BIOL 456 Microbe-Microbe Symbiosis pt. 2
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Red Algae
• Primary Endosymbiosis
• Mostly marine, but some freshwater and terrestrial
• Can be unicellular or multicellular
• a.k.a. Rhodophyta ( greek for ‘rose plant’)
• color is from phycoerythrin, an accessory pigment
Green Algae
Primary Endosymbiosis
• are also called chlorophytes
• Closely related to plants
• Most inhabit freshwater, but some are marine or terrestrial
• Can be unicellular to multicellular
• Have sexual and asexual reproduction
Diatoms
Secondary Endosymbiosis (red algae)
• Responsible for ~40% of primary productivity in the ocean!
• Over 100,000 species of diatoms
• Unicellular
• Freshwater and marine habitats
• Cell walls are made of silica
• Exhibit radial and pinnate symmetry
• Appeared on Earth about 200 million years ago
Diatoms
a naturally occurring, soft, sedimentary rock
Many uses
• Abrasive
• Insecticide
• Absorbent
• a stabilizing component of dynamite
• thermal insulator.
Coccolithophore
Secondary Endosymbiosis (red algae)
• Calcium carbonate plates (or scales) called coccoliths
• Important for global Carbon cycle- production of CaCO3 is a CO2 sink
• Calcification can:
• Accelerate photosynthesis
• Protect from photodamage
• Protect from viruses and grazing organisms
• Almost exclusively marine and are found in large numbers throughout the sunlight zone of the ocean.
Coccolithophore
• Chalk
• soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock
• Primarily CaCO3
• formed by coccoliths fallen to the sea floor.
Dinoflagellates
• Secondary endosymbiosis (red algae)
• Diverse marine and freshwater phototrophic organisms
• Single celled
• Have two flagella with different insertion points on the cell
• Some are free-living, and others live symbiotically with corals
• Dense suspensions of these cells are called red tides (Figure 17.10)
Dinoflagellates
• can bloom and have harmful effects in nutrient polluted warm waters
• Some associated with red tides produce a neurotoxin
• Associated with fish kills and human poisoning
• Pfiesteria piscicida is a genus of toxic _______ responsible for massive fish kills
Microbe-Microbe Ectosymbiosis
A symbiotic relationship where one organism lives on the outside of another organism.
• The smaller symbiont is often attached to the surface of the larger organisms.
Lichens
• A mutualistic relationship between a fungus and an alga or cyanobacterium
• Alga is photosynthetic and produces organic matter
• The fungus provides a habitat within which the phototrophic partner can grow protected from desiccation and erosion
Lichens
• Leafy or encrusting microbial symbioses
• Often found growing on bare rocks, tree trunks, house roofs, and the surfaces of bare soils.
Lichens
Morphology of the _______ is primarily determined by the fungal partner – many fungi can form
_____ while the diversity of phototrophs is much lower
• Fungi can secrete organic acids that promote dissolution of organic nutrients from rock surfaces
• Fungal partner protects phototroph from dehydration
• Typically grow slowly – a 2cm diameter lichen may be several years old.
Consortia
In freshwater there are microbial mutualisms called _______
Consortia “Chlorochromatium aggregatum”
Consist of green sulfur bacteria (called epibionts) and a flagellated rod-shaped bacterium
• _______ given a "genus species" name
• Green sulfur bacteria are obligate anaerobic phototrophs
• Provide partner with organic carbon (food)
• Flagellated rod allows for movement- also anaerobes
• Provide cyanobacteria with access to ideal niche via motility
Consortia
• Often found in the thermo/chemocline of stratified freshwater lakes worldwide.
• Can account for over half of the bacterial biomass in lakes
• Movement allows them to adjust to changing gradients of light, oxygen, and sulfide,
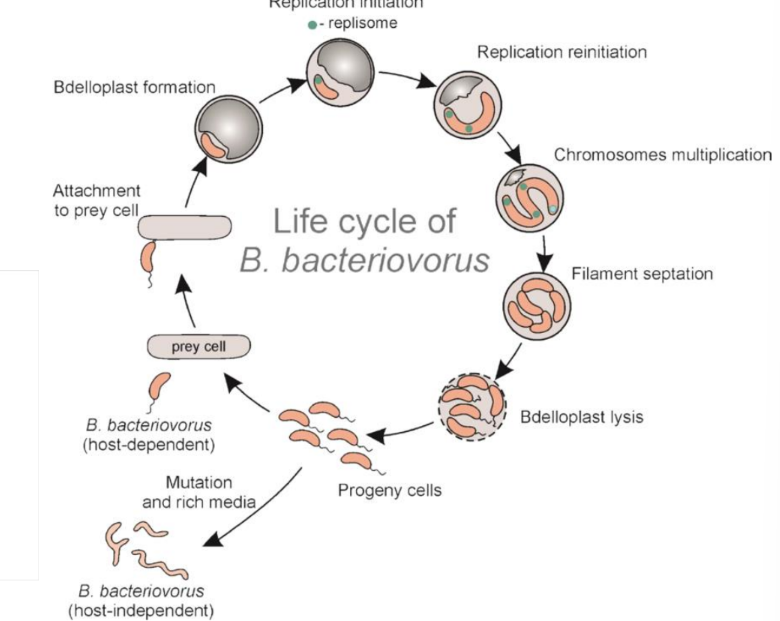
Predatory Bacteria
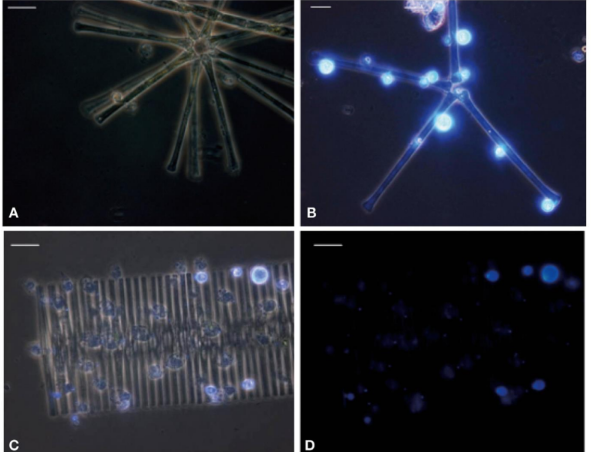
Fungal Parasites of Algae
reduced genomes
Many prokaryotic protist symbionts have _______
Prokaryote- Protist
_________ symbiosis are very common.
Evolutionary Pressures
prokaryote-protist vs prokaryote-animal symbioses:
• Many Similarities
• Common ________