Blood & Lymphatic System Infections
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Know the importance of the cardiovascular system, blood, and the main constituents of blood (RBC’s, WBC,s & platelets)
Cardiovascular systems supply nutrients and oxygen to cells and remove waste. Infections can go systemic- carries throughout the body (septicemia)
RBCs: carry oxy and waste, WBCs immune system cells, platelets clogging
Know what systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) is and what causes it
Dangerous whole-body inflammation triggered by vasodilation which causes the septic shock because the blood pressure decreases.
Know what lymphangitis and lymphadenitis are and how they present
Lymphadenitis: inflammation of lymph nodes
Lymphangitis: inflammation in the lymphatic vessels
Know the difference between sepsis/septicemia and septic shock (also toxemia and toxic shock)
sepsis/septicemia: contaminated blood (infection)
Septic shock: the rapid systemic, dramatic drop in blood pressure
Toxic shock: rapid systemic drop in blood pressure + toxin in bloodstream
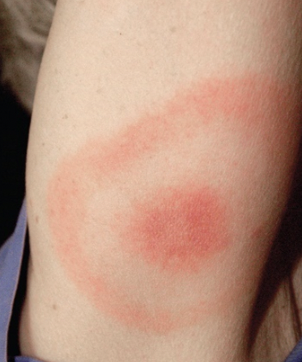
Lyme Disease
S/S: 1. Early Localized Infection: erythema migrans = bulls eye rash + inflammation. 2. Early Disseminated Infection: after rash- spread to the nervous system (memic meningitis) 3. Late Persistent Infection: Chronic Nervous System impairments
CA: Borrelia burgdorferi
Pathogenesis: indirect damage cause rash (inflammation) + endotoxin exacerbates the inflammation
Epidemiology: zoonosis , spread by ticks
Treatment: antibiotics in early stages to kill bacteria, once it goes to the nervous system it's much harder to treat. Once chronic the damage is done
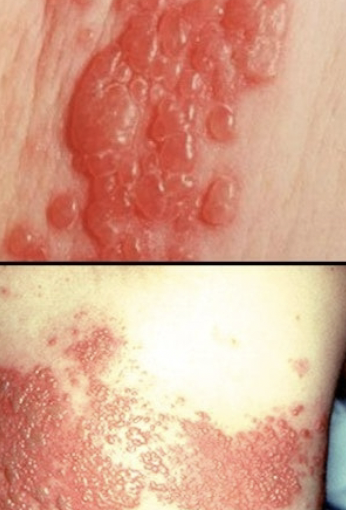
Ebola and Marburg
S/S: fever, headache, muscle pain, sore throat, abdominal pain, diarrhea, macular rash/maculopapular rash case fatality rate 25%-905 depending on strain and supportive care, septic shock
CA: Ebola Virus or Marburg Virus
Pathogenesis: virus targets immune system cells release cytokines to kill infections and destroy the immune system. The “rogue” immune cells attack Helper T cells which can't make memory cells.
Epidemiology: both seen in outbreaks in Africa. Ebola is spread through human tissue exposure . Marburg is spread through exposure to bat