Gas & Equilibrium
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Pressure
Force per unit area. (P)
- atmospheres (atm)
- 1 atm = pressure at sea level
physics: atm = 101.3 Kila Pascals KPa = 760mm Hg
Temperature
measure in Kelvin with gasses (T)
Celsius + 273 = K
Volume
How much space an object takes up (V)
- mL or L
Amount of gas
amount of gas (n) - moles
how many particles
1 mol = molar mass
Ideal Gas Law / constant
PV=nRT
PV/nT = R = 0.0821
units: atm(P) x L(V) / mol(n) x K(T)
Ideal Gas
an imaginary gas whose particles are infinitely small and do not interact with each other (no IMF’s)
La Chatelier's Principle
Equilibrium will adjust its ratio to counter stresses and maintain equilibrium, shifting left or right minimizing effect
Temp impact on equilibrium
Heat is the same as a chemical = shift right or left, changes K and Q catches up
exothermic reactions
heat is a product, being released, delta H (system looses energy)
endothermic reactions
heat is a reactant, being used, delta H (system gains energy)
Pressure impact on equilibrium
- dec vol, inc pressure, get rid of gas
- inc vol, dec pressure, more gas
only if changing vol
Catalyst
no effect on equilibrium- just speeds up reaction by lowering activation energy needed to reach activated complex
study of chemical Kinetics
how long a reaction takes
collision theory
states that atoms, ions, and molecules must collide in order to react
- if collision is not w/ enough energy or right orientation, the reaction wont happen
Reaction rate
how likely atoms are to react
- to inc use collision theory: inc reactans, inc temp, inc surface area (break pieces up)
energy diagram
Visual representation of energy changes in a reaction
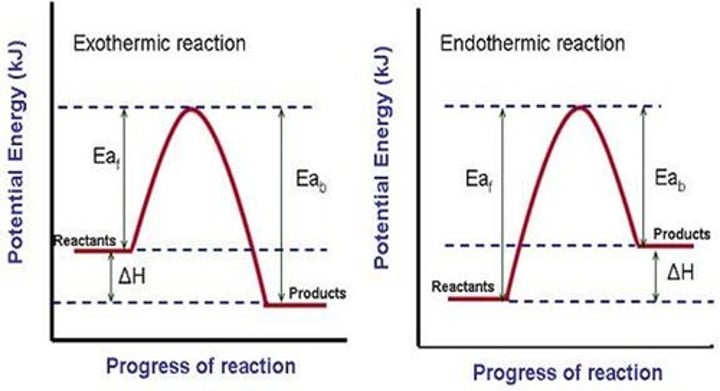
activation energy
Energy needed to get a reaction started -> activated complex (vertex)
STP
standard temperature and pressure: 1 atm, 0C, 273K
enthaply
change in energy (delta H)
units for measuring rate of reaction
molarity per unit of time
brackets around a chemical mean….
the molarity of that chemical
Reaction quotient
Q - changes when concentrations r changed
K - changes when temp is changed
Equilibrium
A state at which the reactions products and reactants are constant
Equilibrium constant
the ratio of products to reactants at equilibrium