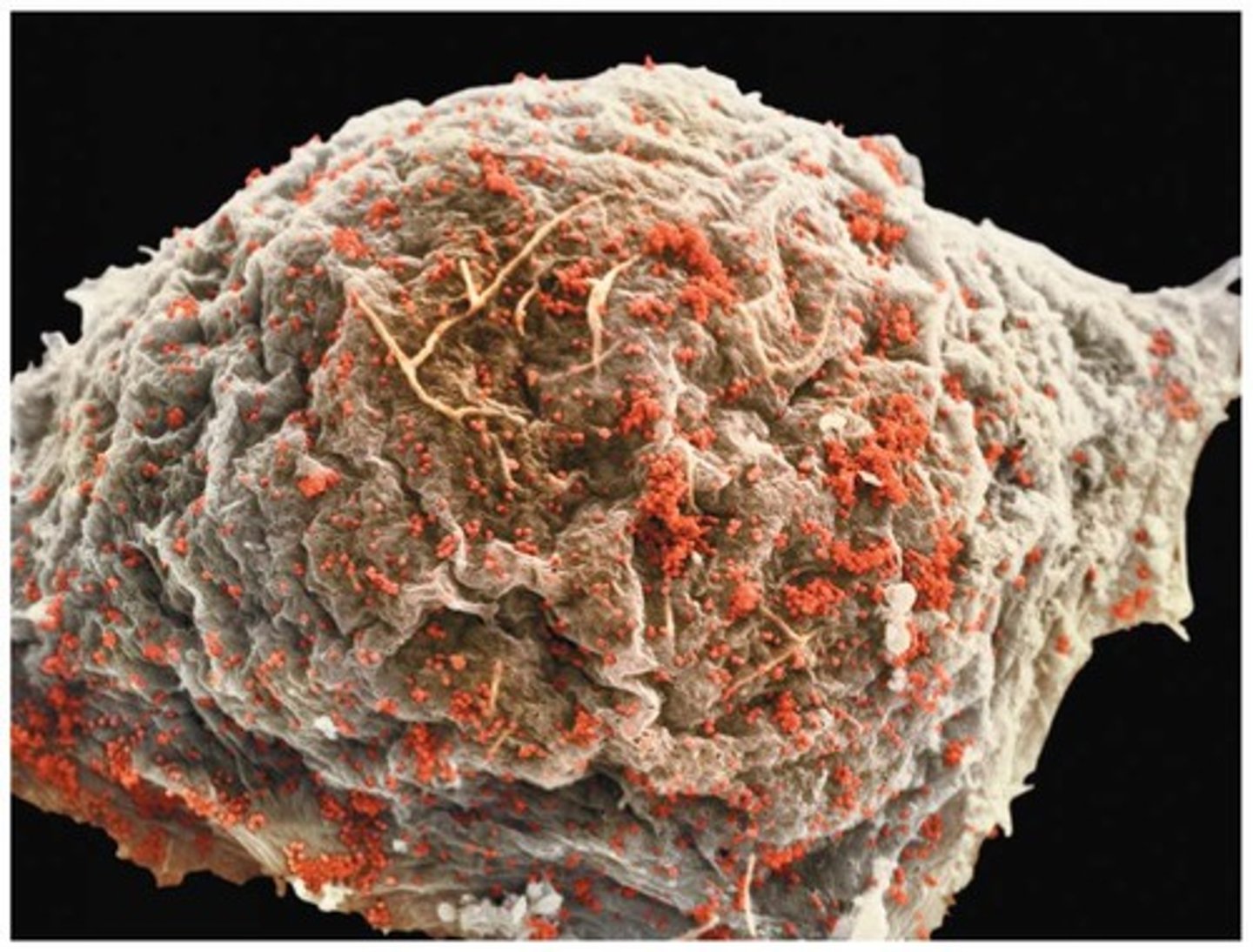
Measles Virus
Rubeola virus causing fever and rash.
Prokaryotes
Smallest living organisms, include bacteria and archaea.
Bacteria
True living organisms, divided into two domains.
Cyanobacteria
Photosynthetic bacteria, significant for oxygen production.
Thiomargarita namibiensis
Largest known bacterium, lives in oxygen-poor waters.
Heterotrophic Bacteria
Decomposers obtaining energy from organic matter.
Autotrophic Bacteria
Producers making organic compounds via photosynthesis.
Stromatolites
Calcareous mounds formed by cyanobacteria.
Extremophiles
Organisms thriving in extreme environmental conditions.
Methanocaldococcus jannaschii
Methane-producing archaeon from hydrothermal vents.
Fimbriae
Attachment structures on some prokaryotic surfaces.
Ribosomes
Sites of protein synthesis in cells.
Cell Wall
Rigid structure outside prokaryotic cell membranes.
Peptidoglycan
Main component of bacterial cell walls.
Gram-positive
Bacteria with thick peptidoglycan cell walls.
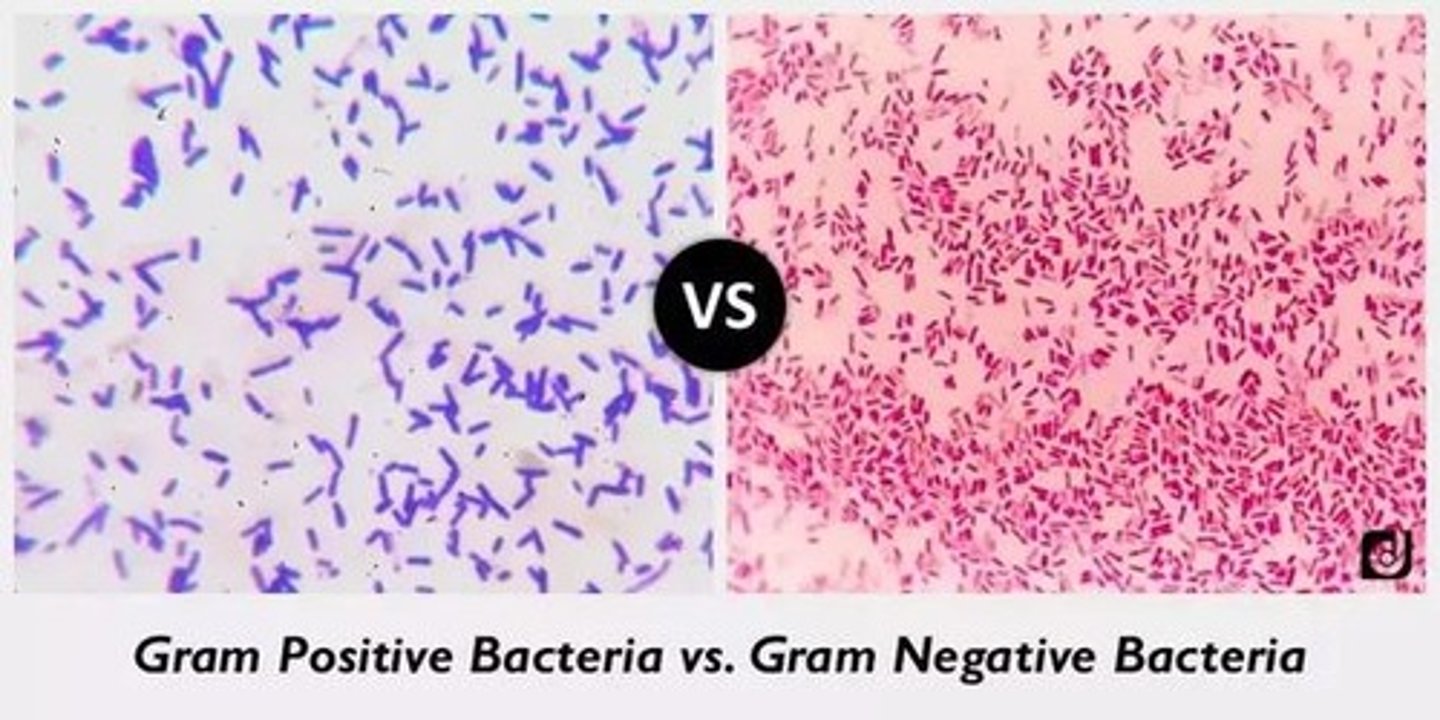
Gram-negative
Bacteria with thin peptidoglycan cell walls.
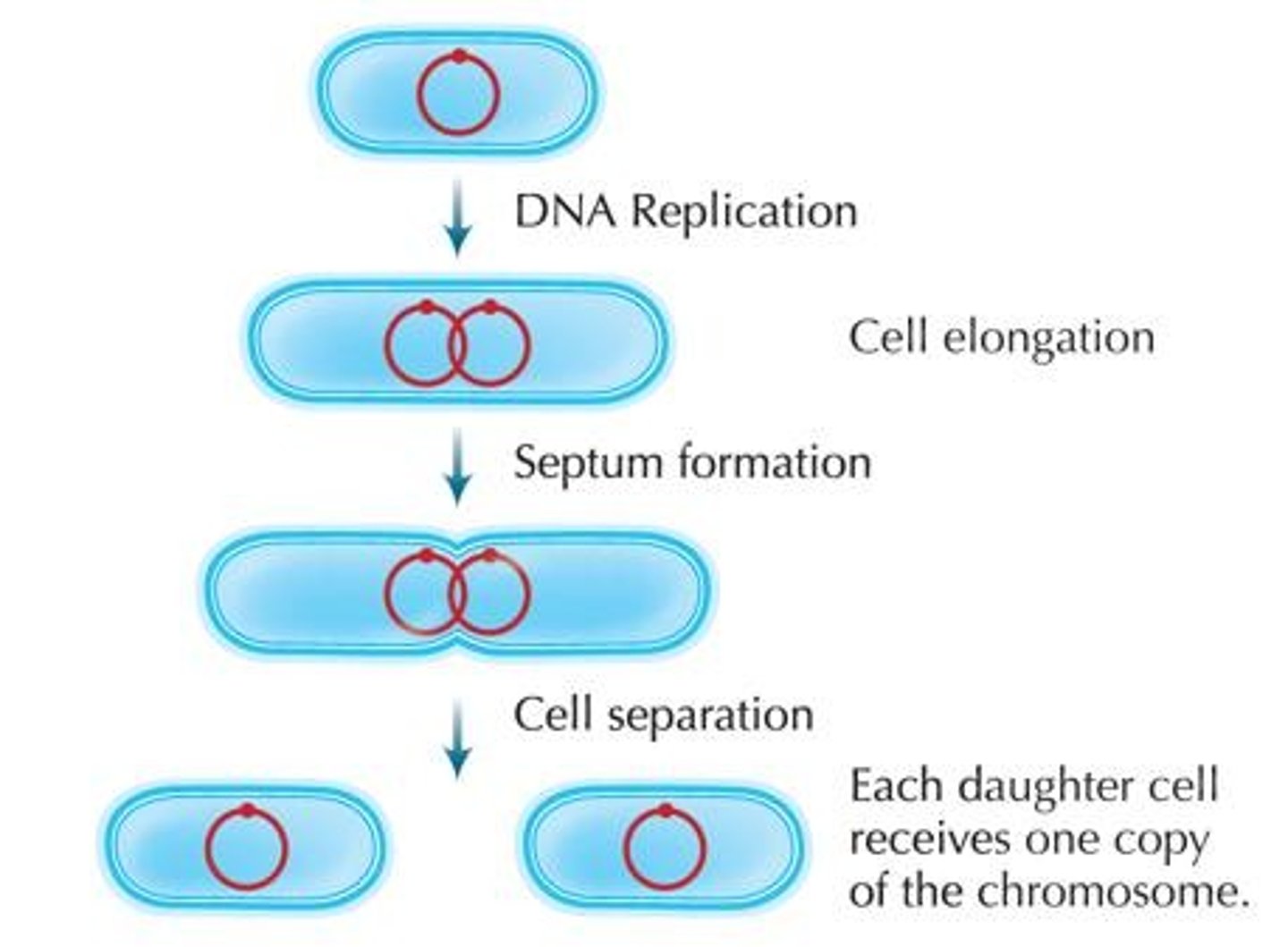
Binary Fission
Asexual reproduction method in prokaryotes.
Transformation
Uptake of foreign DNA by prokaryotic cells.
Transduction
DNA transfer via bacteriophages between host cells.
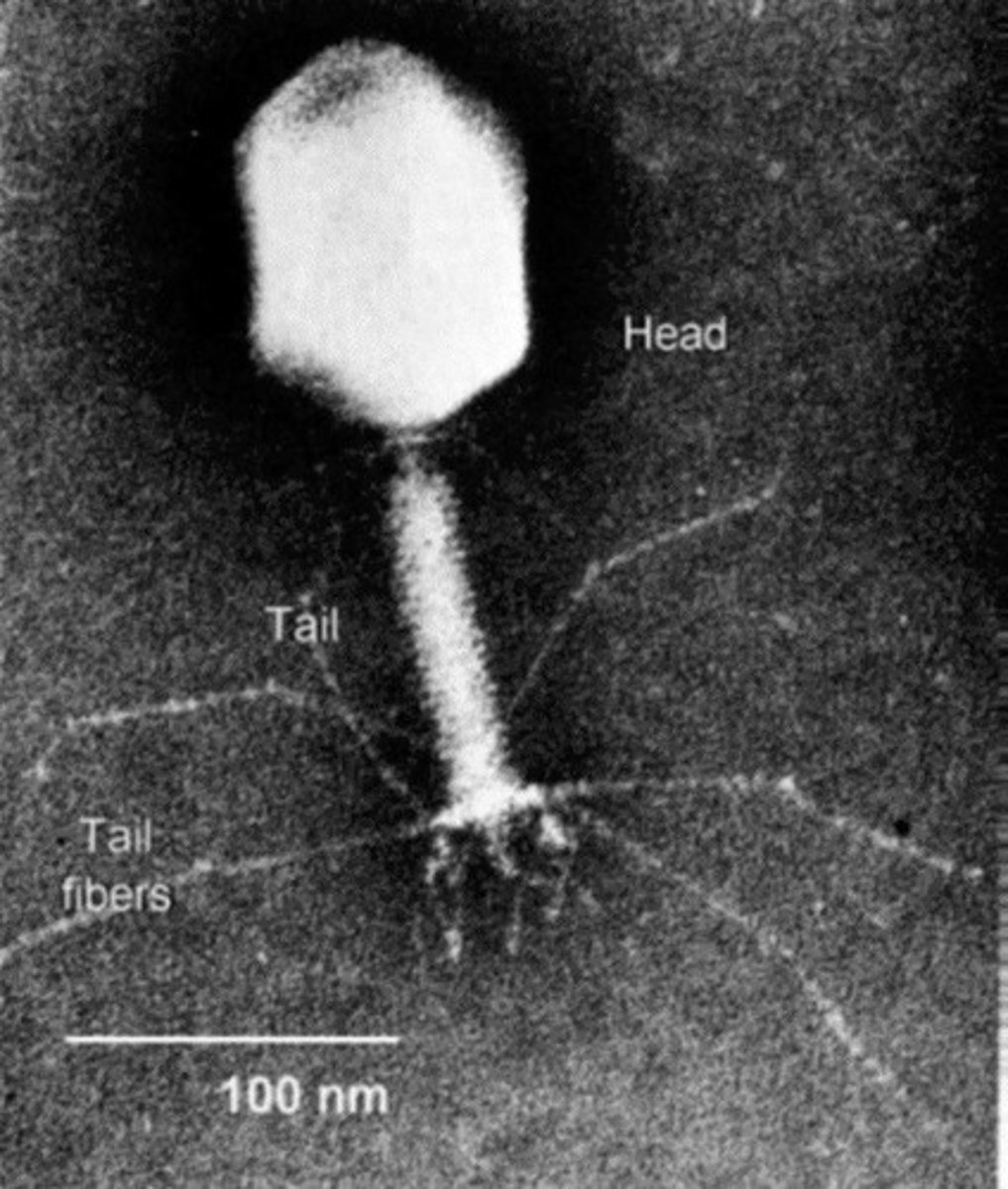
Conjugation
Direct DNA transfer between temporarily joined prokaryotes.
Coccus
Round or spherical bacterial shape.
Bacillus
Rod or pill-shaped bacterial structure.
Helical
Spiral-shaped bacteria.
Antibiotic Resistance
Resistance due to overuse and misuse of antibiotics.
MRSA
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, common in healthcare.