Topic 12 - Titration curves and buffers
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
1
New cards
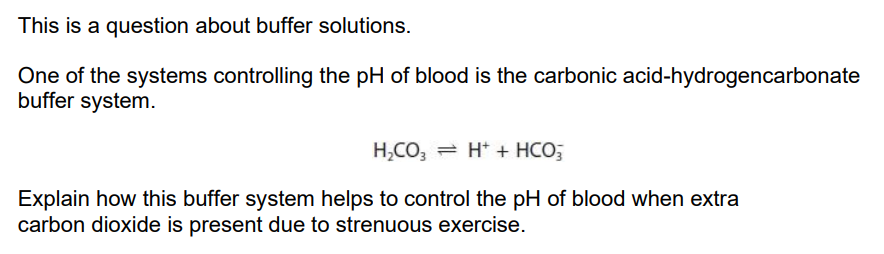
Carbon dioxide dissolved in the blood forms carbonic acid (H2CO3), so this concentration increases.
The equilibrium will shift to the right and produces more H+ acid ions.
The high concentration of hydrogencarbonate ions suppress the ionisation of carbonic acid to help control PH. / Excess hydrogencarbonate ions combine with H+ ions to help control blood PH.
2
New cards
Calculate PH of a buffer solution, using Ka.
Calculate amount of salt formed, initial amount of acid and amount of acid left.
Total volume.
Salt (concentration) = mol salt/ volume, acid (concentration) = mol acid left/ volume.
H+ = ka * (acid/salt)
PH = -log H+
3
New cards
.
.
4
New cards
ll
ww