Unit 7: DNA Structure & Replication
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
what biomolecule makes up DNA
nucleotide
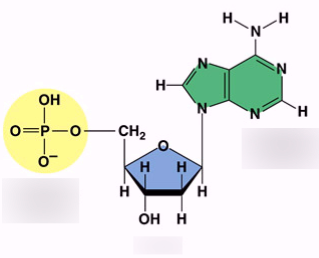
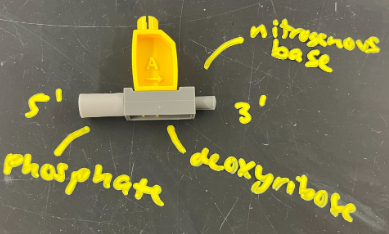
parts of nucleotide
sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base
bonds between sugar, phosphate and nitrogenous base
covalent
bonds between nitrogenous bases RNA-RNA
hydrogen bonds
DNA is made up of
2 helix
RNA is made up of
1 helix
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
DNA is a biological molecule that contains instructions for our cells to produce proteins, the building blocks of lifeand is composed of two strands forming a double helix structure.
DNA structure
nucleotides stack
sugars + phosphates = backbone (sides of ladder)
basses = rungs of ladder
nitrogenous bases pair with what
their complementary bases through hydrogen bonding
Thymine, Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine for DNA
Uracil, Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine for DNA
DNA vs RNA
Single-strand vs double-strand
ribose sugar vs deoxyribose sugar
UAGC vs TAGC
Purine bases
Adenine and Guanine have double ring structure
Pyrimidine bases
Thymine and Cytosine have single ring structure
1 base pair consists of
1 Purine (double ring) + 1 Pyrimidine (single ring)
A + T
G + C
Adenine + Thymine creates
2 hydrogen bonds
Cytosine + Guanine
3 hydrogen bonds
antiparallel
the strands of DNA are flipped/go in opposite directions
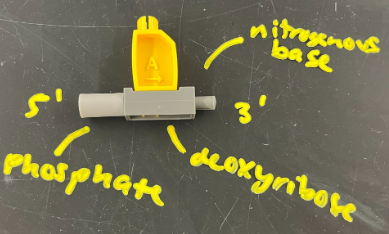
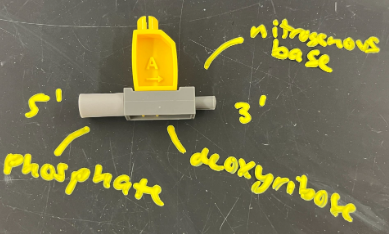
each polynucleotide (strand) has 5’ end and 3’ end
DNA is synthesized from
5’ → 3’
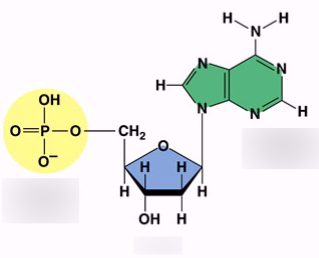
5’ end is
phosphate group
3’ end is
hydroxyl group (on base)
DNA Replication
the process by which a DNA molecule makes a copy of itself on a molecular level from a parent molecule to 2 identical daughters
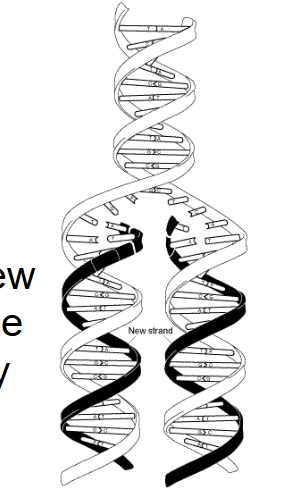
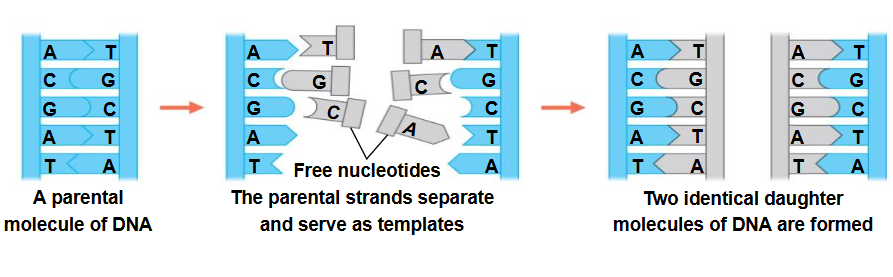
DNA Replication is
semi-conservative → each new molecule consists of 1 original + 1 newly synthesized strand
occurs at thousands of places @ the same time
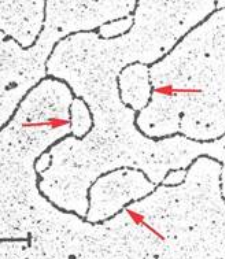
consists of thousands of replication bubbles
Parental DNA
2 diff strands from which create —> 2 identical molecules form
1 half newly synthesized DNA and 1 half original DNA strand
At the center of the replication bubble is
the origin of replication
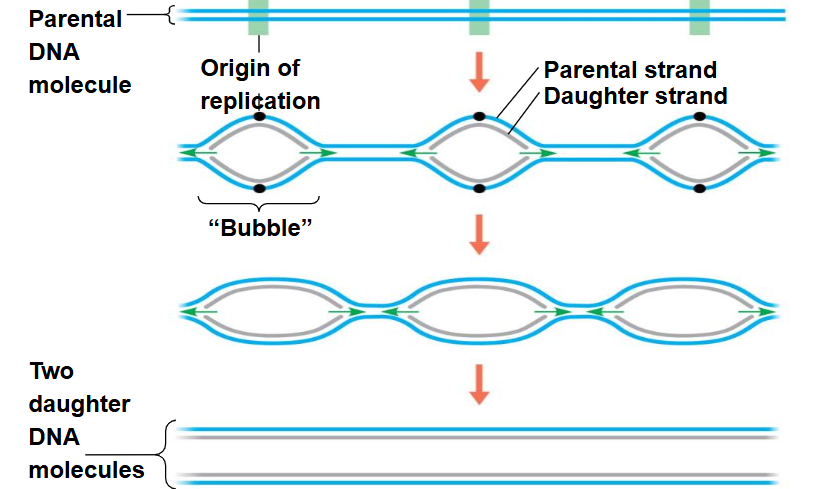
replication bubble is visible
under microscope
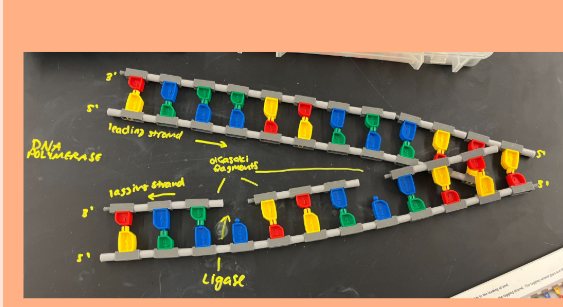
Leading strand
daughter strand that builds from 5’ to 3’ on parental DNA
creates 3’ → 5’ strand (left to right)
Lagging strand
daughter strand that builds from 3’ to 5’ on parental DNA
creates 5’ → 3’ strand (left to right)
one inside of fork (must wait)
forms via Okazaki fragments
okazaki fragments
Short segments of DNA that are synthesized on the lagging strand so it can go 5’→ 3’
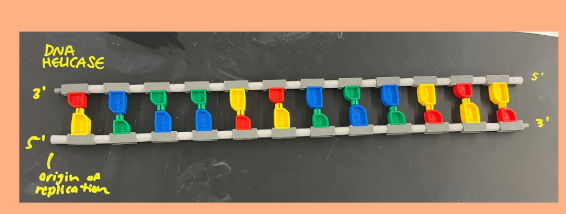
Step 1 of DNA replication is
Unzipping: Helicase enzyme unzips the DNA = REPLICATION FORK
Step 2 of DNA Replication
Stabilizing: Single-strand binding proteins stabilize unwound parent replication fork
(preventing them from re-annealing)
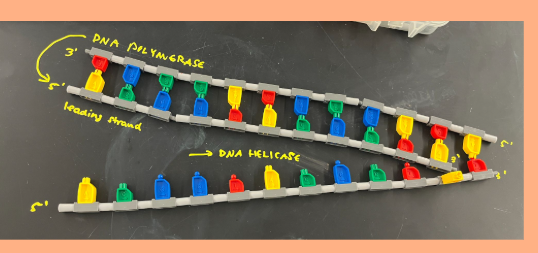
Step 3 of DNA replication
Priming: Primase
leading strand: Primase binds initial nucleotide base to fork
lagging strand: primase binds initial nucleotide base to fork for Okazaki fragments
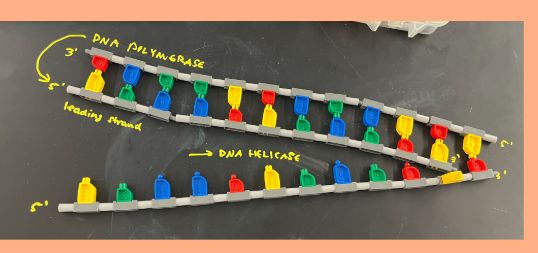
Step 4 of DNA replication
Elongating: DNA Polymerase
leading strand: DNA Polymerase synthesizes off/elongates primer
lagging strand: DNA Polymerase synthesizes off/elongates fragment
Step 5 of DNA replication
Replacement of RNA primer w/ DNA: DNA Polymerase
leading strand: DNA Polymerase replaces
lagging strand: DNA Polymerase replaces
Step 6 of DNA replication
Joining of fragments: Ligase
leading strand done
lagging → ligase connects Okazaki fragments
Proofreading + Correcting DNA
Proofread/correct:
DNA polymerases proofread newly made DNA, replacing any incorrect nucleotides
In mismatch repair of DNA, repair enzymes correct errors in base pairing (ex: nuclease)
Repairing DNA
Repair:
DNA can be damaged by exposure to harmful chemical or physical agents such as cigarette smoke and X-rays; it can also undergo spontaneous changes
Nucleotide excision repair: nuclease cuts out and replaces damaged stretches of DNA
The final error rate is only one per billion nucleotides. This makes for about 3 mistakes per cell division in humans.
PCR
replicates a small amount of DNA to a large
gel confirms PCR