Ch 11 - Structure, governance, and ethics
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
How is the IT department organized?
The organizational structure varies, depending on the organizations size, culture, competitive environment, industry, etc
All IT systems used in an organization require some form of technical support
The department of people who support this is referred to as “IT services” or “information systems services”
Senior-level reporting relationships
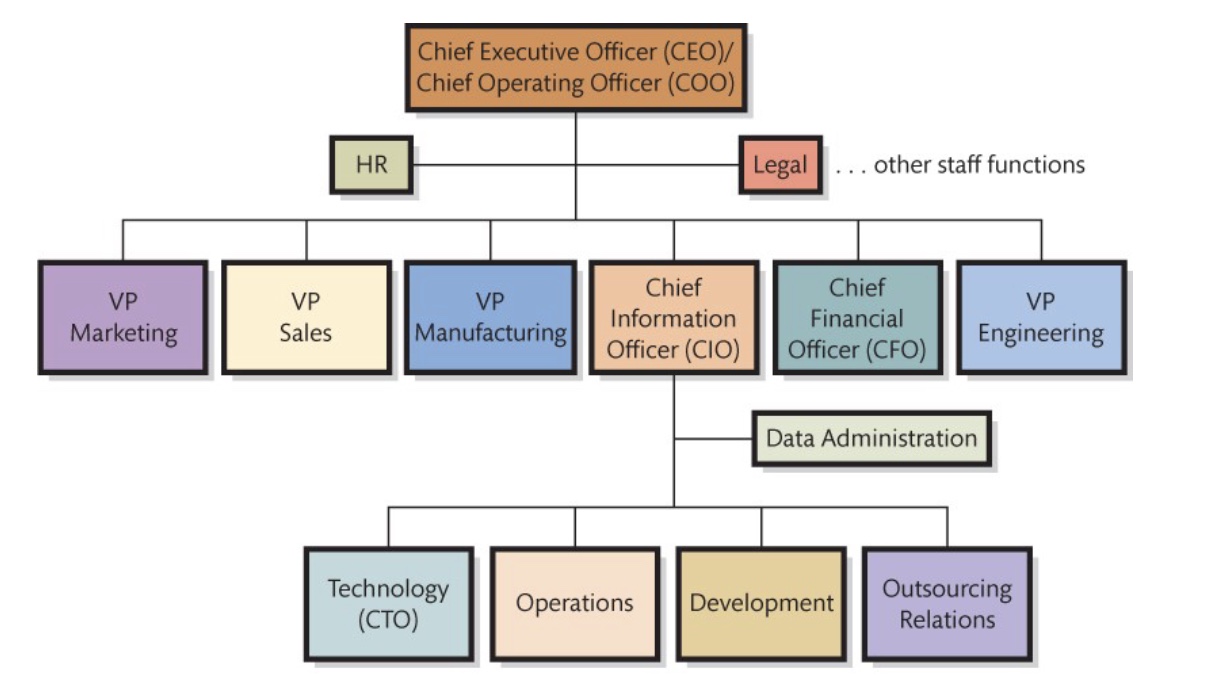
The web and organization of IT departments
The web has had a significant impact on the organization of IT departments
Traditionally, the IT department was responsible for designing and maintaining a website, however, this task now belongs to the marketing department
The marketing department can keep up with branding and control of the website, while IT provides technical support for the website
Creating a well-designed company website requires knowledge of branding and marketing, plus technical skills
IT architecture
Basic framework for all the computers, systems, and information management that supports organizational services (like a city plan)
There are usually few standards as companies are diverse
Usually contains a long document with complicated diagrams, management policies, and discussion of future changes
Enterprise architect
A new title being used to describe a person who manages IT architecture
They:
Create a blueprint of an organizations information systems and the management of these systems
Must understand current investments in technology and plan for changes
How information systems supports organizational strategy
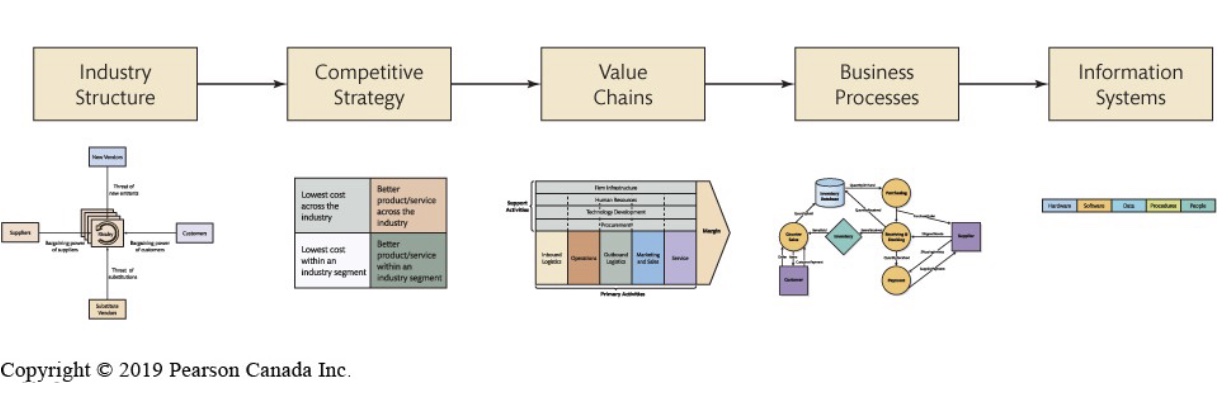
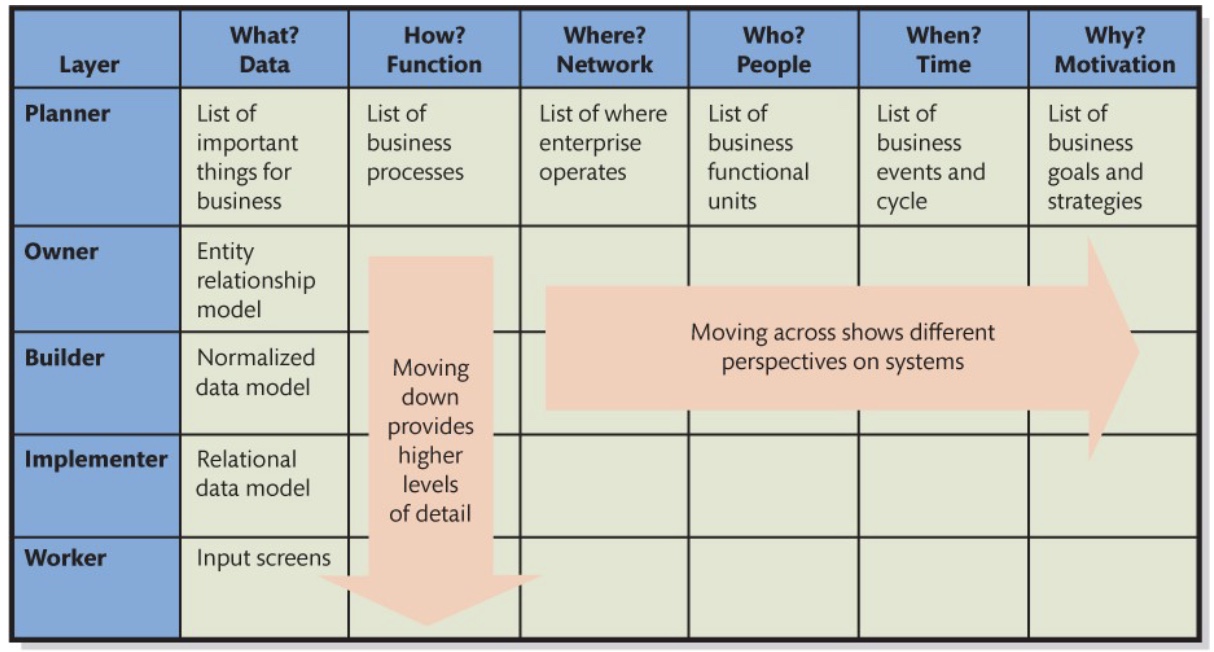
Zachman framework for enterprise architecture
Helps in designing IT architecture, and is divided into:
The 5 reasons for communication
Stakeholder groups
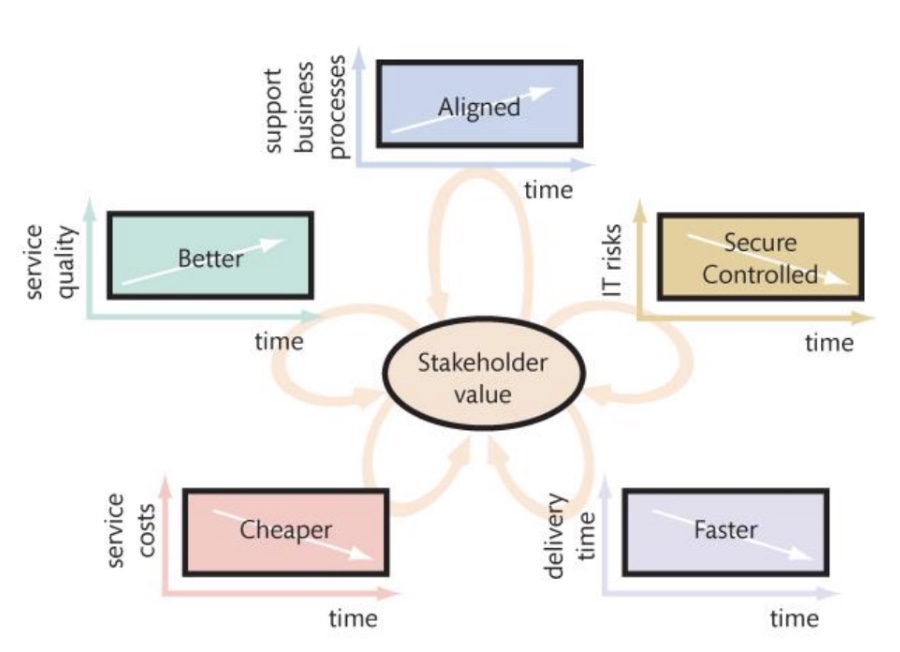
Alignment
The process of matching organizational objectives with IT architecture
This is an ongoing process, as fitting IT architecture to business objectives is a continuous challenge
How is alignment measured?
It is measured as the degree to which the IT departments missions, objectives, and plans overlap with the overall business missions, objectives, and plans
Communication between business and IT executives are the most important indicator of alignment
IS governance
The development of consistent, cohesive, management policies and processes for IT and related services
The goal is to improve the benefits of an organizations IT investment over time
Senior business managers are required to make assertions about the controls on IS that will expose them to both financial and criminal penalties
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (USA) and Budget Measures Act (Canada)
Requires management to create internal controls sufficient to produce reliable financial statements and to protect the organizations assets
Internal controls include the separation of duties and authorities
Exposes both management and the external audtitor to financial and criminal liability
Prevents corporate frauds
Goal is to strengthen and upgrade financial reporting, maintaining and improving trust in public companies’ financial reports
Ex: The computer-based accounting information system used by the company must have appropriate controls, and management must assert that they do, and the order-processing information system used by the company, which store credit card data and customer identities, must prevent unauthorized people from access
Information systems audit
Examination and verification of a company’s information resources that are used to collect, store, process, and retrieve information, including the organizations IS policies and procedures
Many firms offer IS audit services
Control objectives for information and related technology (COBIT)
A framework of best practices designed for IT management
Information systems ethics
There are limits to the use of IT and IS, some use of IT is against the law or unethical
This is not about the hardware or software, but about the people involved in the system
It is important to understand our own behaviour, and our behaviour should be guided by principles
Ethical principles include: the United Nations Declaration of Human rights, Canada’s Charter of Rights and Freedoms, and the Association of Computing Machinery’s code of ethics
Association for Computing Machinery’s (ACM) code of ethics
Contribute to society and to human well-being, acknowledging that all people are stakeholders in computing
Avoid harm
Be honest and trustworthy
Be fair and take action not to discriminate
Respect privacy
Green IT (green computing)
Using IT resources to better support the triple bottom line for organizations
Considers the effects of choices on people and the environment
The triple bottom line
A framework that goes beyond financial reporting by evaluating an organizations success in 3 key areas:
Profit (economic performance)
People (social performance)
Planet (environmental performance)
Its primary goals is to improve energy efficiency, promote recyclability, and reduce the use of materials that are hazardous to the environment
Energy star program
An international government/industry partnership to produce equipment that meets high-energy efficiency specifications or promotes the use of such equipment
E-cycling
The recycling of electronic computing devices