Chemistry Formulas - yearlong
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
q=mc∆T T=
change in temp.
q=mc∆T C=
specific heat
q=mc∆T M=
mass
q=mc∆T q=
heat flow (in units)
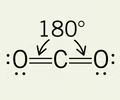
linear
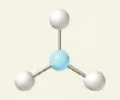
trigonal planar
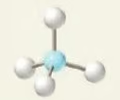
tetrahedral
trigonal pyramidal

bent
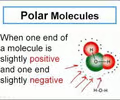
polar
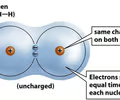
nonpolar
metals
left side of periodic table
nonmetals
right side of the periodic table
diatomic Elements
BrINClHOF
sections of per. table
S, P, D, F
-ide
hydro____ic acid
-ite
____ous acid
ionic
metal and nonmetal
ion-dipole
ion and polar molecule
dipole-induced dipole
polar and nonpolar
dipole-dipole
polar and polar
ion-induced dipole
ion and nonpolar
induced dipole-induced dipole
nonpolar and nonpolar
solvent
water
Solute
what is dissolved
electrolyte
metal and nonmetal
colloid
not see through mixture
suspension
chunky mixture
solution
A mixture that forms when one substance dissolves another. (see through)
most reactive elements location
top of activity series
percent error
experimental value-accepted value/accepted value x 100
density
D=m/v (<3)
1 mole = (count)
6.02 x 10^23
1 mole = (volume)
22.4 L of a gas at STP
1 mole (mass)
molar mass from periodic table
percent composition
part/whole x 100
molarity
moles of solute/liters of solution
dilution
M1V1=M2V2 (M=molarity)
dilution
C1V1=C2V2 (C=any concentration unit)
percent yeild
actual/theoretical x 100
kinetic energy
1/2 x mass x velocity^2
K= C+___
273.15
dalton's law
P total=P1+P2+P3...
EXOthermic
heat out
ENDOthermic
heat in
enthalpy
constant pressure
oxidation
losing electrons
reduction
gaining electrons
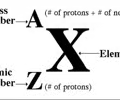
chemical symbol