Ch 6 Nuc Med I
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
161 Terms
Charged Particles and Electromagnetic Radiation
The two classifications of radiation emitted during radioactive decay
Alpha Particles and Beta Particles
Most common two particles used in nuclear medicine
X-rays and Gamma Rays
The electromagnetic radiation that we use in nuclear medicine
transfer energy
Both types of radioactive decay _______ to matter as they pass through it
heat
majority of the energy from ionization and excitation is lost as _____
atomic and molecular vibrations
heat lost in ionization and excitation is ___
ionizing radiations
the radiation emitted during radioactive decay are ____
slow down
high energy charged particles lose energy and ____ as they pass through matter, as a result of collisions with atoms and molecules
collisions with atoms and molecules
what forces alpha and beta particles lose energy ans slow down as they pass through matter
high energy electrons
what are byproducts of alpha and beta collisions with atoms and molecules
when gamma rays and x rays interact with matter and emitted in internal conversion and the Auger effect
When are high-energy electrons generated?
identical
forces experienced by positive and negative electrons are ____
internal conversion event
ICE stands for
high-energy electrons
B+ and B- are ___
not important in nuclear medicine
there are slight differences in +/_ electron interactions however:
both the positive and negative charged particle
concerning interactions with matter, the term “electron” is going to include:
No
Do actual true physical/mechanical collisions occur?
electrical forces of attraction or repulsion
The collisions that occur between a charges particle and atoms or molecules involve:
be separated (or ejected) from the atom, causing ionization
suppose a charged partile passes near an atom and exerts electrical forces on the orbital electrons. If close enough, the forces may be sufficient to cause an orbital electron to …
to overcome the binding energy of the electron, and the rest is converted into kinetic energy to the ejected secondary electron.
During an ionizing interaction (a collision) between a charged particle and orbital electron, why does the particle lose energy
a positive electron (positron) loses all of its kinetic energy and is stopped.
What happens in an annihilation effect?
the emission of characteristic x-rays or auger electrons
Ionization involving an inner-shell electron leads to
outer-shell electrons
most ionization interactions involve:
secondary ionization
The secondary electron may be sufficiently energetic to cause a ____
delta ray
a secondary electron that causes a secondary ionization is called a
excited state; atomic or molecular excitation
encounters that are not as close can cause an orbital electron to be raised to an ____ causing _____
secondary electron
What is B?

Bremsstrahlung
What is A?
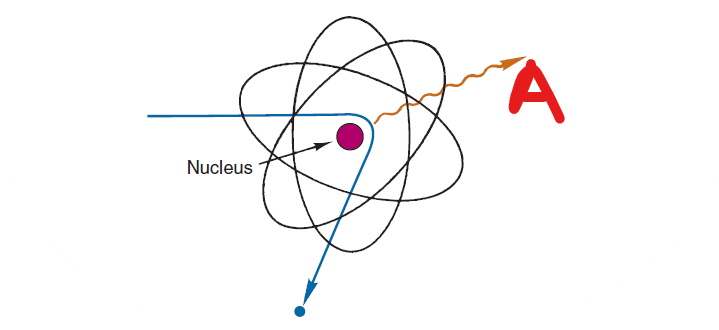
Bremsstrahlung
The interaction that occurs when the charged particle penetrates the orbital electron cloud of an atom and interacts with the nucleus
a particle interacts with the nucleus, is rapidly decelerated and loses energy, the energy appears as a photon called a bremsstrahlung
What creates a bremsstrahlung
braking radiation
bremsstrahlung is German for
transmutational reactions
for heavy charged particles with enough energy, like alpha particles or protons, ______ can occur during nuclear interactions
deflection by strong electrical forces
What is more likely to happen when a heavy particle or electron interacts with the nucleus, transmutation or deflection?
the particle rapidly decelerates and loses energy from this interaction
What happens when “breaking” happens?
bremmstrahlung
The electromagnetic radiation that is released when a particle interacts with the nucleus
nearly zero, slightly deflected or maximum energy, equal to the full energy of the particle which the particle is virtually stopped
Bremsstrahlung energy range
Characteristic x-ray , discrete energy
describe #4 and its energy
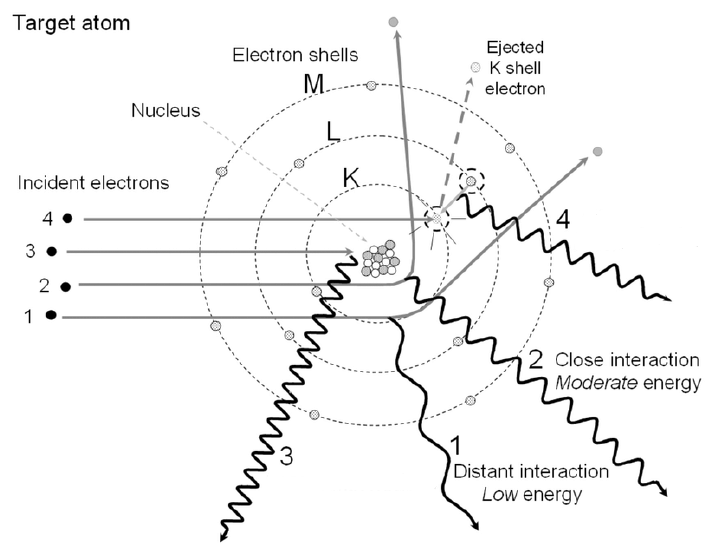
bremsstrahlung, maximum energy
describe #3 and its energy
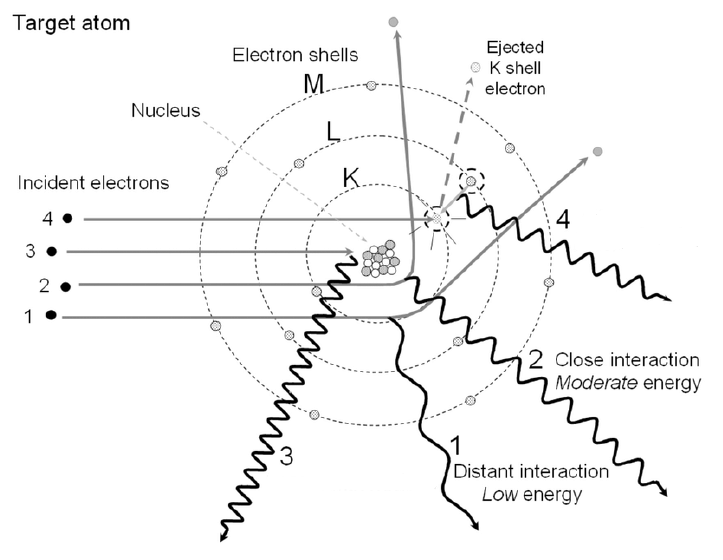
collisional losses
energy losses incurred by a charged particle in ionization and excitation events are called
energy losses incurred by a charged particle in ionization and excitation events
what are collisional losses
radiation losses
energy losses incurred in nuclear encounters, resulting in bremsstrahlung production are called
energy losses incurred in nuclear encounters, resulting in bremsstrahlung production
what are radiation losses
increasing particle energy and increasing atomic number of the ABSORBING medium
radiation losses increase with ____
collisional losses
in nuclear medicine, which of the two, radiation or collisional losses, are by far the more dominating factor of the two?
Beta particles
which particles can be blocked with a small amount of plastic as shielding
the bremsstrahlung photons they generate are much more penetrating than the Beta particle
why would additional shielding be needed around the primary Beta particle shielding?
lead
what is an example of a high Z-material used in shielding bremsstrahlung emissions
82
what is the atomic number of Lead
very small
Bremsstrahlung production and radiation losses for alpha and other heavy charged particles are ______
the amount of bremsstrahlung production is inversely proportional to the mass of the incident charged particle.
why are bremsstrahlung and radiation losses very small in alpha particles and other heavy charged particles?
alpha particle
what is heavier, an alpha particle or electron?
Lead
what shielding is required for Beta particles?
since alpha particles and protons are thousands of times heavier than electrons, they dissipate only a few hundredths of 1% or less of their energy as radiation losses
describe radiation losses in alpha particles and protons
collisional losses
even at energies up to 100 MeV, alpha particles and protons dissipate nearly all of their energy as ______
secondary electrons and ionized atoms
A charged particle passing through matter leaves a track of _______ and ________ in its path
100 um
how wide are tracks in soft tissue and materials of similar density
energetic delta rays
occasionally, longer sidetracks can be generated by _______
microns
alpha particle track lengths are in the order of ____
centimeters
beta particle track lengths are in the fractions of ________
unchanged; only a small fraction of its energy
when an alpha particle or other heavy particle collides with an orbital electron, its direction is virtually _____ and loses ____
bowls ball and a pin
what is the analogy used for a heavy particle like an alpha particle and its charged-particle track?
it is a rather straight track and experience an almost continuous slowing down, losing tiny amounts of energy from large number of individual collisions.
due to an alpha particles few bremsstrahlung collisions and only a small fraction of its energy being dissipates, describe their trach pathway
deposit its energy in the surrounding area
When a heavy particle runs out of energy from traveling, it will _____
the amount of energy that they deposit in the surrounding tissues and cells.
the reason alpha particles are so toxic in biological tissues is due to ______
large angle deflections
charged particle tracks: an electron can undergo _______ with orbital electrons
a large fraction of their energy to be lost in these collisions
The large angle deflections electrons undergo will cause _____
billiards
the analogy used for electron charged-particle tracks
are deflected through large angles and bremsstrahlung radiation is emitted
electrons also undergo occasional collisions with nuclei in which they _____
unpredictable
due to the large angle deflections of electron and nuclei interactions, electron tracks are ____
an alpha particle
This is a charged-particle track of __
an electron or Beta particle
This is a charged-particle track of __
for a given kinetic energy, an electron travels at a much faster speed
Besides charged-particle track, what is another difference between electrons and heavy particles
10%
at 4 MeV, an alpha particle will travel at ____ of the speed of light
4 MeV
at _____, an alpha particle will travel at 10% of the speed of light
90%
at 1 MeV, an electron will travel at ____ of the speed of light
1 MeV
at ____, an electron will travel at 90% of the speed of light
this is due to the low mass size and decreased probability of nuclear interactions with atoms
Why does an electron travel faster than an alpha particle
an electron only carries 1- unit of charge whereas an alpha particle carries 2+
why are the forces an electron exerts weaker than those of the alpha particles?
electrons
which particle experiences less frequent interactions and lose their energy much more slowly?
electron
which particle travels further before they are stopped
alpha particle
which particle is stopped sooner in their charged-particle track?
electron
which particle is much less densely ionizing?
how far it will travel and how dense the ionization along its track will be
the rate at which the charged particle diminishes energy determines ____
the rate at which the charged particle diminishes energy
what determines how far it will travel and how dense the ionization along its track will be
the type of particle and its initial energy (and on the composition and density of the absorbing medium)
the rate at which the charges particle diminishes energy depends on ___
differently
1 MeV of an alpha particle and 1 MeV of an electron act ____
energy loss
density of ionization affects the ___
how closely it interacts with the atoms in its path
density of ionization affects the energy loss due to ____
10 MeV
For nuclear medicine, we deal with energies at or below ____
increase linearly with the density of the absorbing medium
in the cases of energies at or below 10 Mev for nuclear medicine, energy loss rates for charged particles _____
electrons
which charged particle has a longer track length
MeV/cm
the total energy loss rate of a charged particle is expressed in ___
the linear stopping power
he total energy loss rate of a charged particle (MeV/m) is also known as ___
linear energy transfer
LET stands for
Linear energy transfer (LET)
the amount of energy deposited along the track
the amount of energy deposited along the track
Linear energy transfer (LET) is
it is tied to high radiation toxicity for cells when the LET is large
Why is LET parameter important in nuclear medicine
Cerenkov Effect
a phenomenon that occurs when a charged particle travels in a medium at a speed faster than the speed of light in the same medium
No
can a particle travel faster than the speed of light in a vacuum?
0.8 C
In water, a 1 MeV beta particle is able to travel with the velocity of ____