A.5. Special Relativity (HL)
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Formulae and Definitions (HL Only)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Reference Frame
A reference frame is a set of coordinate axes and clocks at all points in space. A non-accelerating frame is called an inertial frame of reference.
Galilean Distance Transformation

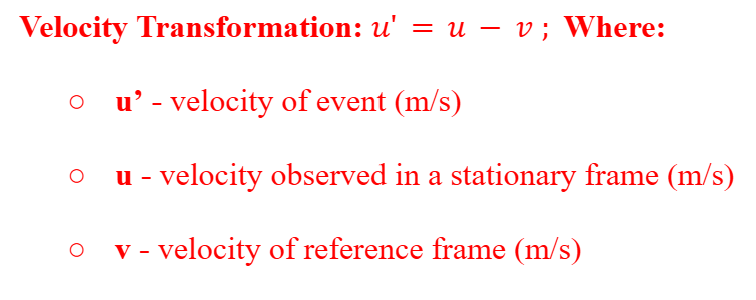
Galilean Velocity Transformation
Galilean Time Transformation

Postulates of Special Relativity
All laws of physics remain the same in all inertial frames.
The speed of light in a vacuum is constant in all frames.
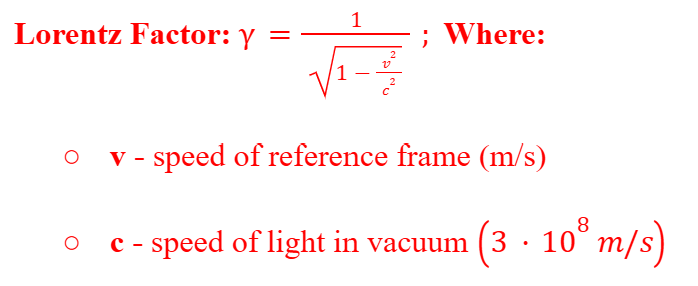
Lorentz Factor
Relativistic Distance Transformation

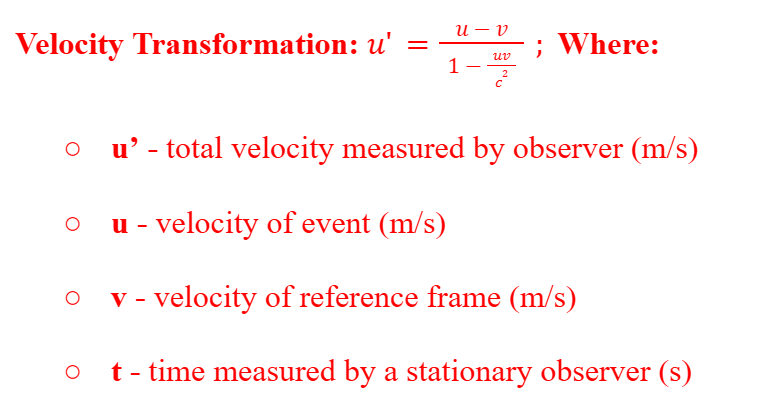
Relativistic Velocity Transformation
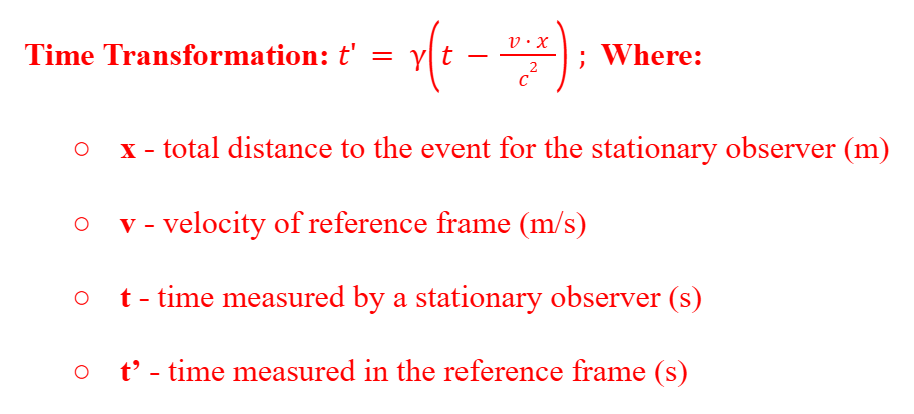
Relativistic Time Transformation
Spacetime Interval
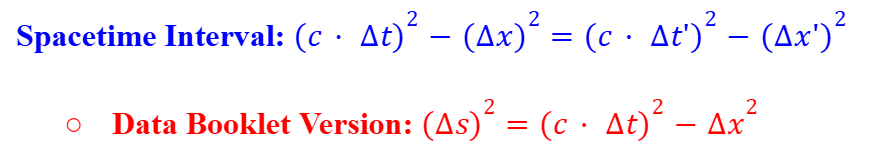
Spacetime Coordinate Differences

Distance Relation
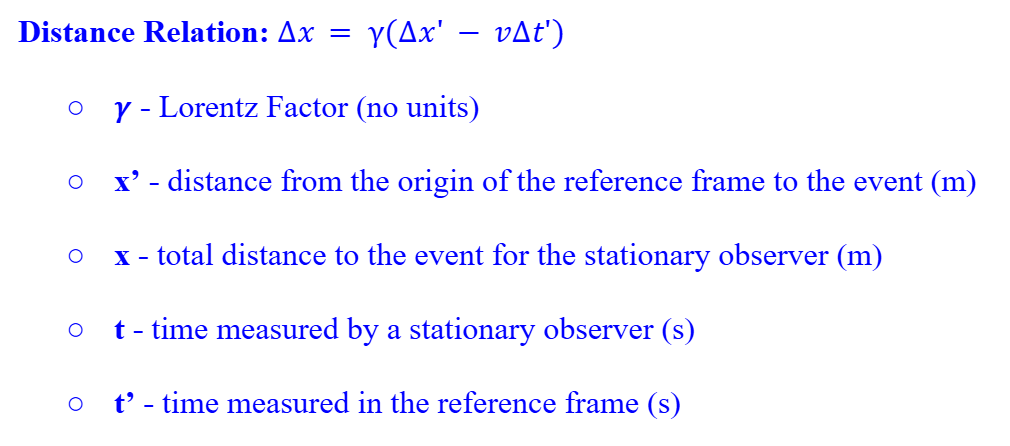
Time Relation

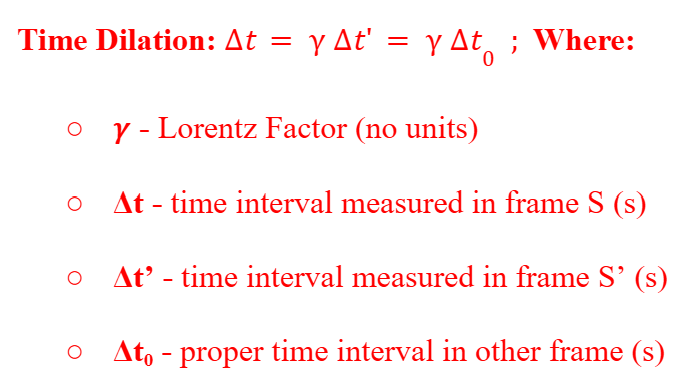
Time Dilation
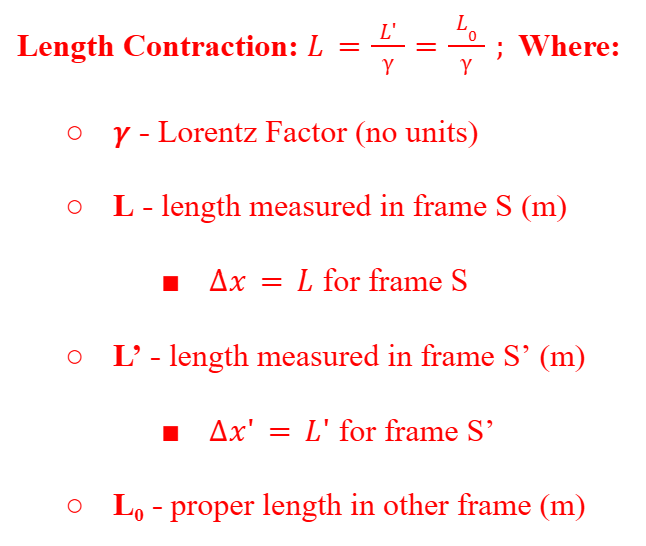
Length Contraction
Proper time and Proper Length
A proper time interval is the time between two events that take place at the same point in space.
A proper length is the length measured when the object is at rest. The object's rest frame is the reference frame where the object is at rest. Only the lengths in the direction of motion are contracted.
Simultaneity
If two events occur simultaneously in frame S’ with a time interval of 0, then the following equation is the time interval in frame S.
If x' = 0, the events will not be simultaneous in other frames.
If x = 0 i.e. the simultaneous events occur at the same point in space, thus they are simultaneous in all frames of reference.

Angle of the Wordline
The angle of the wordline cannot exceed 45o.

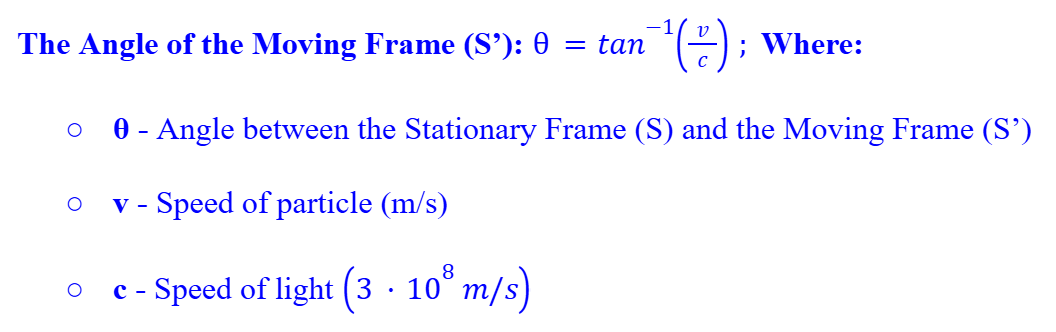
Angle of Moving Frame
The angle of the moving frame cannot exceed 45o.
Causation in Spacetime Diagrams
An event ‘E’ can cause event ‘L’ if the time separating ‘E’ and ‘L’ is greater than or equal to the travel time of a photon from the position of ‘E’ to ‘L’.
Scale Relation of Axes in Different Frames
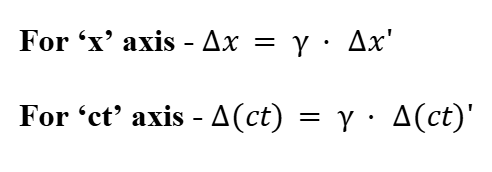
Length Contraction in Spacetime Diagrams
Draw a line parallel to the (ct)’ axis at the start and end of the length in the moving frame and extrapolate it towards the x-axis in the stationary frame to find the proper length.
Draw a line parallel to the (ct) axis at the start and end of the length in the stationary frame and extrapolate it towards the (x’)-axis in the moving frame to find the contracted length.
Lengths are only contracted when in the direction of the velocity.
Time Dilation in Spacetime Diagrams
Draw a line parallel to the x-axis from the start and end points of (ct)’ in the moving frame and extrapolate it towards the (ct) axis to find the proper time.
Draw a line parallel to the (x’)-axis from the start and end points of (ct) in the stationary frame and extrapolate it towards the (ct)’ axis to find the dilated time.
Simultaneity in Spacetime Diagrams
