Topic 5 - Separate Chemistry 1
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is the equation for Atom Economy?
Atom economy = (Total Mr of desired products ÷ Total Mr of all products) x 100
What is the equation for Percentage Yield?
Percentage Yield = (Actual yield ÷ theoretical yield) x 100
What type of solution is used during titration?
A Standard Solution is used during titration as the concentration is known
What is the equation for concentration involving moles?
Concentration (mol dm-3)= No. Moles ÷ Volume of solution (dm3)
What is the equation for concentration involving mass?
Concentration (gdm-3) = Mass (g) ÷ Volume (dm3)
What is the equation for gdm-3 from dm3?
gdm-3 = Mr x dm3
What is the Haber Process?
The Haber Process is the industrial production of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen
What is the metal used as a catalyst in the Haber Process?
Iron is used as a catalyst during the Haber Process
What is Ammonia used for?
Ammonia is used for nitrogen-based fertilisers
How do we obtain hydrogen?
Hydrogen is obtained during electrolysis or from hydrocarbons
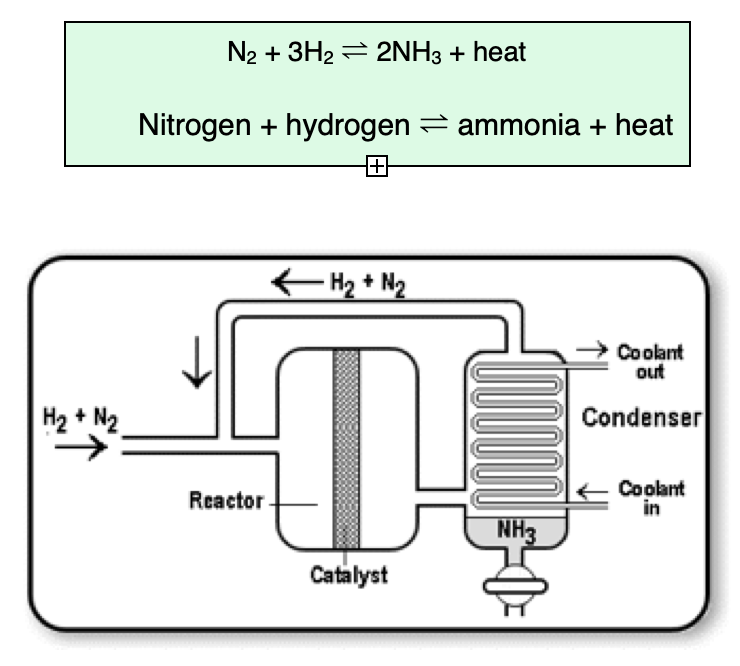
How does the Haber Process produce ammonia on an industrial scale?
Hydrogen and Nitrogen are fed into the reaction vessel which is at 450°C and 200atm where the gases are free to pass over an iron catalyst. Some of the nitrogen and hydrogen react to form ammonia but the reaction is reversible so there is still a lot of nitrogen and hydrogen. Ammonia has a fairly low boiling point so when it enters the cooler condenser, it condenses and changes state from gaseous ammonia to liquid ammonia but the gaseous nitrogen and hydrogen remain gaseous and can be recycled.
Why is 450°C used in the Haber Process?
The forwards reaction is an exothermic reaction so using a lower temperature would favour it and therefore would lead to a higher % yield.
However, a high temperature is necessary for a higher rate of reaction as particles need kinetic energy in order to collide at the activation energy and react.
Therefore, 450°C is used as a compromise.
Generating heat is also expensive
Is the forwards reaction during the Haber Process exo or endothermic?
The forwards reaction during the Haber Process is an exothermic reaction
Why are 200atm of pressure used during the Haber Process?
For a high % yield, high pressure is necessary as there are fewer molecules of the product that the reactants.
Higher pressure leads to more frequent collisions so the rate of reaction increases.
Increasing pressure is very expensive and can be dangerous so they are the limiting factors to pressure.