Surgical Skills - Study Tips 2
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
What are the three distinct areas for surgery?
prep area, scrub area, and surgery room
What types of procedures are done in the prep area?
clip, rough prep, and dirty procedures; also clean procedures that are not considered completely sterile
What is done in the scrub area?
PPE and scrubbing
What procedures are done in the surgery room?
aseptic procedures only
What are the steps for cleaning the surgery room?
-all horizontal surfaces should be wiped with a damp cloth every morning to reduce airborne contaminants
-wet vacuum floor at the end of every day
-scrub using mechanical friction on each surface and pay attention to contact time
-non movable equipment should be wiped daily
-movable items should be cleaned before they are put back in the room if removed
What is the order of the procedures for cleaning instruments?
presoaking, decontaminating, and ultrasonic cleaning
Describe presoaking.
remove most blood, body fluids, and tissue; rinse instruments with cold distilled or deionized water immediately after use
Describe decontaminating.
instruments should be scrubbed with neutral pH detergent, stain remover on surfaces and tools if needed; rinse with distilled water and dry; inspect and check function of tools (wear PPE especially if tools are highly contaiminated)
Describe ultrasonic cleaning.
high frequency sound cleaning: uses enzymatic cleaner; all instruments must be fully submerged with box locks open; rinse with distilled water to remove mineral deposits and allow to air dry before autoclaving
What are some characteristics of chlorine based disinfectants?
-corrosive
-deteriorates materials
-irritating
-fecal matter deactivates
-temp and pH can alter efficacy
-wide germicidal activity
-relatively non toxic
-effective at low concentrations
example: clorox
What are some characteristics of phenol based disinfectants?
-work in the presence of organic matter
-wide germicidal activity
-relatively non corrosive
-limited toxicity
-not must residual activity
-irritating to skin
not used in vet med
examples: lysol, pine-sol
What are some characteristics of quaternary amine based disinfectants?
-wide germicidal activity
-low toxicity
-noncorrosive
-good on clean surfaces
-bind to and inactivated by organic matter so area must be cleaned before
-react with soap so soap must be rinsed well
-stains
-poor residual activity
What are some characteristics of iodine disinfectants?
-wide germicidal activity
-better as sporicidal than chlorine
-relatively non toxic
-not usually used as a disinfectant
- corrosive
-inactivated by organic matter
-stains
-used as an antiseptic
What are some characteristics of Chlorahexidine?
-effective in the presence of organic matter
-nonirritating to tissue
-wide germicidal but not as effective against some bacteria and viruses as other disinfectants
-nontoxic
-effective at low concentrations
-must have contact time
What are some characteristics of alcohol disinfectants?
-wide germicidal activity
-noncorrosive
-requires time
-irritates tissue
-expensive
-doesn't penetrate organic material
-denatures protein which may promote bacterial growth in wounds
What are some methods of sterilization?
autoclaves (gravity air displacement or high vacuum system), flash sterilization, gas, plasma, cold or chemical sterilization
How do we know if an item is sterile?
-chemical (strips or tape)
-biological (culture test)
For what length of time is a pack considered sterile?
it is considered sterile until something happens making it not sterile (ex: dropping on floor, getting the pack wet, etc.); if you aren't sure, assume it's contaminated
How do you properly prepare a pack for sterilization?
-prepare the pack in a place that is frequently cleaned and has little foot traffic
-don't overload the autoclave and on't let the wrap touch the inner surface of the autoclave
Where are the sterile boundaries on packs?
-sterile boundary stops at the outer wrap of pack and below the tables
-you cannot touch the outside of packs or drop your hands below the tables if you are sterile
-the corner/edges are not considered sterile after opened and they drop below the table, so don't touch the outer edges if you are sterile
How do any personnel move around the surgery room?
must do so in a manner that maintains the sterile environment, so movement and air currents around the sterile area need to be kept to a minimum to prevent contamination.
How do scrubbed personnel move around the surgery room?
-scrubbed persons stay as close to the field as possible & always face the field
-scrubbed persons pass face to face or back to back
-scrubbed persons keep arms and hands within the parameters of the sterile field at all times
-scrubbed persons should move only in areas of similar preparation and avoid traffic pathways
-scrubbed persons should not leave the room
How do unscrubbed personnel move around the surgery room?
-unscrubbed persons should always face a sterile field
-unscrubbed persons should stay 12”-18” from the sterile field
-unscrubbed persons should not walk between two sterile fields
-unscrubbed persons touch only the outside of the wrapper when opening sterile supplies
What is included in a pre-op workup?
-signalment
-history
-consent form
-weight
-physial exam: (BCS, head, neck, skin, lungs, heart)
What is included in pre-op prep?
getting any diagnostics performed and ensuring the surgeon has all the information needed for the surgery
What testing can be done for pre-op diagnostics?
-blood work/other lab work
-radiographs
-ultrasound
-advance imaging
What bloodwork should be done pre-op at a minimum?
-packed cell volume (PCV)
-total solids/protein (TS/TP)
-blood glucose (BG)
-blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
-alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
What are the components of the pain pathway?
-transduction
-transmission
-modulation
-perception
What are the best ways to manage pain?
preemptively & multimodal analgesia
What is the first phase of the pain pathway that is triggered when tissue is traumatized and converted to a signal that can be sent to the CNS for processing?
Transduction
What medications can inhibit transduction (peripheral sensitization of nociceptors)?
-local anesthetics
-opioids
-NSAIDs
-corticosteroids
What is the second phase of the pain pathway where propagation of the impulses up toward the spinal cord?
Transmission
What medications can inhibit transmission (impulse conduction)?
-local anesthetics
-α-agonists
What is the sorting process (third phase) where pain signals are said to be “modulated” in the spinal cord?
Modulation
What medications can inhibit modulation?
-local anesthetics
-opioids
-α-agonists
-tricyclic antidepressants
-cholinesterase inhibitors
-NMDA antagonists
-NSAIDs
-anticonvulsants
What is the fourth phase of the pain pathway that occurs in a conscious patient, where they know that pain is present and will usually react?
Perception
What medications can inhibit perception?
-anesthetics
-opioids
-α-agonists
-benzodiazepines
-phenothiazepines
What type of analgesic is the mainstay of acute pain management, binds to specific opioid receptors in the CNS and PNS, and can reduce anxiety and nonpainful distress?
Opioids
Which analgesic is quite efficacious for treating inflammation and pain associated with surgery, and has treated fever, inflammation, and pain for decades?
NSAIDs
What analgesic is a short-duration sedative-analgesic muscle relaxant that can be rapidly be reversed and is a nonnarcotic and nonscheduled agent?
α-agonists
Which analgesic is inexpensive to use and quite effective in blocking the transmission of nociceptive signals at the source, produces true analgesia, is non-scheduled, and is easy to administer?
Local anesthetic
What are the characteristics of a clean wound?
-surgically created wound
-no hollow viscus opened (resp., GI, UG)
-aseptic technique maintained
-no infection encountered
What are the characteristics of a clean-contaminated wound?
-surgical wounds that enter hollow viscus
-minor break in technique occurs
What are the characteristics of a contaminated wound?
-operative wounds with:
•major break in technique
•hollow viscus is opened with gross spillage
-traumatic wounds
What are the characteristics of a dirty or infected wound?
-contain purulent material
-contain contents of perforated hollow viscus
- >100,000 organisms per gram of tissue
What are the characteristics of primary wound closure?
-immediate closure of wound
-clean wounds
-clean-contaminated wounds
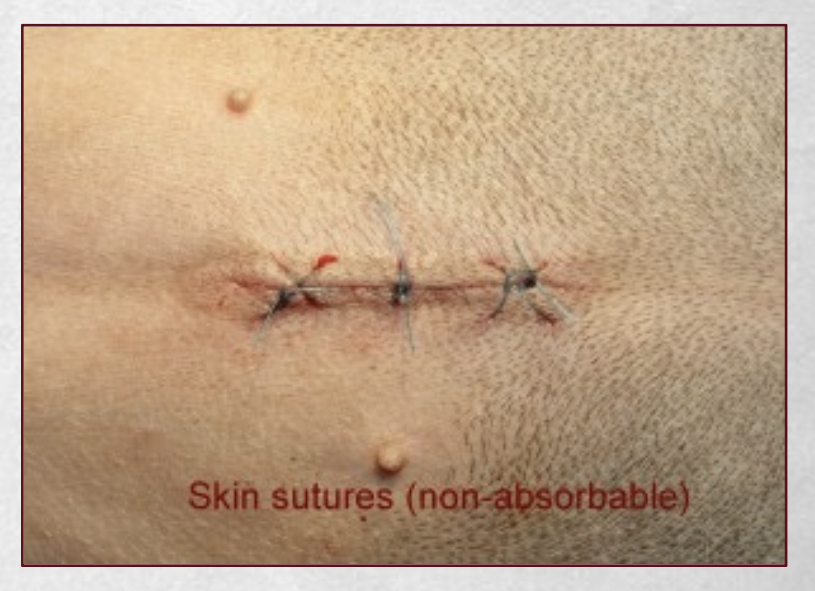
What are the characteristics of delayed primary wound closure?
-wound left open for 2-5 days
-closed prior to granulation tissue formation
-permits repeated lavage and debridement to convert wound to clean-contaminated status appropriate for closure
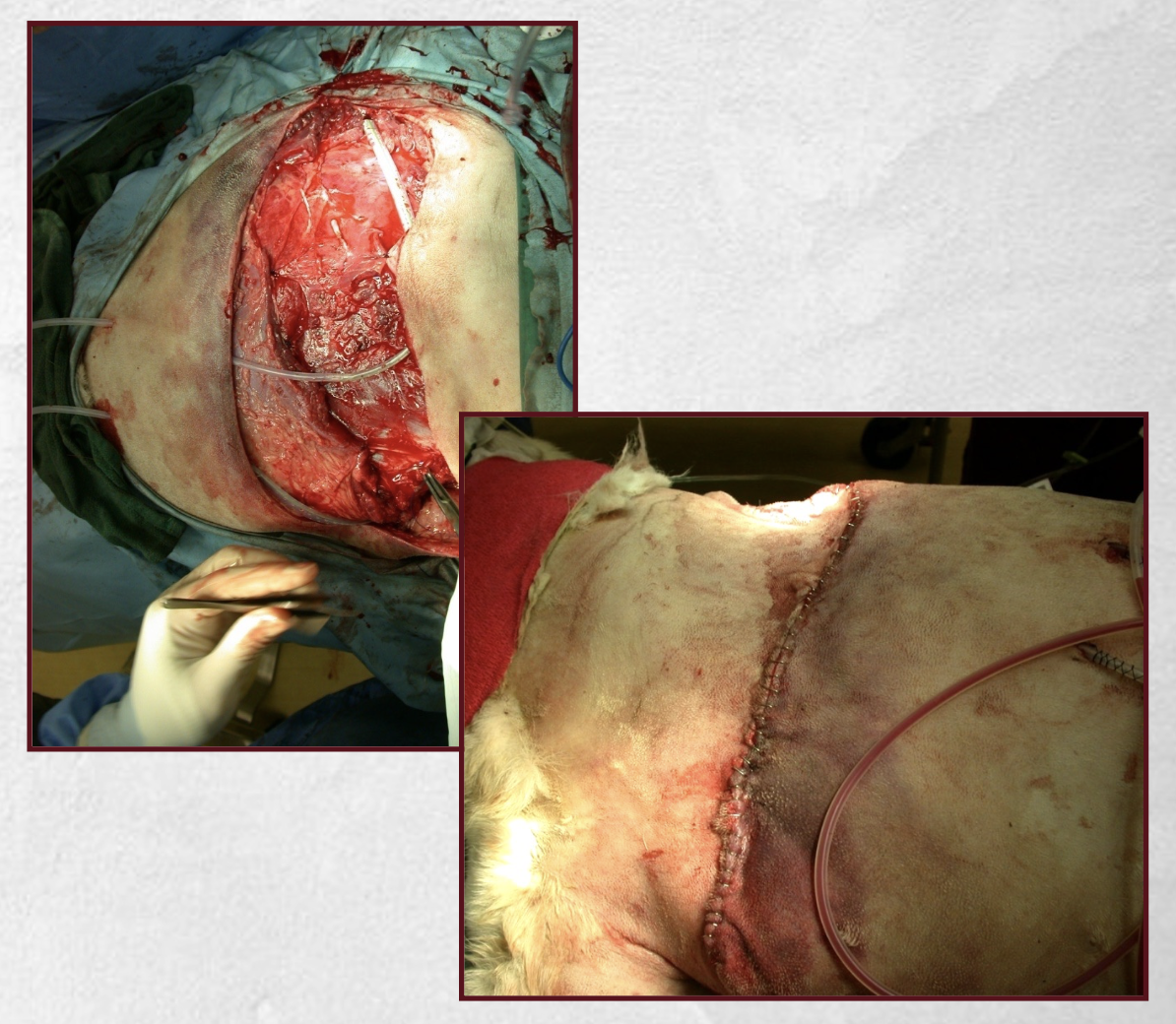
What are the characteristics of secondary wound closure?
-granulation tissue allowed to form in wound prior to closure
-deep narrow wounds-direct apposition over granulation tissue
-wide wounds-mobilize skin edges and advance over granulation tissue
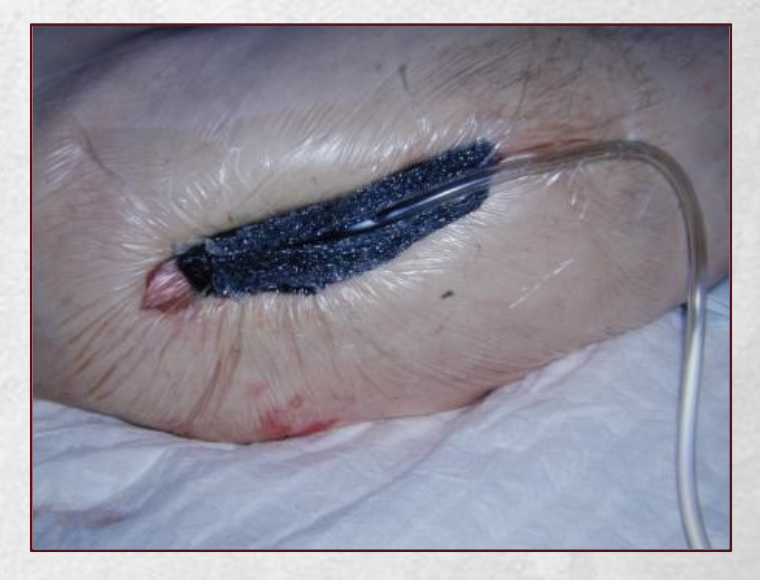
What are the characteristics of second intention wound closure?
-dirty or infected wounds
-large wounds
-granulation, epithelialization, contracture
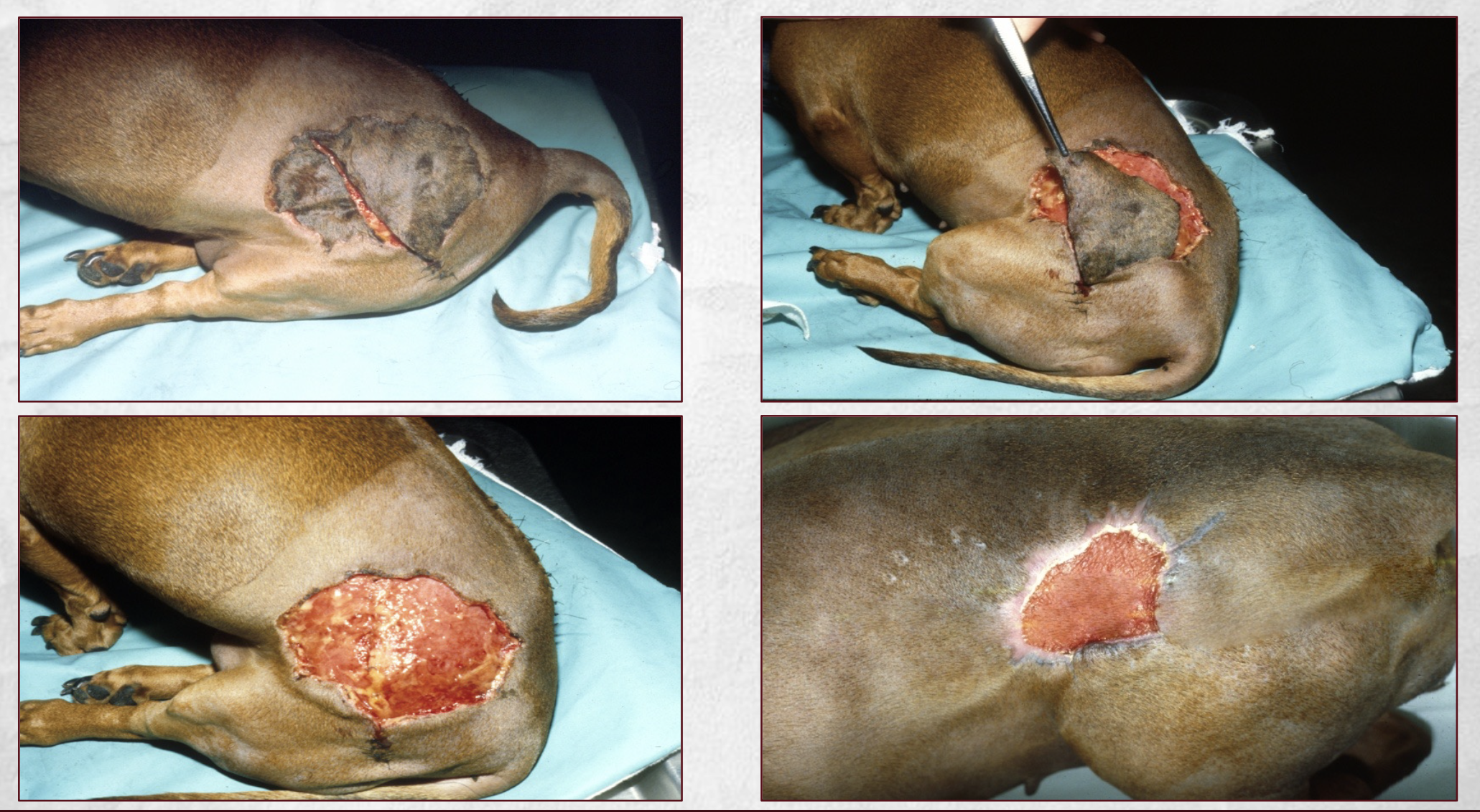
When are antibiotics needed?
-long surgery (>2 hrs)
-orthopedic implants
-break in asepsis
-entering GI tract
-may not use if animal is already on an appropriate antibiotic for a few days prior to surgery
What are the ideal characteristics of an antibioitc?
-intravenous administration
-inexpensive
-target likely contaminant
-minimal side effects to patient
When do antibiotics need to be given if they’re needed for a surgery?
-30 minutes before skin incision
-every 90 minutes during the surgery
What must be done before drawing the first dose of a reconstituted antibiotic?
Ensure all of the antibiotic is dissolved in the sterile water/saline
How should the clippers be operated to remove hair from the surgical site?
-hold with a pencil grip
-use a surgical clipping blade
-hold flat against the skin
-clip hair by going against the grain
How much hair needs to be removed from the patient prior to surgery?
It depends on the procedure, but at least 2 blade widths from the area where the incision will be. Always double-check with the surgeon!
What size blade is used to clip a patient pre-op?
#40
How is the surgical site prepped?
-clipping and vacuuming hair at site
-making skin antiseptic (rough prep)
-sterile prep
What is the purpose of the initial prep?
to ensure the animal is free of external parasites, especially fleas
What is the purpose of the final prep?
to ensure the animal is free of any external parasites missed on the initial prep with sterile materials.
What is the difference in rough prep and final prep?
-initial "rough" prep: in surgical preparation area
-final "sterile" prep: once positioned for surgery in the surgical suite
What are the characteristics of Chlorhexidine?
-good activity in organic debris
-very good residual activity
-broad spectrum
-low tissue toxicity… except mucous membranes: keep away from eyes and mouth!
-does not stain clothing
-generally diluted 60:40 with water for scrubbing
What are the characteristics of iodine?
-cheap
-broad spectrum
-“okay” residual activity
-low tissue toxicity
-will stain clothing/fur
-inactivated by inorganic debris
-generally diluted 50:50 with water when used as a scrub
What are rinsing agents?
-commonly used to “rinse” the surgical site and remove the detergent
-not completely necessary
What are the characteristics of 70% isopropyl alcohol?
-antibacterial
-dries quickly…. but may cool patient
-CAUTION when using cautery…. flammable
What are the characteristics of sterile saline?
-no antimicrobial activity
-non-flammable
How long do you scrub the area?
usually 5 minutes
What recumbency does the patient need to be in for abdominal surgeries?
perfectly dorsal
What recumbency does the patient need to be in for canine castration?
dorsal or a modified version (hind legs secured and the cranial half of the dog rolls toward the side on which the surgeon stands)
What recumbency does the patient need to be in for feline castration?
dorsal with hind legs pulled toward the head
What recumbency does the patient need to be in for orthopedic and extremity surgeries?
lateral with focus leg suspended to the IV pole (left limb is the focus in right lateral)
What recumbency does the patient need to be in for tail and perianal surgeries?
ventral w/ hind legs hanging over the edge of the table
What recumbency does the patient need to be in for back surgery?
ventral with a v-trough or sandbags to prevent falling over
What recumbency does the patient need to be in for thoracic surgery?
lateral or dorsal depending on approach with forelimbs extended as cranially as possible
What is the advantage of hanging leg prep?
-allows the entire extremity to be draped in and manipulated during surgery
-fatigue of muscles for fracture reduction
What is the correct order prep and take the patient from the induction to surgery?
-clip
-rough prep
-sterile prep
What is sterilization?
complete elimination of microbial viability
What is disinfection?
destruction of MOST pathogenic organisms on inanimate objects
What is antisepsis?
prevent growth or action of microorganisms on living tissue by inhibiting activity or killing them (not sterilized)
What is a microbe/microorganism?
living organism too small to be seen with the unaided eye
What is a pathogen?
microbe capale of causing disease
What is an infection?
the detrimental result of invasion by pathogens
What is nosocomial?
infection acquired during hospitalization or during attendance at any veterinary medical facility
What can change the weight of a patient?
-dehydration
-pregnancy
-mass
-ascites
What is nociception?
the perception of pain