CHE 161 - Carbohydrates
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Describe the basic structure of carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are compose of C, H, and O. (carbon + water = carbohydrate) They include simple sugars like glucose, and polymer sugars like cellulose.
What is a chiral carbon?
A chiral carbon is bonded to four different groups. If a carbon is bonded to two H’s, it is not chiral. If a carbon is double bonded to something it cannot be chiral.
When drawing the ring structure of a sugar, how do you denote the number of sides of the ring?
If a sugar has five sides is is a furanose. If a sugar is six-sided it is a pyranose.
What is an anomeric carbon?
An anomeric carbon is a carbon that is bonded to two oxygens. An anomeric carbon is “free” if it is not included in the glycosidic bond.
How do you denote a non-reducing sugar when naming it?
The suffix -ose is added if a sugar is reducing (if it has a free anomeric carbon). The suffix -ide is added if the sugar is non-reducing.
What are polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides are long sugar macromolecules. Some examples include cellulose, starch, and glycogen.
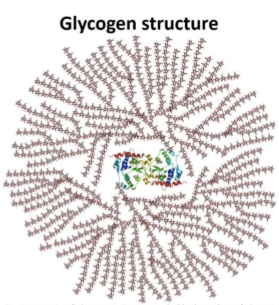
Compare starch and glycogen, in terms of structure and how it is used.
Starch and glycogen are both polysaccharides. However, the high degree of branching in glycogen means there are many chains which can be quickly hydrolyzed for energy. Glycogen is mainly stored in muscles for quick access to energy.
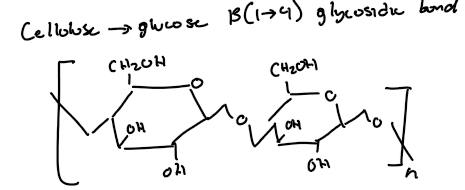
Describe cellulose
Cellulose is the major component of plant cell walls, and it is not easily degraded. Humans cannot digest cellulose. It is formed by B-glucose molecules and has a linear structure, allowing the hydroxyl molecules of one cellulose molecule to form hydrogen bonds with hydroxyl groups of parallel cellulose molecules. Those molecules together form B-sheets.