Finals 3 - Marketing
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
FALSE
In order to survive, companies must continuously generate income.
TRUE or FALSE. In order to survive, companies must stop generating income. To be able to do so, they must be able to sell enough quantity of their products or services.
Marketing
This refers to a group of activities designed to facilitate and expedite the selling of goods and services.
Marketing concept
This concept states that the Engineer MUST try to satisfy the needs of his clients by means of a set of coordinated activities.
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE. When clients are satisfied with what the company offers, they continually provide business.
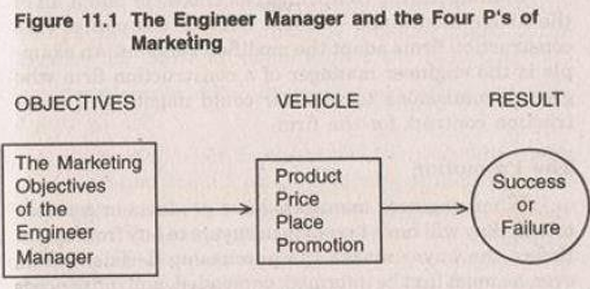
Product
Price
Place
Promotion
Enumerate the Four (4) P’s of Marketing
Product
The term “__________“ includes the tangible or intangible item and its capacity to satisfy a specific need.
FALSE
When a competitor comes into the picture and sells the same type of service, the pressure to improve the quality of services sold will be felt.
TRUE or FALSE. When a competitor comes into the picture and sells a different type of service, the pressure to improve the quality of services sold will be felt.
Extras or Bonuses
These are given to clients when improvements to products are not possible.
Price
This refers to the money or other considerations exchanged for the purchase or use of the product idea or service
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE.
When products are similar in quality and other characteristics, price will be a strong factor on whether or not a sale will be made.
FALSE
When products are similar in quality and other characteristics, price will be a strong factor on whether or not a sale will be made. This does not hold true however, in the selling of services and ideas.
TRUE or FALSE.
When products are similar in quality and other characteristics, price will be a strong factor on whether or not a sale will be made. This is also true in selling of services and ideas.
Place
“If every factor is equal, customers would prefer to buy from firms easily accessible to them. If time is of the essence, the nearest firm will be patronized.“ This refers to what P in marketing?
Hiring sales agents to cover specific areas
Selling to dealers in particular areas
Establishing branches where customers are located
Establishing franchises in selected areas
Enumerate the means to eliminate or minimize the problem of location (4)
Promotion
Before the buyer makes the purchasing decision, the buyer must first be informed, persuaded, and influenced. This activity is called __________.
Promotion
This is defined as communicating information between seller and potential buyer to influence attitudes and behaviour.
McCarthy and Perreault
_________ and _________ define promotion as communicating information between seller and potential buyer to influence attitudes and behaviour. (2 names of people)
Advertising
Publicity
Personal selling
Sales promotion
Enumerate some examples of Promotional Tools (4)
Advertising
Identify what Promotional Tool is being described:
A paid message that appears in the mass media for the purpose of informing or persuading people about particular products, services, beliefs, or action.
Publicity
Identify what Promotional Tool is being described:
The promotional tool that publishes news or information about a product, service, or idea on behalf of a sponsor, but is not paid for by the sponsor.
Personal selling
Identify what Promotional Tool is being described:
Refers to the oral presentation in a conversation with one or more prospective purchasers for the purpose of making a sale.
Sales promotion
Identify what Promotional Tool is being described:
Any paid attempt to communicate with the customers other than advertising, publicity, and personal selling. This includes displays, contests, coupons, demonstrations, referral gifts, etc.
Displays
Contests
Coupons
Demonstrations
Referral gifts
Give some examples of Sales Promotion (5)
Selecting a target market
Developing a marketing mix
Enumerate the Steps in Strategic Marketing (2 and in order)
Selecting Target Market
Identify what Step in Strategic Marketing is being described:
A market consists of individuals or organizations, or both with the desire and ability to buy a specific product or service.
Divide the total market into groups of people who have relatively similar product or service needs.
Determine the profit potentials of each segment.
Make a decision on which segment or segments will be served by the company
Enumerate the three (3) necessary steps in selecting a target market
The size of the market
The number of competitors serving the market
Enumerate the Factors used in Selecting a Target Market (2)
Familiarize
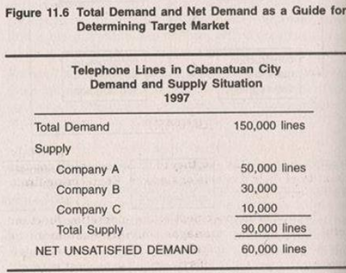
Figure 11.6 Total Demand and Net Demand as a Guide for Determining Target Market
Developing a Marketing Mix
Identify what Step in Strategic Marketing is being described:
After the target market has been identified, a marketing mix must be created and maintained.
Product
Price
Place
Promotion
Enumerate the Four (4) Variables of Marketing Mix
FALSE
Depending on the marketing environment, the Engineer Manager can manipulate any or all variables to achieve the company’s goals.
TRUE or FALSE.
Depending on the marketing environment, the Engineer Manager cannot manipulate any or all variables to achieve the company’s goals.
familiarize
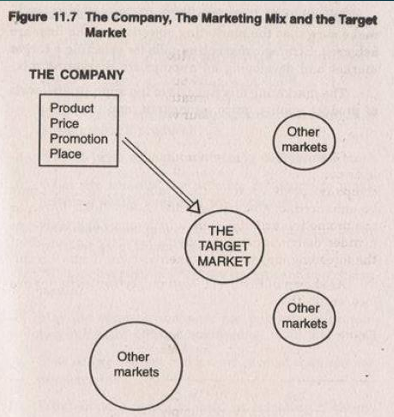
Figure 11.7 The Company, The Marketing Mix and the Target Market