Chemistry 2- Exam 1 (intermolecular forces & colligative properties)
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Part 1
polar bonds- water, carbon dioxide
nonpolar bonds- ozone oxygen
part 2
Carbon dioxide (is the molecule having polar bonds but the molecule is itself a non-polar. Since, carbon dioxide makes a linear shape, therefore, the polarity from the opposites oxygen atoms cancels out and the molecule becomes non-polar
Part 3
Water (is a molecule which contains polar bonds and is a polar molecule itself. the shape of the molecule is bent. therefore, the polarity from oxygen atoms gets add up and give a resultant polar character.
Part 4
Ozone (is the molecule having polar character despite having non-polar bonds. Ozone molecule exists in three resonance forms and delocalization of lone pairs and pi-electrons makes the molecule a polar molecule
Here are visual representations (ball-and-stick and space-filling models) of four molecules: carbon dioxide, oxygen, water, and ozone.
*Which of these molecules contain polar bonds, and which contain nonpolar bonds? Sort the images accordingly.
*Which of these four molecules is nonpolar despite the fact that it contains polar bonds?Choose one:
A. carbon dioxide
B. oxygen
C. water
D. ozone
*Which of these four molecules is polar and contains polar bonds?Choose one:
A. carbon dioxide
B. oxygen
C. water
D. ozone
Which of these four molecules is polar despite the fact that it does not contain any polar bonds?Choose one:
A. carbon dioxide
B. oxygen
C. water
D. ozone

Part one
A. ethanol is polar
C. dimethyl ether has dispersion intermolecular forces
d. ethanol has dispersion intramolecular forces
e. dimethyl ether is polar
f. ethanol has covalent intramolecular attractions
The physical and chemical properties of a molecule depend on its structure. Here are two ball-and-stick models for two compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structures and different chemical properties.
(ethanol & dimethyl ether)
Part one-
Using the models, which of the following is true?Choose one or more:
A.Ethanol is polar.
B.Ethanol is a carboxylic acid.
C.Dimethyl ether has dispersion intermolecular forces.
D.Ethanol has dispersion intermolecular forces.
E.Dimethyl ether is polar.
F.Ethanol has covalent intramolecular bonds.
G.Dimethyl ether has ionic intramolecular attractions.
H.Dimethyl ether forms hydrogen bonds.
part two
1.dispersion forces
2. dipole-dipole interactions
3. hydrogen bonds
4. covalent bonds
Rank the following in order of increasing strength
-dispersion forces
-dipole-dipole interactions
-hydrogen bonds
-covalent bonds
part one
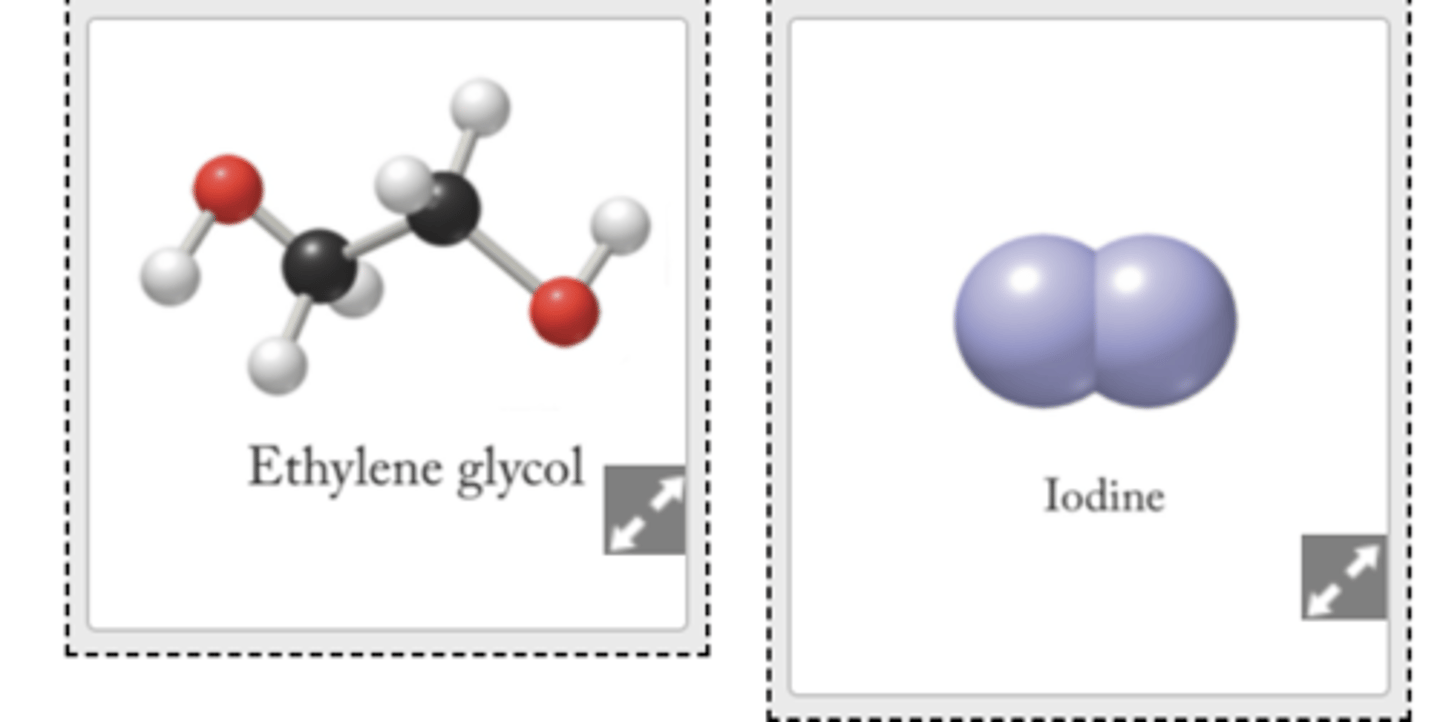
what will dissolve in ethanol- ethylene glycol
what will dissolve in carbon tetrachloride- iodine
Part two
London dispersion forces, hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interaction
Part three
London dispersion forces because iodine is non-polar molecule during dissolution in hexane, it exhibit dispersion forces. No induce polarity in iodine.
Consider ethylene glycol and iodine. Which will dissolve in ethanol? Which will dissolve in carbon tetrachloride? Match the solute with the solvent in which it will dissolve.
Which intermolecular forces are responsible for the dissolution of ethylene glycol? Select all that apply.Choose one or more:
A.ion–dipole interactions
B.London dispersion forces
C.hydrogen bonding
D.dipole–dipole interactions
Which intermolecular forces are responsible for the dissolution of iodine? Select all that apply.Choose one or more:
A.London dispersion forces
B.dipole–dipole interactions
C.hydrogen bonding
D.ion–dipole interactions
Hydrogen bonding- *CH3COOH (ethanoic acid) due to the OH group in the carboxylic acid, there is hydrogen bonding with H atom and -Ke oxygen atom of another CH3COOH
*NH2NH2 (hydrozin) it can form hydrogen bonds because the nitrogen atom has lone pairs
*CH3OH (methanol) intramolecular hydrogen bonding occurs methanol when the hydrogen atom in one atom of methanol have significant +charge
oxygen atom in ethanol atom has significant -charge
No hydrogen-
*CH3OCH (dimethyl ether) due to the atomic of OH group there is no hydrogen bonding
*CH3CH3 (ethane) has no hydrogen bonding because the absence of the CH group or lone pair of electrons.
Which of the following compounds can form hydrogen bonds among their own molecules in pure samples of bulk material?
NH2NH2, CH3COOH, CH3OH, CH3OCH3, CH3CH3
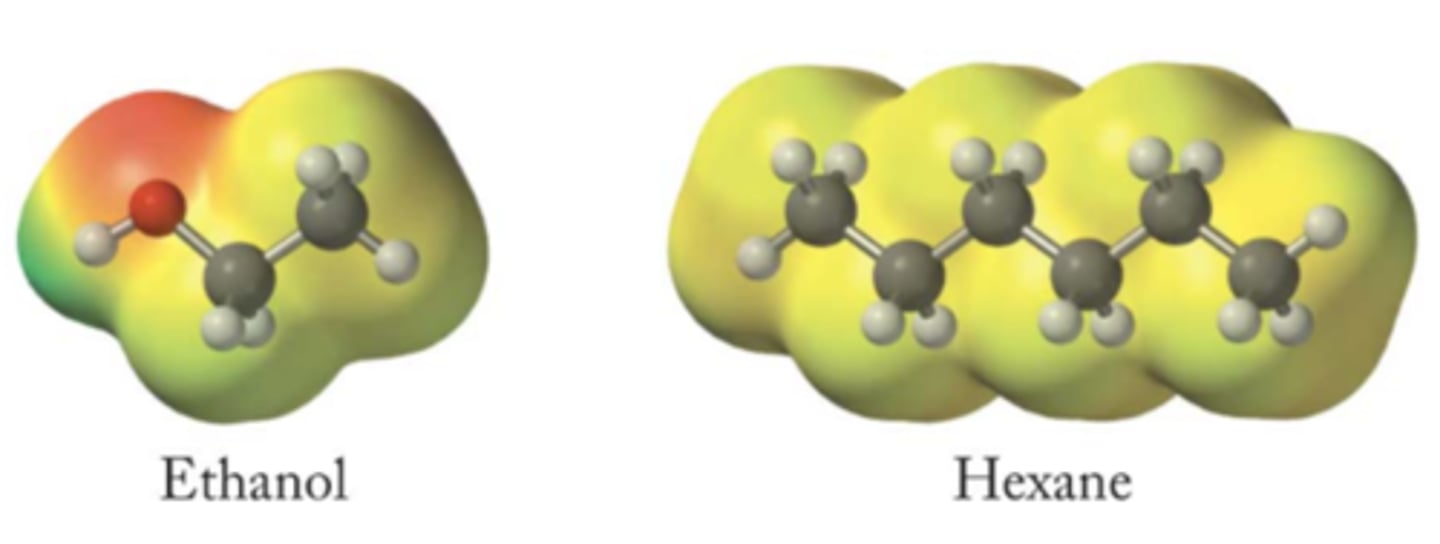
Part one (ethanol & hexane)
London dispersion
part two (Ethanol & ethanol)
London dispersion
dipole-dipole
hydrogen bonding
part three (Hexane & hexane)
london dispersion
Which intermolecular force(s) do the following pairs of molecules experience?
ethanol and hexane
Choose one or more:
A.London dispersion
B.hydrogen bonding
C.ion-induced dipole
D.dipole-dipole
ethanol with another molecule of ethanol
Choose one or more:
A.London dispersion
B.dipole-dipole
C.hydrogen bonding
D.ion-induced dipole
hexane with another molecule of hexane
Choose one or more:
A.London dispersion
B.dipole-dipole
C.hydrogen bonding
D.ion-induced dipole
Ionic Bonding- stronger ionic bond results from smaller ions, greater absolute charges
KI, CaCl2
Dispersion-
CH4, Cl2
dipole-dipole-
PCl3
hydrogen-
NH2OH
Highest to lowest melting point
CaCl2, KI, NH2OH, PCl3, Cl2, CH4
4 kinds of bonding
with
KI
CaCl2
CH4
Cl2
PCL3
NH2OH
Ar, HCl, H2O
Rank H2O, Ar, and HCl in order of increasing strength of intermolecular forces.
H-atom should be attached with high electronegativity atom (F,O,N)
hydrogen bonding