Biology - Chap. 7 Vocab & Study Guide
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Good luck!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Prokaryotic Cell
A type of cell that lacks a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic cells are typically smaller and simpler than eukaryotic cells, and they include bacteria and archaea.
Eukaryotic Cell
A type of cell that contains a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, found in organisms such as plants, animals, and fungi.
Vacuoles
Membrane-bound organelles that store substances such as nutrients, waste products, or other materials in a cell.
Mitochondria
Organelles known as the powerhouse of the cell, responsible for producing energy (ATP) through cellular respiration.
Nucleus
The control center of a eukaryotic cell, containing the cell's genetic material (DNA) and coordinating activities such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
Nucleolus
A structure within the nucleus that is responsible for producing ribosomes and synthesizing ribosomal RNA (rRNA).
Ribosomes
Cellular structures that produce proteins.
Golgi Apparatus
A cellular organelle involved in modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to other organelles.
Cytoplasm
The gel-like substance within the cell membrane that contains organelles and is the site for many metabolic reactions.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
A type of endoplasmic reticulum with ribosomes on its surface, involved in the synthesis and processing of proteins.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
A type of endoplasmic reticulum that lacks ribosomes, involved in lipid synthesis, detoxification, and calcium ion storage.
Lysosomes
Membrane-bound organelles that contain enzymes for digestion and waste removal within the cell.
Chloroplasts
Organelles found in plant cells that conduct photosynthesis, converting sunlight into chemical energy.
Cell Wall
A rigid outer layer found in plant cells, fungi, and some bacteria that provides structural support and protection.
Cell Membrane
A semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the cell, regulating the movement of substances in and out.
Hypertonic Solution
A solution with a higher concentration of solutes compared to another solution, causing water to move out of a cell.
Hypotonic Solution
A solution with a lower concentration of solutes compared to another solution, causing cells to swell as water enters.
Isotonic Solution
A solution with equal concentrations of solutes compared to another solution, resulting in no net movement of water into or out of the cell.
Concentration Gradient
The difference in concentration of a substance across a space, influencing the direction of diffusion.
Phospholipid Bilayer
A double layer of phospholipids that makes up the cell membrane, providing a barrier between the inside of the cell and its external environment.
Active transport
The process by which cells move substances across the cell membrane against their concentration gradient, requiring energy (usually in the form of ATP) to transport molecules from areas of lower concentration to areas of higher concentration.
Passive Transportation
The movement of substances across a cell membrane without the need for energy input, relying on concentration gradients.
Protein Channels
Membrane proteins that form pores or channels in the cell membrane, allowing specific molecules or ions to pass through the membrane in a regulated manner.
Nonpolar molecules
Molecules that do not have distinct positive and negative poles; they share electrons evenly, leading to a balanced distribution of electric charge, which makes them hydrophobic (water-repelling) and unable to dissolve in water.
Organelle Names
Mitochondria
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Ribosomes
Golgi Apparatus
Cytoplasm
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Lysosomes
Chloroplasts
Cell Wall
Cell
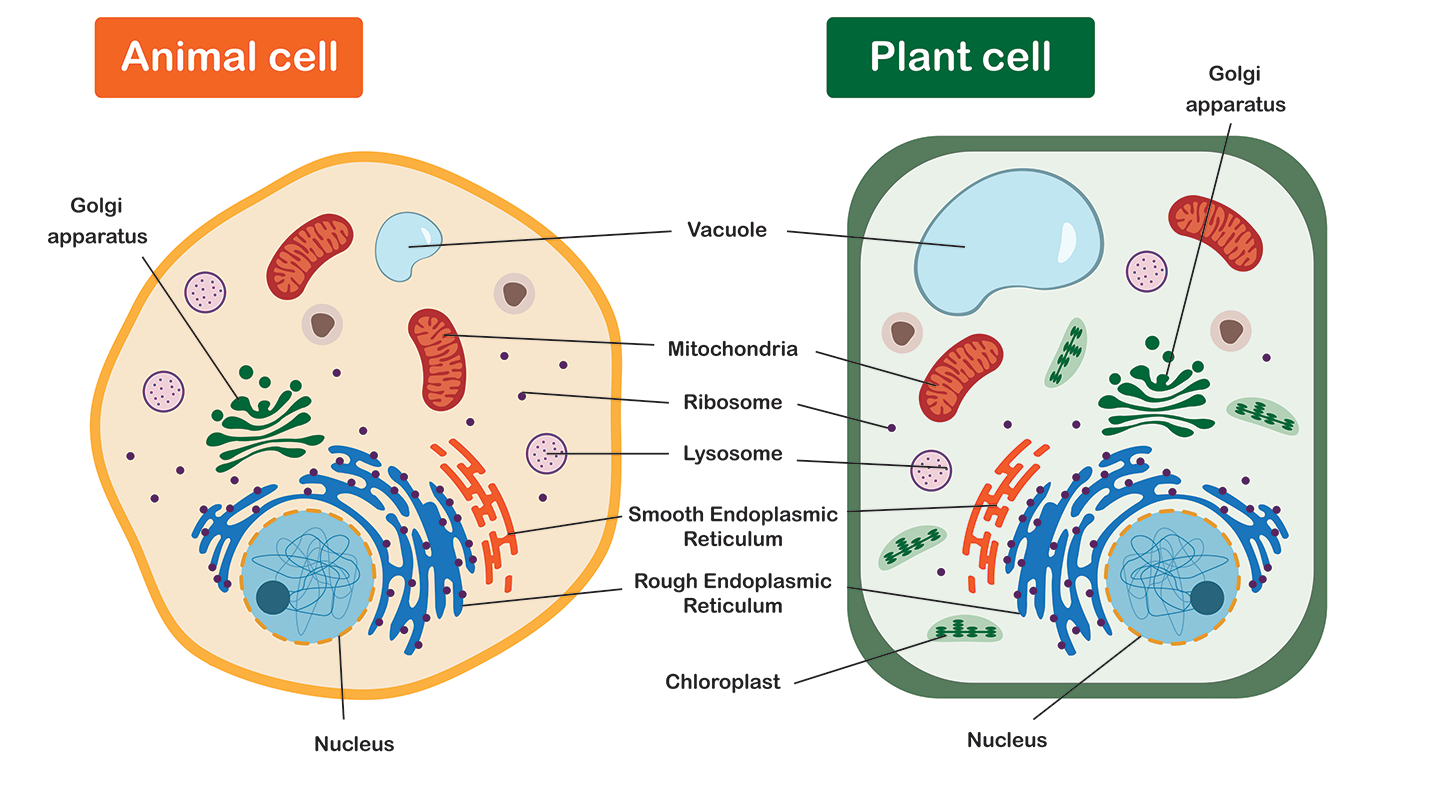
What organelles are ONLY found in plant cells?
The organelles that are ONLY found in plant cells include chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis, and the cell wall, which provides structural support and protection. Additionally, large central vacuoles are often present in plant cells to store nutrients and waste products.
Describe how the phospholipid bilayer works to separate the cell’s contents from the surrounding environment.
A double layer of phospholipids that makes up the cell membrane, providing a barrier between the inside of the cell and its external environment. Each phospholipid molecule has a hydrophilic (water-attracting) 'head' and two hydrophobic (water-repelling) 'tails', resulting in the formation of a bilayer that separates the cell's contents from the surroundings.
The phospholipid bilayer acts as a barrier to separate the cell's internal environment from the external environment. The hydrophobic tails face inward, away from water, while the hydrophilic heads face outward, toward the water inside and outside the cell, creating a semi-permeable membrane that regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Types of Active Transport and Definitions.
Bulk Transport (Vesicular Transport)
Definition: The movement of large quantities of materials into or out of a cell via vesicles, which includes exocytosis (exporting materials out of the cell) and endocytosis (importing materials into the cell).
Explain the relationship between cells, tissues, organs and organ systems in multicellular organisms.
In multicellular organisms, cells combine to form tissues, tissues combine to form organs, and organs work together within organ systems, creating a hierarchical organization that allows for complex life functions.