Finals - Solid Mixing
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Solid mixing
This refers to the process of combining two or more solid materials to create a uniform blend, often using mechanical devices like blenders or mixers.
Solid mixing
This process can involve solids mixing with other solids, or solids mixing with liquids or gases, but it is generally understood as the intermingling of solid particles to achieve a consistent mixture.
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE. The principle of solid mixing is to achieve a uniform distribution of different solid particles or components within a mixture.
Perfect Mixture
Random Mixture
Segregated Mixture
Enumerate the Types of Mixtures (3)
Perfect mixture
This is a type of mixture with a theoretically uniform distribution, where every sample taken has the same composition.
Random mixture
This type of mixture is a practical approximation where particles are distributed randomly, but some variability may exist.
Segregated mixture
This is a type of mixture with a non-uniform distribution due to differences in particle properties like size, density, or shape.
Convective mixing
Shear mixing
Diffusive mixing
Enumerate the Mechanisms of Mixing (3)
Convective mixing
Identify the Mechanism of Mixing being described:
Deliberate bulk movement of packets of powder around the powder mass
Convective mixing
Identify the Mechanism of Mixing being described:
This includes stirring or tumbling, which redistributes group of particles
Shear mixing
Identify the Mechanism of Mixing being described:
Shear stresses give rise to slip zones and mixing takes place by interchange of particles between layers within the zone
Shear mixing
Identify the Mechanism of Mixing being described:
Sliding of layers of particles over one another, breaking up agglomerates and promoting uniformity
Diffusive mixing
Identify the Mechanism of Mixing being described:
This occurs when particles roll down a sloping surface
Diffusive mixing
Identify the Mechanism of Mixing being described:
Random motion of individual particles, similar to molecular diffusion, which occurs at a smaller scale.
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE. For free-flowing powders, both diffusive mixing and shear mixing give rise to size segregation.
Convective mixing
For other powders, _________ is the major mechanism promoting mixing.

Segregation
This occurs primarily as a result of size difference.

read lang
read lang

Tumbling mixer
Convective mixer
Fluidized bed mixer
High-shear mixer
Enumerate the Types of Solid Mixers (4)
Tumbling mixer
Identify what Type of Solid Mixer is being described:
This mixer comprises a closed vessel rotating about its axis. Common shapes for the vessel are cube, double cone and V.
Cube
Double cone
V
What are common shapes of a tumbling mixer? (give 3)
Diffusive mixing
What is the dominant mixing mechanism in a tumbling mixer?
Convective mixers
Identify what Type of Solid Mixer is being described:
In this solid mixer, circulation patterns are set up within a static shell by rotating blades or paddles.
Rotating blades or paddles
In convective mixers, circulation patterns are set up within a static shell by ________ or __________.
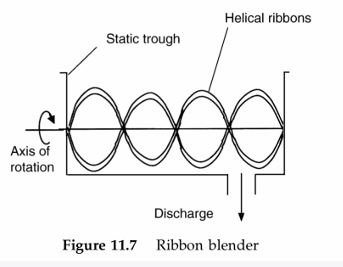
Ribbon blender
This is one of the most common convective mixers. It has helical blades or ribbons that rotate on a horizontal axis in a static cylinder or trough.
Convective mixing
*although this is accompanied by some diffusive and shear mixing.
What is the main mixing mechanism in a Ribbon blender?
Fluidized bed mixers
Identify what Type of Solid Mixer is being described:
These rely on the natural mobility afforded particles in the fluidized bed.
FALSE
In fluidized bed mixers, the mixing is largely convective with the circulation patterns set up by the bubble motion within the bed.
TRUE or FALSE. In fluidized bed mixers, the mixing is largely diffusive with the circulation patterns set up by the bubble motion within the bed.

TRUE
TRUE or FALSE. In a fluidized bed mixer, several processing steps may be carried out in the same vessel.
High shear mixer
Identify what Type of Solid Mixer is being described:
Local high shear stresses are created by devices similar to those used in comminution; high velocity rotating blades, low velocity–high compression rollers.
FALSE
In high shear mixers, the emphasis is on breaking down agglomerates of cohesive powders rather than breaking individual particles.
TRUE or FALSE. In high shear mixers, the emphasis is on breaking individual particles rather than breaking down agglomerates of cohesive powders.
Shear mixing
What is the dominant mixing mechanism in high shear mixers?
FALSE
The end use of a particle mixture will determine the quality of mixture required, which imposes a scale of scrutiny on the mixture.
TRUE or FALSE. The initial use of a particle mixture will determine the quality of mixture required, which imposes a scale of scrutiny on the mixture.
Scale of scrutiny
The end use of a particle mixture will determine the quality of mixture required, which imposes a ___________ on the mixture.

Scale of scrutiny, Danckwerts (1953)
This is a term which means ‘the maximum size of the regions of segregation in the mixture which would cause it to be regarded as imperfectly mixed
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE. The quality of a mixture decreases with decreasing scale of scrutiny until in the extreme we are scrutinizing only individual particles.

read lang
read lang

puro ni statistics hehe ikaw na bahala inchindi
READ LANG PAGE 23-29 SA SOLID MIXING PPT (see answer)
Lacey mixing index (Lacey, 1954)
This is a measure of the degree of mixing. It is the ratio of ‘mixing achieved’ to ‘mixing possible’.
0
What is the value of the Lacey mixing index that represents complete segregation?
1 (unity)
What is the value of the Lacey mixing index that represents a completely random mixture?
0.75 - 1.0
These are practical values of the Lacey mixing index. Values found in this range does not provide sufficient discrimination between mixtures.
Poole et al. mixing index
(Poole et al., 1964)
This index gives better discrimination for practical mixtures and approaches unity for completely random mixture.
Particle properties
Equipment design
Operating conditions
Enumerate the Factors Affecting Mixing (3)
Particle properties
Identify what Factor affecting mixing is being described:
Size, shape, density, and surface characteristics influence how particles interact and mix.
Equipment design
Identify what Factor affecting mixing is being described:
The type of mixer (e.g., ribbon blenders, tumblers, fluidized beds) affects the efficiency and uniformity of mixing.
Operating Conditions
Identify what Factor affecting mixing is being described:
Mixing time, speed, and fill level in the mixer play critical roles in achieving homogeneity

read lang
read lang

High shear mixer
What type of mixer is most suitable for breaking agglomerates in cohesive powders?
Shear mixing
According to Lacey, which mechanism involves particle interchange across layers?