Biochem Lab Midterm
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
146 on a p20
14.6 microliters
072 on a p200
72 microliters
053 on a p1000
530 microliters
P(20) tip color and range
clear 2-20
P(200) tip color and range
yellow 20-200
P(1000) tip color and range
Blue 100-1000
precise
all points close together
accurate
all points close to the theoretical data
R²=1
percise and accurate
R²=0
Not precise or accurate
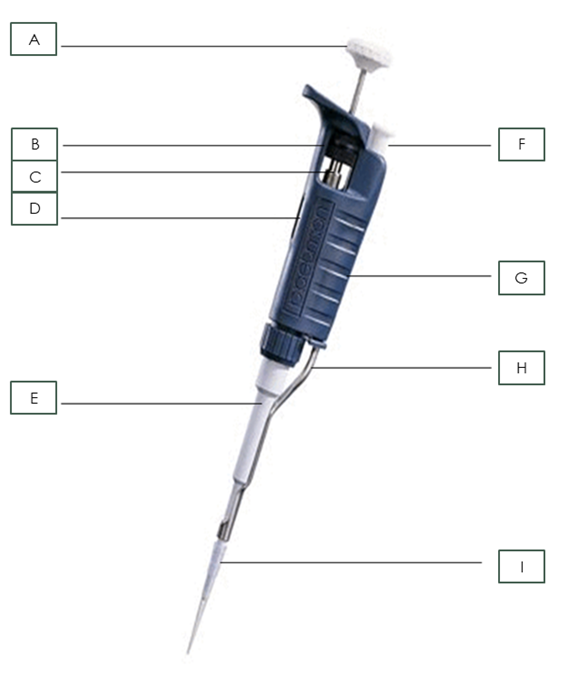
what is part A?
Plunger
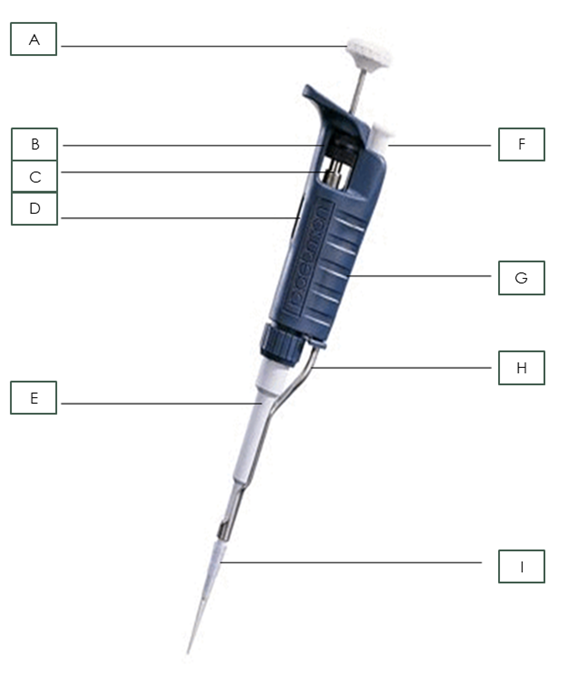
What is part B?
Friction Ring
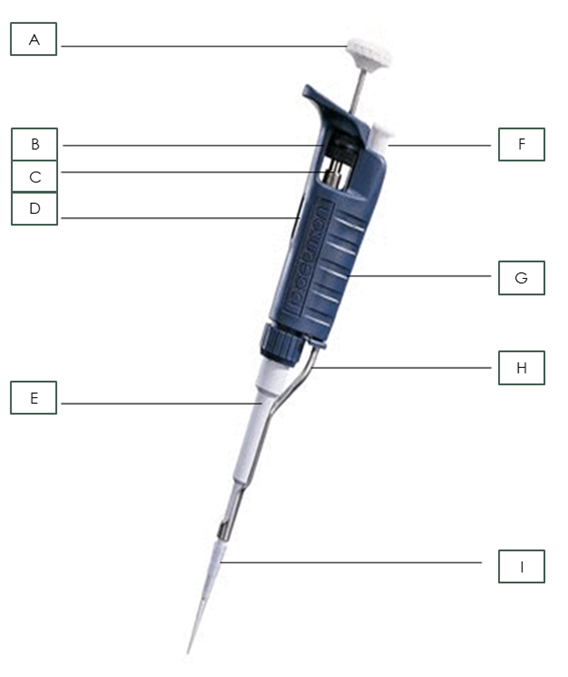
What is part C?
Micrometer
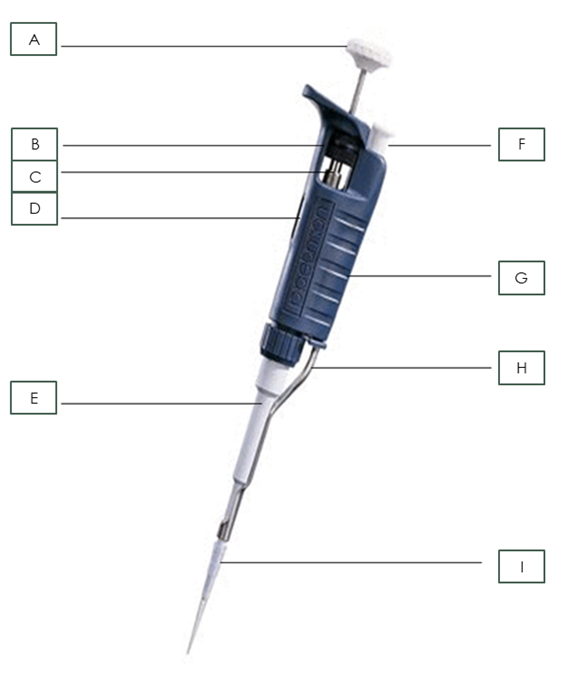
What is part D?
Digital Volume Indicator
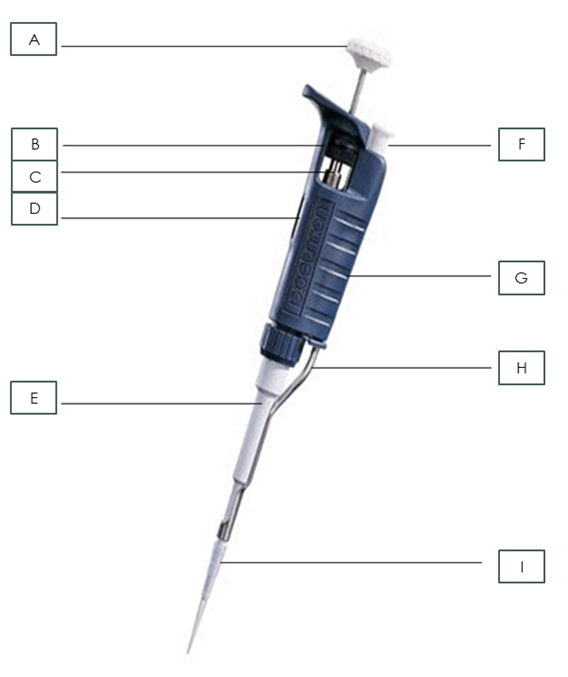
What is part E?
Shaft
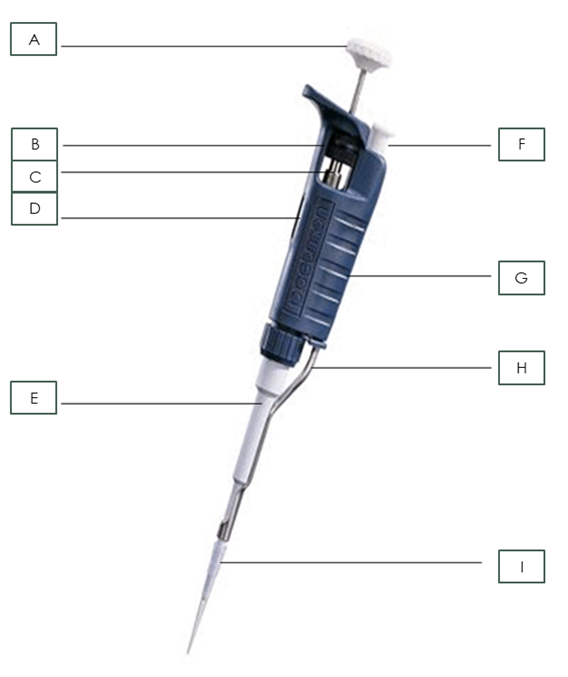
What is part F?
Tip Ejector Button
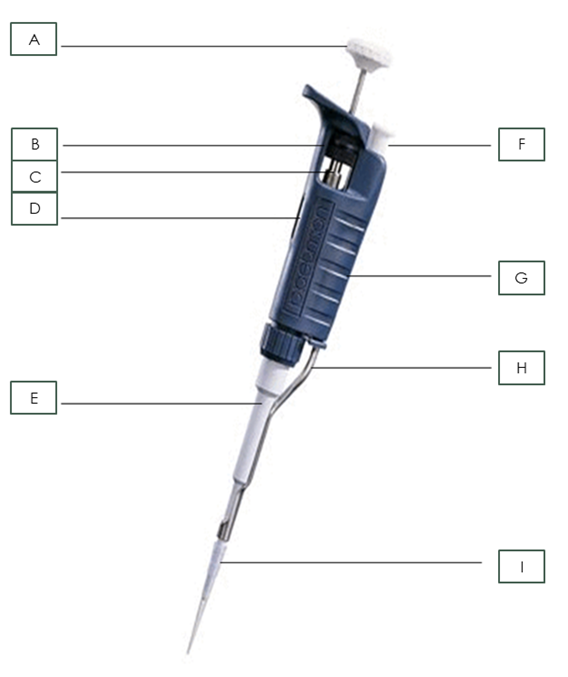
What is part G?
body
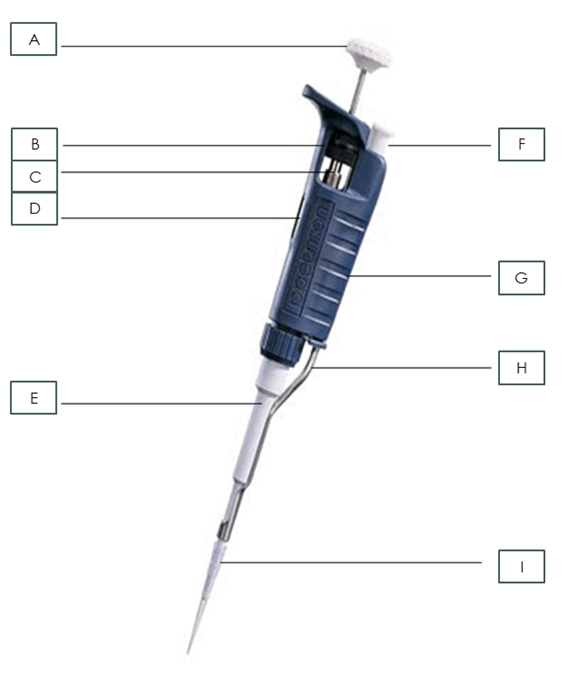
What is part H?
Tip Ejector
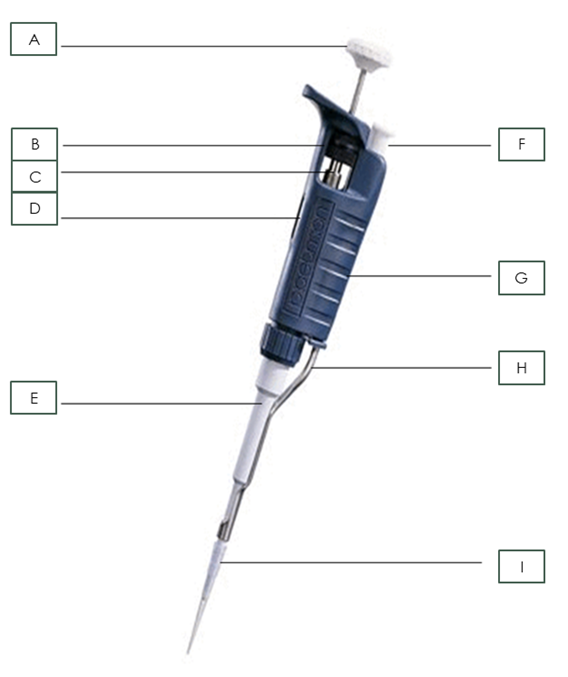
What is part I?
Pipette Tip
Affinity Chromatography
Beads are linked to a biomolecule that interacts with the protein
Size exclusion chromatography
Beads with small pores separate based on size. large biomolecules elute first then small
Ion-Exchange Chromatography
positive charged beads interact with negative charged protiens.
Which one elutes first?
hemoglobin 65000 Daltons
myoglobin 17000 Daltons
myosin 180000 Daltons
myosin 180000 Daltons
Which one elutes last?
hemoglobin 65000 Daltons
myoglobin 17000 Daltons
myosin 180000 Daltons
myoglobin 17000 Daltons
what gives hemoglobin/ myoglobin its color?
iron containing heme
what does high altitude do to red blood cells
more are produced
gene therapy
provide working copy of the gene
vitamin B12
breakdown of fats
buffer
liquid used in mobile phase
myoglobin
transports oxygen to muscles
hemoglobin
transports oxygen to tissue
immune system Vs. disease
physically blocks pathogens/ makes molecules and cells that recognize pathogens
immune response
expose the immune system to a weak/ inactive pathogen
how do diseases spread?
vector transfer/ exchange of body fluids/ ingestion of contaminated food or water/ inhalation
diseases that attack the immune system
lupus/ HIV
why would immune systems not work?
genetic disorder/ infection with a pathogen/ immunosuppressive meds/ overreaction to an antigen/ autoimmune disorder
immunosuppressants
immune system wont attack transplant tissue
rapid detection of disease exposure
who gets treated/ minimizing exposure
ELISA
enzyme linked immuno sorbent assay
enzymes in immunoassay
convert substrate into a colored compound
inate immunity
born with immunological defenses
passive immunity
acquisition of antibodies from external source
aquired immunity
specific response to specific foreign substance. born with it but must be activated
humoral immunity
production of antibodies in the blood stream/ lymph that bind to foreign antigens
cell mediated
production of T cells that bind/ destroy infections
antigen
foreign to the body
epitope
single shape on an antigen recognized by antibodies
antibody
first line of defense against invading microorganisms
IgG
most abundant in internal body fluids
IgM
serum responsable for primary immune response
IgA
only antibody passed from mom to baby in external secretion
IgD
regulating immune response
IgD
regulating immune response
IgE
allergic reactions
Macrophages
removes foreign cells from blood/ processing antigens
infection transmission
person to person/ animal to person (Zoonosis)/ environment to person
hypersensitive reaction
immune system overreacts to an antigen
Immunodeficiency
unable to mount effective immune response
primary immunodefficincy
genetic basis
secondary immunodefficency
external cause
anaphylactic
allergies
cytotoxic
transfusion reactions/ Rh incompatibilty
immune complex
inhaling mold spores
Delayed hyper sensitivity
contact sensitivity
autoimmune disease
immune system mistakes and attacks own body
immunofluorescent assay (IFA)
detected with fluorescently labeled antibodies
agglutination
visible precipitates appear when antibodies and specific antigens come in contact
immunochromatography test
dip-stick immunoassays
microplate test
ELISA detects microbial antigensM
molecular methods
detects microbial RNA/ DNA
microscopy
visual identification with staining/ physical characteristics
live attenuated vaccines
weakened (attenuated) microbes
killed/ inactivated vaccines
microbes killed by heat or chemicals
subunit vaccines
made of pieces of microbes
DNA vaccines
DNA that codes for microbial antigens
mRNA vaccines
mRNA molecules encode the antigen
Antibody Vaccines
construct human monodonal antibodies using recombinant DNA tech
post exposure vaccines
vaccine regimen begun promptly after exposure
polyclonal antibodies
immunize/ fuse cells to create hybridoma/ culture cells in liquid growth medium/ growth medium
Genetically engineering antibodies
antibodies that recognize the antigen attached with a drug
hybridoma immortalization
combining human and mouse genes to camoflauge a mouse monoclonal antibody cheaper and quicker
phage display
phage that binds to a specific antigen and can be used like an antibody
phage library
libraries of billions of potentially useful antibodies created by inserting shuffled genes from billions of humans into the bacteriophage lambda so that the lambda phages display the binding sites from human antibodies on their surface
inderect detection
uses polyclonal secondary antibodies to bind to primary antibodies. only one type of enzyme-linked secondary body is needed
immunostaining
localizes antigens in organelles, cells, tissues, or whole organisms, and can be used to distinguish one cell type from another
immunoblotting/ western blotting
tells protien’s size and relative abundance in a given sample
dot blotting
sample is sotted onto a membrane directly rather than being blotted from a ggel
what are four diffrent ways light can interact with biomolecules?
light scattering/ reflection/ absorption/ transmission
in the bradford assay, the protien-dye complex at 545 mm makes the protien dye compllex blue while the dye alone (without proteins) absorbs blue light at 470 nm making the dye…
reddish brown
what has an unprotonated peak absorbance of 595 nm?
coomassie G-250 dye
what are some colorimetric methods?
biuret/ bradford/ lowry
what is the first step of bradford assay?
preparation of a dillution series of known protein standards and preparation of unknowns
what is the second step of bradford assay?
addition of bradford dye and incubation for >5 min
what is step 3 of the bradford assay?
binding of dye to protein, resulting in a color change and reading of the asorption at A595 in a spec
what is step 4 of the bradford assay?
compilation of the data into a standard curve and unknown protein concentration detemination
what is the primary interaction that occurs between Coomassie G-250 dye and proteins in the Bradford assay?
electrostatic interactions between arginine and sulfate groups
why is it important to use a fresh tip for each standard and sample when adding them to the cuvettes in the Bradford assay?
to avoid cross contamination and ensure accurate readings
the closer the correlation coefficient (R²) is to ___ the better the fit of the standard curve
1
biophotonics
technology that focuses on the interaction of bio materials with light and other forms of radiant energy