Kinetics and equilibria
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
3 parts of the collision theory
For particles to react they must collide
When particles react, chemical bonds must be broken in the reactants( This happens when particles collide with enough energy)
Particles must collide in the correct orientation
What is the rate of reaction proportional to?
The number of effective collisions per second.
What happens when you increase the concentration of reactants?
At a higher concentration, there will be more reactant particles in the same volume.
Because reactant particles are closer together, likelihood of collisions increase
Thus increasing the rate of reaction
What happens when you increase gas pressure?
Increasing the pressure makes the particles closer together
Increasing the frequency of collisions
Resulting in an increased rate of reaction
How can you measure the rate of reaction?
Measuring how quickly reactants are used up
Measuring how quickly products are formed
How can you measure the rate of reaction on a graph?
Drawing a tangent and working out the gradient
Change in Y/ Change in X
Define activation energy (Ea)
The minimum amount of energy required by particles, in order to start a chemical reaction.
What is the transition state?
The process where existing bonds are breaking and new bonds are forming products are formed as result of this stage.
(The definition of Ea can also be the enthalpy difference between the reactants and the transition state)

How do catalyst increase the rate of reaction?
Provide an alternative pathway for the reaction to take place with a lower activation energy
Reaction profile when catalyst is used.
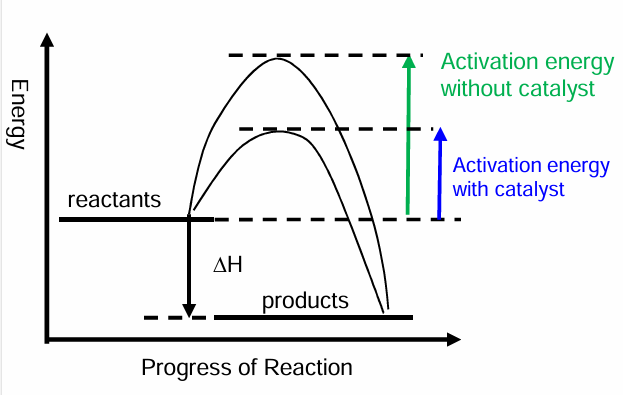
Important idea to remember about catalysts
They are not used up in the reaction
And are not permanently changed so they can be re-used
Advantages of using catalysts
Speed up reactions even at low temperatures.
Reduces amount of energy required
Reducing the amount of fossil fuels burnt to provide this energy
Saving money
Less CO2 emissions
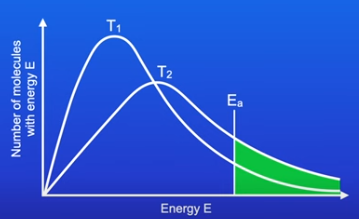
The Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution curve
Shows the spread of energies that molecules of a gas, liquid or solution have at a particular temperature.
As you go up the Y-axis the number of molecules is higher
As you go across the X-axis the energy (molecules posses) increases
Very few molecules have high energy.
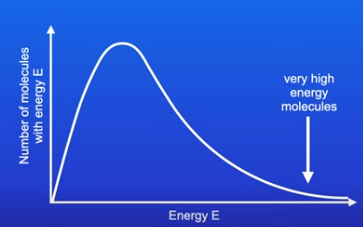
Key points about the curve
The curve starts at 0 because no molecule has no energy
The curve does not touch the x-axis because there is no maximum energy that a molecule can have
Area under the curve is the total number of molecules in the system( reaction)
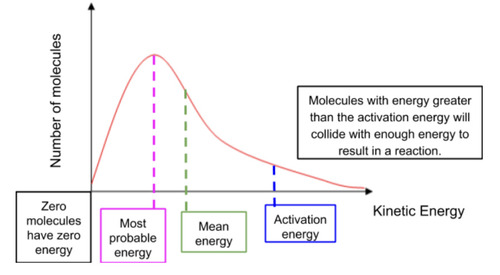
Parts of the curve
Most probable energy is the energy most molecules have
The section right of the activation energy shows the amount to molecules that have energy higher than the Ea. Only the molecules in that section are able to collide
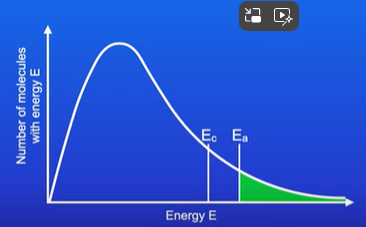
What happens to the curve when a catalyst is used in the reaction?
Activation energy is lowered
So more molecules are able to collide
What happens to the curve when the temperature is increased?
When you increase the temperature the curve shifts right
At higher temperatures, there are molecules with high energies
The most probable energy (Emp) increases. But the number of particles with the most probable energy falls
Area under the curve will not change
The number of molecules with the activation energy has increased
define rate of reaction and its units
Change in concentration of a substance in unit time
mol dm-3 s-1
what happens to the curve when the concentration is increased?
Shape of the curve will stay the same
But the curve will be higher and the area under the curve will be greater
Because when you increase the concentration, there will be more particles per unit volume.
Causing a greater frequency of collisions

Define a reversible reaction
Products can react to from reactants
What is a closed system?
No atoms can enter or leave the system
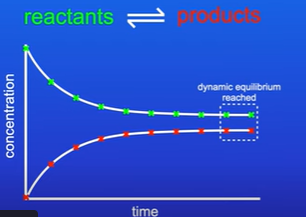
When does a reaction reach dynamic equilibrium?
The forward and backward reactions are taking place simultaneously
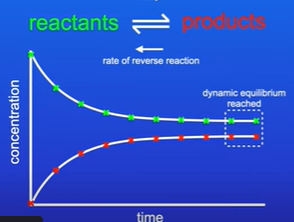
What are two features of dynamic equilibrium?
Forward and reverse reactions are occurring at equal rates
The concentration of the reactants and products stay the same (does not mean that the concentration of the products and reactants are the same)
Equilibrium can be approached from either side

What does dynamic equilibrium tell you?
The position of equilibrium
In this example the position of equilibrium lies to the left as there is a greater concentration of reactants
Le Chateliers Principle
When an external change is applied to a system at equilibrium, the equilibrium moves in the direction that reduces the effect of that change.
What happens to equilibrium when concentration is increased?
The equilibrium will shift in the direction which will reduce the effect of this change
So if the concentration of the reactants is increased
Equilibrium will shift to the right
The yield of the product will increase
What happens to equilibrium when pressure is increased ?
Equilibrium will shift to the direction with fewer moles
What happens to equilibrium when pressure is reduced?
Equilibrium will shift to the direction with the higher moles
In order to counteract the change and increase the pressure
When is the equilibrium position not effected by a change in pressure?
When the moles of the reactants and products are the same
What does it mean when the enthalpy change for a reaction is negative?
The forward reaction is exothermic
What happens to equilibrium when temperature is increased or decreased?
Equilibrium will shift to oppose the change
If temperature is increased it will shift towards endo
If temperature is decreased it will shift towards exo
Effect of catalyst on equilibrium position
No effect
Used to speed up the reaction only (reaction will just reach equilibrium faster)
It will increase the rate of the forward and reverse reaction by the same amount
Equation for the equilibrium constant (Kc)
Concentration of products/ Concentration of reactants
Square brackets indicate concentration (moldm-3) is being used
The power that the concentration is raised to is the moles of that substance

Define homogenous equilibrium
When reactants and products are all the same state of matter
What does the equilibrium constant tell you?
Kc < 1 = Equilibrium lies towards the reactants ( The concentration of reactants is greater at equilibrium)
Kc = 1 Equilibrium lies midway between reactants and products ( The concentration of reactants and products are equal at equilibrium)
Kc > 1 = Equilibrium lies towards the products. ( The concertation of products is greater at equilibrium)
What are the units of Kc?
Changes depending on the equation
Sometimes there are no units
What are equilibrium moles ?
Number of moles of reactants and products present in a reaction when equilibrium is achieved
How do you calculate moles at equilibrium?
Moles of reactant at equilibrium = Initial moles- moles reacted
Moles of products at equilibrium = Initial moles + moles formed