Price determination in a competing market (supply and demand)
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What does demand tells us?
Demand tells us the quantity of a good that consumers are willing and able to buy at a given price at given point in time.
What determines demand (3)?
1) Diminishing marginal utility
2) Income effect (as prices decrease consumer real income effectively increase so they can buy more units of a good.
3) Substitution effect (as price of good X decrease it becomes relatively more attractive compared to alternatives so we buy more of it)
What’s a contraction?
An increase in price leads to a decrease in quantity demand. (a rightward movement along the curve)
What’s an extension?
A reduction in price leases to an increase in quantity demanded. (a leftward movement along the curve).
What does a shift in the demand curve mean?
For every price level, consumers are willing to buy a lower of higher quality of goods/ services.
What can lead to a shift in the demand curve?
Change in income (normal goods), successful advertising/promotion, increasing population, decreasing income (inferior good), increase in price of substitute good, decrease in price of complimentary good.
What’s derived demand?
The demand for a factor of production that results from the demand for the product that it is used to make.
What’s a normal good?
When an increase in income leads to an increase in demand and a decrease in income leads to a decrease in demand.
What’s an inferior good?
When an increase in income leads to a fall in demand and a decrease in income leads to a rise in demand.
What’s cross elasticity of demand?
How do you calculate it?
Cross elasticity of demand measure the responsiveness of demand to changes in the price of another good.
XED= proportionate change in QD(good A)/ proportionate change in P (good B)
What does price elasticity of demand measure?
PED measure the responsiveness of demand to a change in price
How do you a calculate price elasticity of demand?
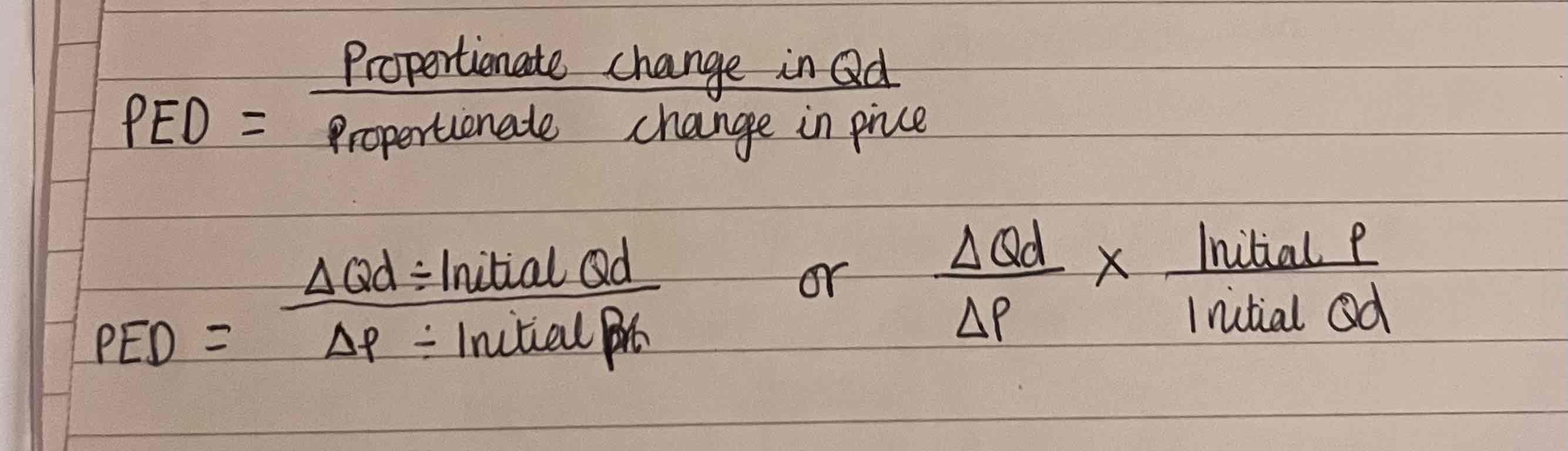
What PED values correlate to different elasticities?
What do they suggest?
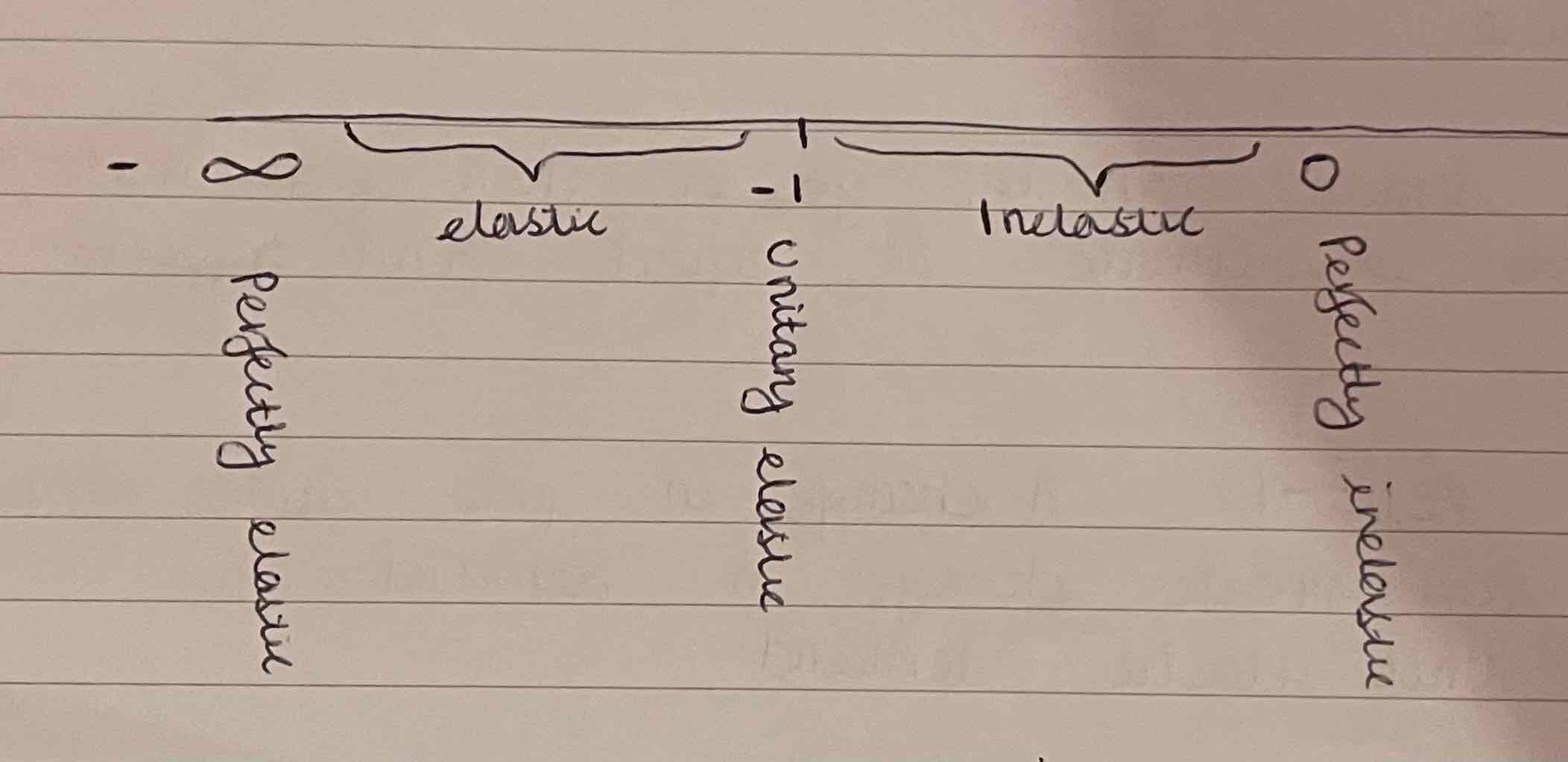
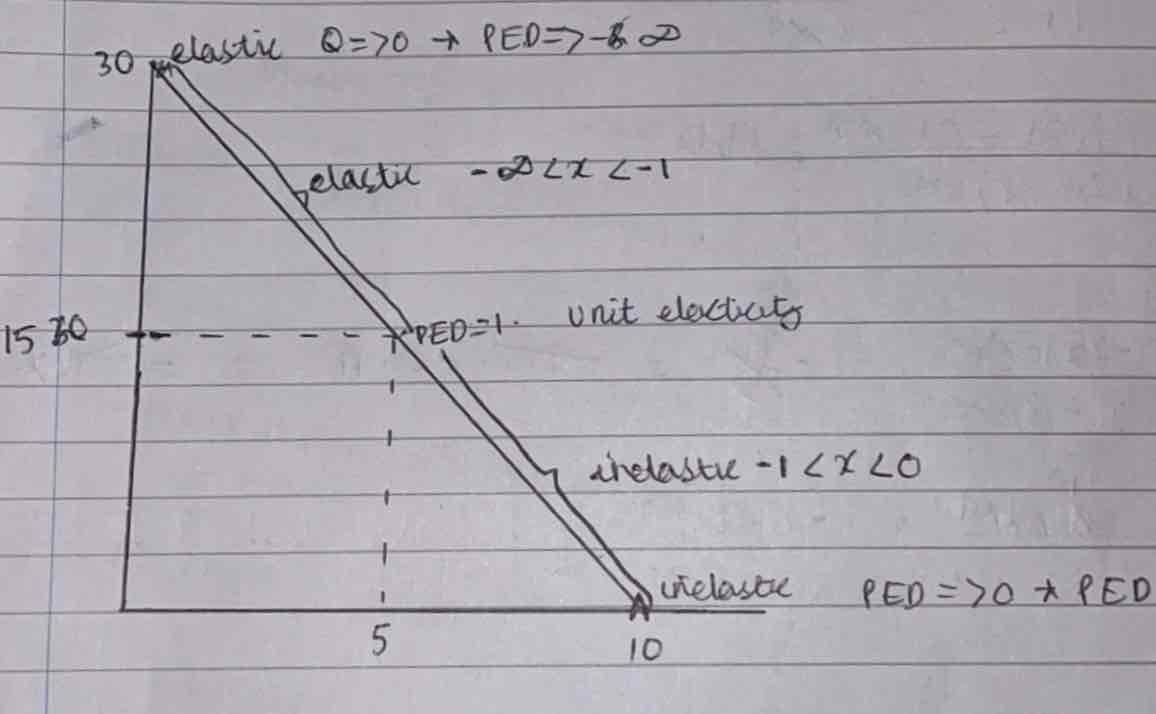
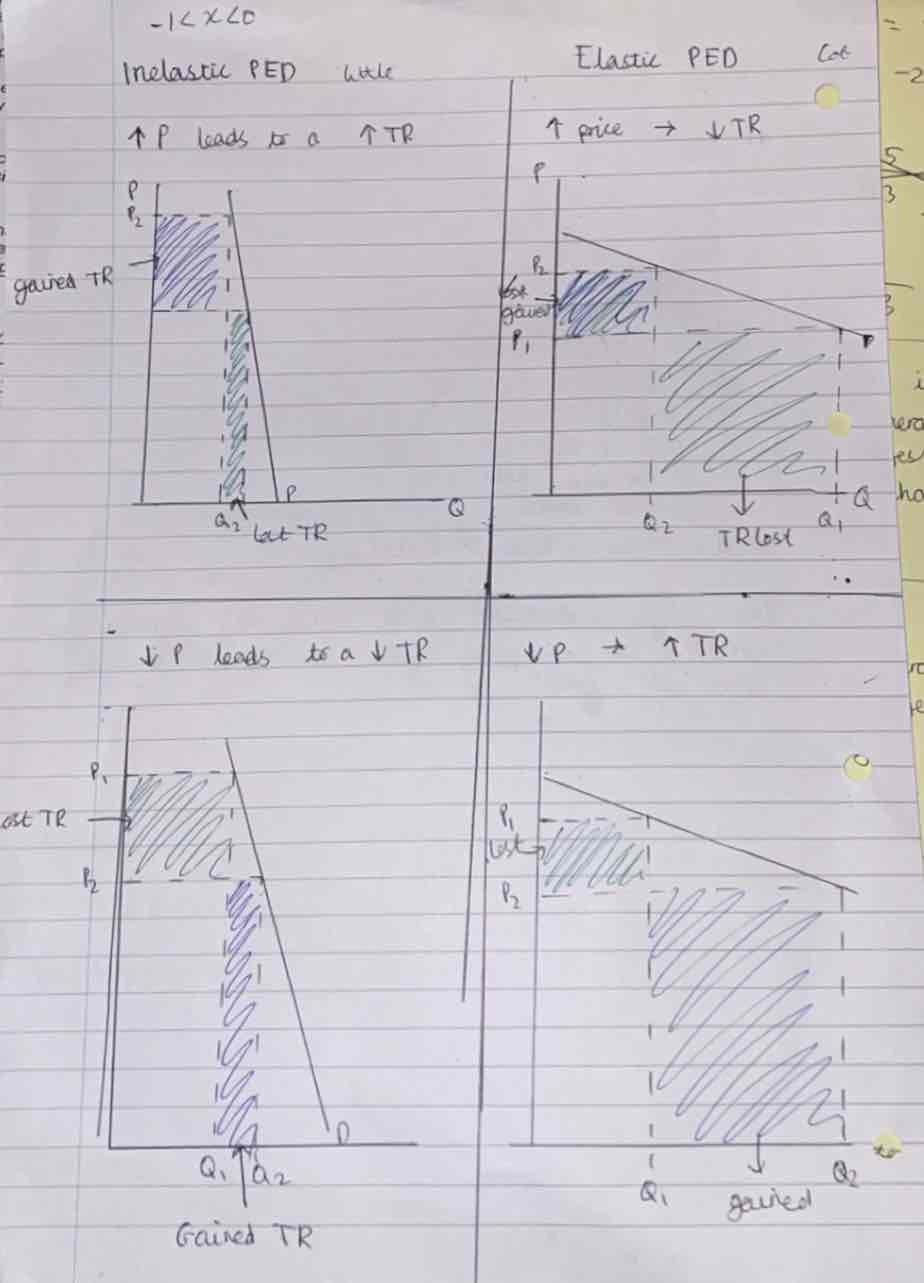
Inelastic -1<PED<0 - demand is relatively unresponsive to a change in price
Perfectly inelastic PED= 0 demand is totally unresponsive to change in price.
Unitary elastic PED= -1 change in demand= change in price
Elastic -infinity<PED< -1 Demand is relatively responsive to changes in price. (Vertical)
Perfectly elastics PED=-infinity. Any increase in price will result in demand falling to zero. (Horizontal)
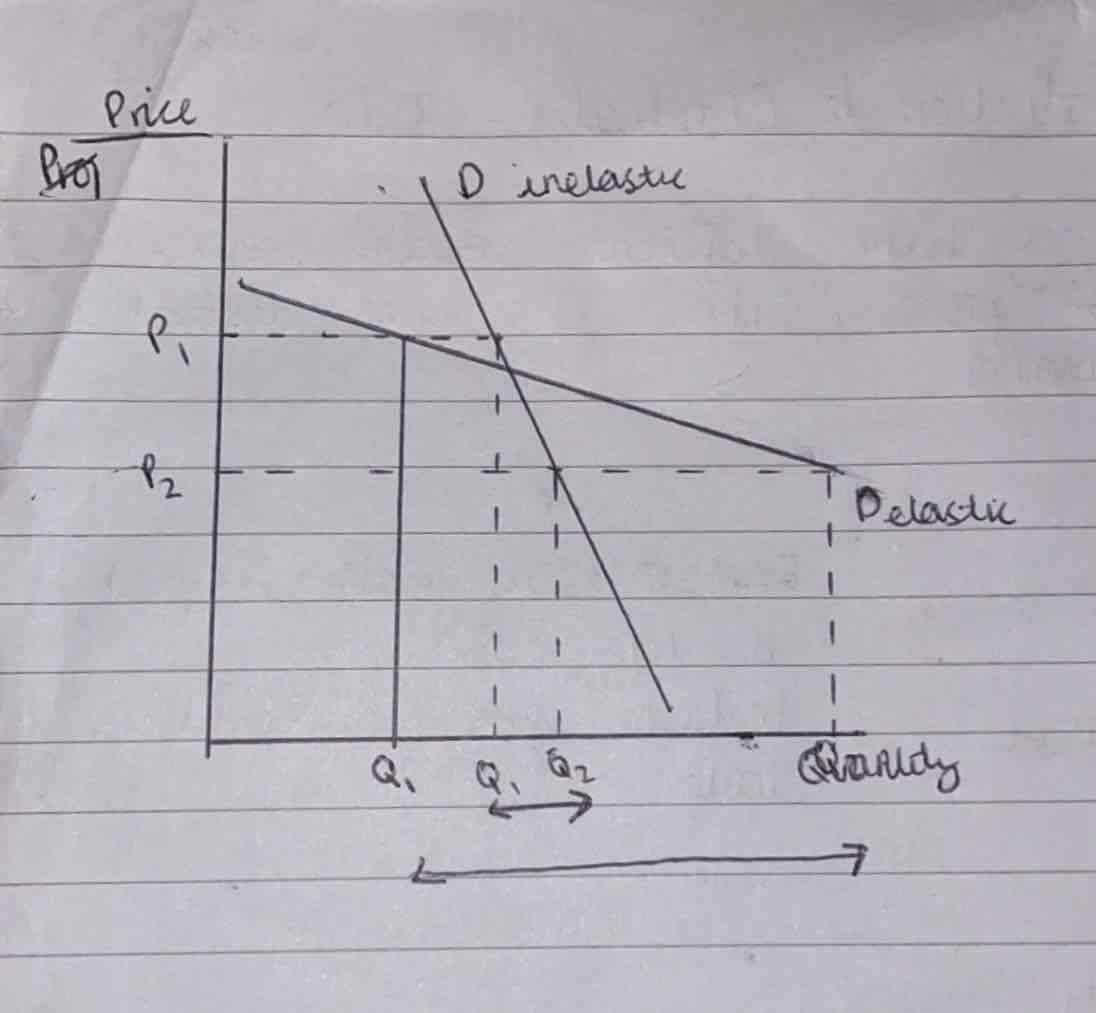
What does the graph of an inelastic and elastic hood look like?
Inelastic- steep, touches x-axis.
Elastic- shallower, touches y-axis.
Where are the PED values on a demand graph?
What does the area under the demand curve at a given price represent?
The total revenue from the sale of goods.
What is income elasticity of demand?
YED measures the responsiveness of demand to changes in income.
How do you calculate Income elasticity of demand?

What is the YED value of an inferior good?
YED<0
As income falls, demand for the good increases. As income rises, demand for the good decreases. An inverse relationship.
What’s the YED value for a normal good?
How do you determine if this is a necessity or a luxury?
YED>0
As income falls, demand falls. As income rises, demand rises. A positive relationship
Luxury: YED>1
Necessities 0<YED<1
What does cross elasticity of demand measure?
XED measures how the demand for one good responds to changes in price of another good.
How do you calculate cross elasticity of demand?

What are complementary goods?
What’s the XED value of complementary goods?
Two goods that are complements/ consumed together experience joint demand.
XED value is negative (-) as a fall in the price of one good leads to a fall in demand of the other. - x + = -
What is a substitute good?
What’s the value of the cross elasticity of demand for substitute goods?
Substitute goods are alternate goods that can be used for the same purpose.
XED is positive. + x + = +
Define market.
A market is a voluntary meeting of buyers and seller with exchange taking place.
What’s a competitive market?
Markets in which the large number of buyers and sellers possess good market information and can easily enter or leave the marker.
Define effective demand.
Effective demand is the desire for a good or service backed with the ability to pay.
What’s the difference between market demand and individual demand?
Market demand is the quantity of a good or service that all of the consumers within a market are willing and able to buy at different marker prices, whereas individual demand is the demand of one particular consumer or individual.
What factors determine price elasticity of demand?
Substitutability, percentage on income, necessities or luxuries, the ‘width’ of the market definition, time.
What are examples of goods/cases which produce an upward sloping demand curve?
Veblen goods, speculative demand and goods for which consumers use price as an indicator of quality.
What’s elasticity?
The proportionate change in one variable in response to another variable.
What is market supply?
The quantity of a good or service that all the firms in a market plan to sell at given prices in a given period of time. It is the amount of a product that is available to purchase at any given price.
Why do supply curves slope upwards?
There is a direct relationship between the price and quantity supplied due to: firms objective of maximising profit and production costs. Higher prices also increase market supply as more firms enter the market
Waht are reasons for a shift in the supply curve?
Costs of production, technical progress, taxes imposed on firms and subsidies.
Productivity, indirect taxes, number of firms, technology, subsidies, weather, costs of production. PINTSWC
What is price elasticity of supply and how can you calculate it?
PES measures the responsiveness of supply to changes in price.
PES= proportionate change in QS/ proportionate change in price.
What are the different PES and their values?
Elastic: PES>1- a change in price causes a more than proportionate change in QS. Touches y-axis.
Inelastic: 0<PES<1. a change in price causes a less than proportinate change in income.Touches x-axis.
Perfectly Elastic: PES= infinity, any amount is supplied at or above a given price level. Horizontal.
Unit elastic: PES=1
Perfectly inelastic: PES=0, QS is the same at any and all prices. Vertical.
What are the factors that determines PES?
The length of the production period(quicker-more elastic, slower- inelastic), availability of spare capacity (a lot-elastic, little/none-inelastic), factor substitutability (hoses easily factors of production can be switched between different productive processes) , barriers to entry (obstacles- inelastic, easy to enter- elastic), the ease of accumulating stock.
what is joint supply?
When one good is produced, another good is also produced from the same raw materials, perhaps a by-product. E.g beef and leather.
What is composite demand?
Demand for a good or service which has more than one use, which means that an increase in demand for one use of the good reduces the supply of the food for an alternative use. It is related to the concept of competing supply. E.g land- biofuels and wheat.
What is perfectly elastic demand?
The same quantity is always demanded at or below a given price, an increase in price will cause quantity demanded to fall to zero as there are perfect substitutes available. It is represented by a horizontal line.
What is perfectly elastic supply?
Supply will remain the same at or above a given price point, if the price falls below this price (the supply curve), the amount supplied will fall to zero as there is no incentive to stay in the market due to the profit available being too low.
What is market equilibrium?
A market is in equilibrium when planned demand equals planned spending, where the demand curve crosses the supply curve.
What is excess demand?
When consumers wish to buy more than firms either to sell, with the price below the equilibrium price.
What is excess supply?
When firms wish to sell more than consumers wish to buy, with the price above the equilibrium price. In response, firms will reduce their prices to clear excess stock.
What happens when the market is in disequilibrium?
In a competitive market, there will be changes in the market price, creating a new equilibrium.
What is consumer surplus?
The difference between what a consumer is willing and able to pay for a good and what they actually pay (the excess utility that they receive).
What is market surplus?
The difference between how much a producer is willing and able to supply for good and what they actually pay (excess utility).
What is total welfare?
Consumer surplus + producer surplus = total welfare
What is market equilibrium?
Where demand equals supply and there is no tendency for price or quantities to change.
What is joint demand/ compliments?
Goods are consumed together. E.g consoles and games.
What’s competitive demand?
Goods which are substitutes (alternatives) e.g beef and pork
What’s derived demand?
Demand for a good or factor of production is demanded but not for it’s own sake but but as the consequence of the demand for something else.
What is composite demand?
Demand for a good which has more than one use. An increase in the demand for one use of the good reduces the supply of the alternative use of the good. For example land can be used for both the production of wheat and biofuels.
What is joint supply?
Two goods are produced simultaneously e.g beef and leather.
What does the analogy PSSST stand for?
PSSST- determinants of PES. Production lag, Stocks, Spare capacity, Substitutability of the factors of production, Time (short run- inelastic, long run-elastic)
What does the analogy SPLAT stand for?
Determinants of PED. Substitutability, Percentage of income, Luxury/ necessity, Addictive/ habitual, Time period (short- inelastic, long-elastic)