Principles of Macroeconomics Chapter 25,26,27,28
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
aggregate accounting
a set of rules and definitions for measuring economic activity in the economy as a whole
GDP
the total market value of all final goods and services produced in an economy in a one-year period
consumption
spending by households on goods and services
investment
spending for the purpose of additional production
government spending
goods and services that government buys
net exports
spending on exports minus spending on imports
Calculating GDP
C+I+G+(X-M)
consumption + investment + government spending + net exports
wealth accounts
a balance sheet of an economy's assets and liabilities and its is a stock concept
final output
goods and services purchased for final use
intermediate products
used as an input in the production of some other product
value added
the increase in value that a firm contributes to a product or service
depreciation
the amount of capital used up in producing that year's GDP
NDP
measures output available for purchase
Calculating NDP
C+I+G+(X-M) - depreciation
GNP
the aggregate final output of citizens and businesses of an economy in one year
calculating GNP
GDP + net foreign factor income
net foreign factor income
the income from foreign domestic factor sources minus foreign factor income earned domestically
aggregate income == Aggregate Production
the total income earned by citizens and businesses in a country in a year
Employee compensation + Rents + Interests + Profits
inflation
a continual rise in the overall price level
price index
a measure of the composite price of a specified group of goods
nominal GDP
the amount of goods and services produced measured at current prices
real GDP
the total amount of goods and services produced, adjusted for price-level changes
GDP delfator
the price index that includes all goods and services in the economy expressed relative to a base year of 100
consumer price index (CPI)
measures the prices of a fixed basket of goods, weighted according to each components share of an average consumer's expenditures
personal consumption expenditure deflator (PCE)
is a measure of prices of goods that consumers buy that allows yearly changes in the basket of goods that reflect actual consumer purchasing habits
producer price index (PPI)
an index of prices that measures the average change in the selling prices received by domestic producers of goods and services over time
nominal interest rate
the rate you pay or receive to borrow money
real interest rate
the nominal interest rate adjusted for inflation
real wealth
the value of the productive capacity of the assets of an economy measured by the goods and services it can produce now and in the future
nominal wealth
the value of those assets measured at their current market prices
asset price inflation
a rise in the price of assets unrelated to increases in their productive capacity
Purchasing power parity
a method of comparing income that takes into account the different relative prices among countries
Genuine Progress Indicator (GPI)
makes a variety of adjustments to GDP to better measure the progress of society rather than just economic activity
potential output
the highest amount of output an economy can sustainably produce from exist- ing production processes and resources OR potential income
productivity
output per unit of input
Long-run growth analysis focuses on
supply
Say's law
supply creates its own demand. According to Say's law, aggregate demand will always equal aggregate supply.People work and supply goods to the market because they want other goods. The very fact that they supply goods means that they demand goods of equal value.
Rule of 72
The number of years it takes for a certain amount to double in value is equal to 72 divided by its annual rate of increase.
Compounding
growth is based not only on the original level of income but also on the accumulation of previous-year increases in income.
specialization
the concentration of individuals on certain aspects of production
division of labor
the splitting up of a task to allow for specialization of production
per capita growth
producing more goods and services per person
you can approximate per capita growth
Per capita growth % change in output % change in population
The Sources of Growth
1. Growth-compatible institutions.
2. Investment and accumulated capital.
3. Available resources.
4. Technological development.
5. Entrepreneurship.
The flow of invest- ment leads to
the growth of the stock of capital
human capital
the skills that are embodied in workers through experience, education, and on-the-job training, or, more simply, people's knowledge
social capital
the habitual way of doing things that guides people in how they approach production
technology
the way we make goods and supply services
Entrepreneurship
the ability to get things done
Classical growth model
a theory of growth that emphasizes the role of capital in the growth process
law of diminishing marginal productivity
as more and more of a variable input is added to an existing fixed input, eventually the additional output produced with that additional input falls.
new growth theory
a theory of growth that emphasizes the role of technology in the growth process
positive externalities
positive effects on others not taken into account by the decision maker
patents
legal protection of a technological innovation that gives the owner of the patent sole rights to its use and distribution for a limited time
learning by doing
is meant to improve the methods of production through experience
Network externality
is an externality in which the use by one individual makes a technology more valuable to other people
real sector
is the market for the production and exchange of goods and services
financial sector
is the market for the creation and exchange of financial assets
Federal Reserve Bank (the Fed)
The U. S. central bank, whose liabilities (Federal Resreve Notes) serve as cash in the United States
Bank
A financial insitituiton whose primary function is accepting deposits for, and lending money to, individuals and firms
M1
Currency in the hands of the public, checking account balances, and traveler's checks
M2
M1 plus savings and money market accounts, small-denomination time deposits (also called CD's), and retail money funds
Asset Management
How a bank handles its loans ad other assets
Liability Management
How a bank attracts deposits and what it pays for them
Reserves
Currency and deposits a bank keeps on hand or at all the Fed or central bank, to manage the normal cash inflows and outflows
Reserve Ratio
The ratio of reserves to total deposits
Money Multiplier
The measure of the amount of money ultimately created per dollar deposited in the banking system, when people hold no currency
Excess Reserves
Reserves held by banks in excess of what banks are required to hold
Transaction Motive
The need to hold money for spending
Precautionary Motive
Holding money for unexpected expenses and impulse buying
Speculative Motive
Holding cash to avoid holding financial assets whose prices are falling
Financial Assets
are assets such as stocks or bonds, whose benefit to the owner depends on the issuer of the asset meeting certain obligations
Financial liabilities
are obligations by the issuer of the financial asset
Saving
outflows from the spending stream from government, households, and corporations
Loans
made to government, households, and corporations
interest rate
is the price paid for use of a financial asset
Equilibrium output
the level of output toward which the economy gravitates in the short run because of the cumulative cycles of declining or increasing production
Potential output
the highest amount of output an economy can sustainably produce using existing production processes and resources
Paradox of thrift
an increase in saving can lead to a decrease in spending, output, causing a recession and lowering total saving
Aggregate Demand (AD) Curve
a curve that shows how a change in the price level will change aggregate expenditures on all goods and services in an economy
Short-Run Aggregate Supply (SAS) Curve
a curve that specifies how a shift in the aggregate demand curve affects the price level and real output in the short run, other things constant
Long-Run Aggregate Supply (LAS) Curve
Is a curve that shows the long-run relationship between output and the price level
Interest rate effect
the effect that a lower price level has on investment expenditures through the effect that a change in the price level has on interest rates
International effect
as the price level falls (assuming the exchange rate does not change), net exports will rise
Money wealth effect
a fall in the price level will make the holders of money richer, so they buy more
Multiplier effect
the amplification of initial changes in expenditures
Slope of AD curve
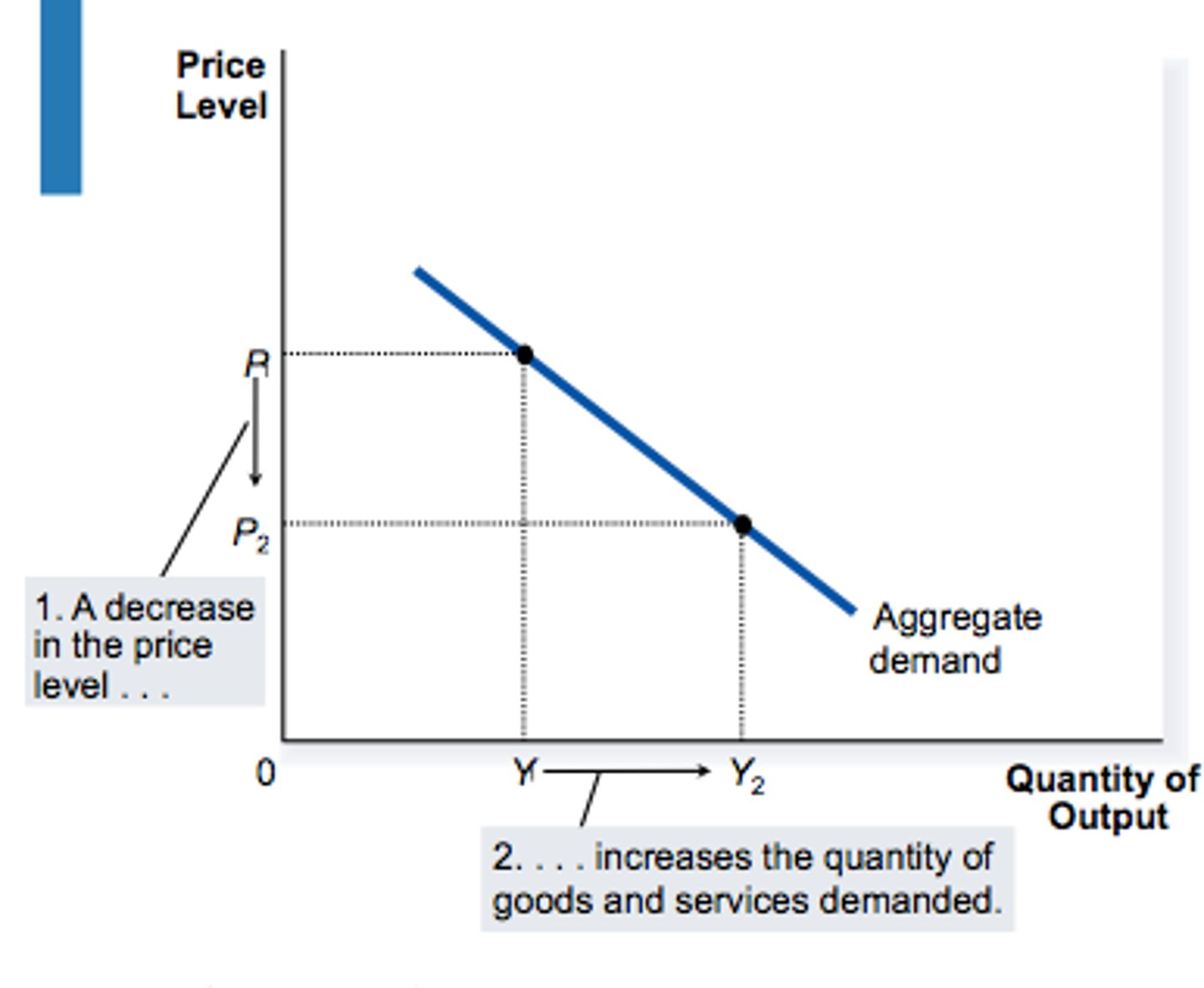
Shifts in the AD Curve
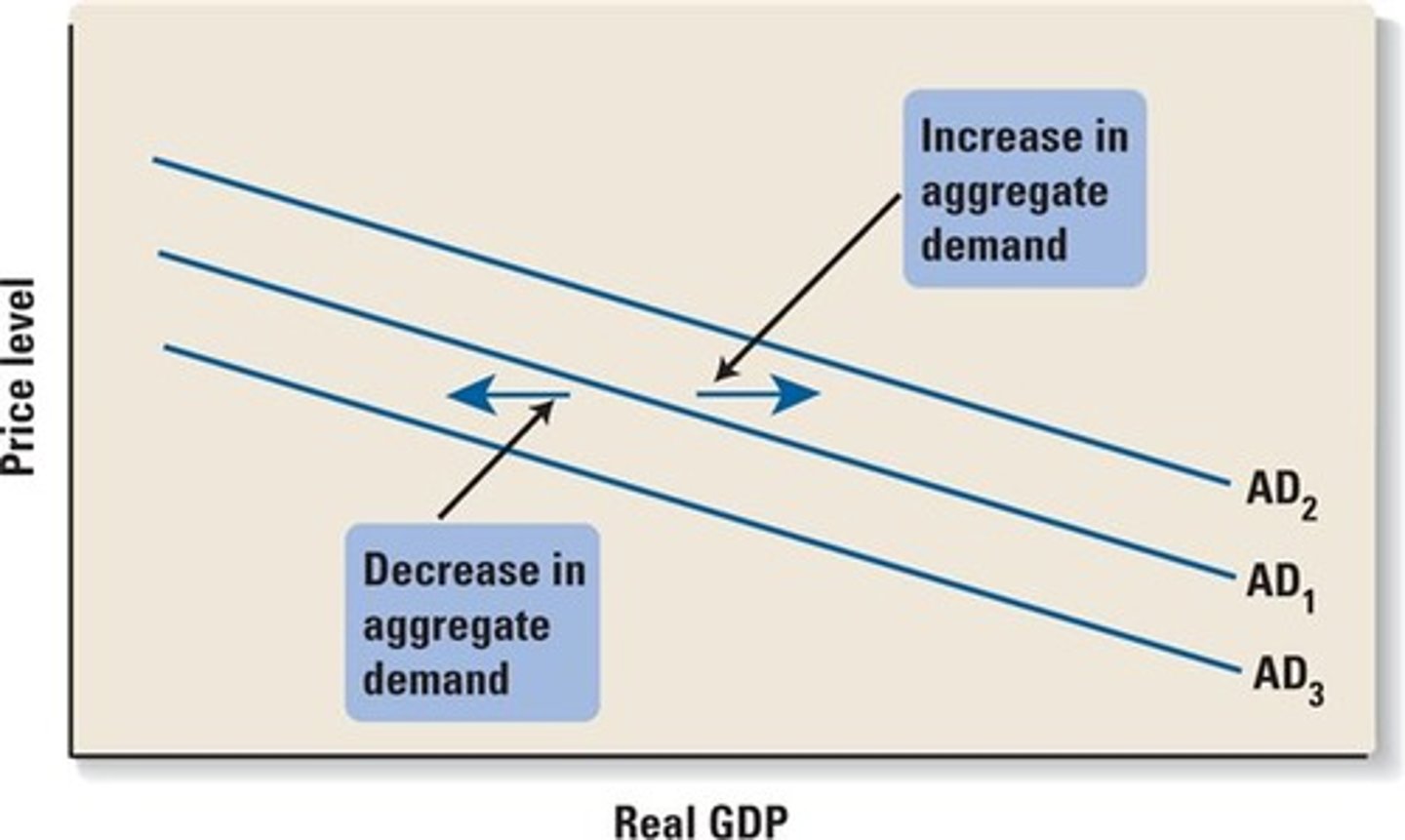
A shift in the AD curve means that at every price level, total expenditures have changed. the 5 important shift factors
1 - Foreign income
2 - Exchange rate fluctuations
3 - Distribution of income
4 - Expectations
5 - Government policies
The Slope of the Short-Run Aggregate Supply (SAS) Curve
reflects auction markets and posted price markets
Auction market
The markets represented by the supply/demand model
Posted price markets == quantity-adjusting markets
markets in which firms respond to changes in demand primarily by changing production instead of changing their prices
Shifts in the SAS Curve
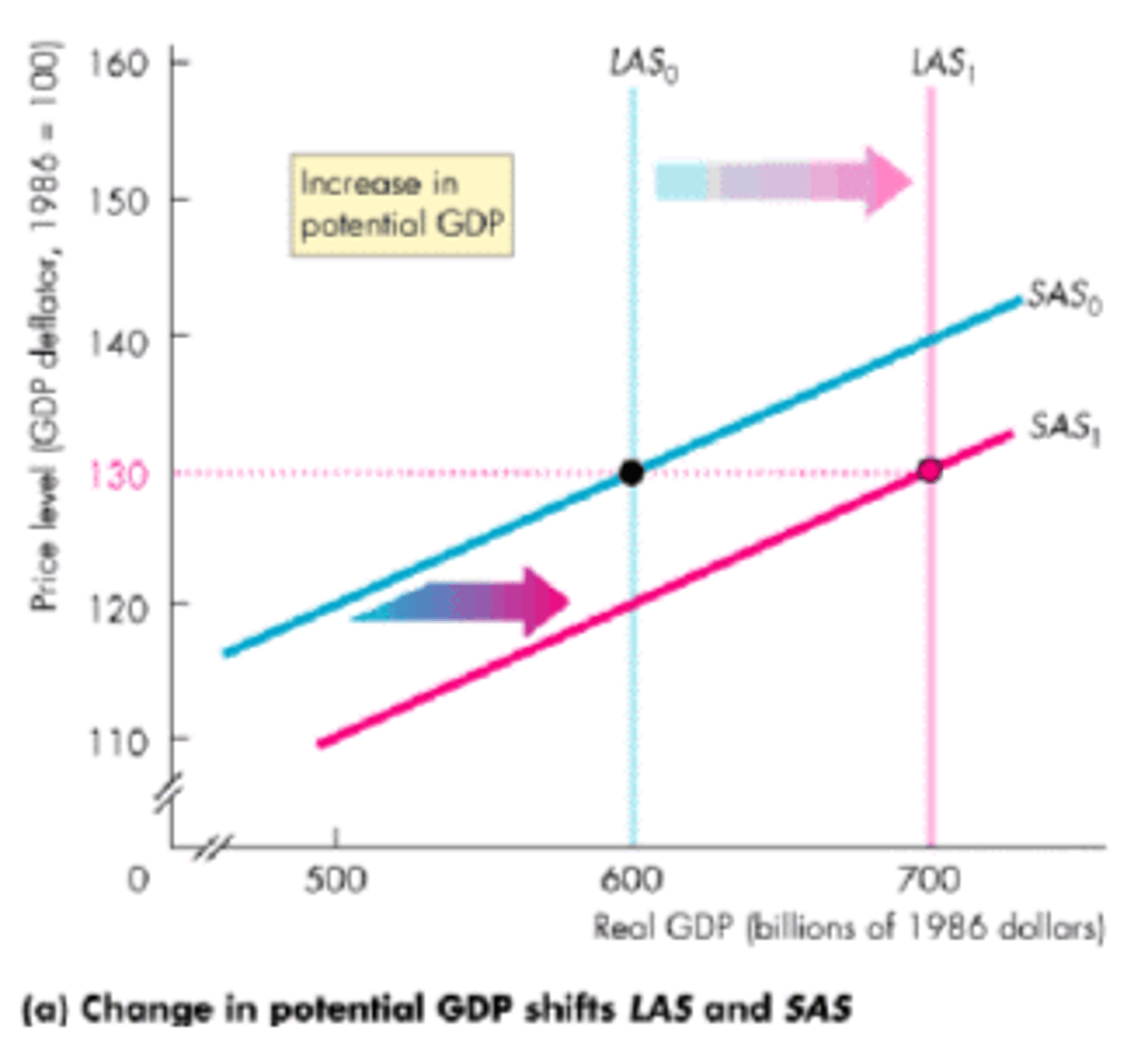
long-run aggregate supply (LAS) curve
shows the long-run relationship between output and the price level
Monetary policy
involves the Federal Reserve Bank changing the money supply and interest rates
Fiscal policy
is the deliberate change in either government spending or taxes to stimulate or slow down the economy