225 Midterm- Eyes, ears, nose, mouth, lungs, heart
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
Main functions of cardiovascular system?
Deliver oxygen and nutrients to body cells, remove waste products, & maintain perfusion to organs and tissues
Where is the pulmonary artery?
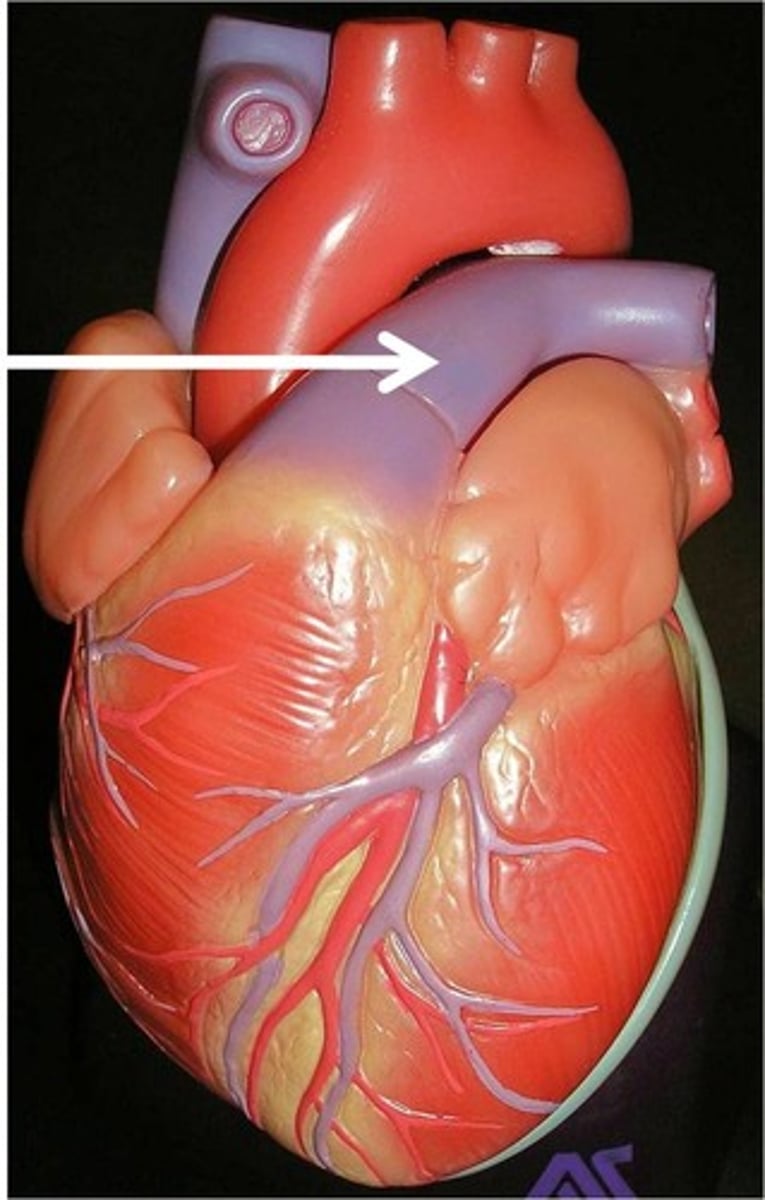
Where is the superior vena cava?
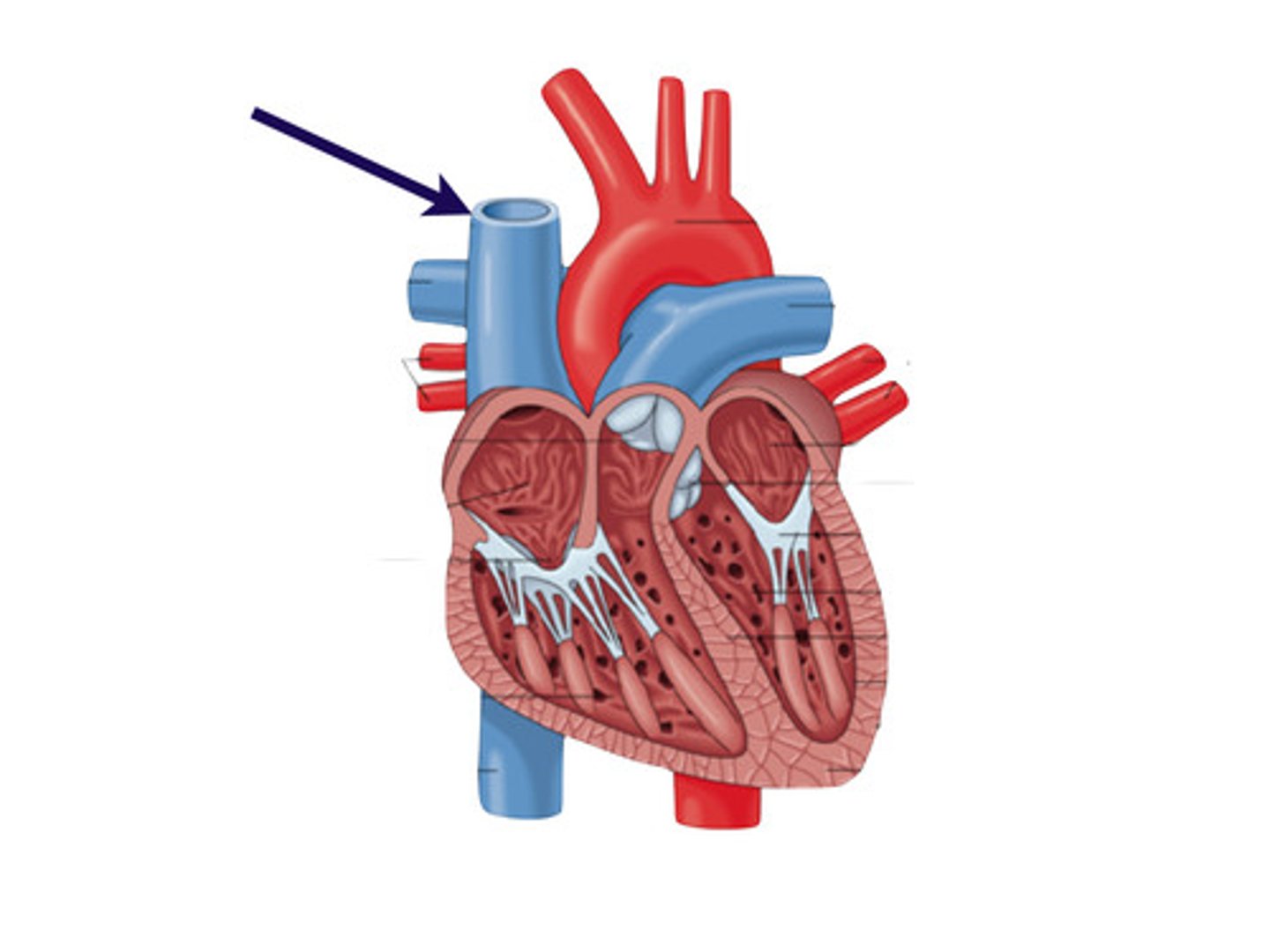
What are the layers of the heart wall?
Pericardium- outer protective layer
Myocardium- middle muscular layer
Endocardium- inner smooth layer
Where is the tricuspid valve?
between right atrium and right ventricle
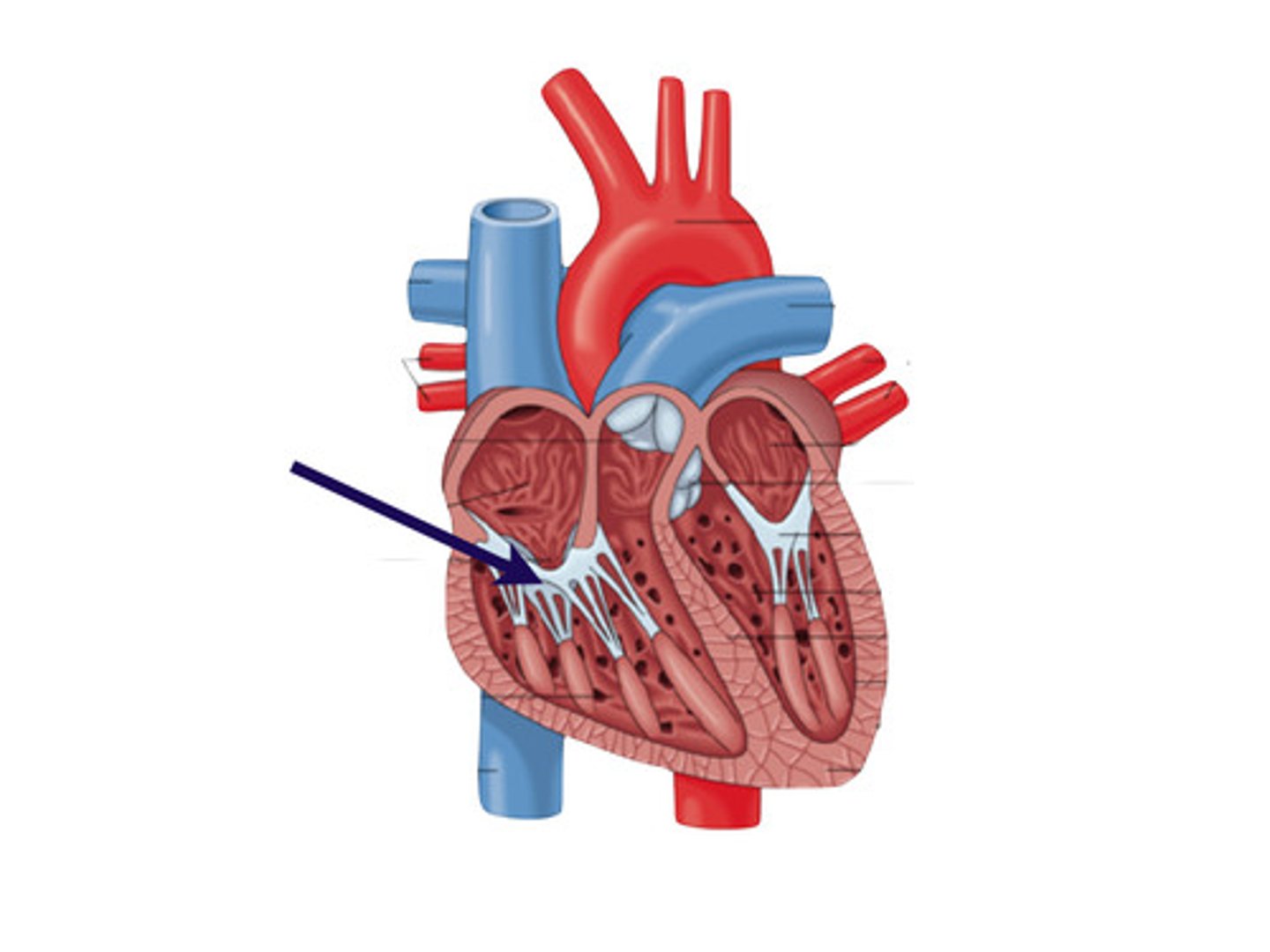
Where is the pulmonic valve?
between right ventricle and pulmonary artery
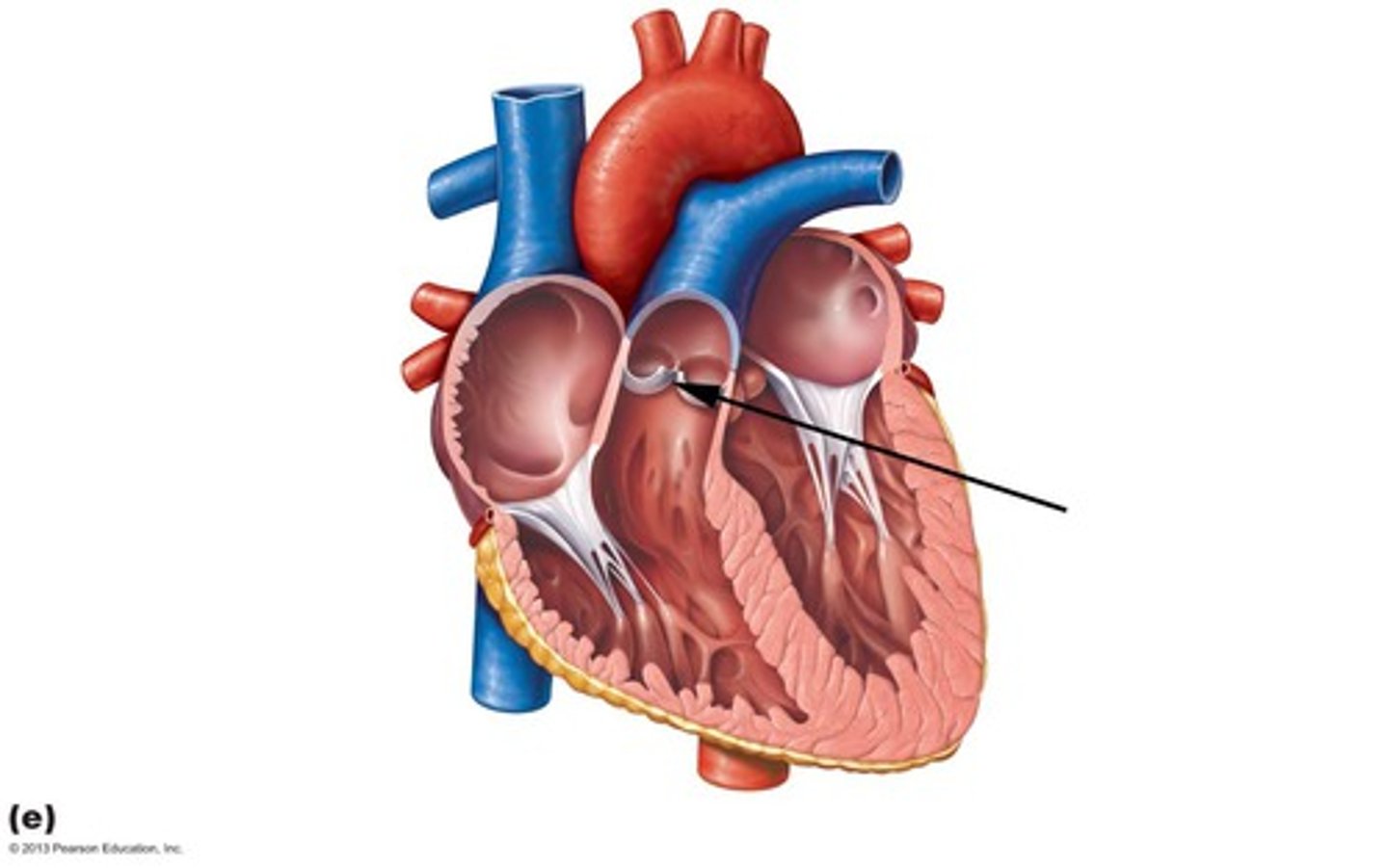
Where is the inferior vena cava?
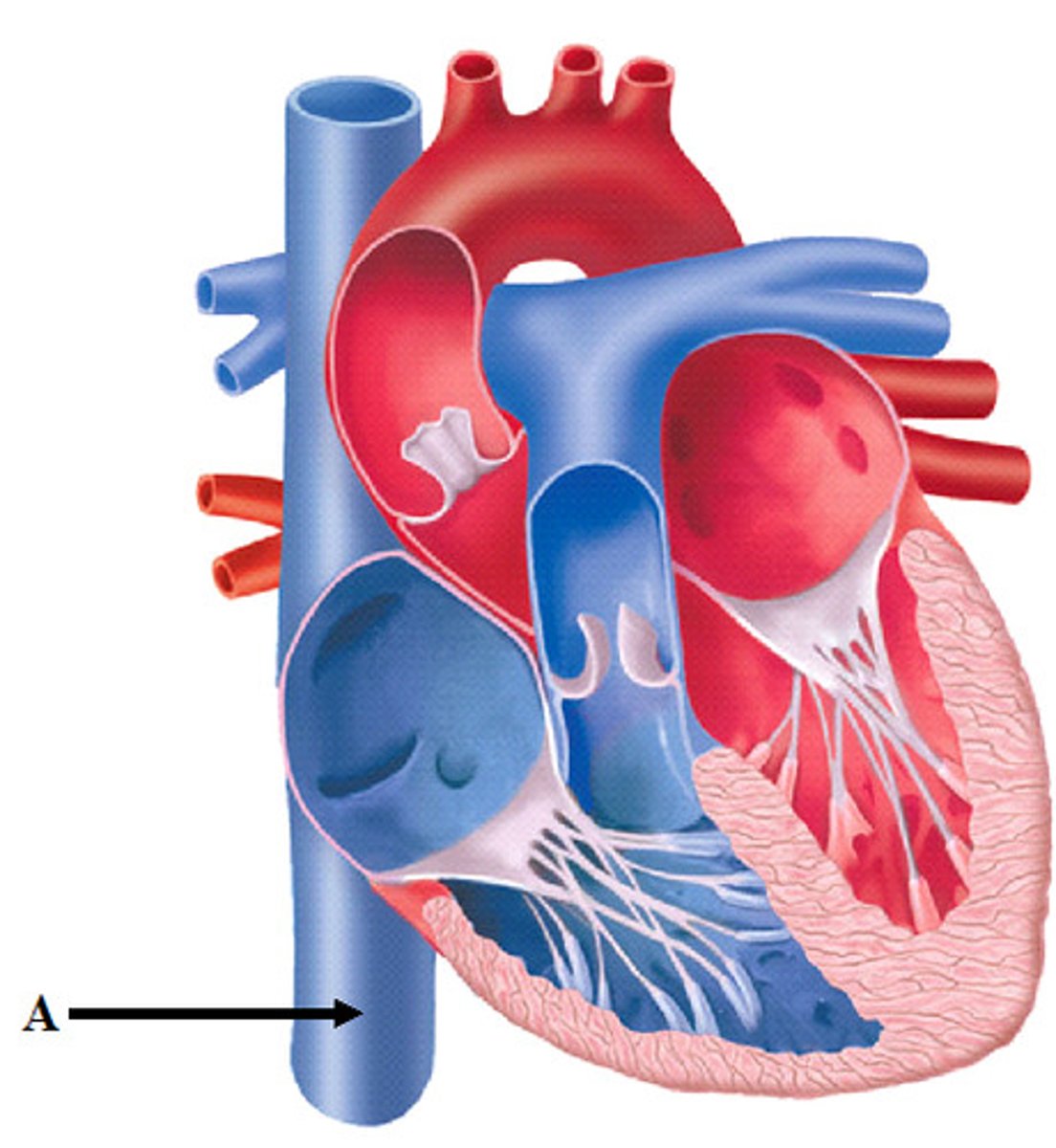
Where is the aortic valve?
between left ventricle and aorta
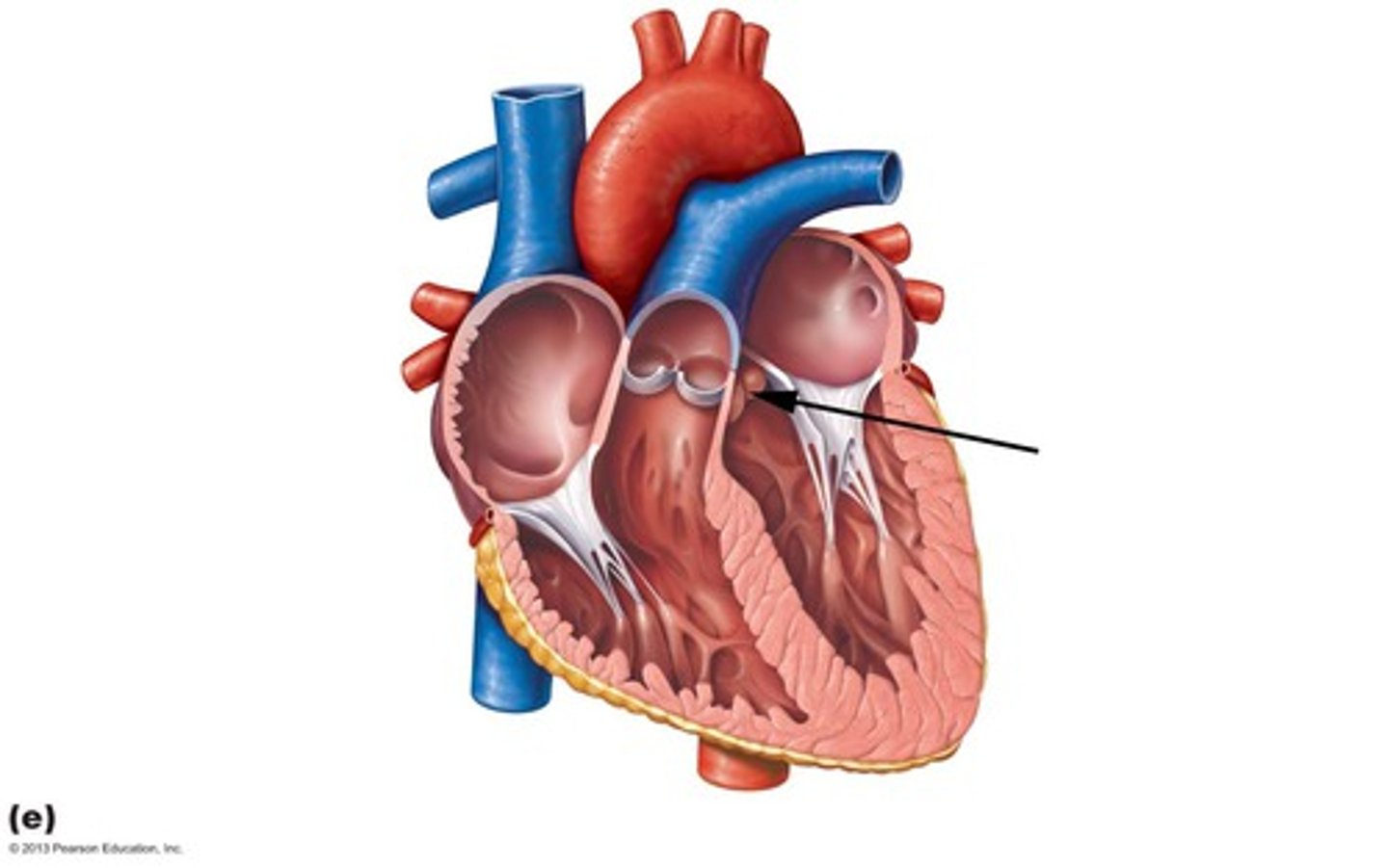
Where is the mitral valve?
between left atrium and left ventricle
Difference between systole and diastole?
Systole: period of ventricular contraction
Diastole: period of ventricular relaxation
What is the SA node and where is it?
It is the pacemaker of the heart
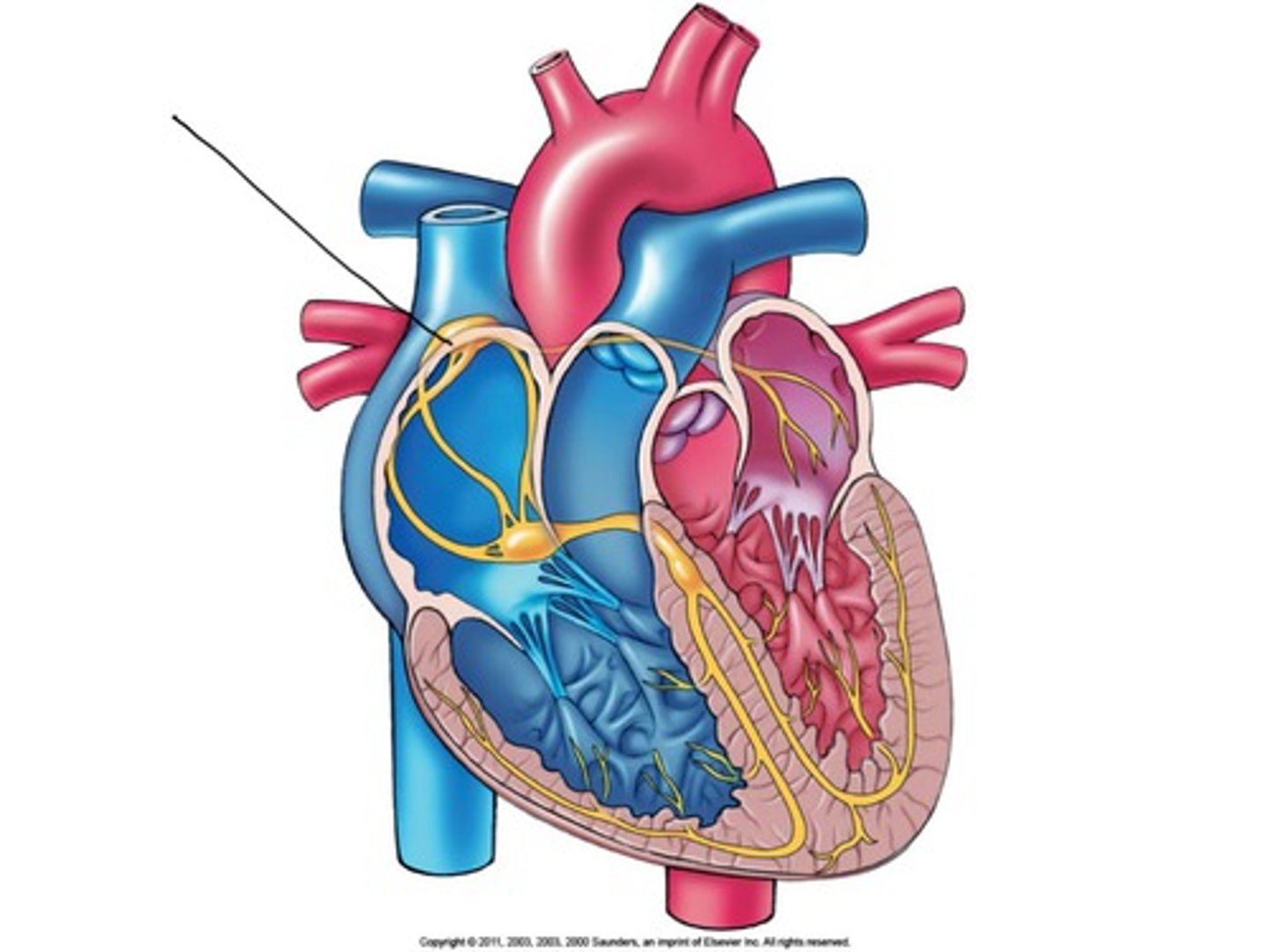
What is the AV node and where is it?
Electrically connects the heart's atria and ventricles to coordinate beating in the top of the heart
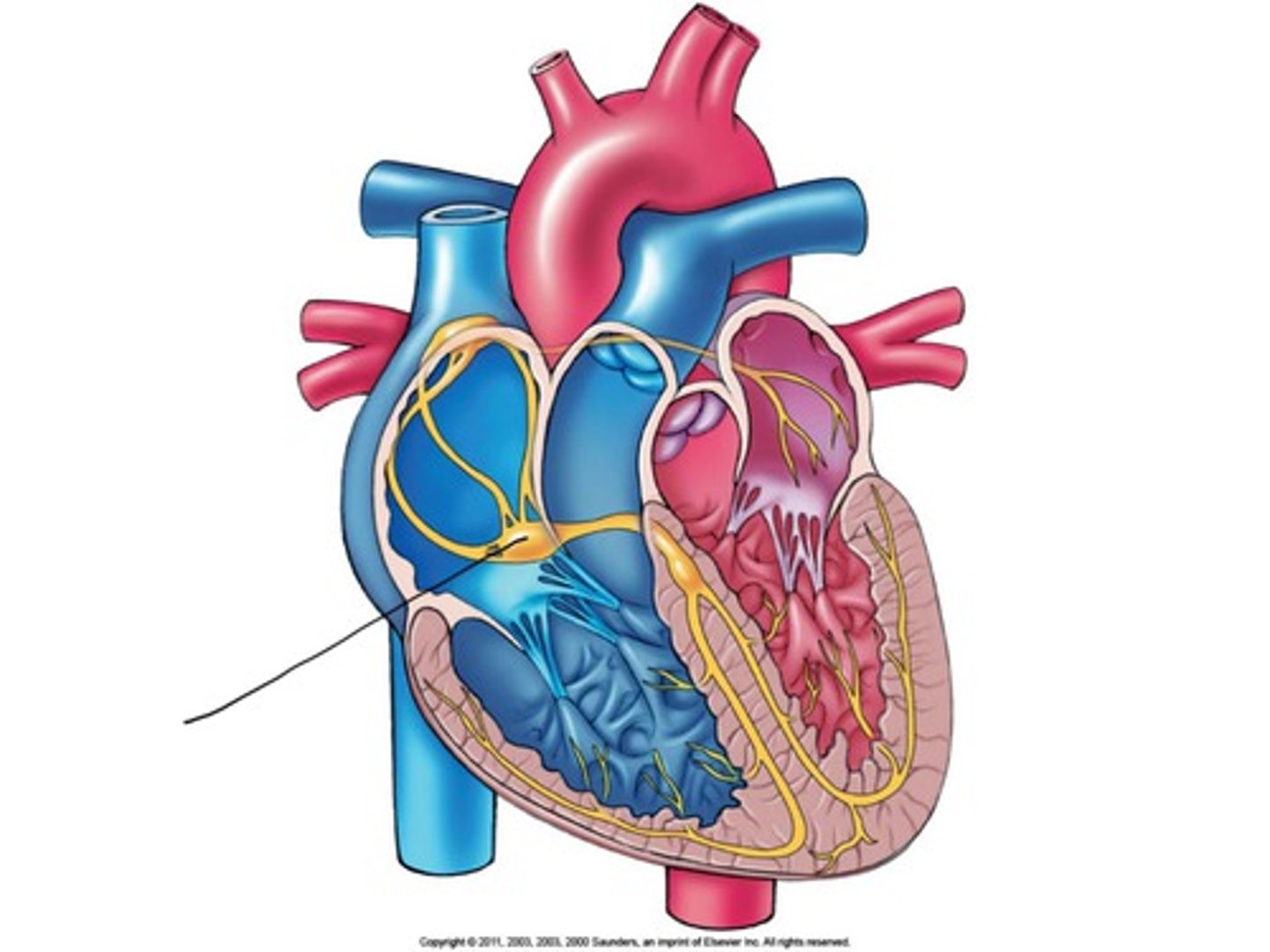
What is cardiac output?
Volume of blood ejected from each ventricle in one minute
What is stroke volume?
Volume of blood ejected with each heartbeat
What is preload?
Volume of blood in ventricles at end of diastole
What is afterload?
Resistance left ventricle must overcome to circulate blood
What is a bruit?
blowing, swishing sound indicating turbulent blood flow
How to auscultate carotid artery?
-Ask patient to hold breath (to eliminate tracheal sounds)
-Assess with bell and diaphragm
-Assess with bruit
How to palpate the carotid artery?
-Medial to the sternocleomastoid muscle
-Avoid excessive pressure
-PALPATE ONLY ONE AT A TIME
How to assess the JVP
-Raise the head of the bed or examining table to about 30 degrees. Turn the patient's head slightly away from the side you are inspecting.
-Use tangential lighting and examine both sides of neck. Identify the external jugular vein on each side, and then find the internal jugular venous pulsations.
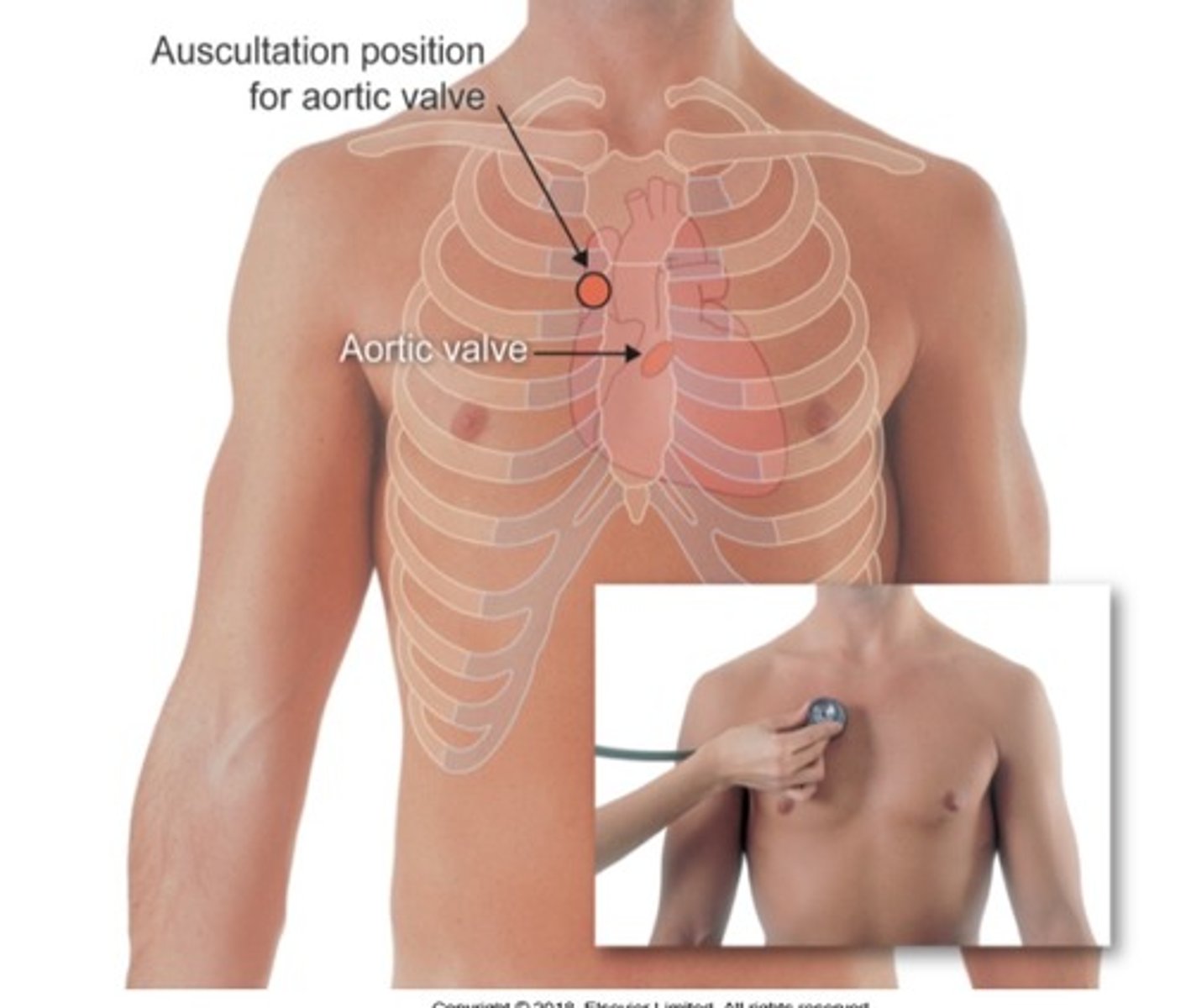
Where to auscultate the aortic valve?
2nd ICS, right sternal border
Where to auscultate the pulmonic valve?
2nd ICS, left sternal border
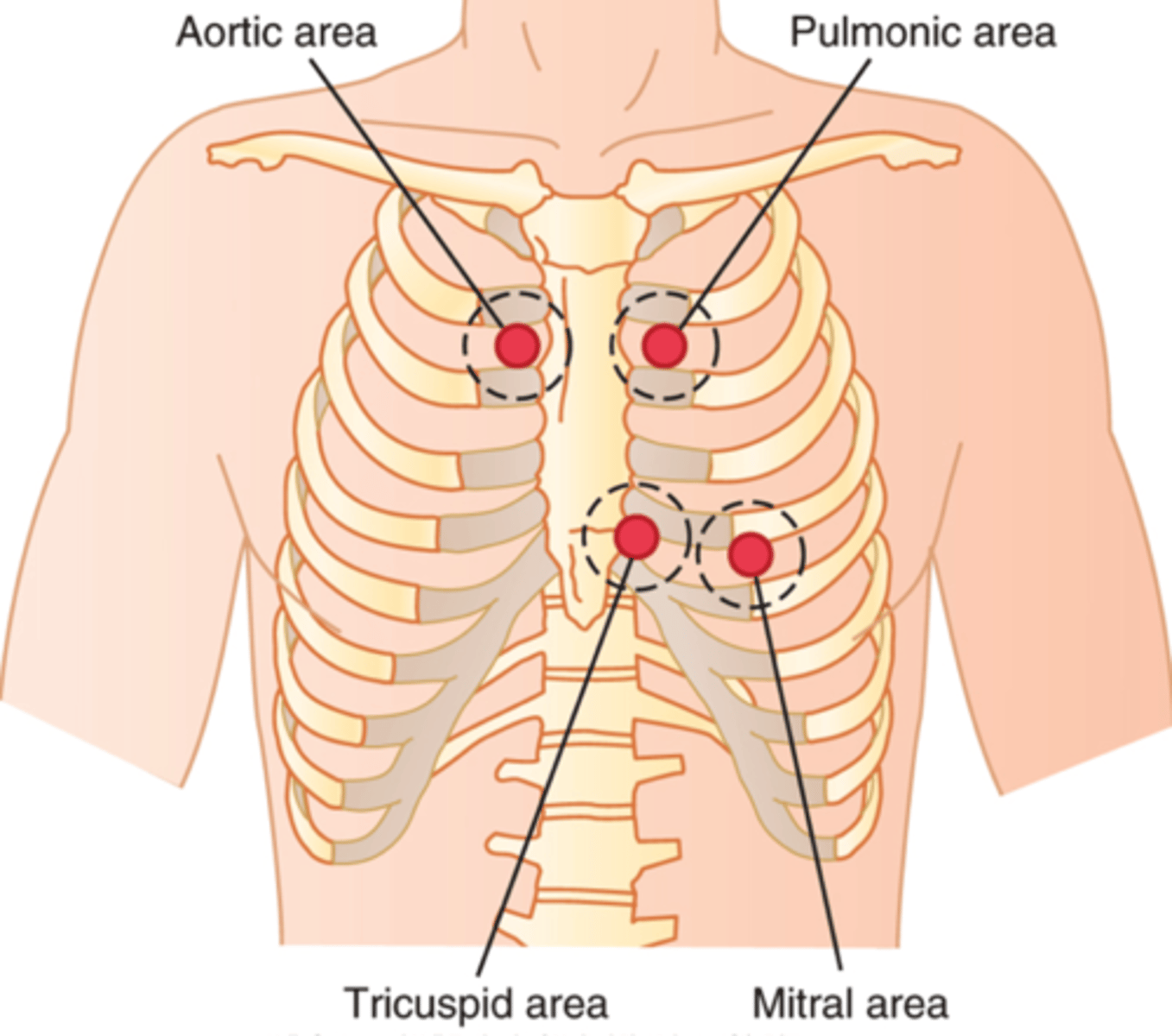
Where to auscultate erbs point?
3rd ICS, left sternal border
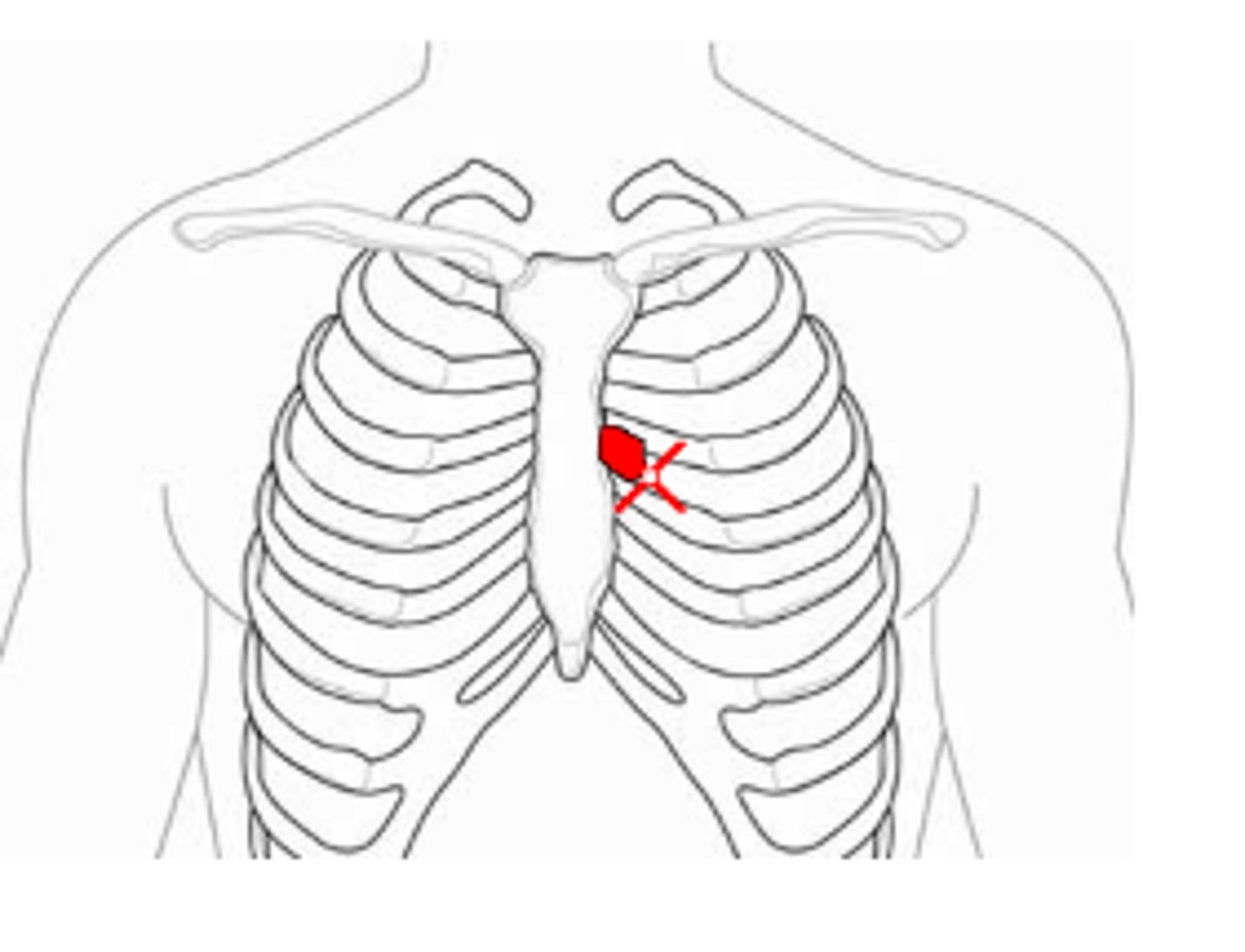
Where to auscultate tricuspid valve?
Left 4th/5th ICS, left sternal border
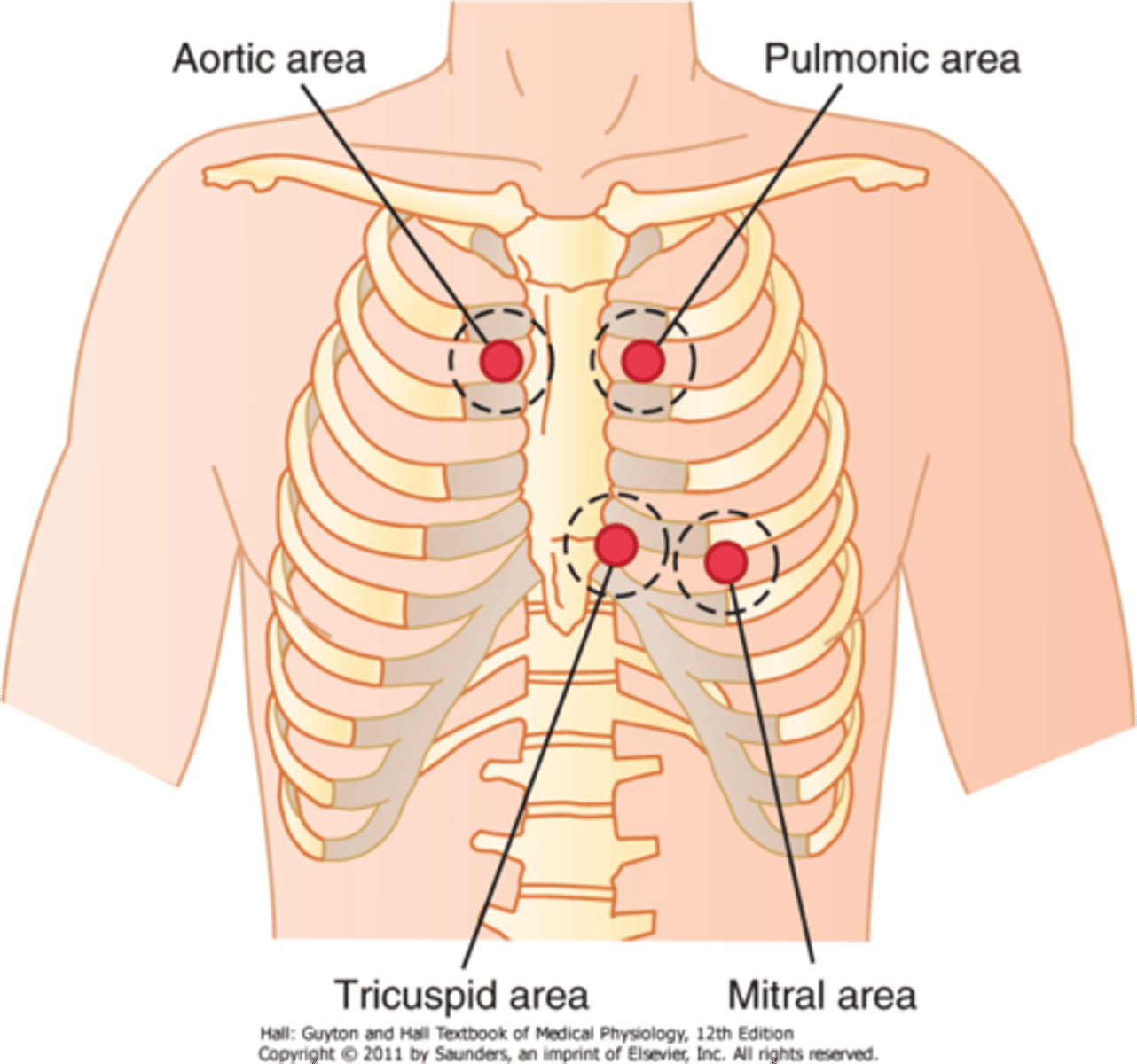
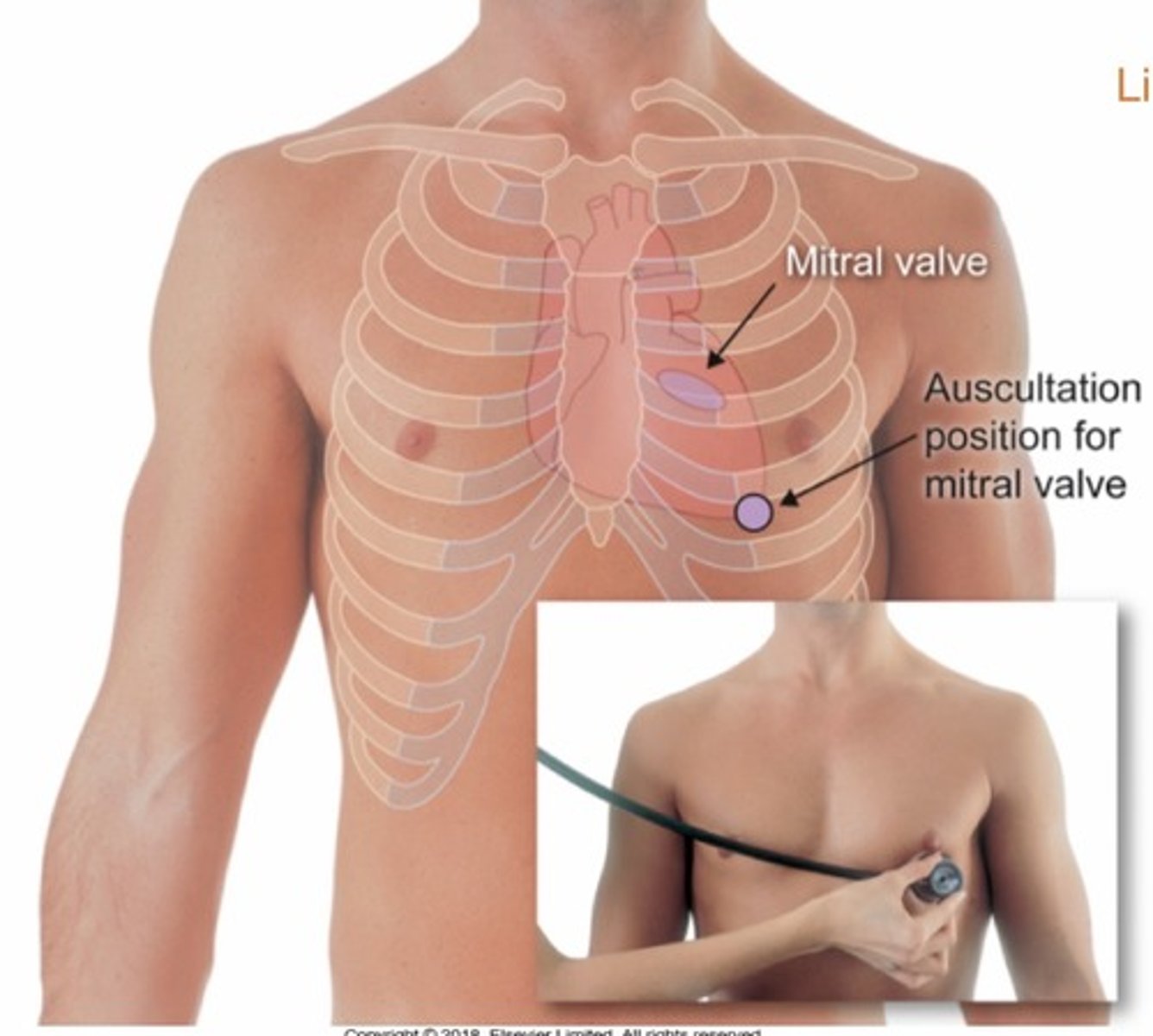
Where to auscultate mitral valve?
5th ICS, mid clavicular line
What is S1?
-1st heart sound
-"lub"
-occurs with closure of AV valves (mitral and tricuspid) and signal beginning of systole
-loudest at apex
What is S2?
-2nd heart sound
-"dub"
-occurs with closure of semilunar valves (aortic and pulmonic) and signals end of systole
-loudest at base
Risk factors for coronary heart disease?
-diabetes
-hypertension
-increased cholesterol and/or triglycerides
-smoking
-obesity
-physical inactivity
-increasing age
-history of cardiovascular disease
-family history of early heart disease
Risk factors for hypertension?
-obesity
-physical inactivity
-smoking
-microalbuminuria
-excess dietary sodium
-insufficient intake of potassium
-excess alcohol consumption
-age
-family history of hypertension
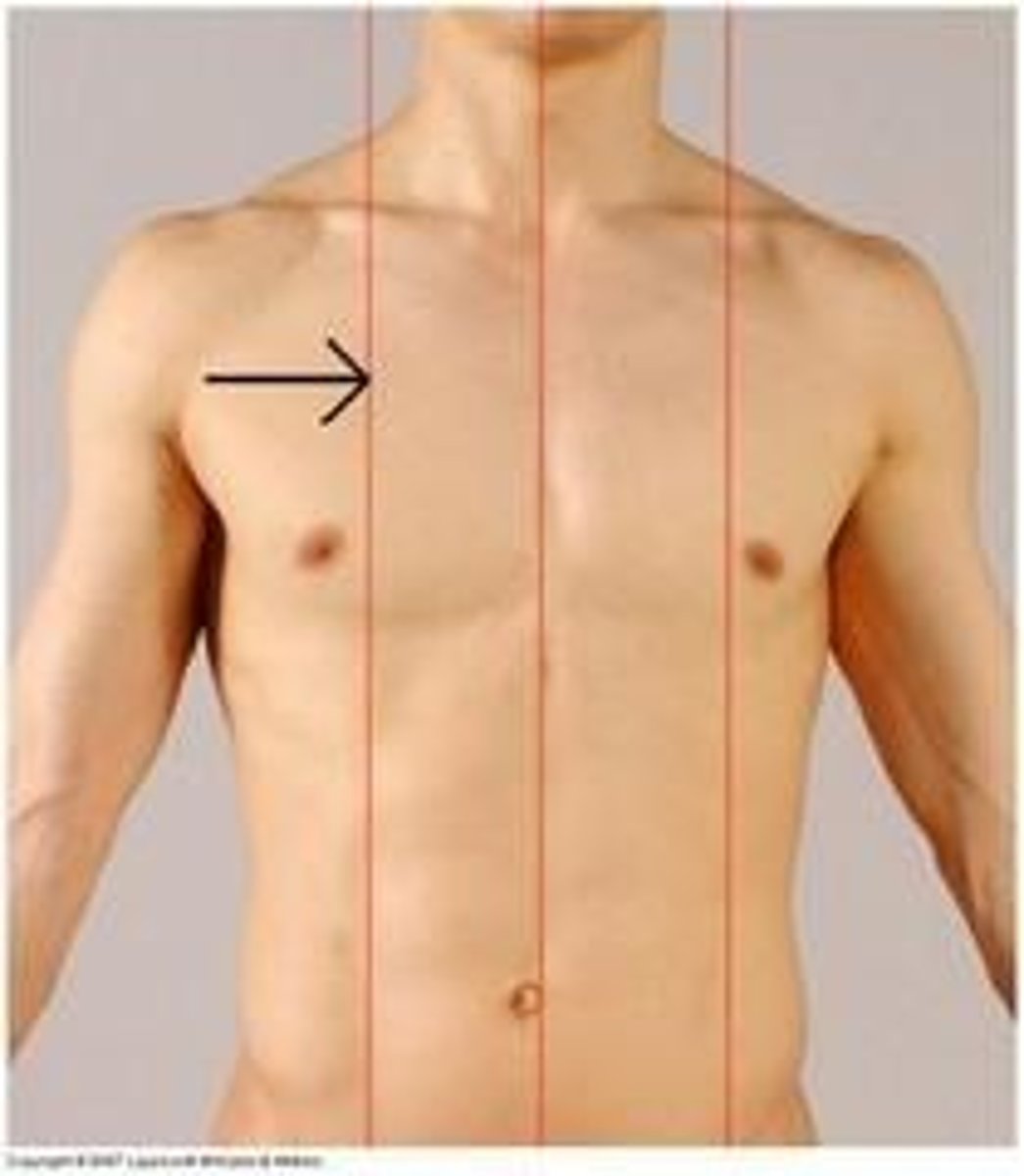
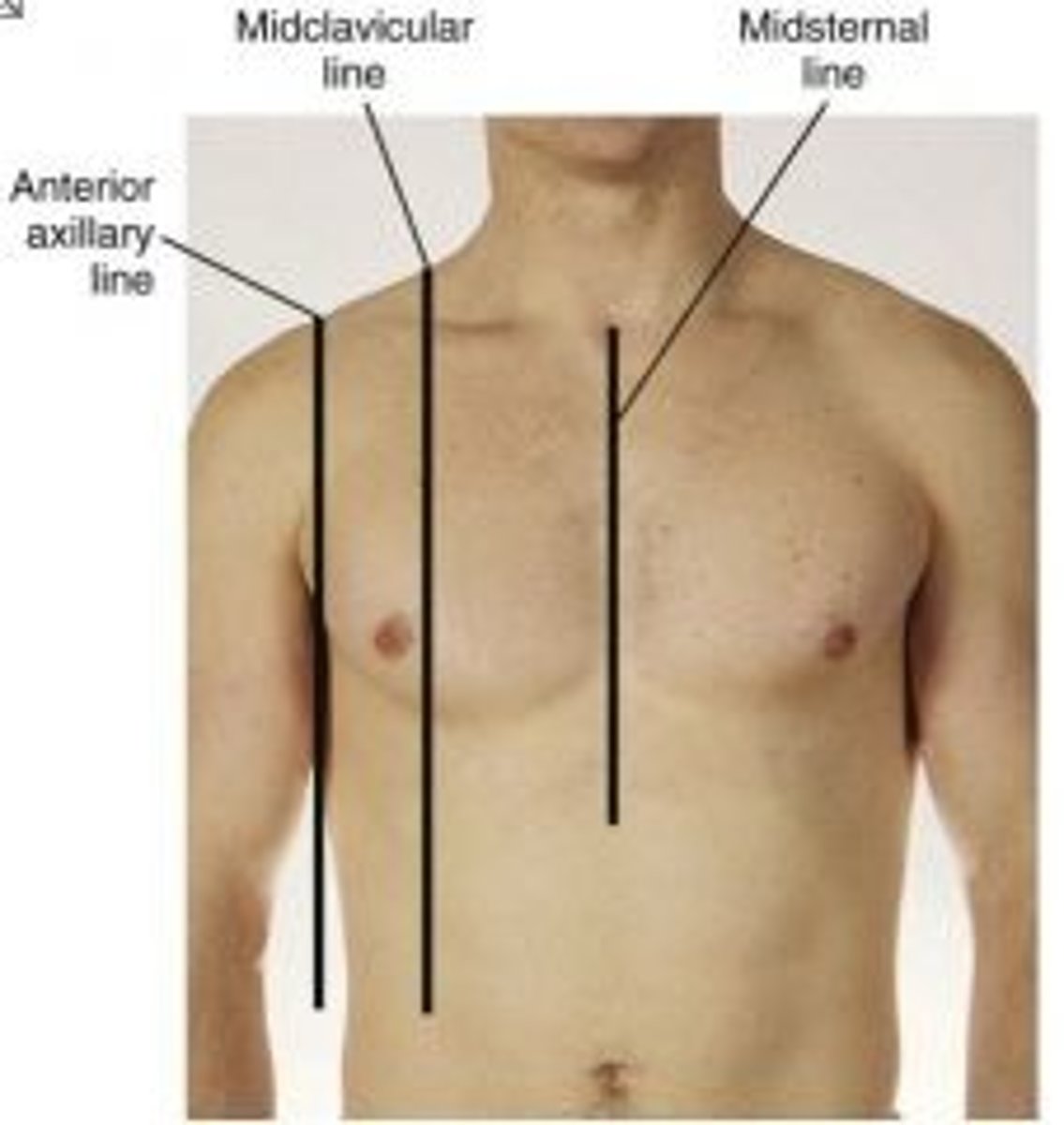
Where is midclavicular line?
Middle of the clavicle
Where is midsternal line?
Middle of sternum
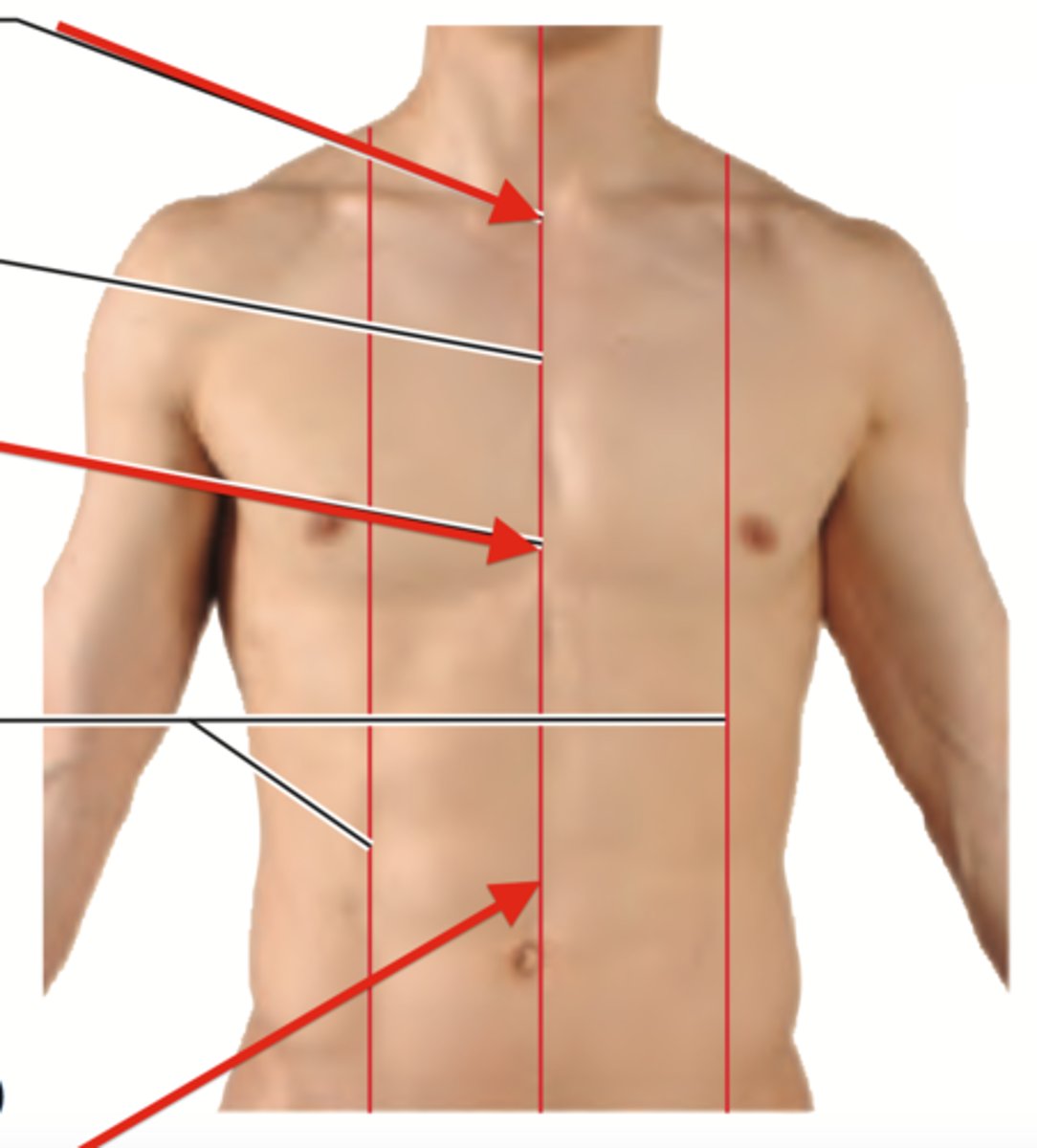
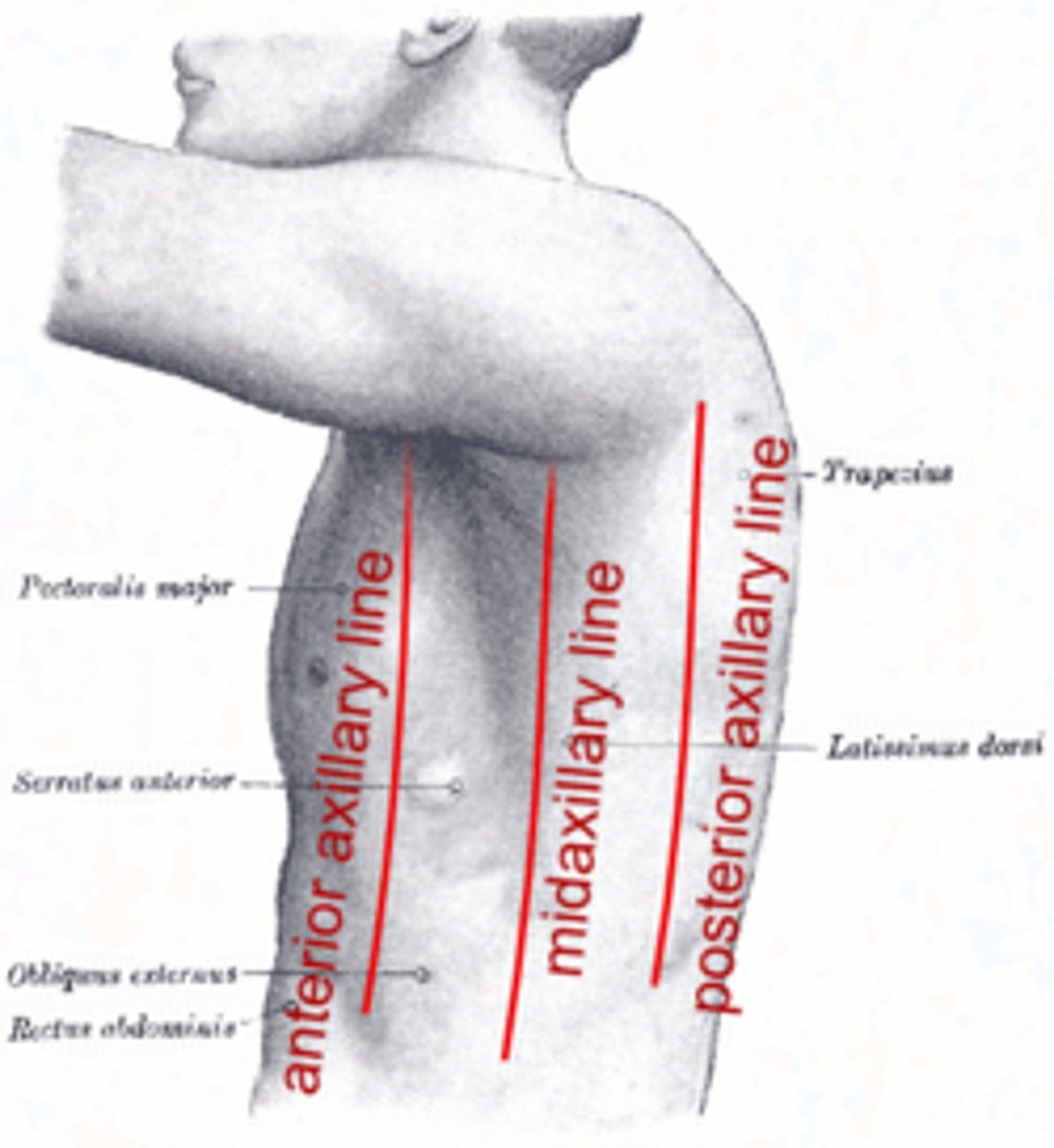
Where is anterior axillary line?
Front of armpit
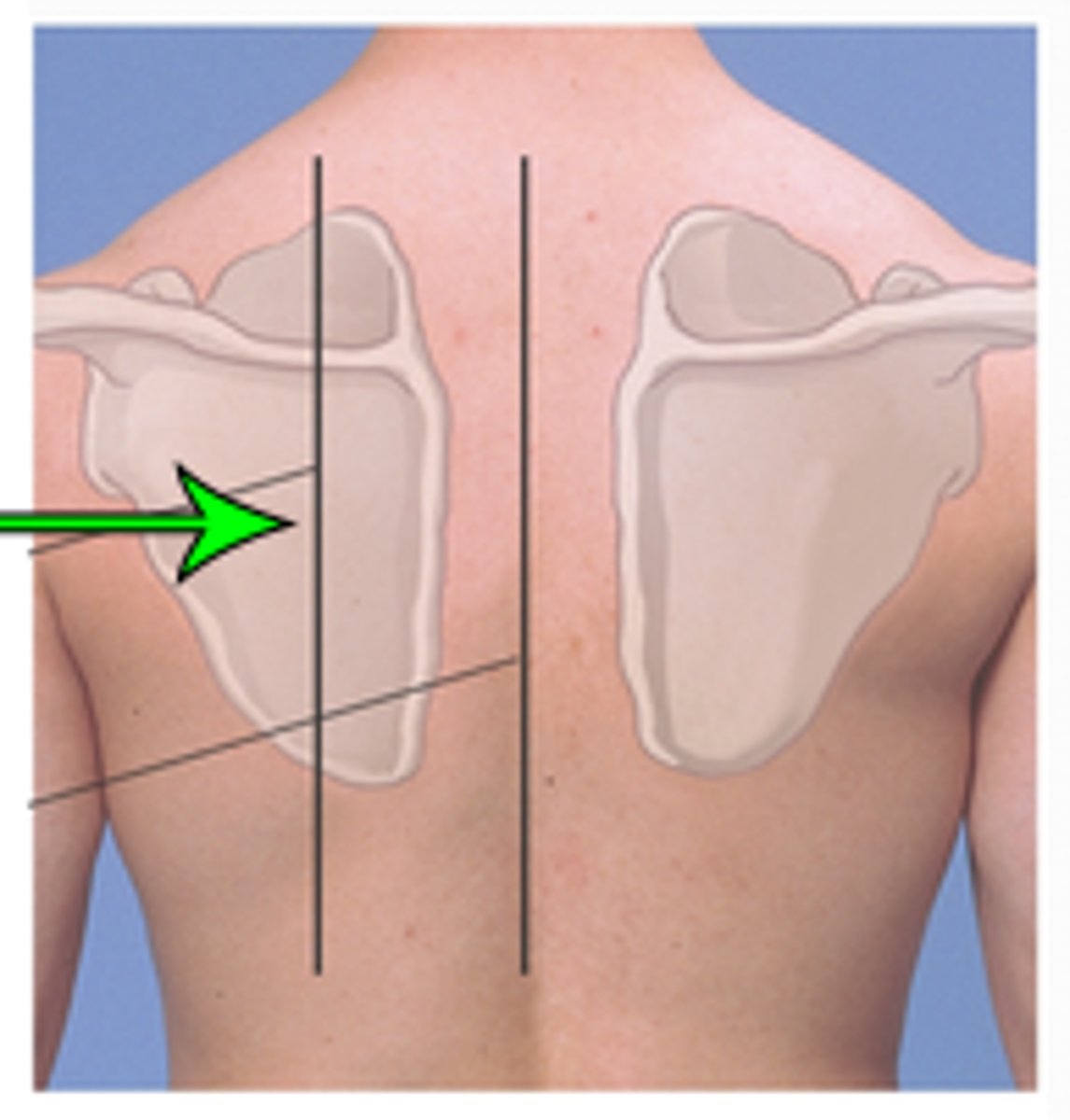
Where is scapular line?
Line through the inferior angle of the scapula
Where is midaxillary line?
Middle of the armpit
How many lobes do the right and left lungs have?
Right has 3, left has 2
What accessory muscles are used during breathing?
-Sternocleidomastoids
-Scalenes
-Abdominal muscles
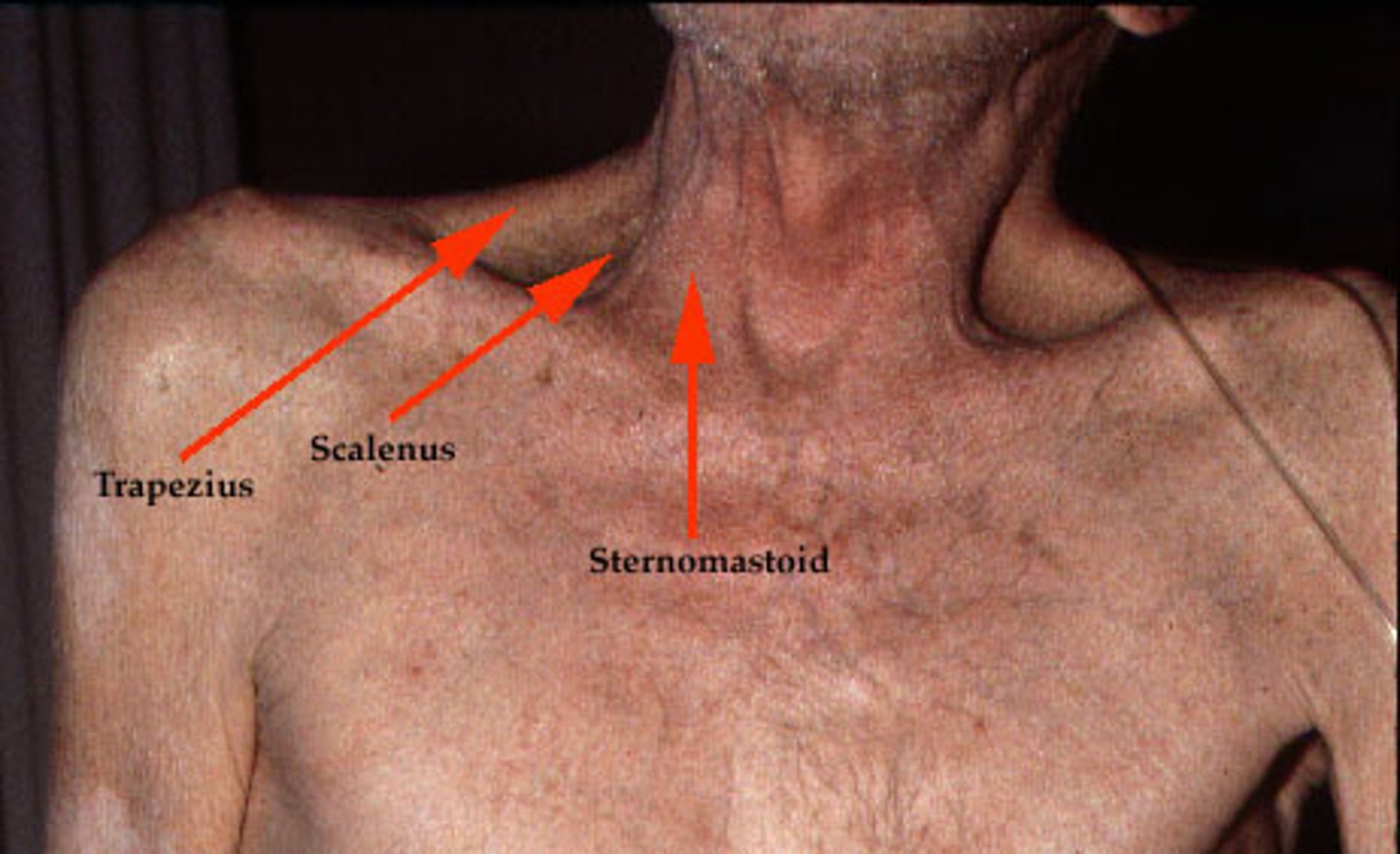
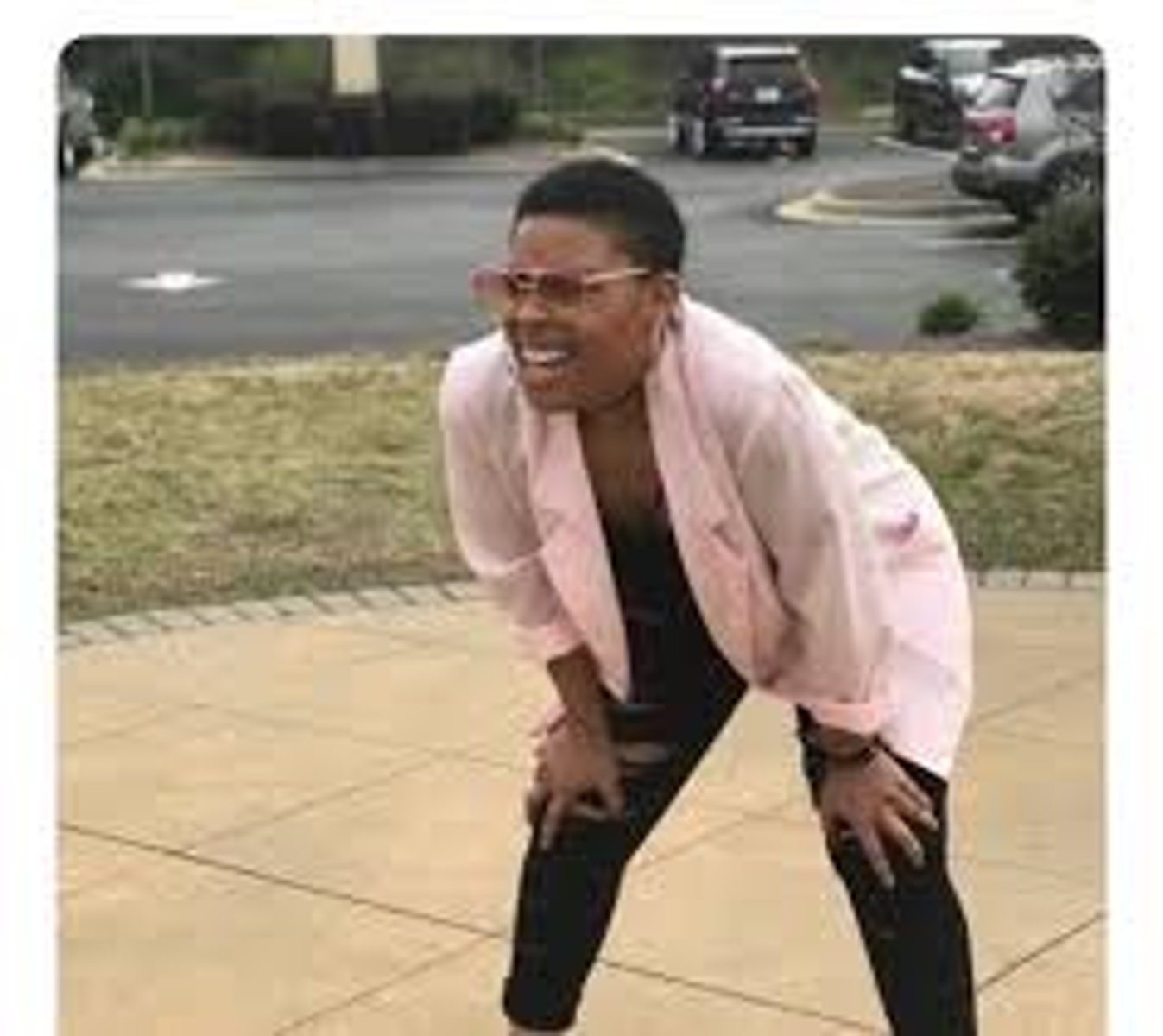
Tripod position?
A position that may be assumed during respiratory distress to facilitate the use of respiratory accessory muscles.

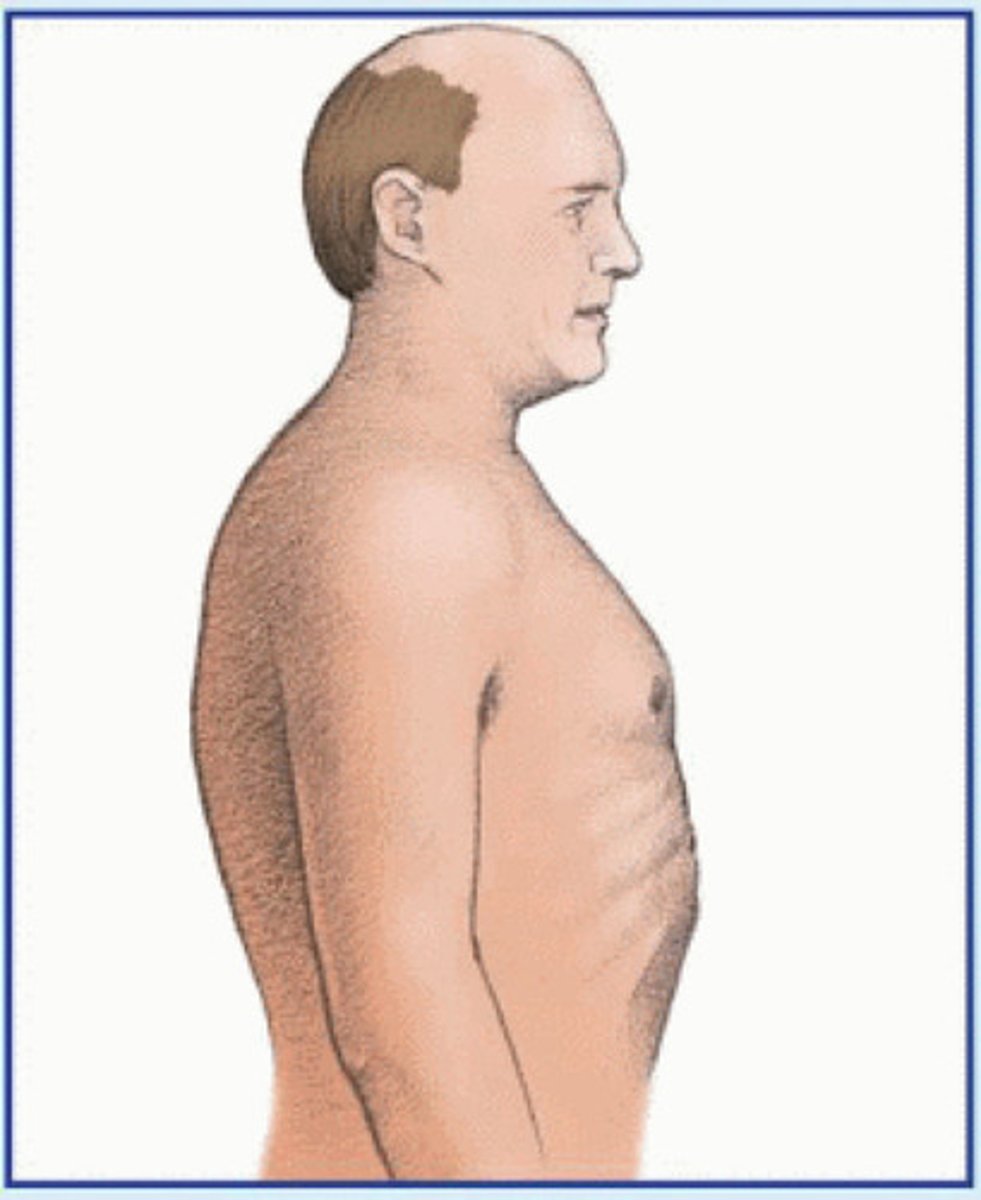
What is barrel chest?
Increased anterior-posterior diameter of chest
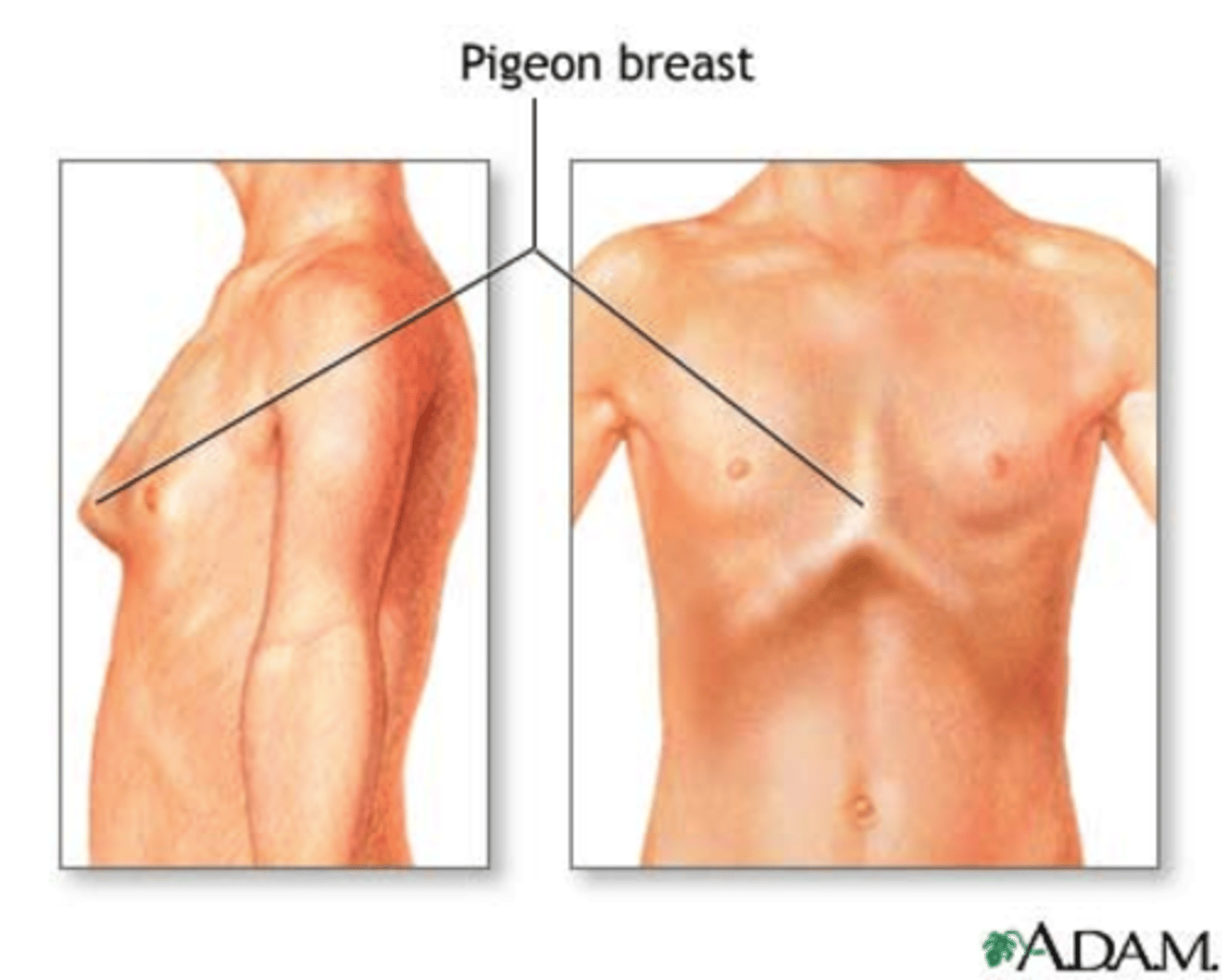
What is pigeon breast?
Softening of bones in the chest, bowing of the chest
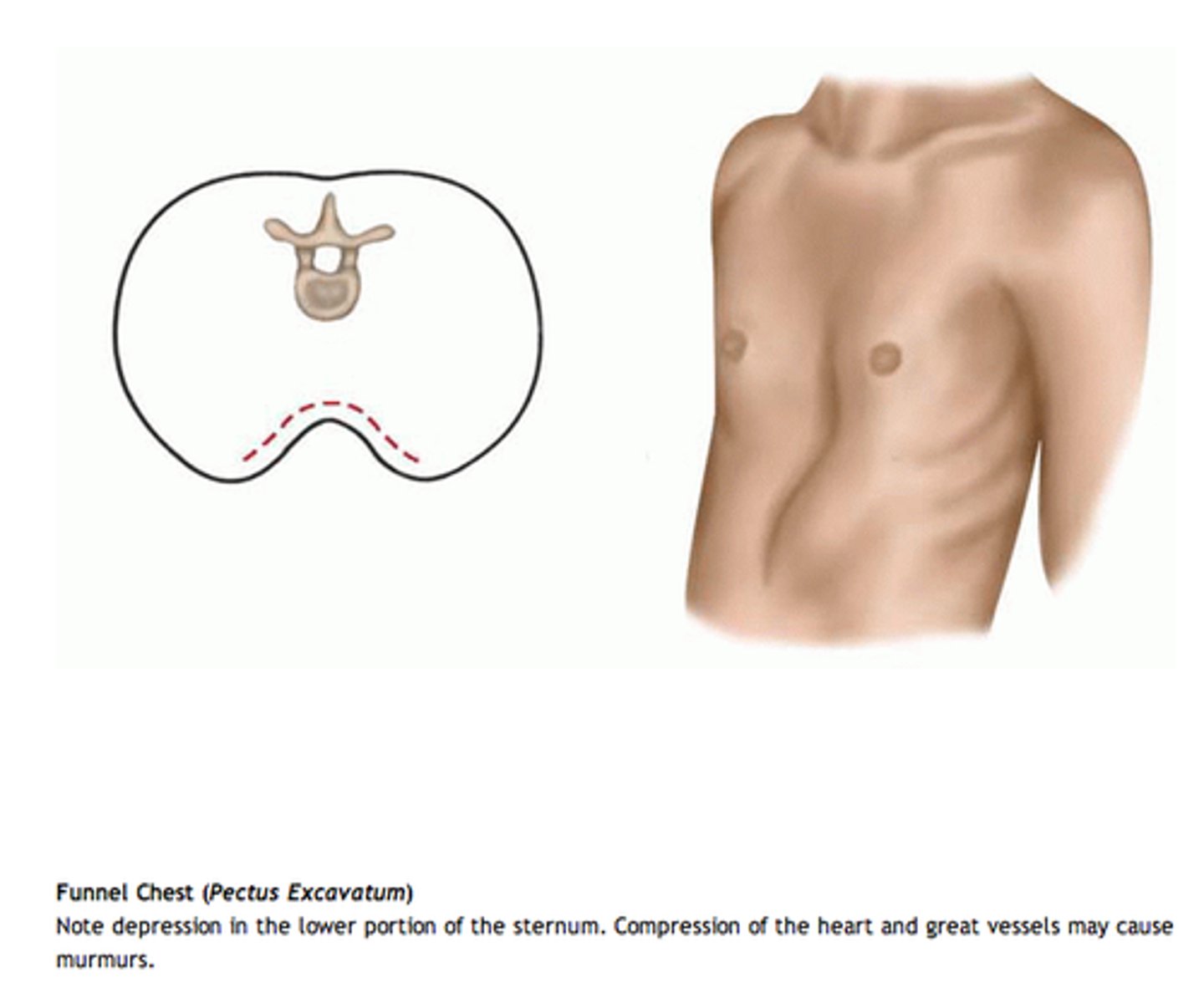
What is funnel chest?
Depression of lower portion of sternum
How to palpate the trachea?
-Place your fingers and thumb on either side of trachea and note its position
-Trachea should be midline
What can cause increased or decreased tactile fremits?
Increased: occurs with consolidation of lung tissue
Decreased: occurs with obstruction of vibrations
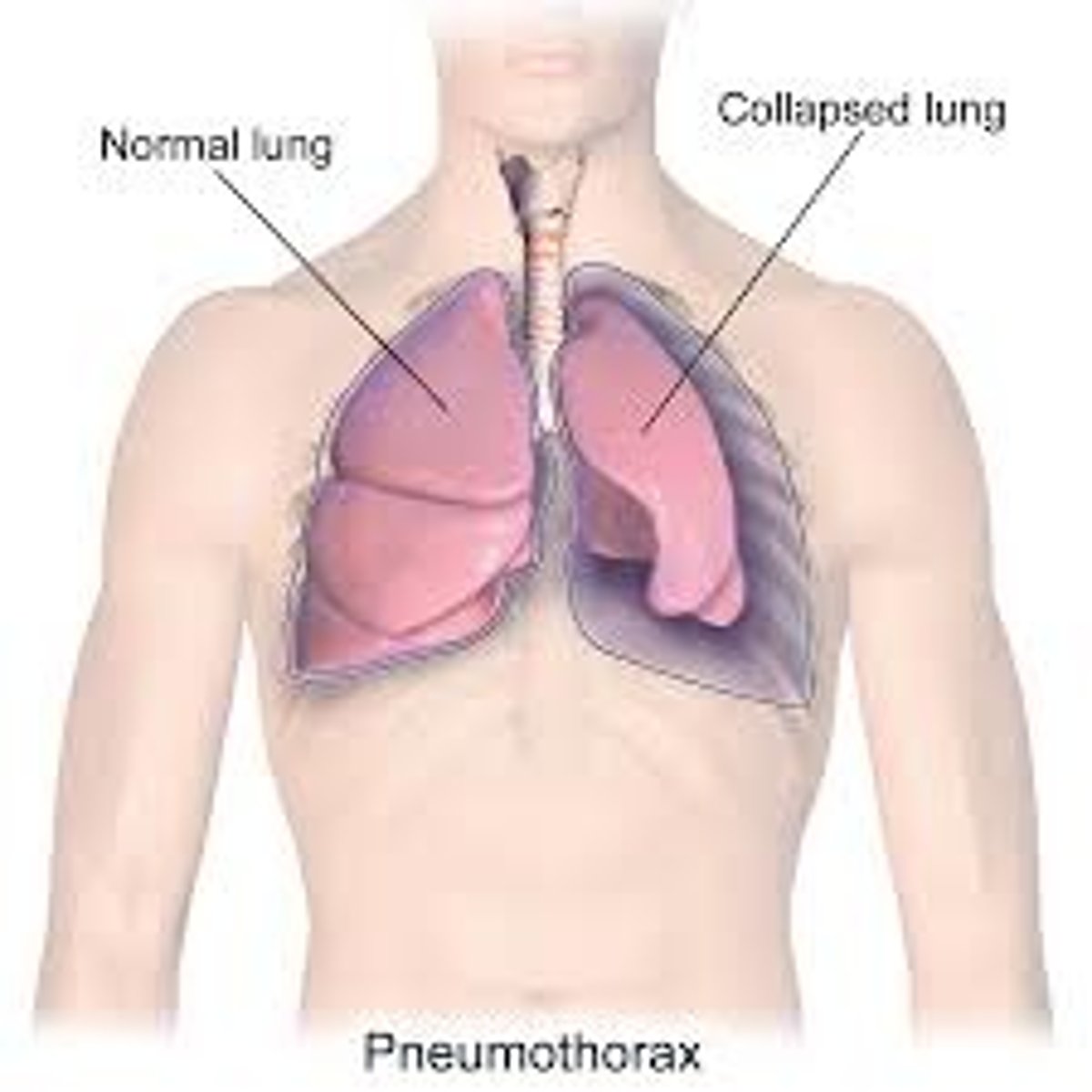
What is a pneumothorax?
Air in the pleural space, collapsed lung
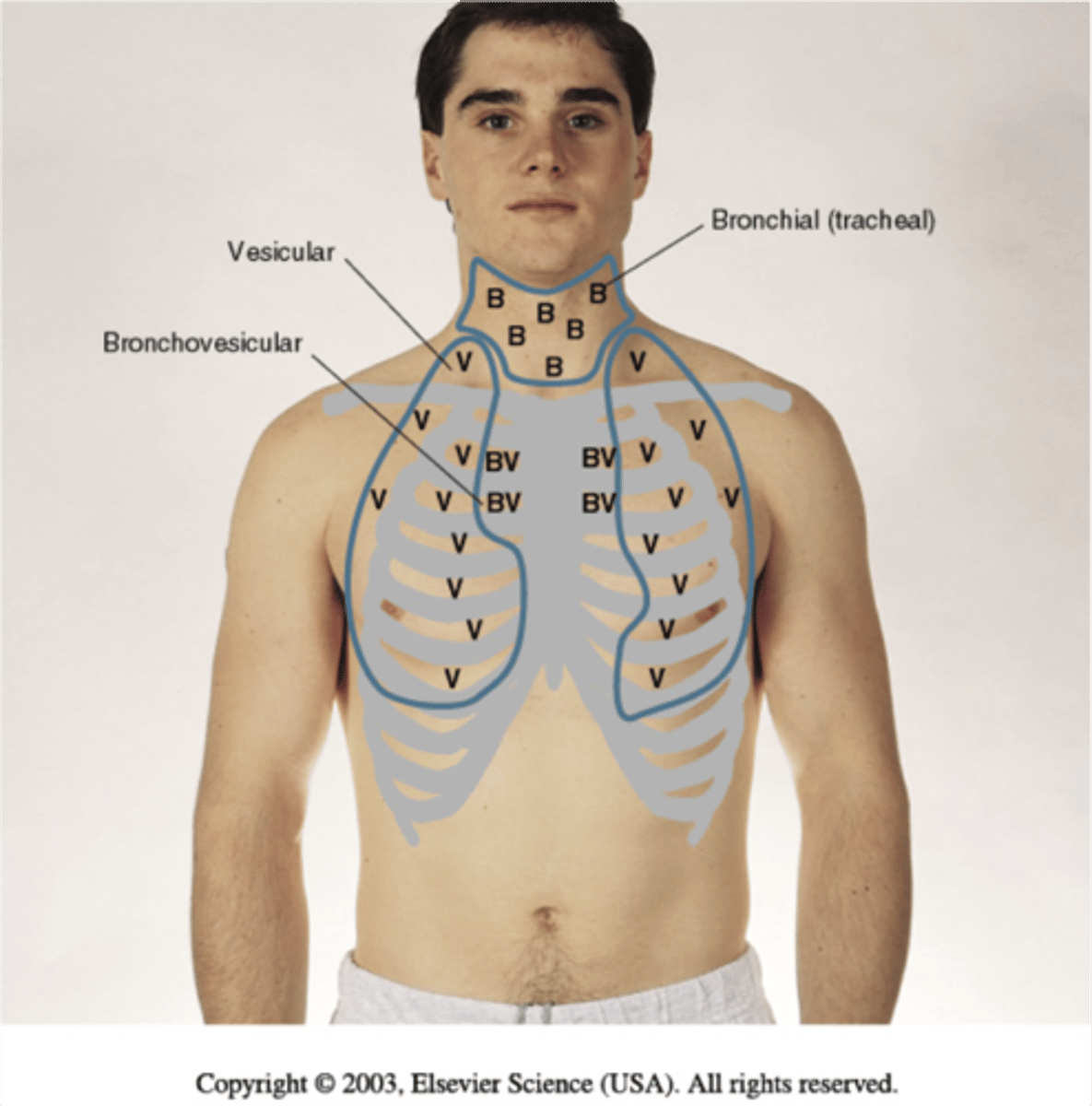
Where are bronchial breath sounds?
Heard over trachea and larynx
-short inspiration/longer expiration
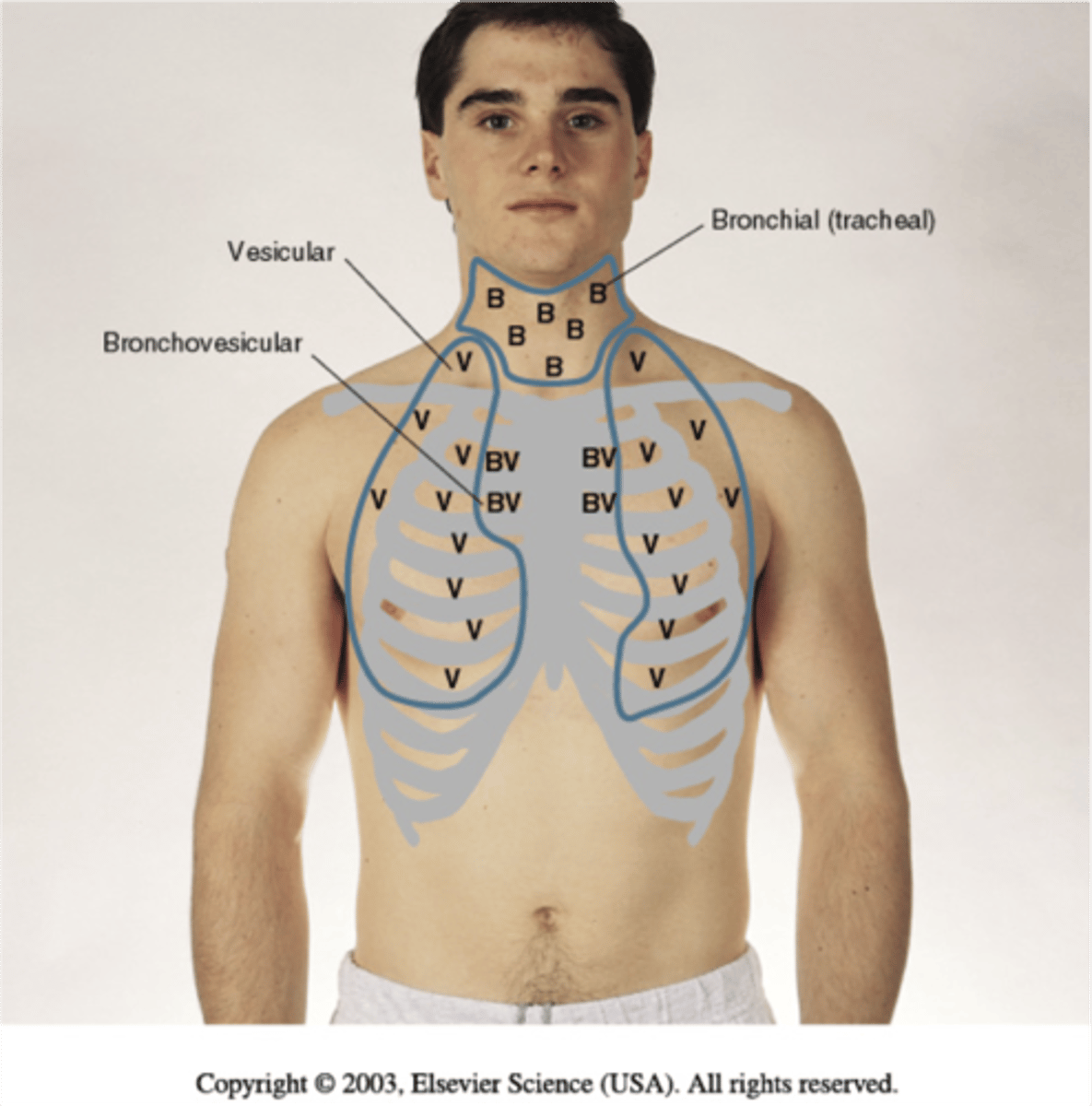
Where are vesicular breath sounds?
Heard over periphery of lung
-longer inspiration/short expiration
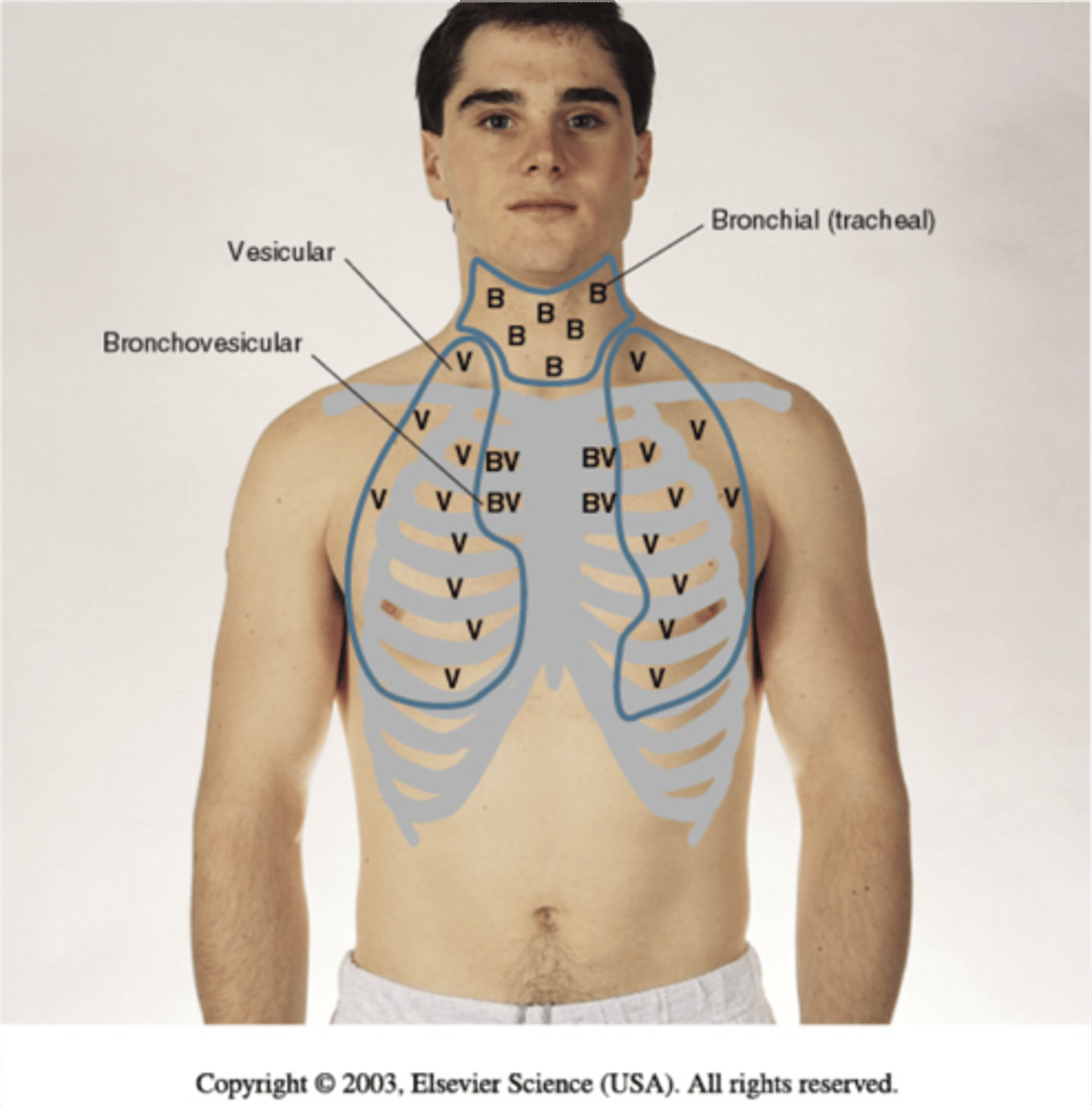
Where are bronchovesicular sounds?
What are crackles (rales)?
-Short popping sounds usually heard during inspiration
-Caused by inhaled air colliding with previous deflated airways, airways popping open creates the sound
-Fluid in alveoli
-Usually not cleared by coughing
-Can be caused by pneumonia, heart failure, and atelectasis
-Can sound like rolling hair between fingers near ear or ripping open velcro
What are wheezes?
-High-pitched, musical sound usually on expiration, but may also occur on inspiration. (high and squeaky)
-Caused by air trying to squeeze through a passage narrowed by airway obstruction from collapse, or swelling
-Bronchospasm, Bronchoconstriction
, Asthma, chronic bronchitis
What is rhonchi?
-Low pitched moan, rumbling or snoring or gurgling sound, heard on inspiration and expiration, but usually more prominent on expiration (low and dull)
-Caused by passage of airflow obstruction by thick secretions; foreign bodies.
-May clear with coughing
-Bronchitis, obstruction from tumor
What is stridor?
-EMERGENCY
-High pitched musical crowing sound, often louder in the neck than over the chest wall
-Caused by upper airway obstruction, from swollen tissue or lodged foreign body.
-Croup, epiglotitis, foreign body
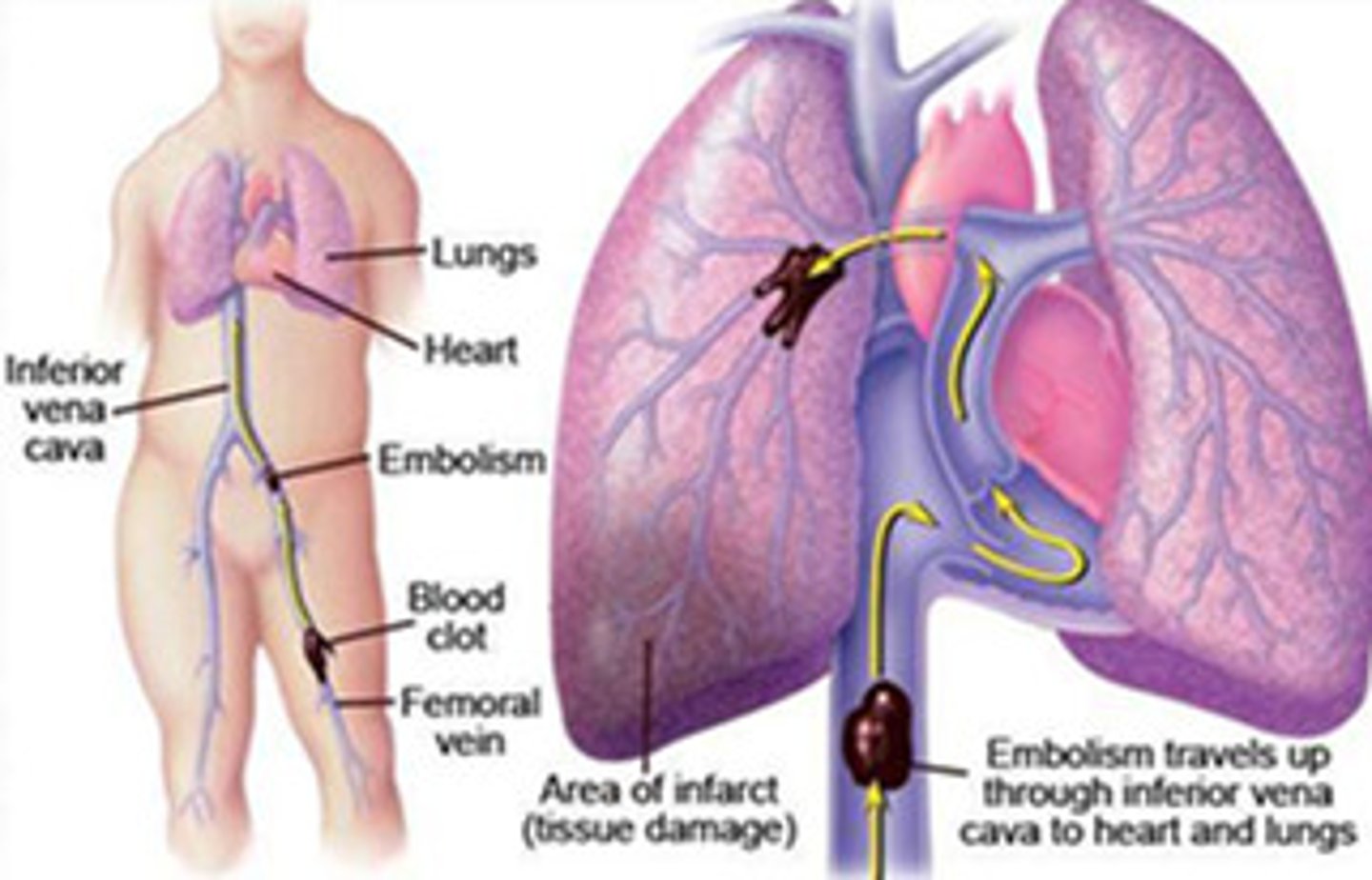
What is a pulmonary embolism?
A clot that formed somewhere else in the body that traveled to the lungs
-Usually caused by a large bone injury
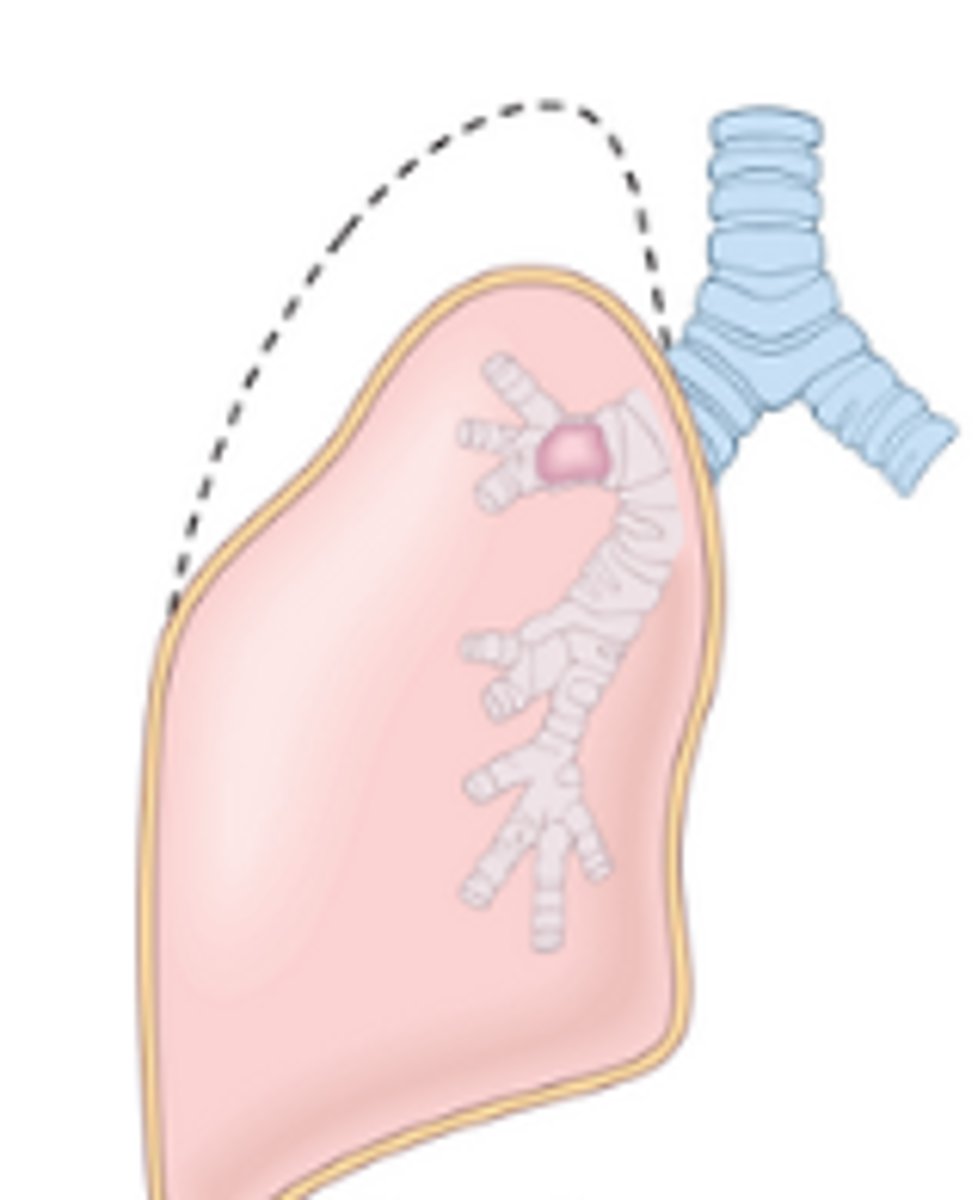
What is atelectasis?
Collapse of alveoli
What is a pleural friction rub?
-Grating sound with the quality of old leather crackling, heard on inspiration and expiration.
-Caused by rubbing together of inflamed or roughened of visceral and parietal pleurae. Heard best at anterolateral wall.
What can cause a sudden onset of dyspnea?
Anaphylaxis, pulmonary embolism, spontaneous pneumothorax, anxiety
Focused history questions to ask when assessing the eyes?
-Have you noticed any changes in your vision?
-Do you wear glasses or contact lens?
-Have you ever had an eye injury?
-Have you ever had an eye infection?
-Do you have any problems with excessive tearing or dry eyes?
-Have your ever had eye surgery?
-Have you ever experienced blurred vision, halos of light, spots, floaters, of flashes of light?
Where is the lacrimal gland?
Below eyebrow
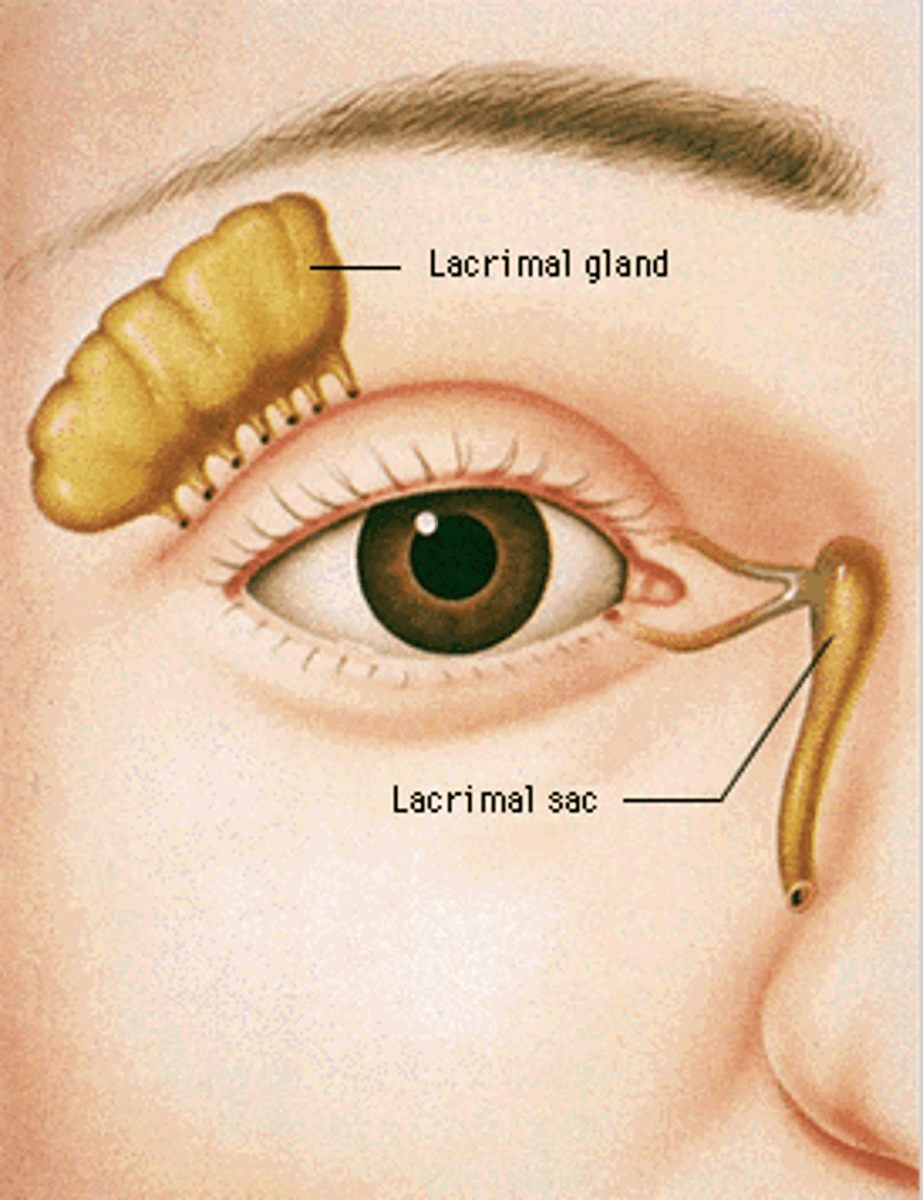
Where is the lacrimal sac?
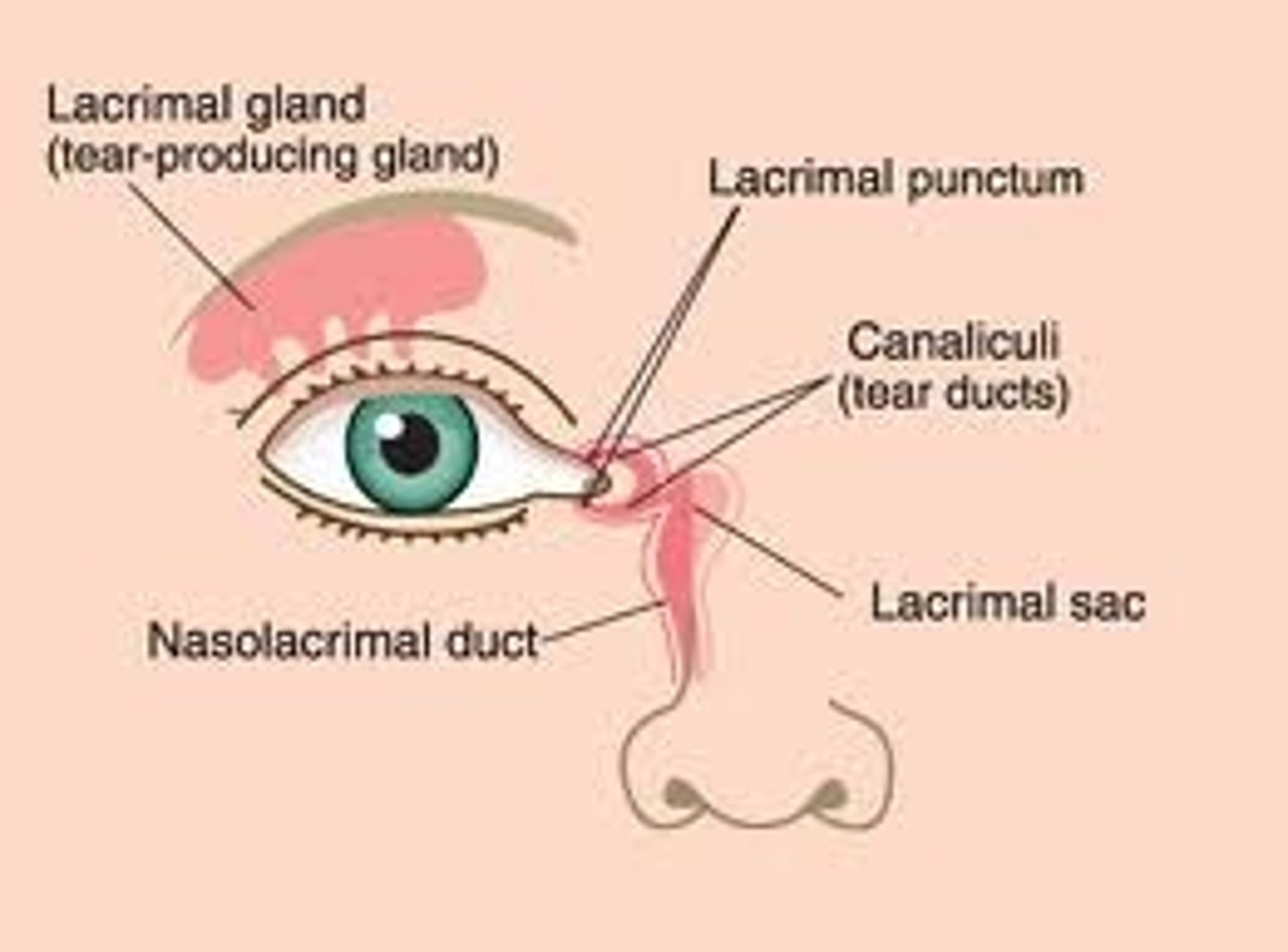
How to test distance vision?
-Use snellen chart
-Stand 20 feet away from chart
-Leave patients glasses or contact lenses on
-Record result using the numeric fraction at the end of the last successful line read; indicate whether any letters missed or corrective lenses worn (20/30—with glasses).
-Numerator indicates distance person is standing from chart; denominator is the distance at which a normal eye could have read that particular line. 20/30 means that you can read at 20 feet what a normal person can read from 30 feet away
What are abnormal findings when using snellen chart?
-A smaller fraction (20/100) indicates diminished distant vision or myopia. -A larger fraction (20/15) indicates diminished near vision- hyperopia
How to test near vision?
-Near vision tested in all individuals over age 40 and those reporting increasing difficulty reading.
-Use a Jaeger card (handheld vision screener) with various sizes of print or newsprint. Hold card 14 inches from the eye.
-Test each eye separately with corrective lenses on.
-Normal result is 14/14 in each eye without hesitancy in reading and without moving card closer or farther away.

What is presbyopia?
Decrease in accommodation with aging
How to test peripheral vision?
-Confrontation test
-Peripheral vision of patient is compared to peripheral vision of examiner.
-Examiner is positioned at eye level with person, about 2 feet away. Person covers one eye with an opaque card, and the other eye looks straight at examiner. Examiner covers own eye, opposite to person.
-Use a pencil or flicking fingers as a target, move the target in from the periphery to the center of the visual fields.
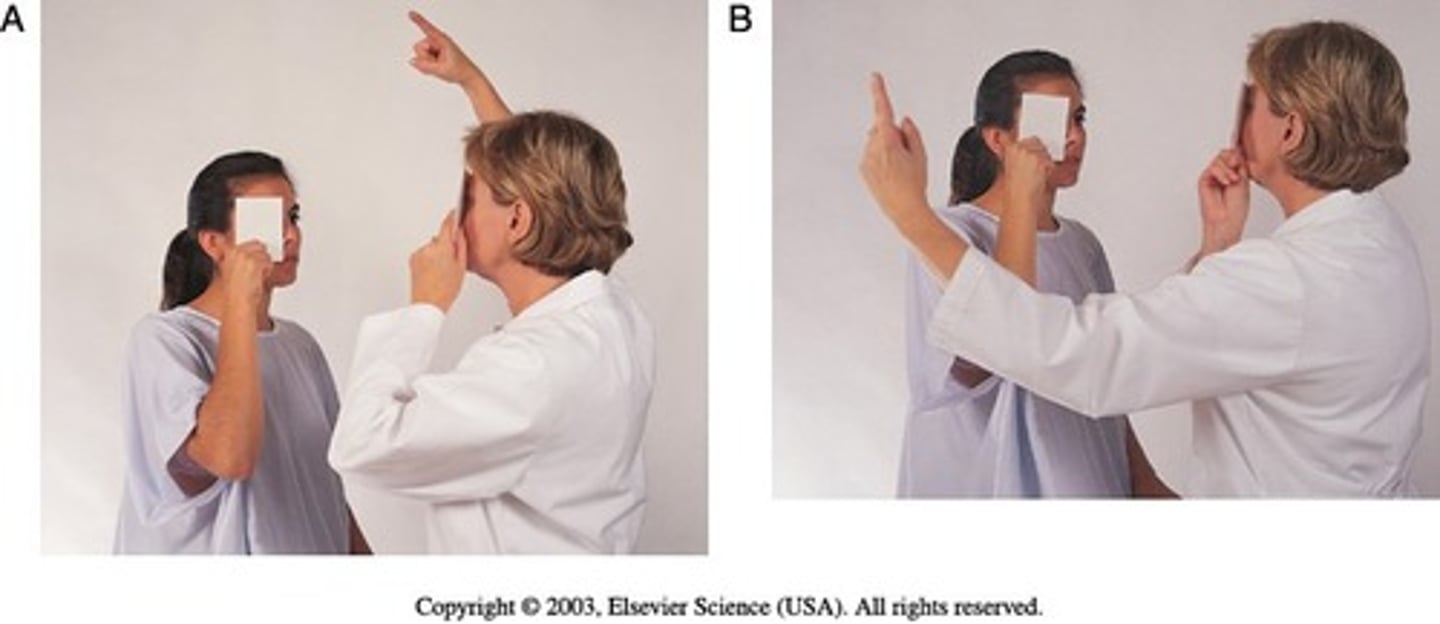
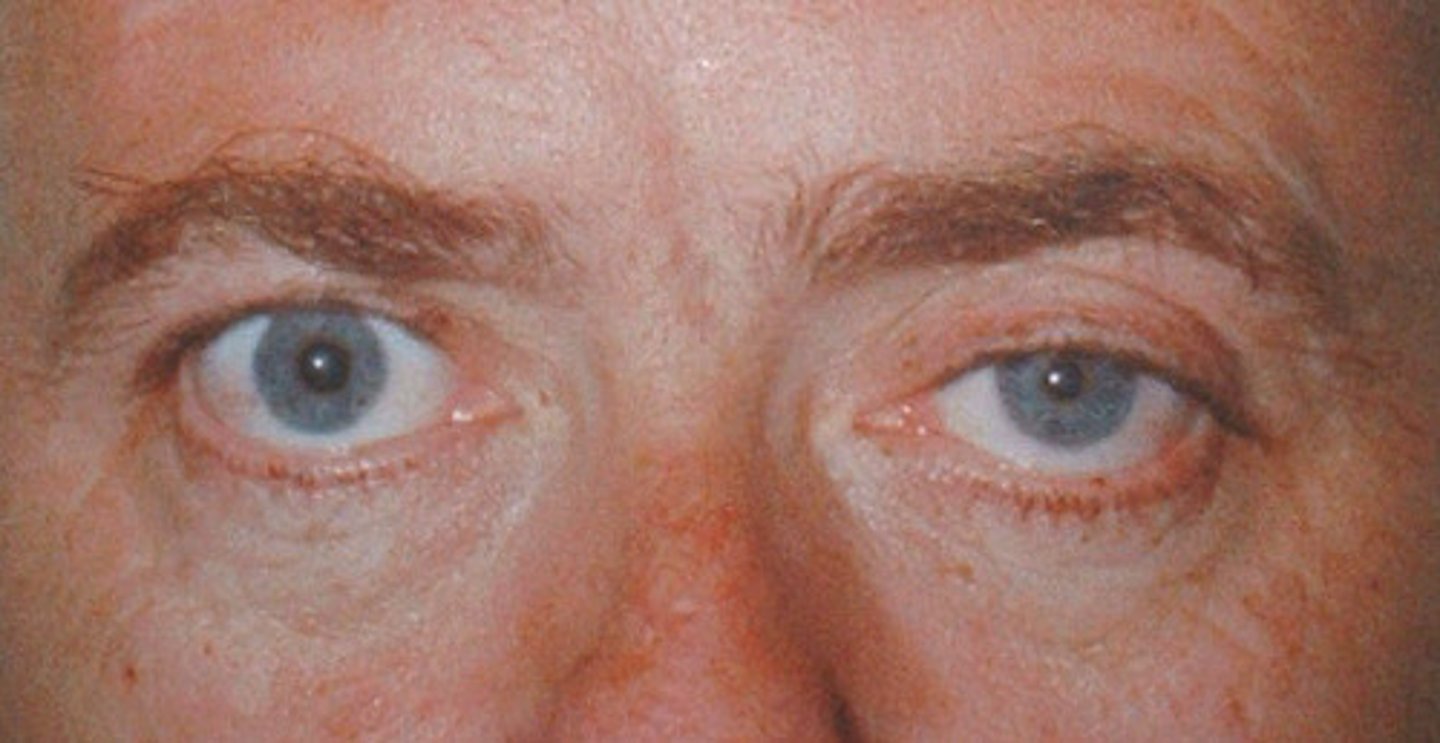
What is ptosis?
Drooping of the upper eyelid
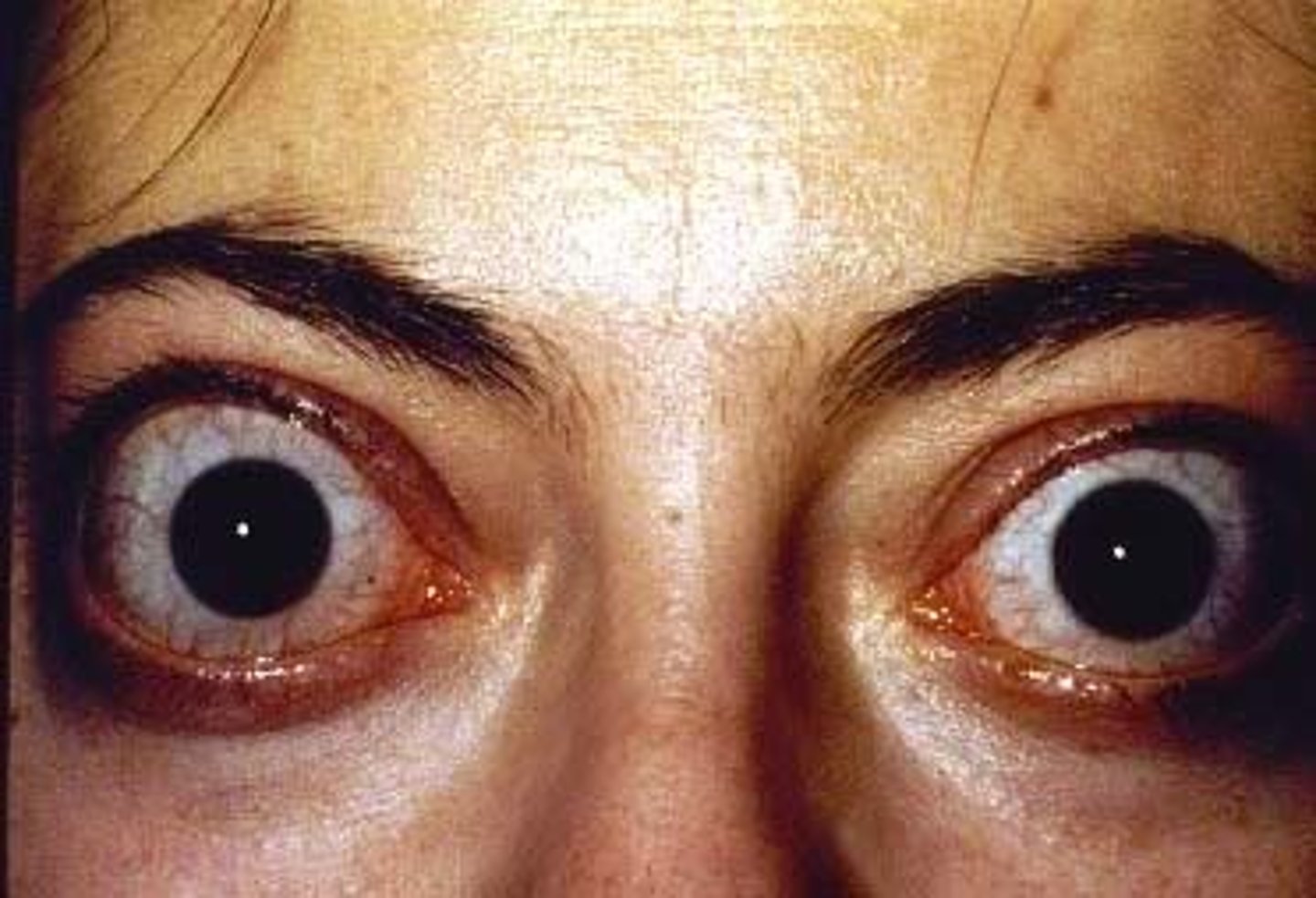
What is lid extraction/exophthalmos?
Bulging eyes
What is PERRLA
Pupils equal, round, reactive to light and accommodation
Focused history questions to ask when assessing the ears?
-Do you have any hearing problems?
-Have you ever had ringing/buzzing in your ears?
-Have you ever had any changes is your hearing?
-Do you have any ear drainage?
-Do you have any ear pain?
-Do you have any balance problems, dizziness, or vertigo?
-Do you have a history of head trauma?
-Are you exposed to noise pollution at work or in your home environment?
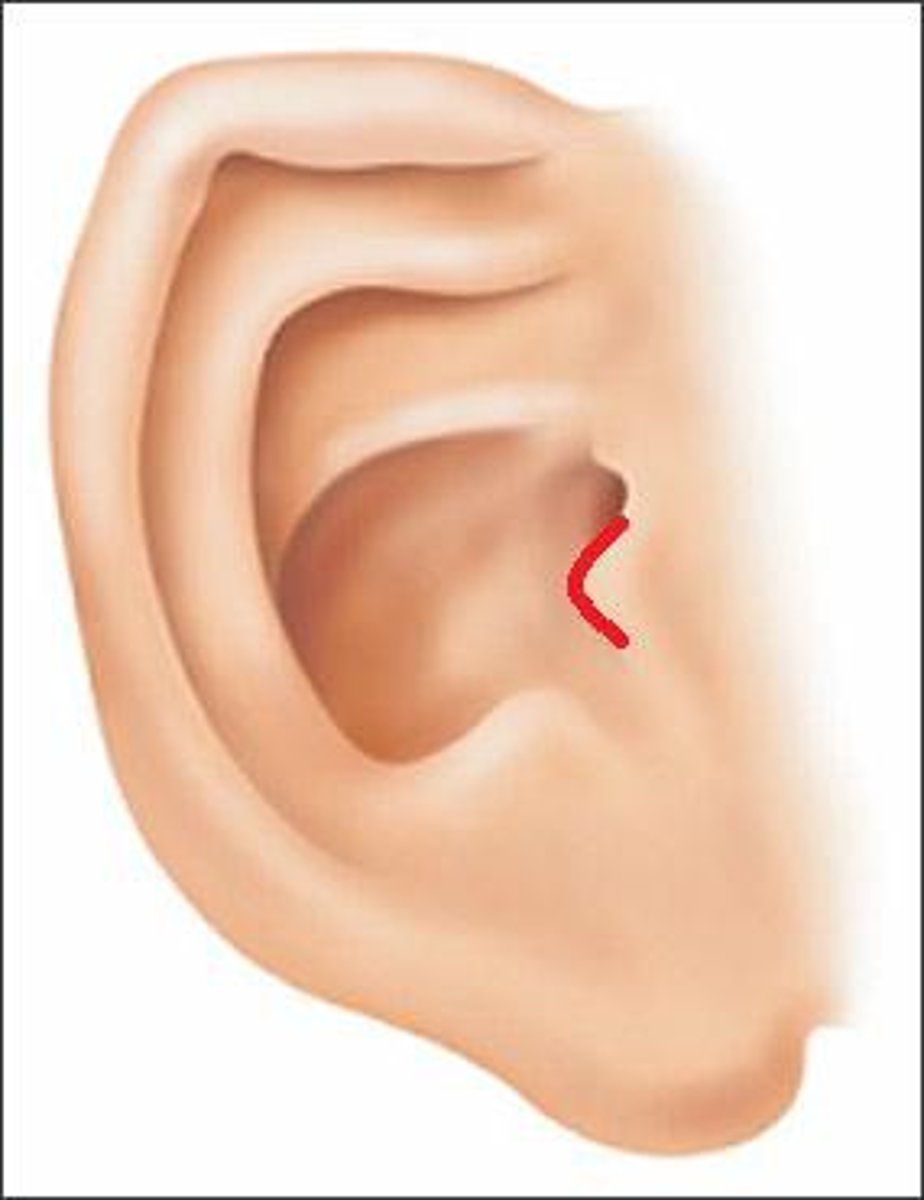
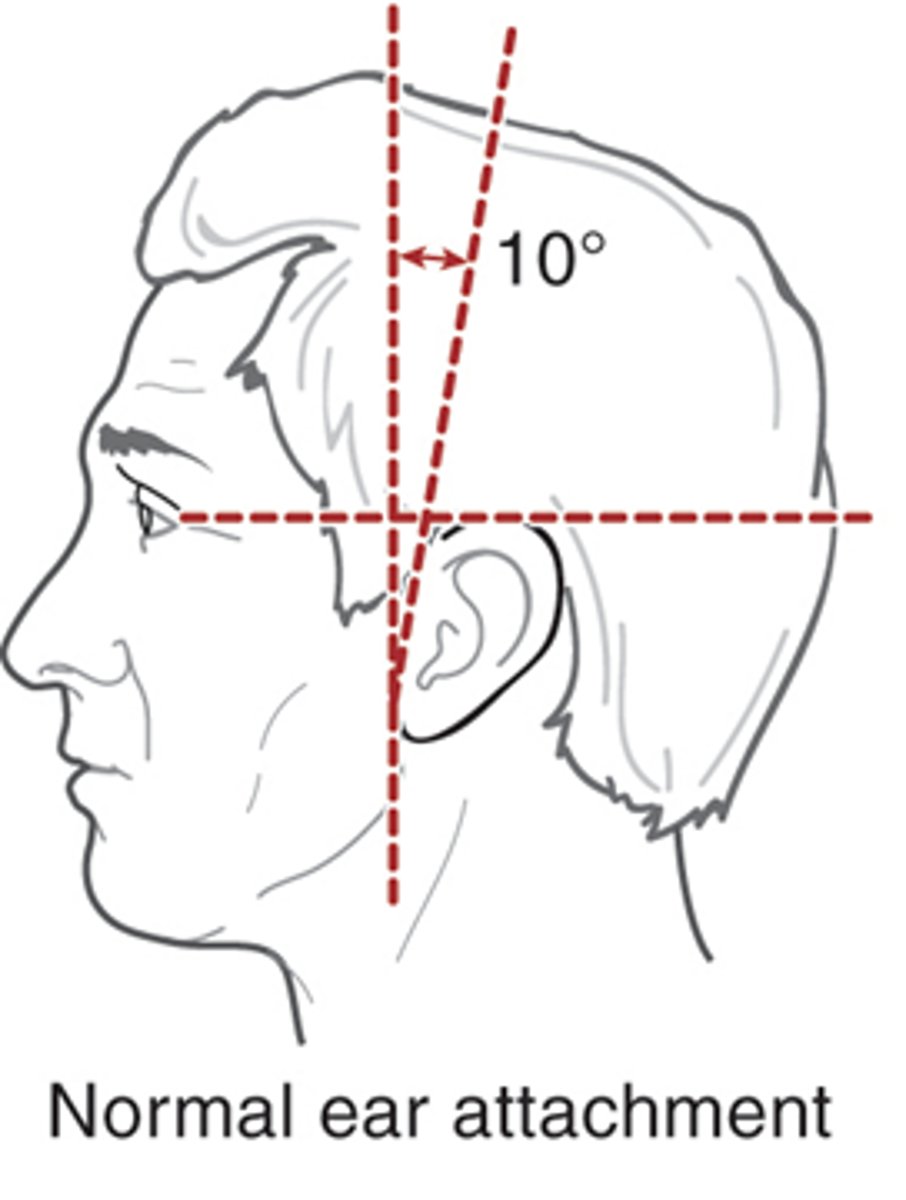
What is the normal angle of attachment for the ear?
10 degrees
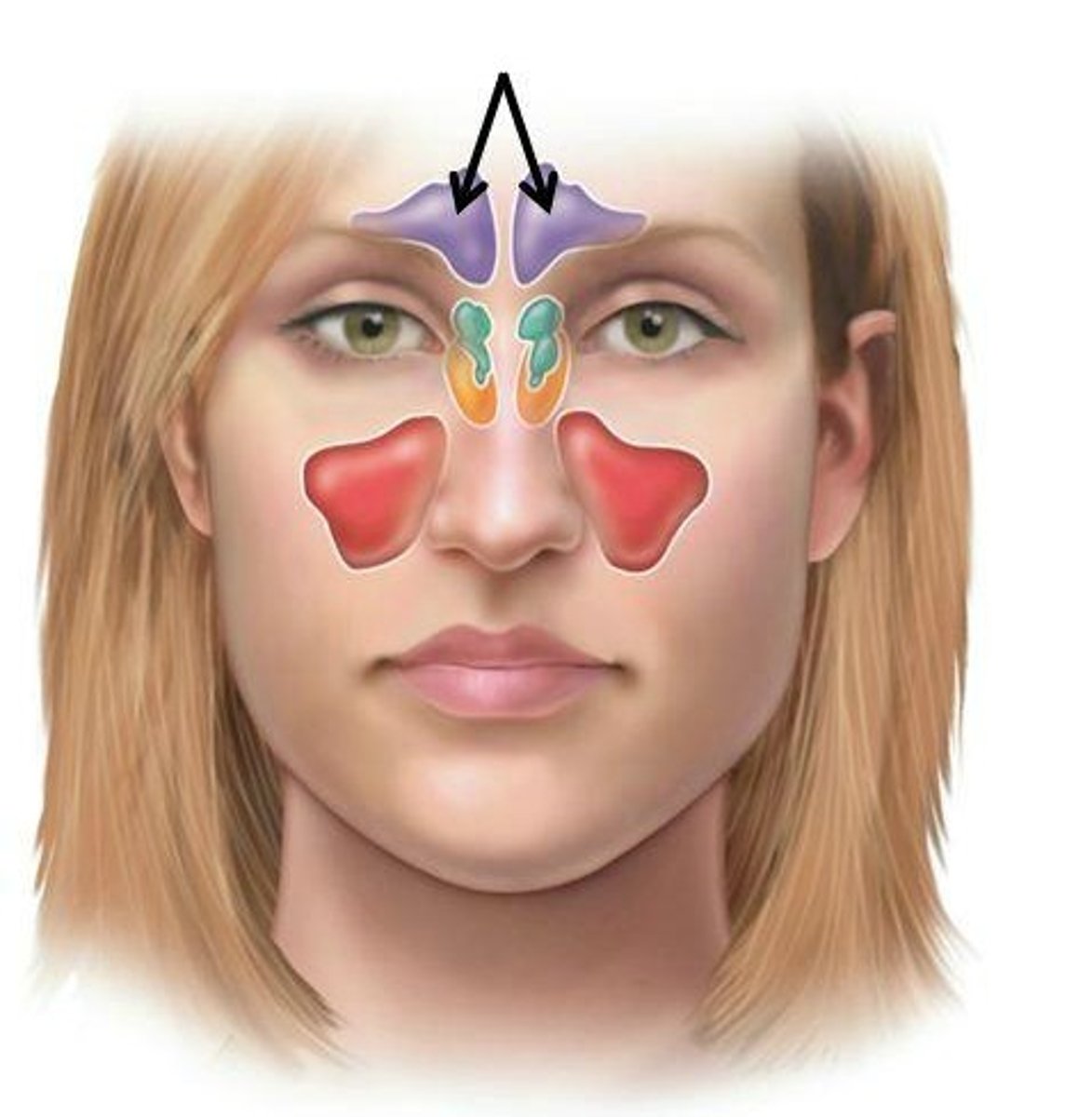
Function of the nose and paranasal sinuses
-Inspiration and expiration
-Filtration, warmth, and moisturization of the air exchanged
-Sensation of smell
-Resonance of speech
Focused history questions to ask when assessing the nose?
-Do you have any nasal congestion?
-Do you have a history of nose or sinus problems?
-Do you have problems with seasonal or environmental allergies?
-Do you have a history of sinus headache?
-Do you experience nose bleeds (epistaxis)?
-Have you ever broken your nose?
-Have you had any changes in your sense of smell?
-Do you use any nasal sprays or allergy medications?
How to inspect internal structures of nose?
-Use a nasal speculum
-Tilt the patient's head back
-Brace your index finger against nose as speculum is inserted.
-Insert speculum about 1 cm into nares
-Nasal mucosa should be pink and moist. Septum is intact & midline no lesions noted
Where are frontal sinuses?
Above eyebrows
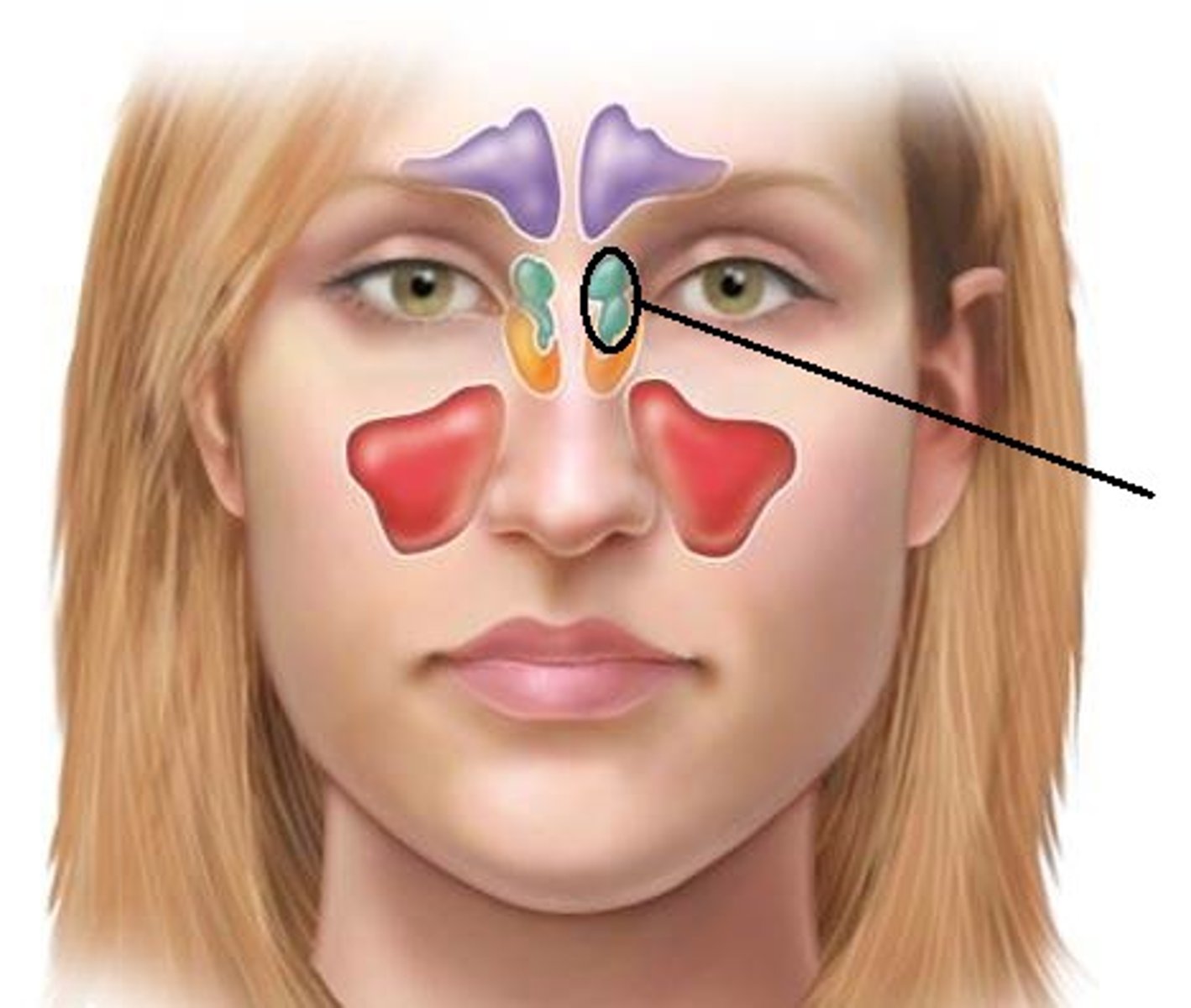
Where are ethmoid sinuses?
Between the eyes
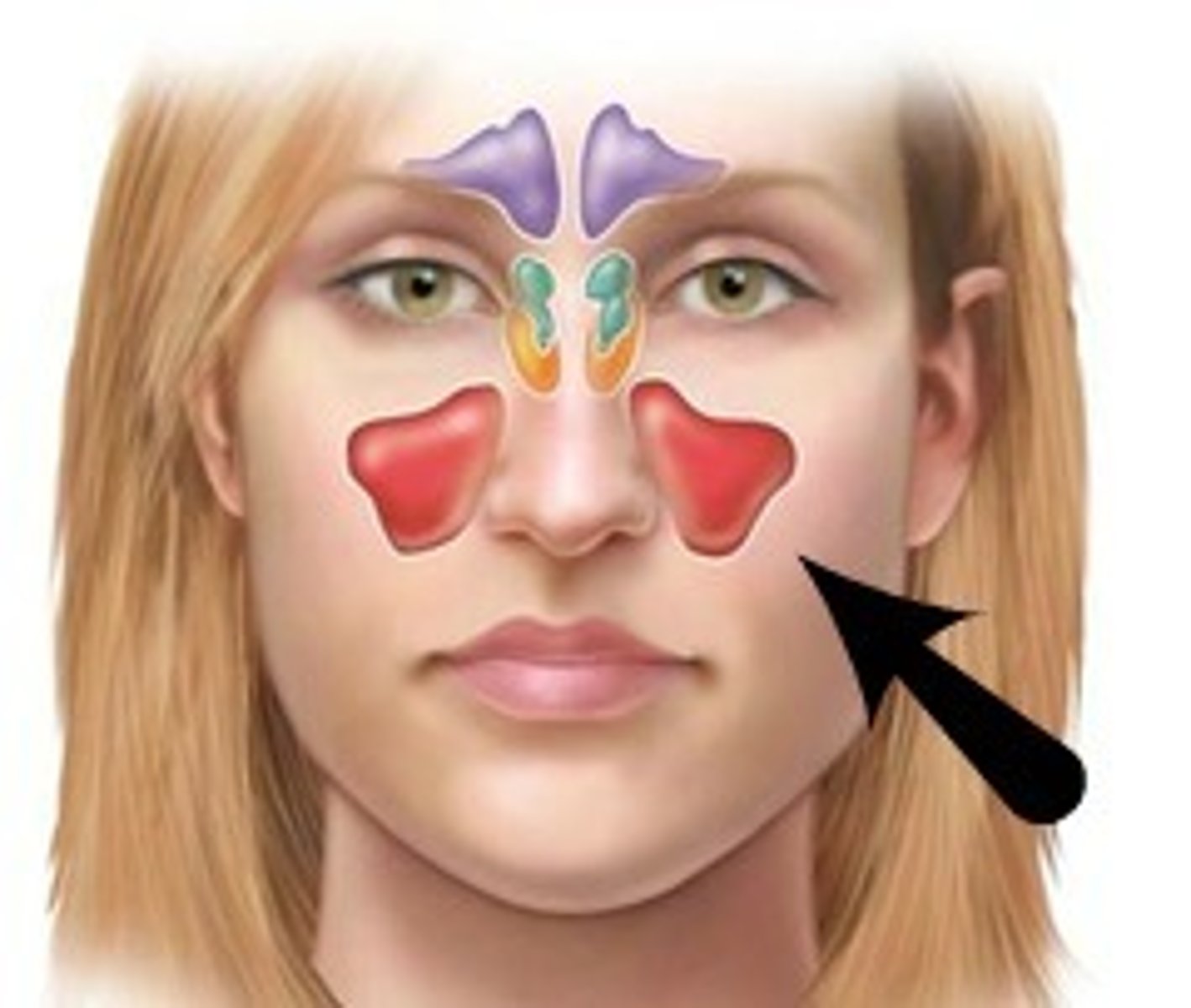
Where are maxillary sinuses?
Cheek bones
Where are sphenoid sinuses?
Deep within the skull in the sphenoid bone
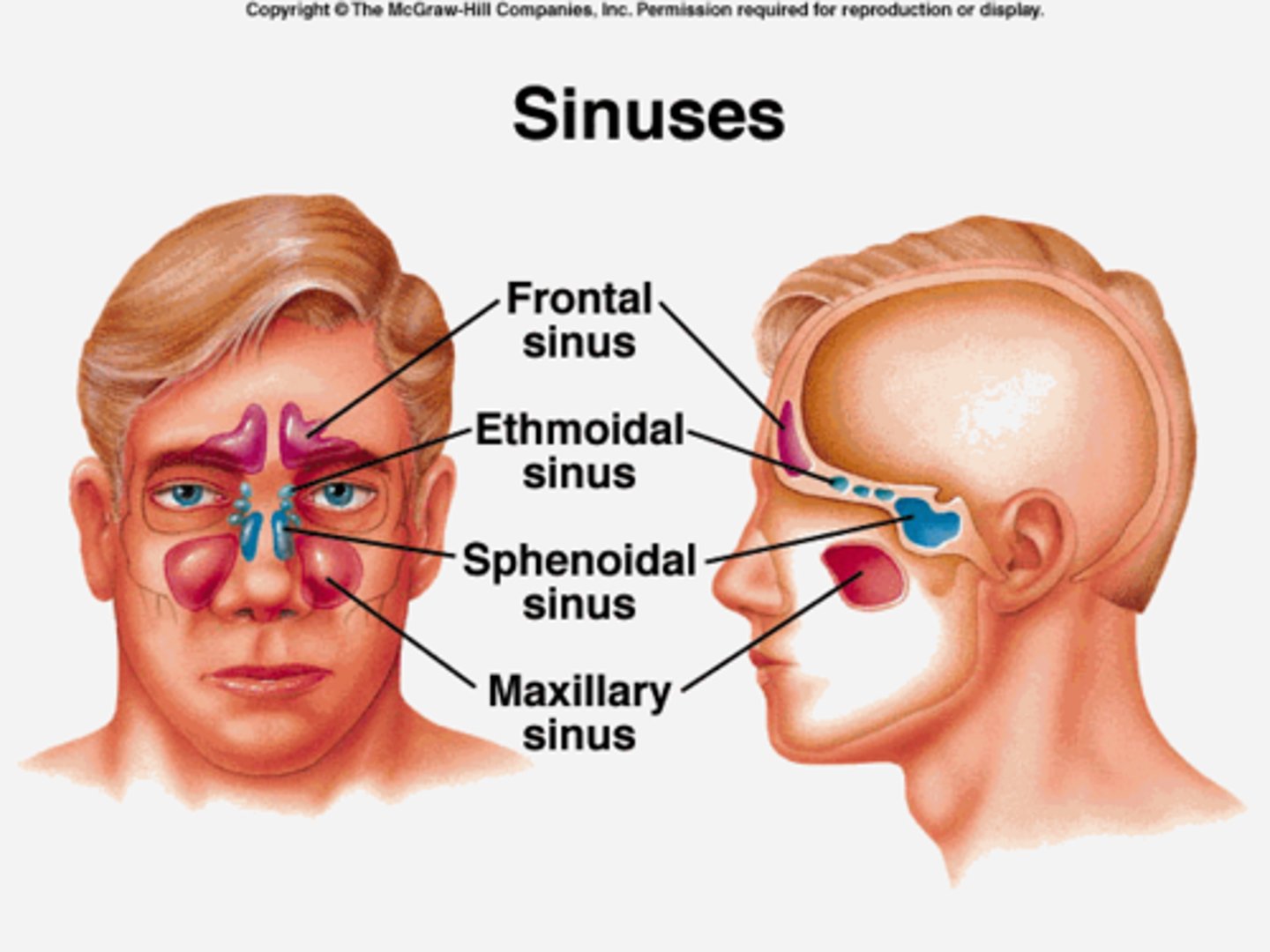
How to inspect and palpate sinuses?
-Inspect frontal and maxillary sinuses for swelling
-Palpate frontal sinus (press up under bony brow, using thumb on each side of nose)
-Palpate maxillary sinus (press up under) zygomatic process, using thumb)
How to inspect the throat?
-Inspect tonsils, note color, size, exudate
-Inspect posterior wall of pharynx for color, exudate, or lesions
-Elicit gag reflex; touch posterior wall of pharynx on each side
-Notice any breath odor (halitosis)
What is candidiasis?
A yeast infection of the mouth or vagina
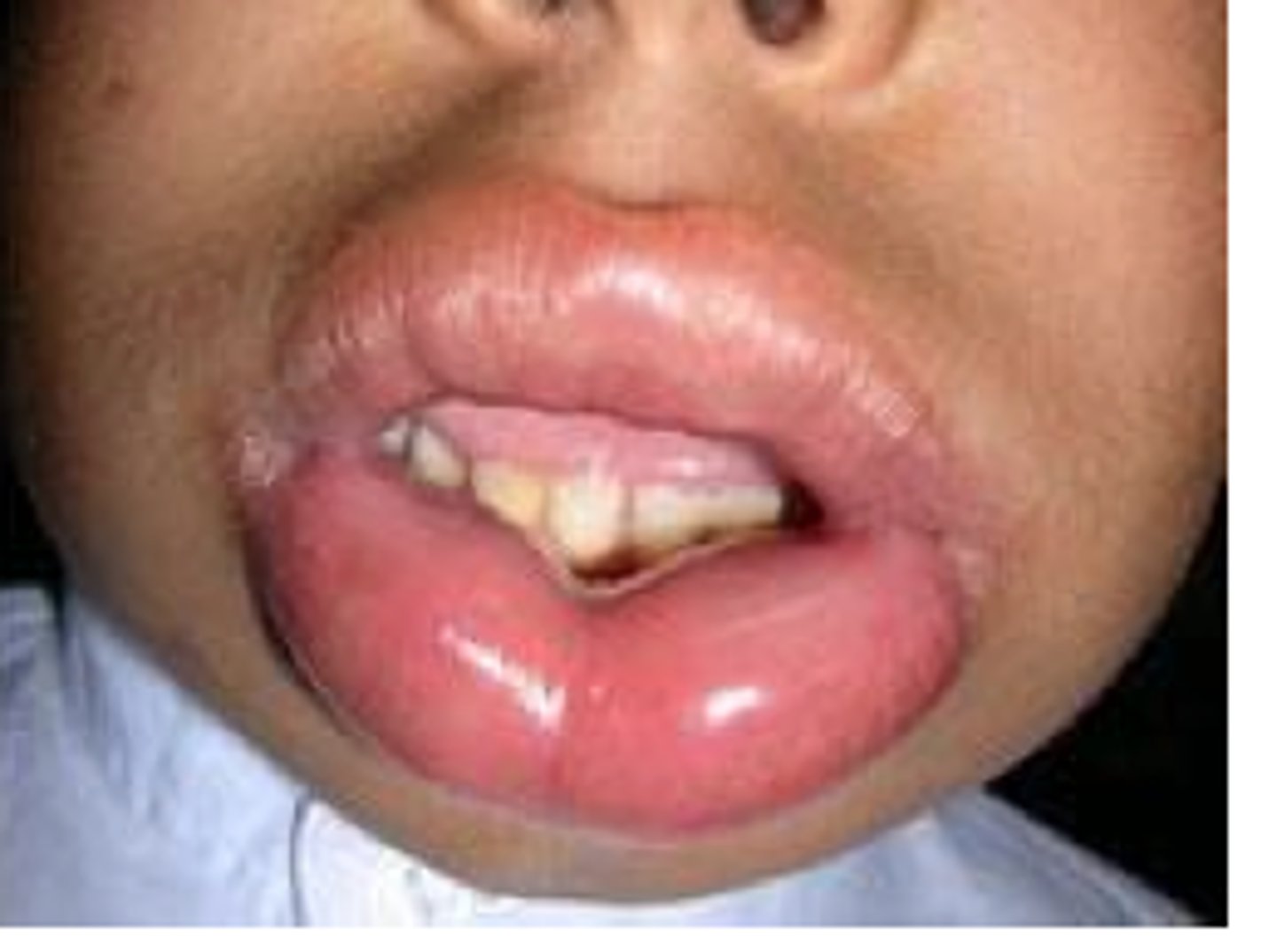
What is angioedema?
Swelling of lower lip caused by allergies.
Sign of anaphylaxis
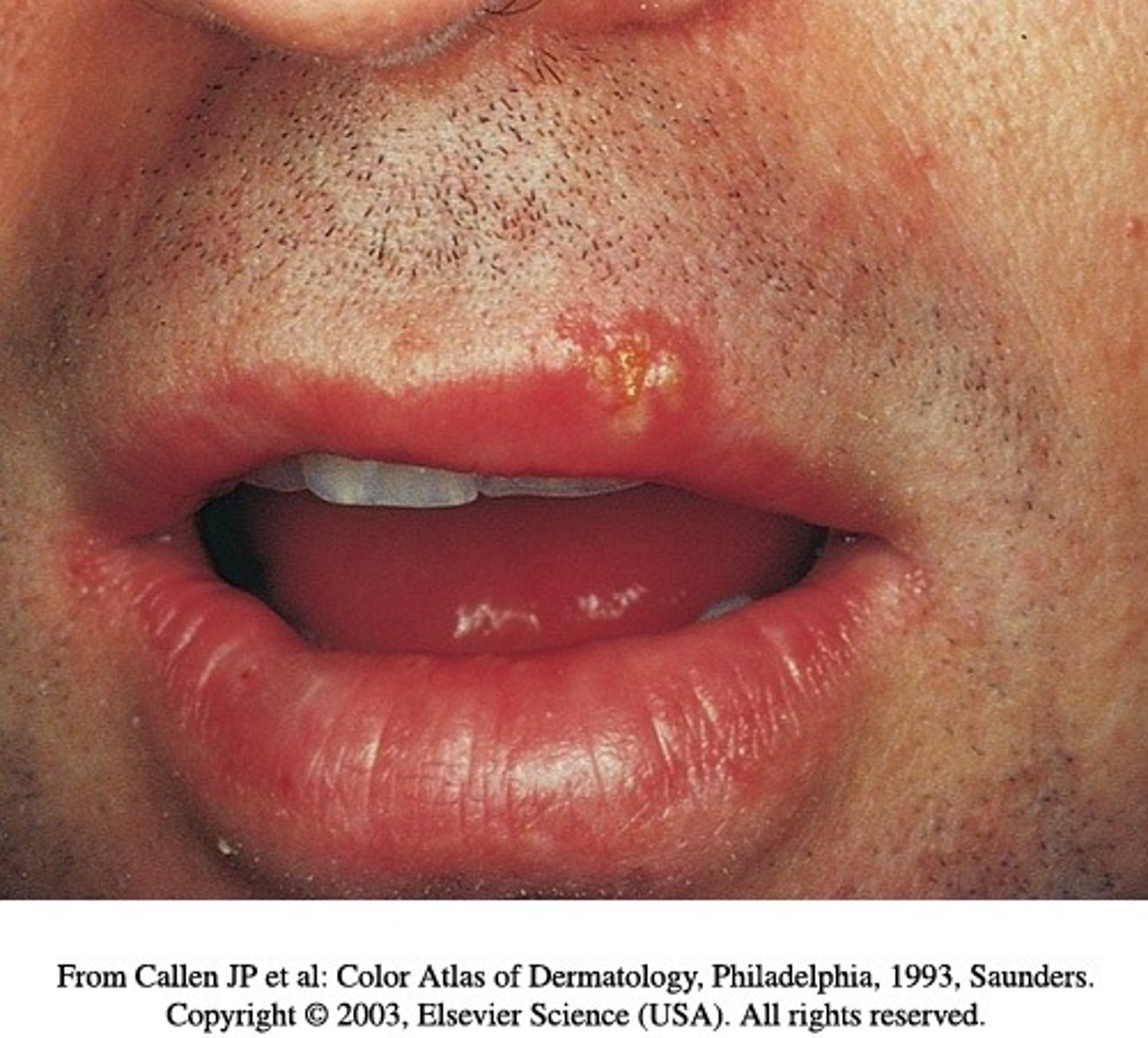
What is herpes simplex 1?
Oral herpes (cold sores)
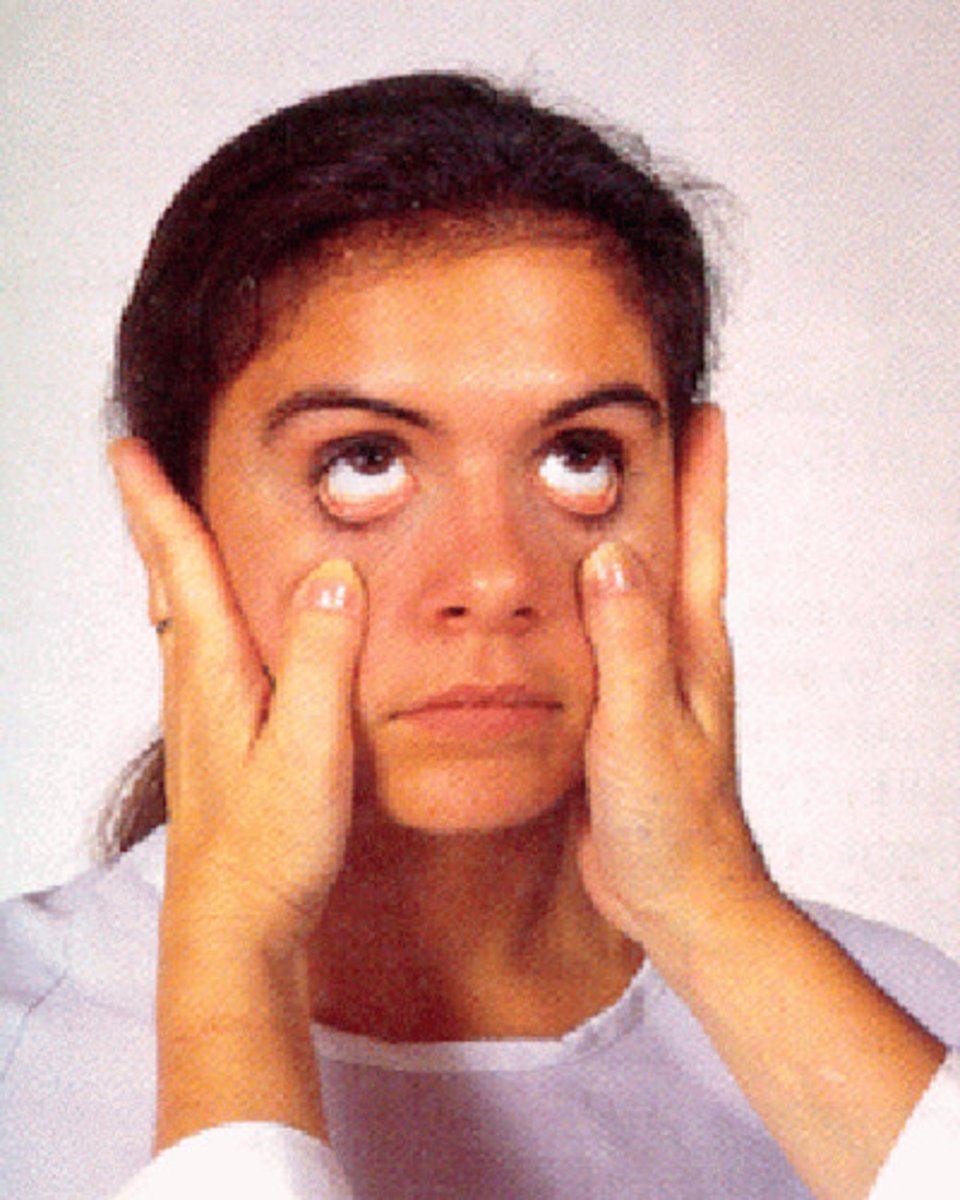
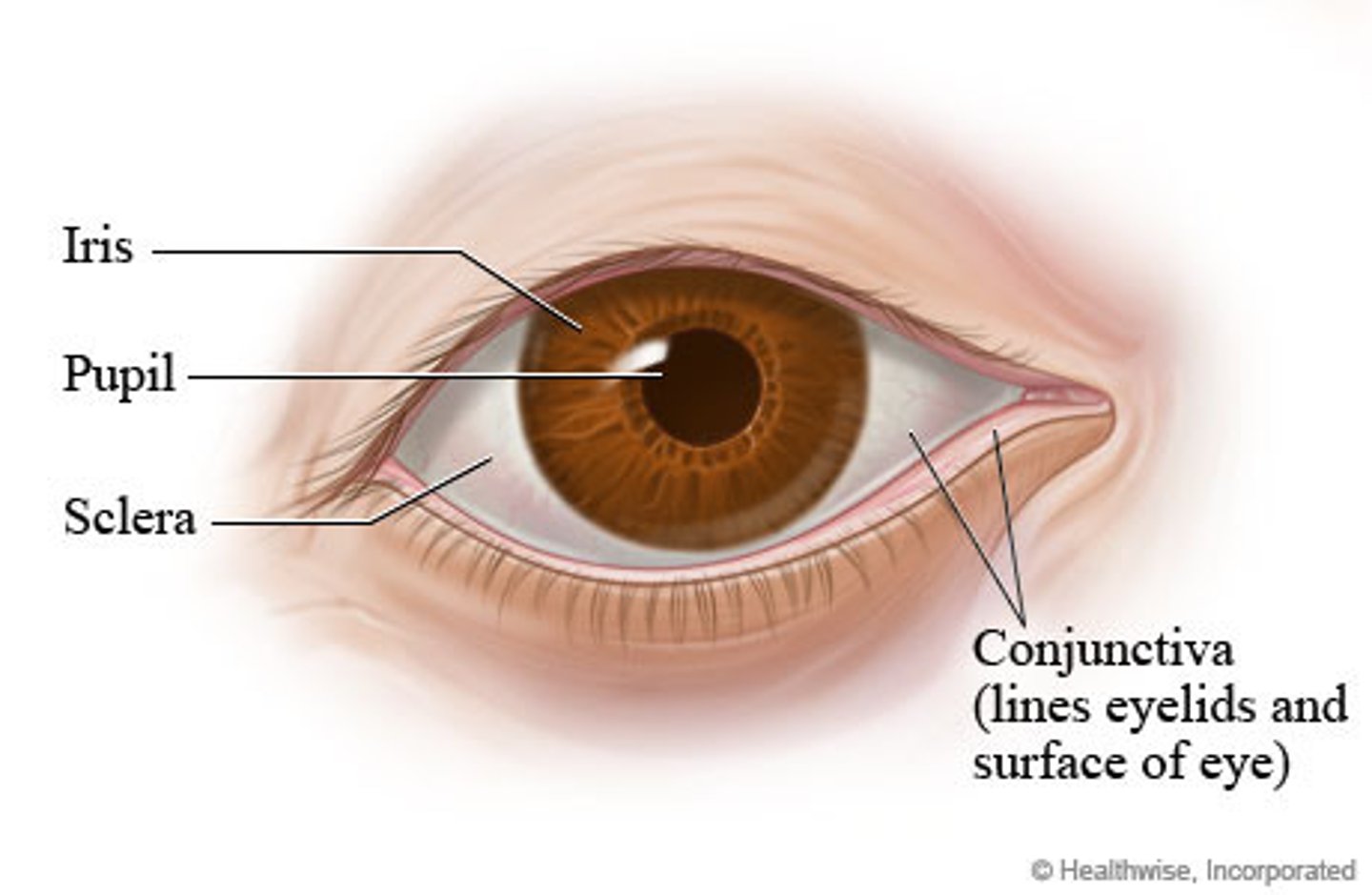
How to inspect the conjunctivae?
-Note the color, moisture, and contour of the conjunctivae.
-The palpebral conjunctivae cover the lids: to assess, have the patient look up as you place a cotton-tipped applicator on the upper lid, gently grasp the upper lid and lashes, and evert the lid over the cotton-tipped applicator.

What is the external auditory meatus?
External ear canal
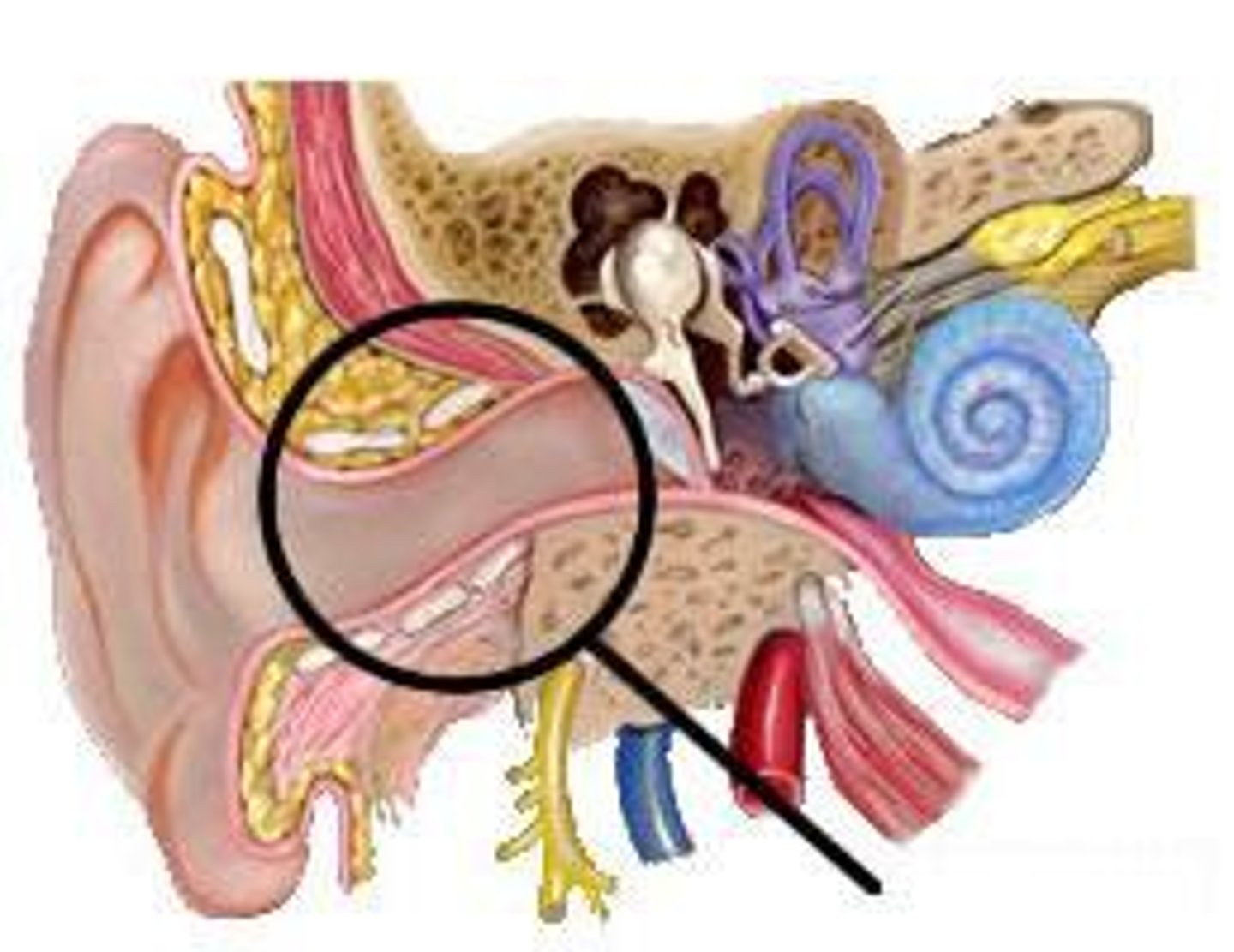
What is cerumen?
Ear wax
What should the tympanic membrane look like?
Translucent, pearly gray color
-When looking with light, the cone of light being on the right side means it is the right ear
Cranial nerve XII?
-12
-Hypoglossal
-Controls the tongue muscles
What is hyperopia?
farsightedness, can't see close up
What is myopia?
nearsightedness, have trouble seeing objects at a distance
Expected findings and abnormal findings when testing distance vision (Snellen chart)?
Expected: 20/20 in each eyes and both eyes together. In mid aged adults the lens of the eye begins to lose some ability to accommodate to near objects
Abnormal: A smaller fraction (20/100) indicated diminished distance vision or myopia. A larger fraction (20/15) indicated diminished near vision, hyperopia.
Expected findings when testing near vision (Jaeger chart)?
Normal result is 14/14 in each eye without hesitancy in reading and without moving card closer or farther away
Expected findings and abnormal findings when testing peripheral vision?
Expected: No deficits in the visual fields
Abnormal: Loss of peripheral vision, follow up with ophthalmologist
Expected findings for 6 cardinal fields of gaze?
The eyes move through all 6 positions
What cranial nerves are used during the 6 cardinal fields of gaze test?
CN III, IV, VI
(3, 4, 6)
Cranial nerve III?
-3
-Oculomotor nerve
-Controls eye movement
-Used when testing 6 cardinal gazes
Cranial nerve IV?
-4
-Trochlear nerve
-Controls eye movement
-Used when testing 6 cardinal gazes
Cranial nerve VI?
-6
-Abducens nerve
-Controls eye movement
-Used when testing 6 cardinal gazes
What is the cover test and what are its expected findings?
-Done when corneal light reflex appears different in each eye
-Detects if eyes are deviated from normal alignment
-Person stares straight ahead at examiners nose while covering one eye with an opaque card. As eye is covered, note the uncovered eye.
Expected: gaze should steady when the eye is covered and uncovered
How to inspect the external structures of eye?
Expected findings?
-Check the color and alignment of the eyes
Expected: eyes clear, bright, and in parallel alignment
How to inspect the eyelids?
Expected findings?
-Note the presence of any lesions, edema, or lid lag
Expected: no lesions present. Lids move freely. Upper eyelid covers half of the upper iris
Expected findings when inspecting the conjunctivae?
The palpebral conjunctivae are smooth, glistening, and peach in color with minimal blood vessels. The bulbar conjunctivae are clear with few blood vessels and white sclera visible.
How to palpate the external ear?
Move pinna and push on tragus
-They should feel firm, and movement should produce no pain
-Palpating mastoid process should also produce no pain
Tragus of ear?