International Trade and Economic Development
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
How does international trade boost economic development?
By opening access to larger global markets, allowing countries to expand production and innovate.
What does international trade encourage in terms of specialization?
It encourages specialization based on each country's strengths, leading to greater efficiency, productivity, and a wider variety of goods for consumers.
What are the benefits of connecting nations to global value chains?
It attracts investment, creates jobs, and supports technology transfer.
What are some outcomes of integrating into the global economy?
Countries can diversify industries, reduce poverty, and strengthen their resilience to economic challenges.
What is international trade?
The purchase and sale of goods and services by companies in different countries.
What are the two primary types of International Trade Theory?
Classical Country-Based Theories and Modern Firm-Based Theories.
What characterizes Classical Country-Based Theories?
They are historical theories that evolved from 1500 onwards, focusing on the country perspective rather than the firm.
What characterizes Modern Firm-Based Theories?
These theories emerged after World War II, developed by business school professors, focusing on multinational companies.
What is Import Substitution Industrialization (ISI)?
A strategy where a country produces goods locally instead of importing them, aimed at growing local industries and reducing dependence on imports.
What are the necessary conditions for Import Substitution Industrialization to work?
Selective domestic production, focus on labor-intensive goods, industry subsidies, and protectionist trade policies.
What is Absolute Advantage in trade theory?
A theory developed by Adam Smith stating that a country has an absolute advantage if it can produce a good in greater quantities with the same resources than another country.
How does selective domestic production work in ISI?
The government chooses specific goods to produce locally, reducing reliance on imported products.
What type of goods does ISI prioritize?
Labor-intensive goods, such as clothing and footwear, which can be easily produced with local labor.
What role do industry subsidies play in ISI?
They provide financial support and incentives to help local industries grow and compete.
What are protectionist trade policies?
Tariffs and import restrictions used to shield domestic industries from foreign competition.
What is Export-Led Growth (ELG)?
A strategy where a country focuses on selling goods to other countries to stimulate its economy, relying on openness and international trade.
What are the economic benefits of Export-Led Growth?
Increases income, GDP, and employment opportunities by producing competitive products for global markets.
What is Comparative Advantage according to David Ricardo?
The principle that countries should produce goods and services that utilize freely available resources and have lower opportunity costs.
What are the limitations of Absolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage?
Assumes two countries and two goods, no transportation costs, fixed factors of production, free trade, and ignores technological change.
What is the role of the World Trade Organization (WTO)?
Regulates and facilitates international trade between nations, established in 1995, replacing GATT.
What are the main functions of the WTO?
Trade rule-making, dispute settlement, trade monitoring, and capacity building for developing countries.
What is a Floating Exchange Rate?
Allowing currency to float with market forces to enhance export competitiveness.
What infrastructure improvements are necessary for Export-Led Growth?
Building and upgrading roads, ports, power, and telecommunications to boost production efficiency and exports.
What is the significance of deregulation in export-led growth?
Deregulating businesses allows market forces to spur entrepreneurship and attract foreign investment.
Which countries are referred to as the East Asian Tigers?
South Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Singapore.
What strategy did the East Asian Tigers adopt for economic growth?
They focused on producing goods for export markets instead of substituting imports.
What is the Most-Favoured-Nation (MFN) principle in WTO agreements?
Treating all trading partners equally and not discriminating between them.
How did the East Asian Tigers integrate into global trade?
By producing textiles, electronics, and high-value manufactured goods for wealthier countries.
What role did government play in the success of the East Asian Tigers?
Governments provided education, infrastructure, and export incentives while promoting openness to foreign markets.
What policies are necessary for achieving Export-Led Growth?
Liberalized trade, liberalized capital flows, and minimal government intervention.
What is the impact of removing tariffs and quotas on trade?
It simplifies exporting goods and importing inputs, facilitating international trade.
What is the relationship between opportunity cost and comparative advantage?
Opportunity cost refers to what is sacrificed to produce one unit of a good instead of another, guiding countries to focus on their comparative advantages.
What is the significance of international trade rules created by the WTO?
They create a framework for fair trade practices and help resolve trade disputes.
What is the importance of capacity building in the context of the WTO?
It provides technical assistance and training to developing countries to enhance their trade capabilities.
What is the expected outcome of adopting policies for export-led growth?
Increased competitiveness in international markets and economic development.
What were the economic strategies of the East Asian Tigers?
They relied on comparative advantages like low labor costs and pursued international competitiveness.
What is the historical context of Export-Led Growth?
It emerged as a formal, state-supported national strategy during the 1960s to 1980s.
What is national treatment in the context of international trade?
Treating foreigners and locals equally, ensuring imported and locally-produced goods are treated the same after entering the market.
What are the characteristics of developing countries?
Nations with a low standard of living, poor infrastructure, and a lack of industrialization, also known as less-developed, Third World, or nonindustrialized countries.
Can you name some examples of developing countries?
Philippines, Bangladesh, Kenya, India, and Vietnam.
How do countries declare themselves as developing in the WTO?
There is no fixed definition; countries self-declare their status as developing.
What is one importance of the WTO for developing countries?
It provides access to new markets, helping them reach larger economies and create opportunities for export growth.
What is the Washington Consensus?
A policy framework that emerged in the 1980s promoting free markets, trade liberalization, and reduced government intervention for developing countries.
Who outlined the Washington Consensus and when?
Economist John Williamson in 1989.
What shift in economic strategy did the Washington Consensus encourage in developing countries?
A shift from state-led, protectionist Import Substitution Industrialization (ISI) to open, export-driven growth strategies.
What preferential treatment do developing and least-developed countries (LDCs) often receive?
Duty-free access to some markets and technical assistance to help them participate in global trade.
What is one goal of the WTO's global system of trade rules?
To lower trade barriers, reduce production costs, and decrease prices for finished goods and services.
What significant economic strategies were adopted between the 1940s and 1970s?
Widespread adoption of Import Substitution Industrialization (ISI).
What economic strategy succeeded in East Asia from the 1960s to the 1980s?
Export-Led Growth (ELG).
What role does the WTO's dispute resolution system play for developing countries?
It provides a mechanism for addressing trade-related disputes, potentially reducing trade tensions.
What is one challenge developing countries face regarding WTO agreements?
Implementation difficulties due to a lack of financial and human resources.
What is a potential risk of the WTO for developing countries?
Exploitation, particularly in agriculture, where developed nations may maintain subsidies while pushing for liberalization.
What is the consequence of reduced normal tariff rates for developing countries?
They may lose some preferential treatment, making it harder to compete with developed nations.
What does the term 'loss of policy space' refer to in the context of the WTO?
The limitation of available policy options for developing countries to pursue their own development strategies.
What is the significance of the IMF and World Bank's promotion of liberalization policies starting in the early 1980s?
It marked a shift towards encouraging open market policies in developing countries.
What is the impact of the WTO on consumer prices in developing countries?
Lowered trade barriers can potentially lead to lower prices for finished goods and services.
What is the relationship between the Washington Consensus and neoliberal economic reforms?
The Washington Consensus typically embodies neoliberal principles, advocating for free markets and reduced government intervention.
What economic model did the Washington Consensus encourage developing nations to move away from?
The state-led, protectionist Import Substitution Industrialization (ISI) model.
What is a key event that occurred in 1989 regarding the Washington Consensus?
The Washington Consensus was officially articulated.
What are trade barriers?
Regulatory measures implemented by governments to control international trade and protect domestic industries.
What are the three main purposes of trade barriers?
To protect local jobs and industries, raise government revenue, and ensure national security and safety.
What are the two major types of trade barriers?
Tariffs and non-tariff barriers.
What is a tariff?
A tax imposed on imported goods, increasing their cost and making domestic products more competitive.
What are the potential downsides of tariffs?
They can lead to higher consumer prices.
What are non-tariff barriers?
Restrictions that limit the amount of goods entering a country without involving taxes.
What is a quota in the context of trade barriers?
A limit on the quantity of specific goods that can be imported, which helps shield domestic producers.
What is a subsidy?
Financial support given to local businesses to lower their production costs, aiding competition against foreign imports.
What is an embargo?
A complete halt to trading activities between two countries, representing one of the most extreme forms of trade barriers.
What is regional integration?
An agreement between groups of countries in a geographic region to reduce and ultimately remove tariffs and non-tariff barriers.
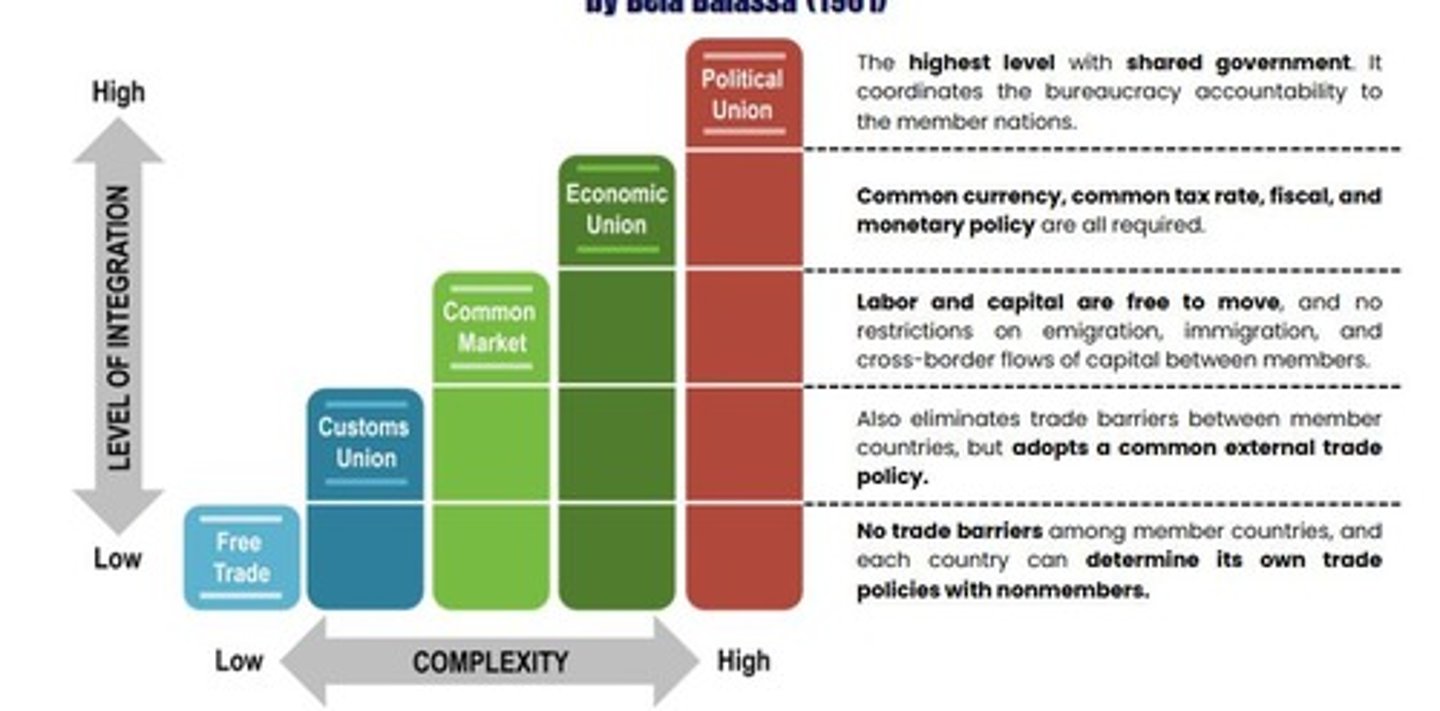
What is the ASEAN?
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations, a regional organization comprising ten Southeast Asian countries that promote economic growth, social progress, and regional stability.
List the ten countries that are part of ASEAN.
Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
How do trade barriers protect local industries?
By making imported goods more expensive or limiting their availability, thereby encouraging consumers to buy domestic products.
What is one economic effect of subsidies on local industries?
They can boost domestic industries but may lead to overproduction.
What is the impact of quotas on consumer choice?
Quotas may reduce consumer choice by limiting the variety of goods available.
What is the relationship between tariffs and government revenue?
Tariffs generate revenue for the government through taxes on imported goods.
How do trade barriers relate to national security?
They can be used to ensure safety by controlling the types of goods that enter a country.
What is one potential negative impact of tariffs on consumers?
Higher prices for imported goods.
What is the goal of regional integration agreements?
To facilitate the free flow of goods, services, and factors of production among member countries.
What are the benefits of regional integration for member countries?
Increased trade, economic growth, and improved regional stability.
What is the significance of the ASEAN in the context of regional integration?
It serves as a platform for Southeast Asian countries to collaborate on economic and social issues.
How do non-tariff barriers differ from tariffs?
Non-tariff barriers do not involve taxes but impose restrictions on the quantity or quality of goods.
What can be a consequence of implementing trade barriers?
They can lead to trade disputes between countries.