anatomy unit 6: the nervous system
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
sensory input
monitors changing occurring inside and outside the body
integration
processes and interprets sensory using “relay neurons” or “interneurons;” mainly occurs in brain and spinal cord
motor output
response to integrated stimuli by activating effector organs (muscles and glands)
central nervous system
integrating and command center; brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
cranial nerves and spinal nerves
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight response
parasympathetic nervous system
rest and digest response
sensory nervous system
aka afferent
carries signal to CNS
motor nervous system
aka efferent
carries information away from the CNS to muscles and glands
somatic nervous system
controls voluntary movements
autonomic nervous system
controls involuntary/subconscious movements
mechanoreceptors
sense touch
thermoreceptors
sense temperature
photoreceptors
sense light
chemoreceptors
sense taste & smell
nociceptors
sense pain
neuroglia
support cells
supports, insulates, and protects neurons
do not transmit impulses
divide continuously
neurons
structural unit of the nervous system
transmits electrical impulses
cannot divide
highly specialized
can conduct electricity
amiotic
describes cells that cannot divide
astrocytes
in CNS
star-shaped
anchor and brace neurons
makes exchanges between capillaries & neurons
cleans up potassium & sodium ions
microglia
in CNS
small ovoid cells with thorny processes
spider-like phagocytes
disposes of debris
ependymal cells
line central cavities of the CNS
cells are squamous and columnar shaped with cilia
circulates cerebrospinal fluid
oligodenrocytes
in CNS
produce myelin sheath
satellite cells
surrounds neurons in PNS
protects and cushions neurons
Schwann cells
in PNS
surrounds & forms myelin sheath in PNS
similar to oligodendrocytes
dendrites
1
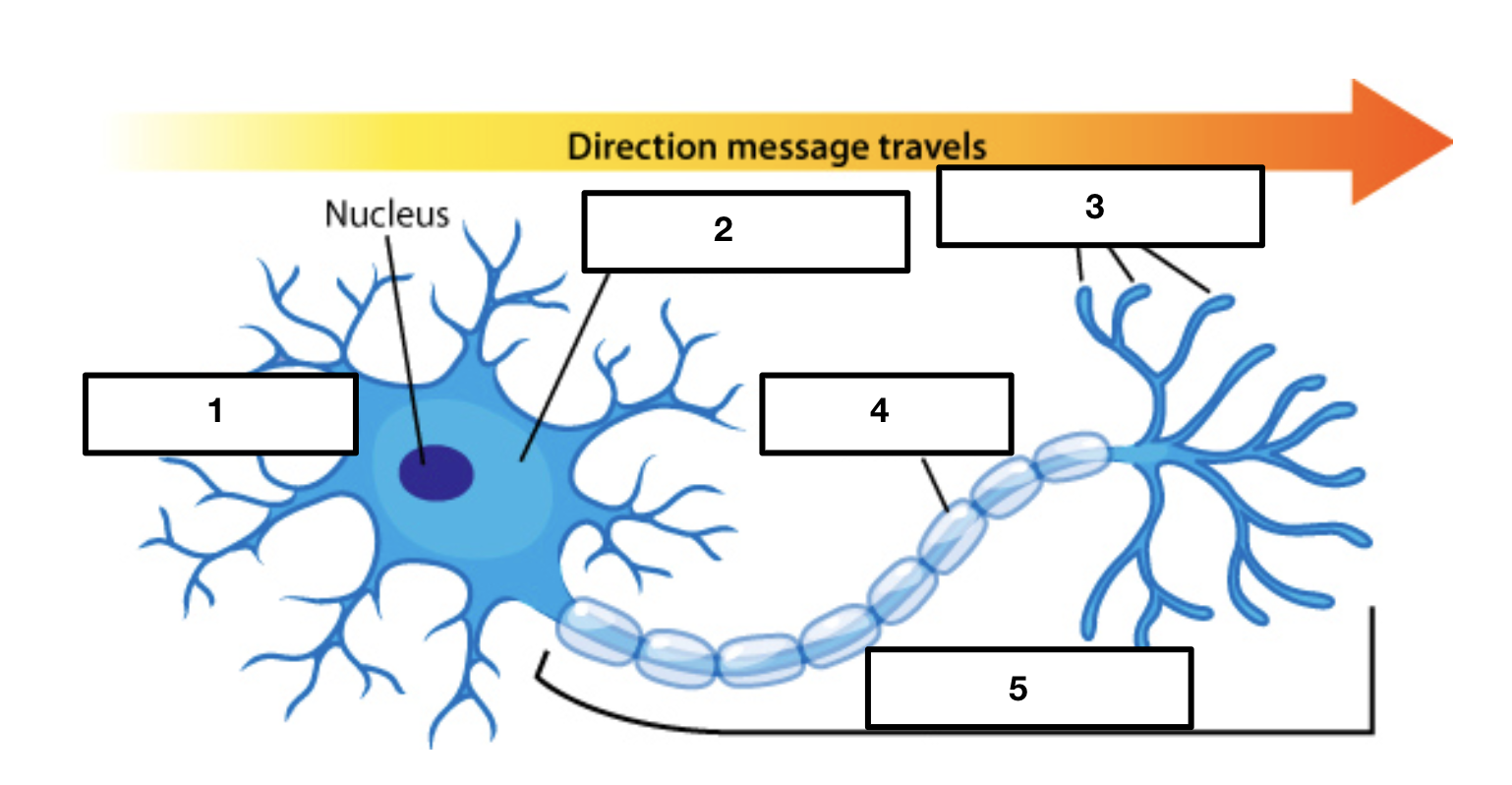
soma/cell body
2
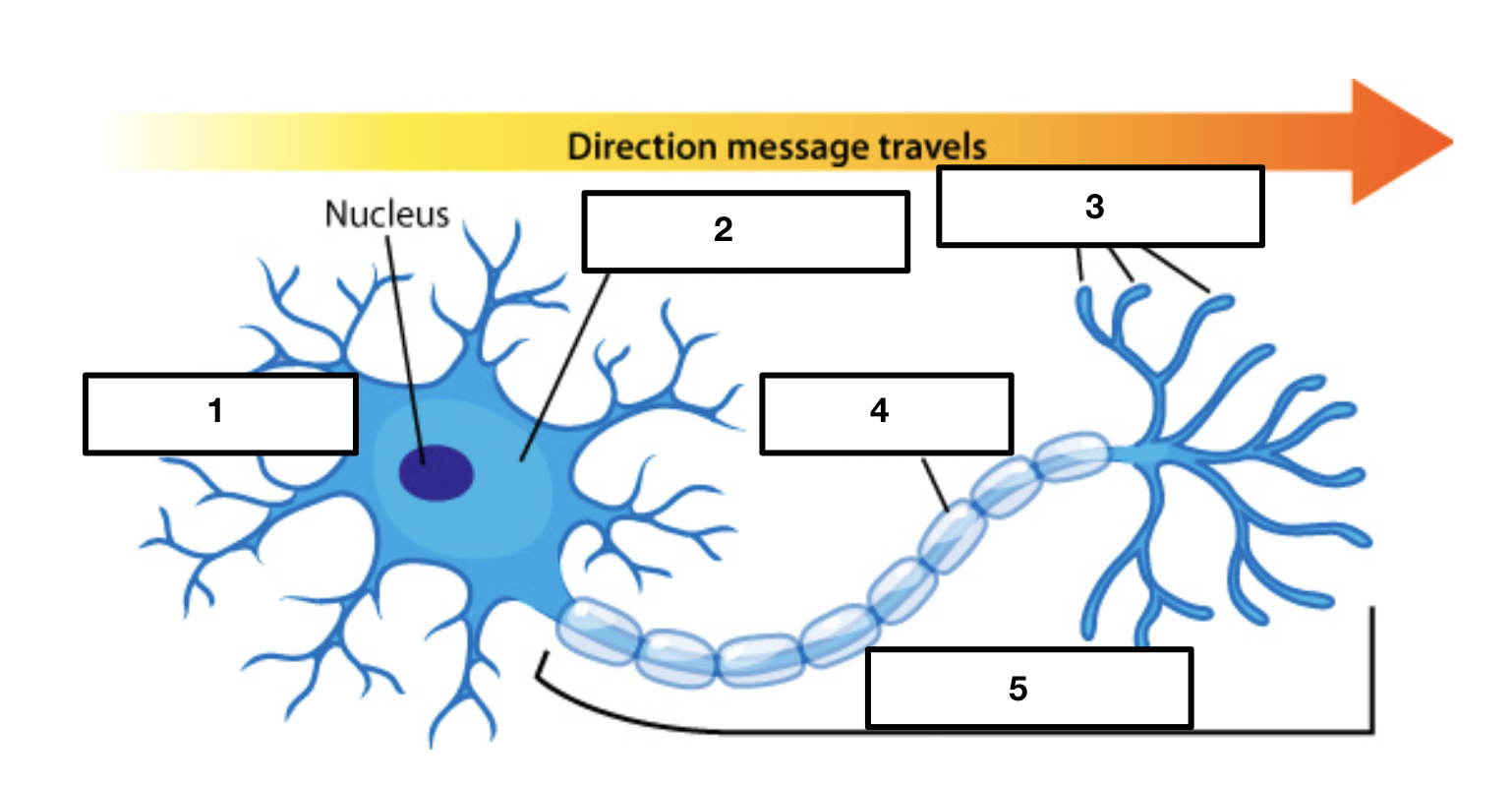
axon terminals
3
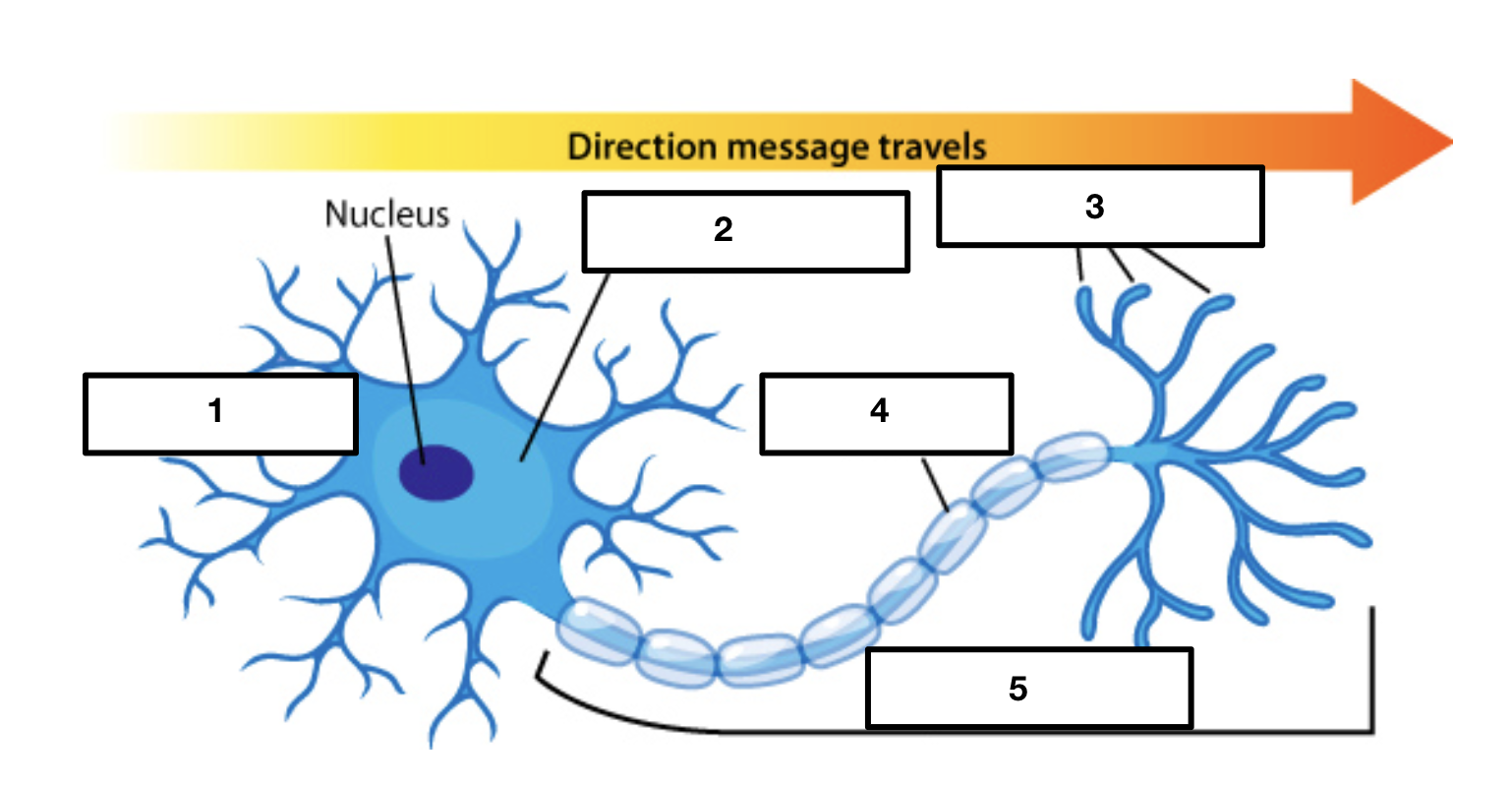
myelin sheath
4

axon
5
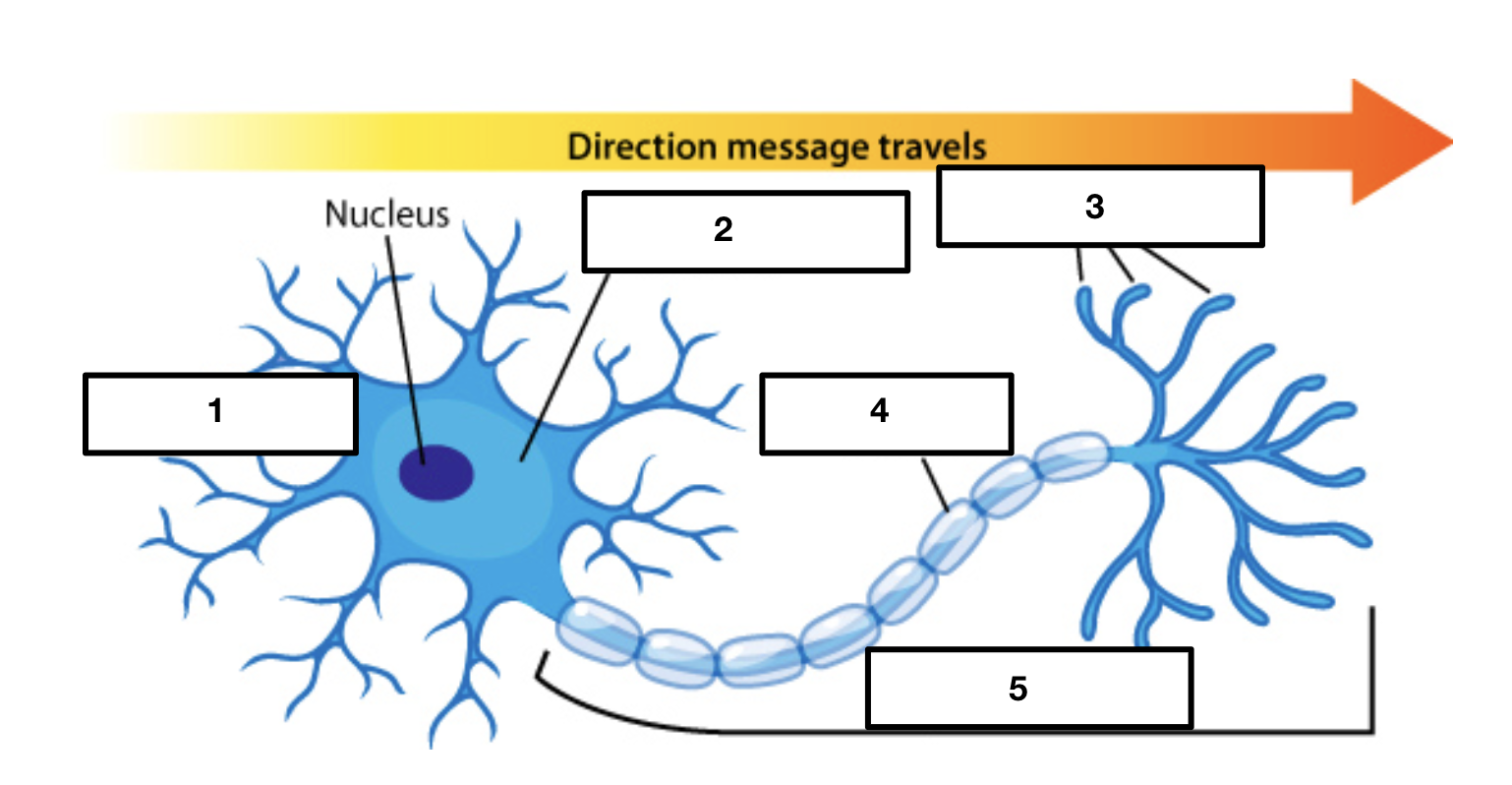
cell body/soma
metabolic center
most found in CNS
dendrites
main input or receptive region
receives signals from other neurons
conducts impulses toward the cell body
axon
each neuron only has one
conducting region of the neuron
some are short and some are long depending on where neurons are
myelin sheath
covers and protects axon
increases speed of impulse
nodes of Ranvier
gaps in the myelin sheath
help conduct impulse more rapidly
multipolar neurons
three or more processes
one axon and many dendrites
most common neuron type
most are in CNS
bipolar neurons
two processes
one axon and one dendrite
only found in sensory organs
unipolar neurons
short, single process leaving the cell body
mostly found in sensory organs
sensory neurons
send signals to the CNS
motor neurons
send signals away from the CNS
interneurons
sit in between the sensory and motor
can also be called relay neurons
99% of neurons in the body
in the brain & spinal cord
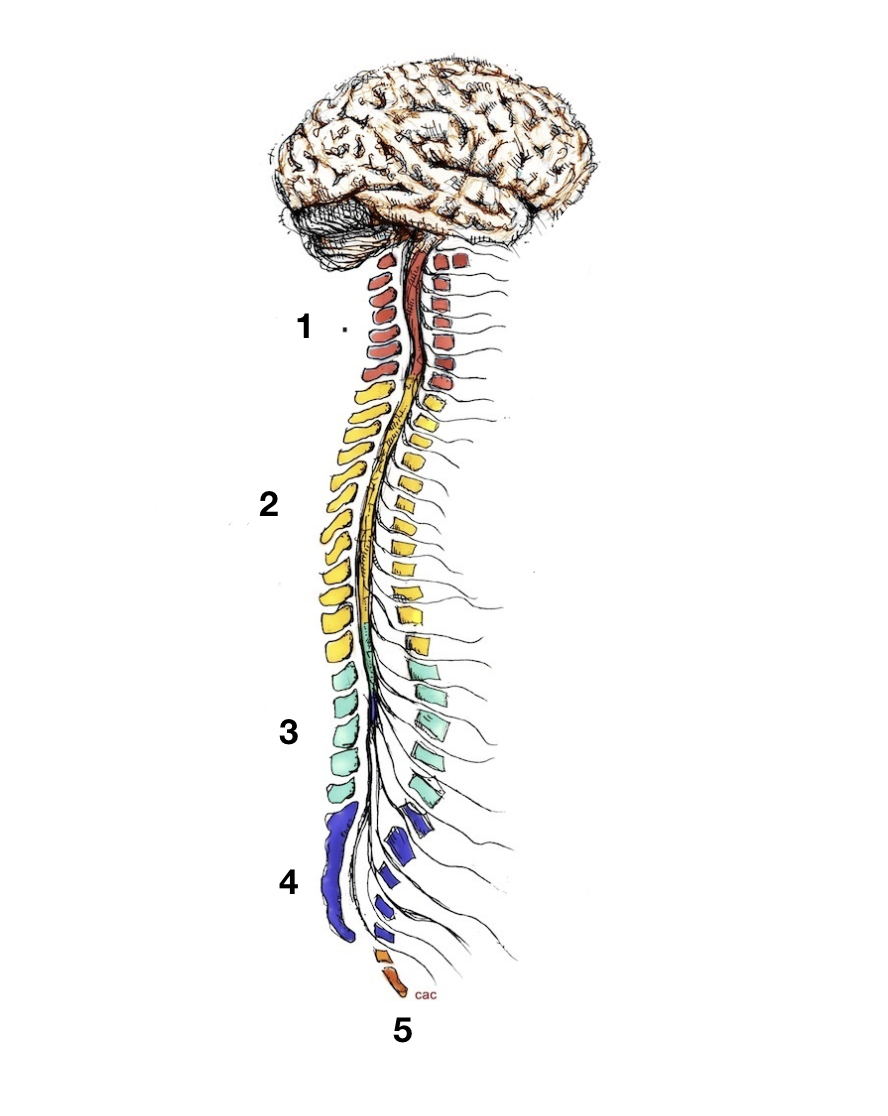
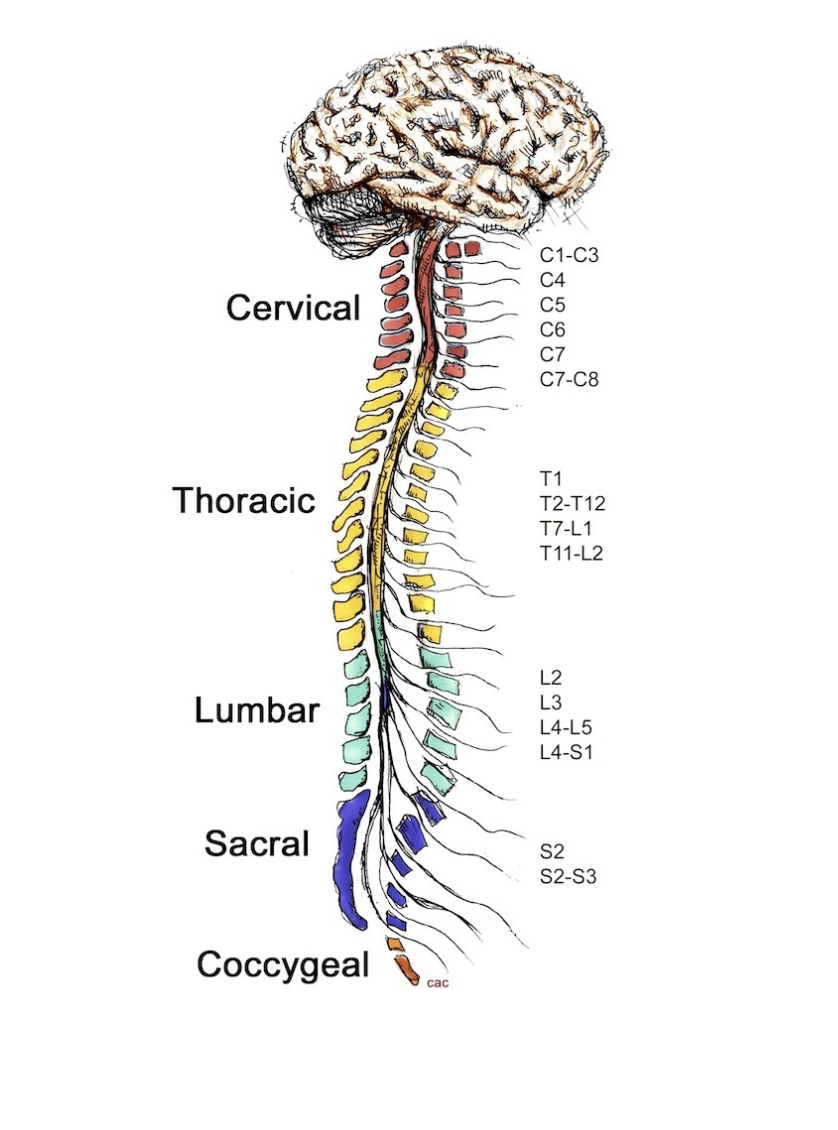
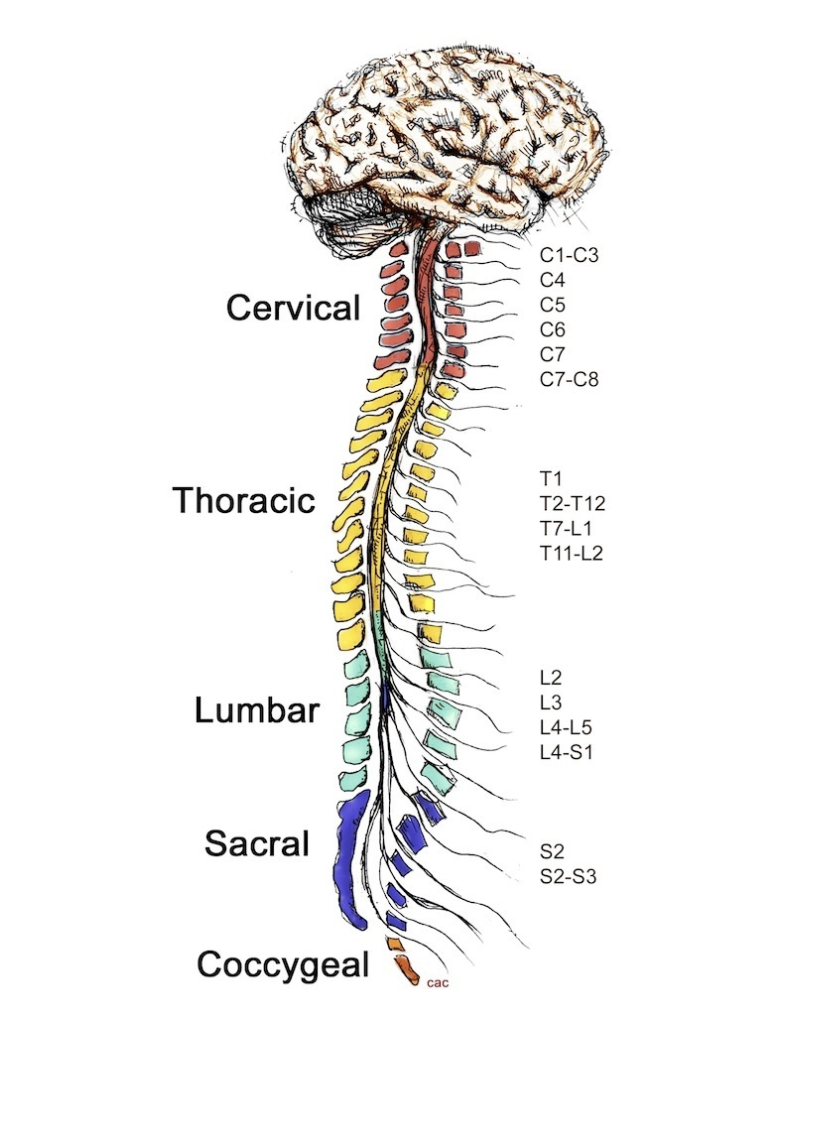
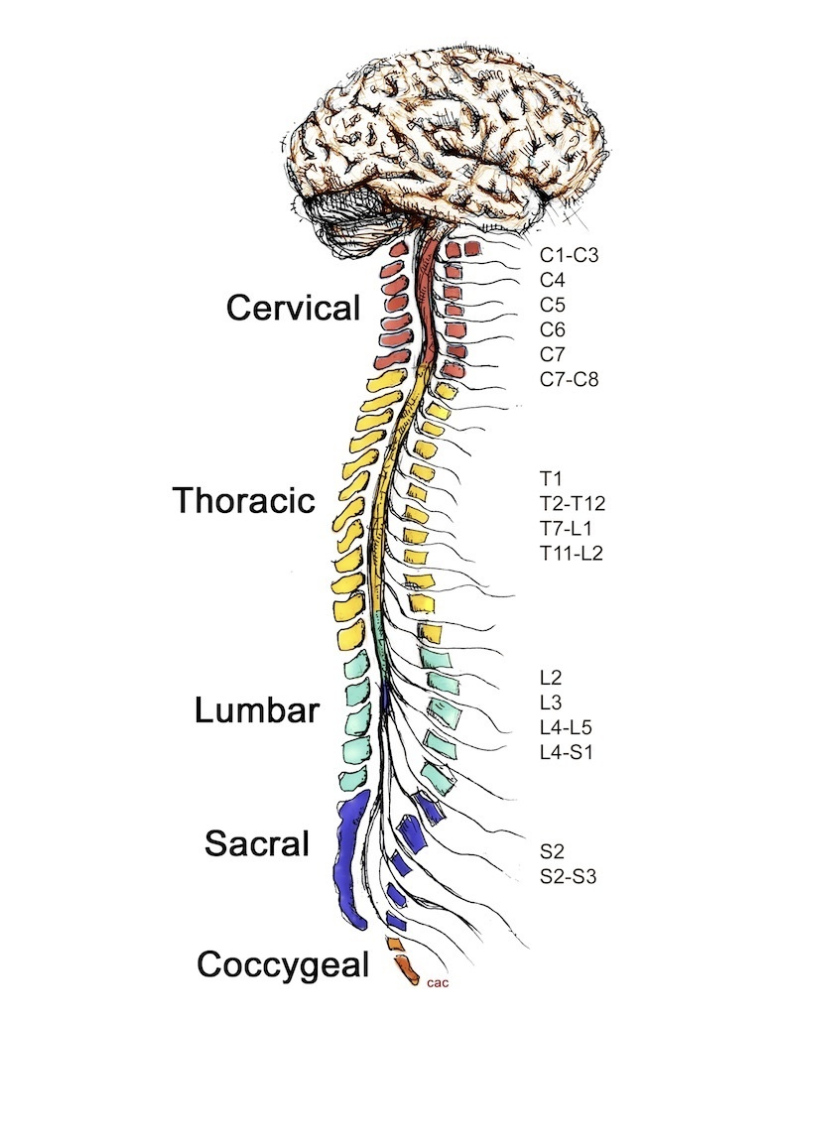
cervical
1
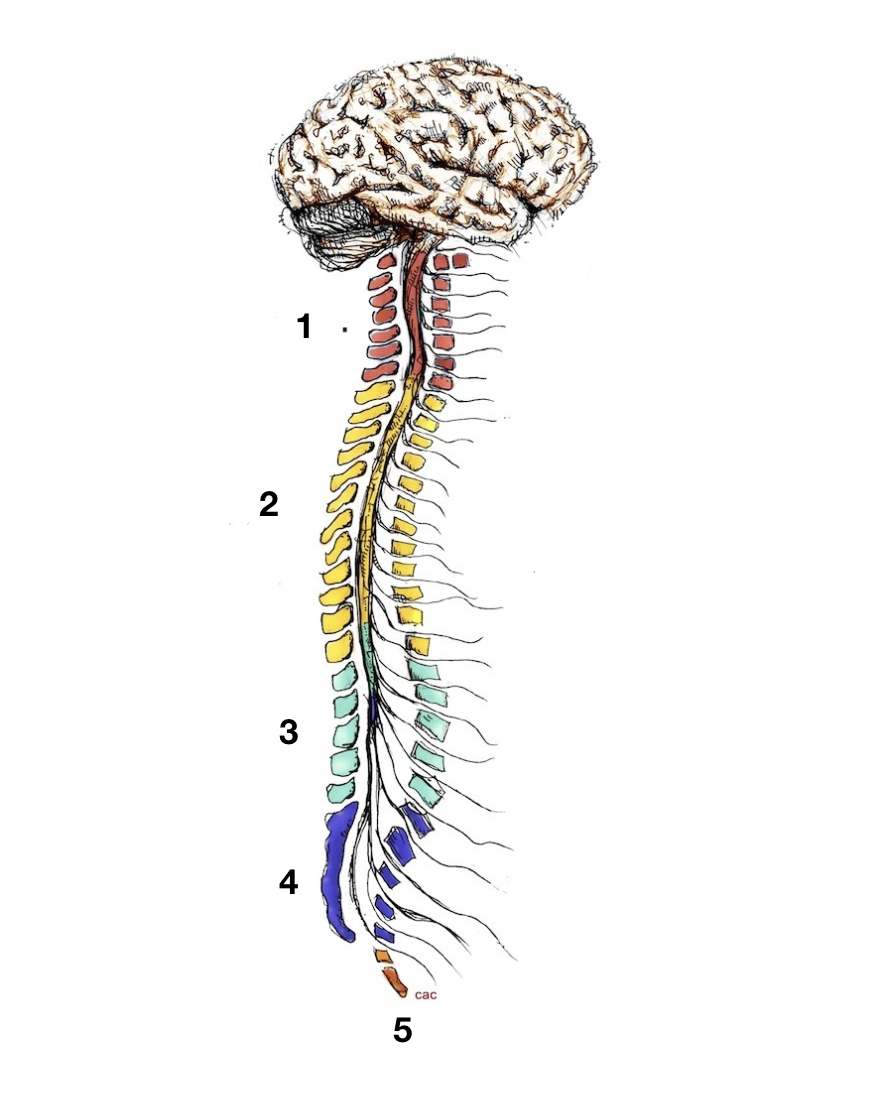
thoracic
2
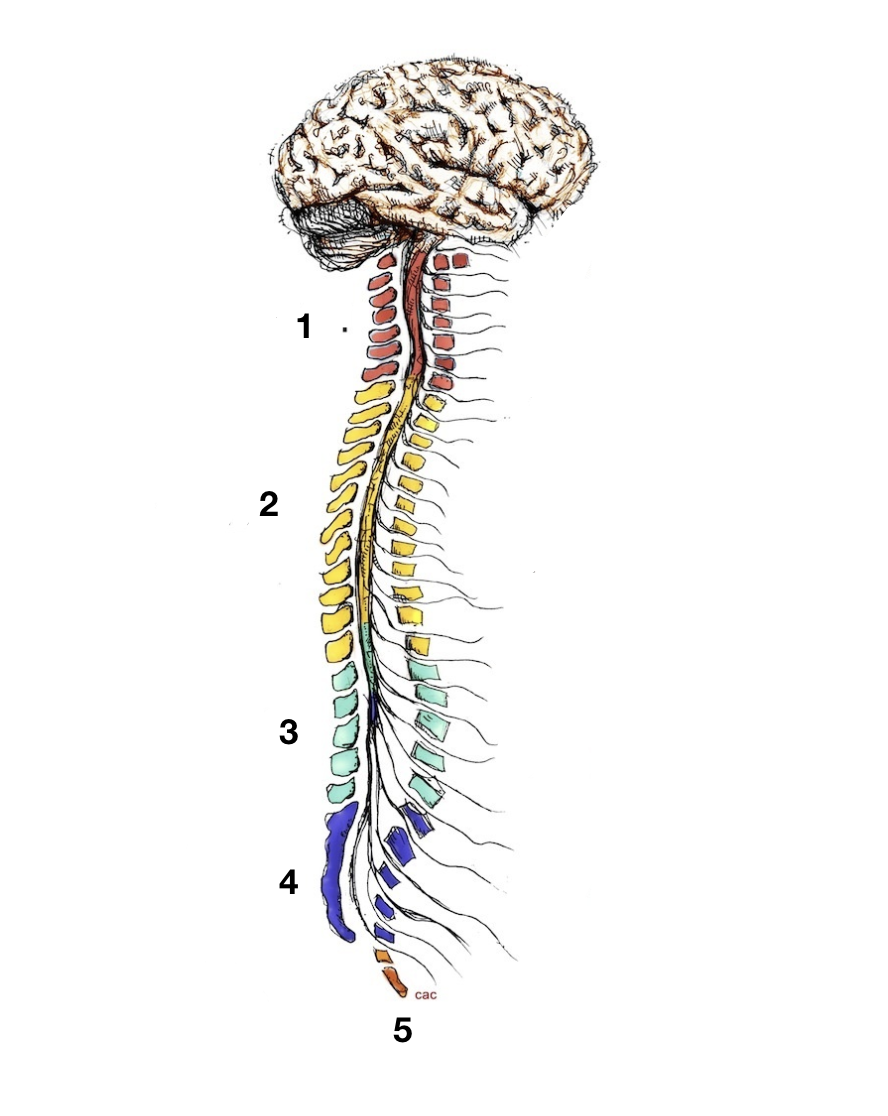
lumbar
3
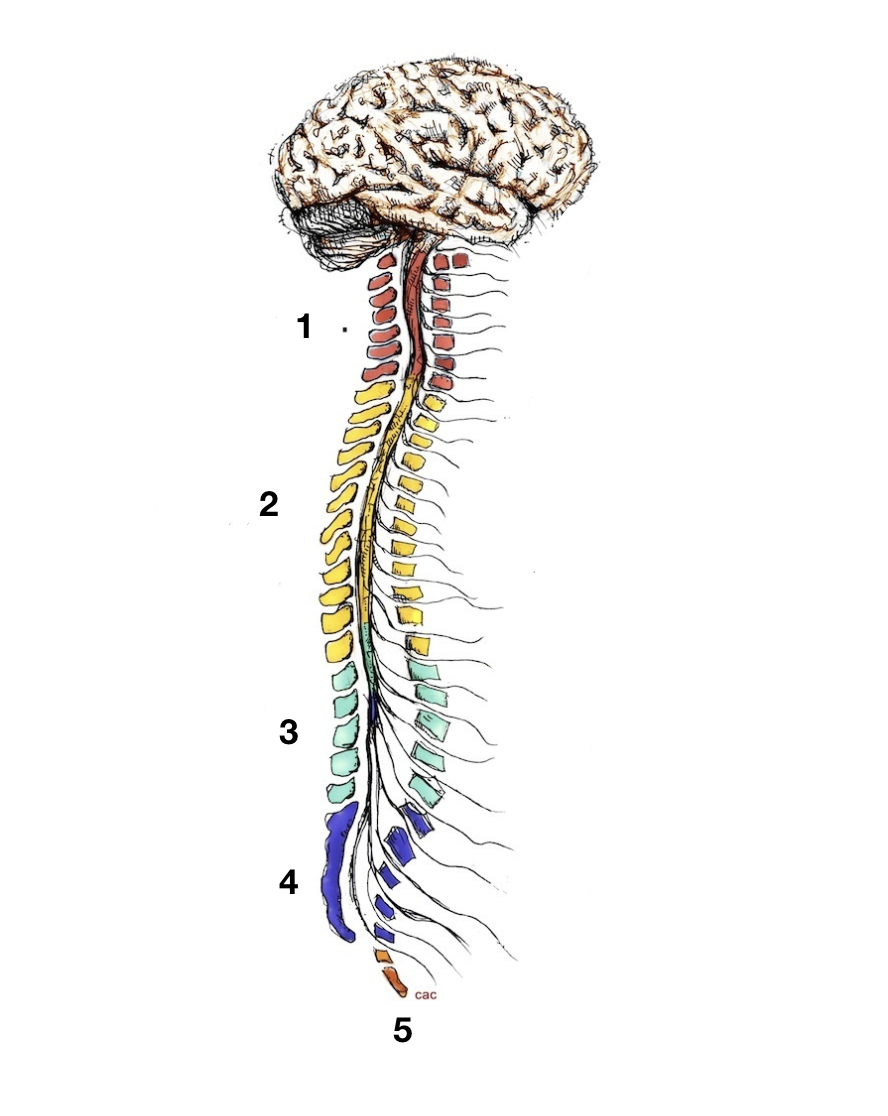
sacral
4
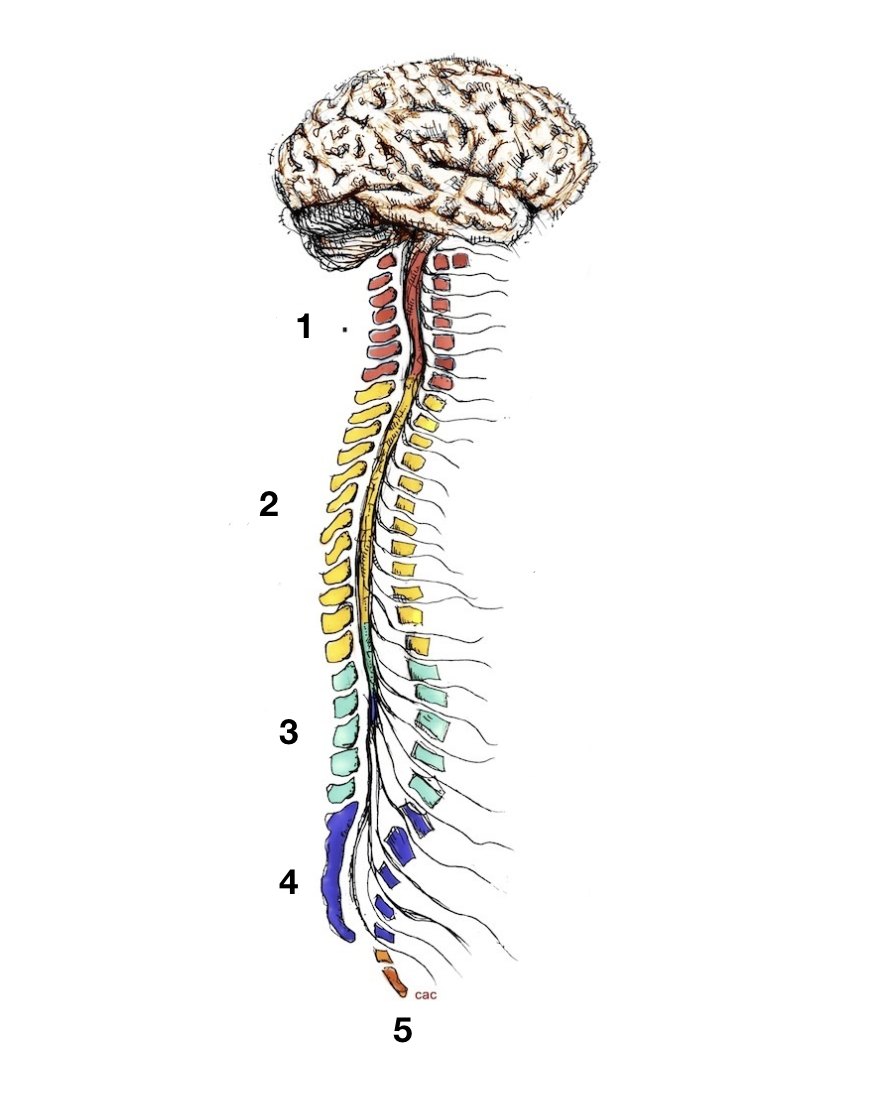
coccygeal
5
neck muscles
C1-C3 control ________
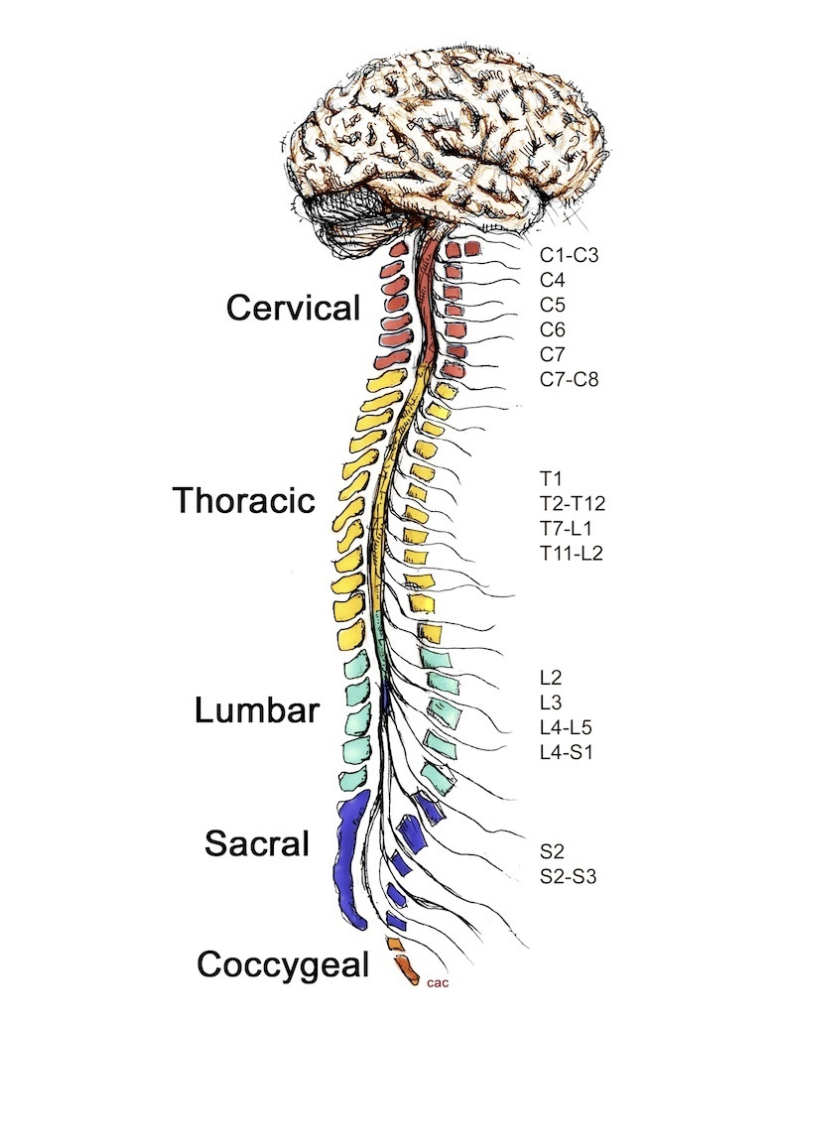
diaphragm
C4 controls __________
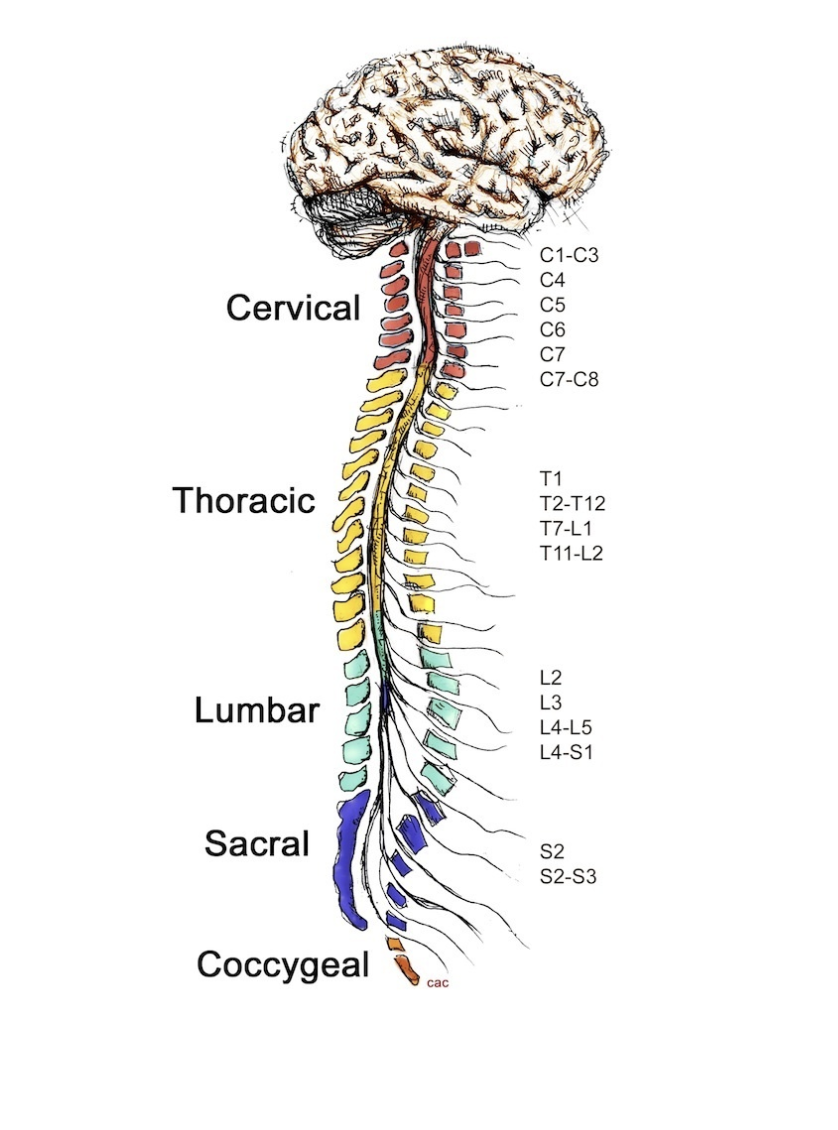
deltoid
C5 controls __________
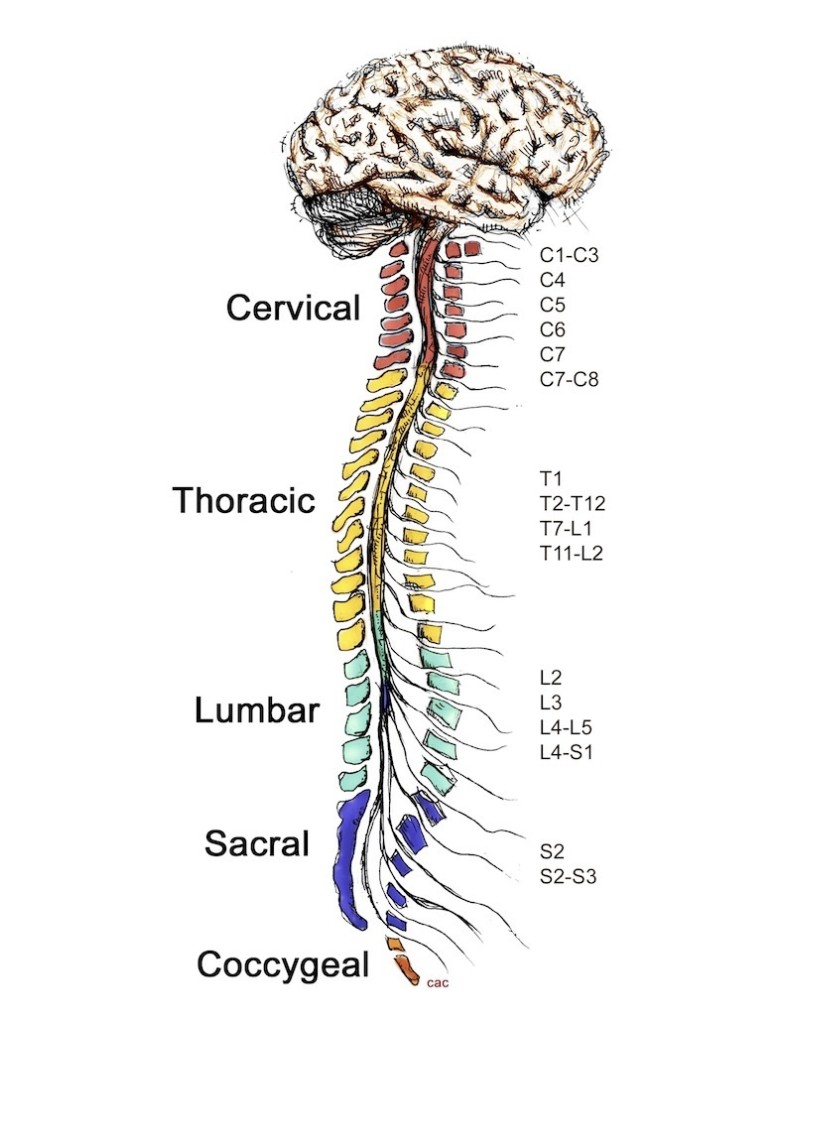
wrists
C6 controls __________
fingers
C7-C8 control __________
hands
T1 controls __________
intercostals
T2-T12 control __________
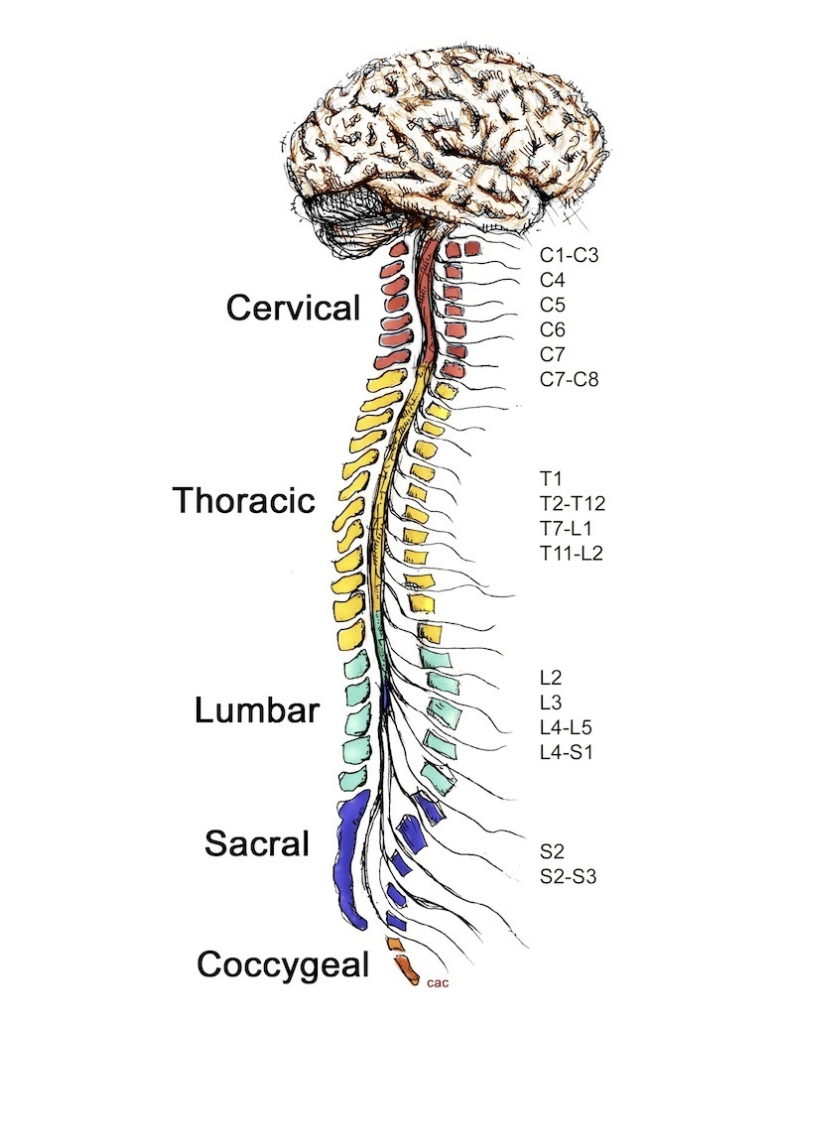
L2 controls __________