AP - gluteal region and posterior thigh
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
what is the hip joint?
articulation of femoral head with acetabulum
what is the femur made up of?
cancellous bone and cortical bone
the ____ of the femur provides the greatest resistance to bending and torsion → strength
shaft
condyle
large prominence
knee joint
femur ends in a medial and lateral condyle which articulates with the tibial medial and lateral condyle
patella
along the anterior aspect of femur and tibia with supporting attachments from the quadriceps tendon superiorly and patellar tendon inferiorly
tibia
the larger part of the “lower leg” bone that provides weight bearing support
the distal MEDIAL prominence of the tibia is called what?
medial malleous
fibula
smaller more lateral leg bone that supports/creates ankle joint
what is the distal LATERAL prominence of fibula?
lateral malleolus
what is cancellous bone?
spongy bone that is porous in appearance
has weight bearing properties but less than cortical bone
high surface area and high metabolic activity (incl cell prod and mineral exchange)
what makes up 20% of bone in body?
cancellous bone
what is cortical bone?
highly dense bone bearing majority of weight
forms protective barrier around cancellous bone
periosteum
nutrient rich outer membrane surrounding shaft of femur
contributes to bone elongation and modeling including when injured
what are the 2 layers of periosteum?
has an outer fibrous layer for structural integrity and inner layer with osteogenic potential
what bones do not have periosteum?
sesamoid bones and the intra-articular ends of bones (joint)
list of sesamoid bones
patella, hands, feet, wrist
what joint formed by the acetabulum and head of femur allows multi-directional movement and stability?
synovial ball-and-socket joint
what are accessory structures of the hip joint structure?
acetabular labrum
iliofemoral ligament
medial and lateral rotator muscles
what is the acetabular labrum?
fibrocartilaginous lip that deepens socket for better fit
what ish te iliofemoral ligament?
prevents HYPEREXTENSION of the hip joint
the iliofemoral (ligament) is more anteriorly or posteriorly placed?
anteriorly (altho can extend posterior aspect)
medial and lateral rotator muscles
assist in hip stability and movement
what are examples of hip joint movement?
flexion and extension
abduction and adduction
medial (internal) rotation and lateral (external) rotation
circumduction (all movements together, it’s like a circle)
what are some important anatomic points of the femur?
femoral head
femoral neck
greater and lesser trochanter
intertrochanteric line
intertrochanteric crest
linea aspera
what is the femoral head?
articulates with the acetabulum
what is the interotrochanteric crest?
the ridge between greater/lesser trochanter
what is a hip fracture?
fracture of the proximal femur between the femoral head and no more than 5 cm distal to lesser trochanter
what is a risk of proximal femur fracture?
avascular necrosis due to retrograde blood supply, can compromise blood supply to femoral head
what is the most common MOA of hip fractures?
fall
what are the RFs for hip fractures?
age, previous history of fall, gait imbalances combined with poor bone quality
tx of hip fractures?
surgery/immobilization
what is the most common post procedural complications for hip fractures?
MI/HF - 35-42% (d/t lack of blood flow to the heart from the anemia from surgery/fracture)
anemia - 24-44% (bleeding can accumulate in the thigh or the glute, incl. bruising, edema, discoloration post surgery)
hip fractures
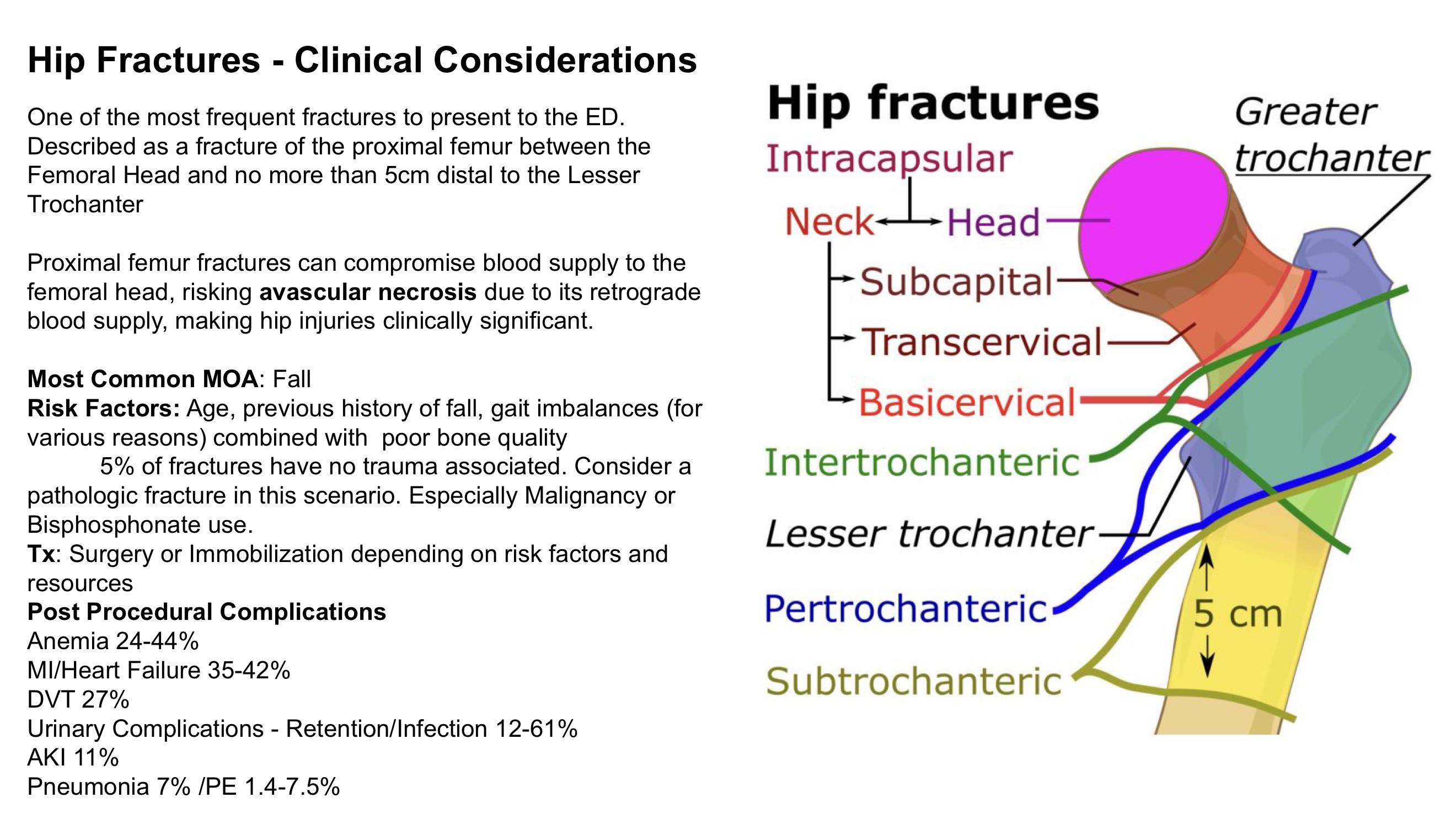
what are the 4 portions of the ischium?
superior ischial ramus
ischial body
ischial tuberosity
inferior ischial ramus
what is the connection point between pubis bone and ischial bone?
ischiopubic ramus
ischiopubic ramus is created by what?
inferior ischial ramus and inferior pubic ramus
ischial spine is an important attachment point for what?
sacrospinous ligament
what allows passage of the sciatic nerve, piriformis muscle, and the lesser sciatic notch?
greater sciatic notch
what are the three portions of the innominate bone?
ilium, ischium, and pubis
what is acetabulum?
concave surface surface where femoral head articulates
ball and socket joint that allows for full movement
what are stabilizing ligaments for the pelvis?
sacrospinous ligaments and sacrotuberous ligament
where does the sacrotuberous ligament extend from?
sacrum to ischial tuberosity
what is medial to sacrotuberous ligament?
the sacrospinous ligament
the crossing of sacrotuberous ligament and sacrospinous ligament creates what two openings?
greater and lesser sciatic foramen
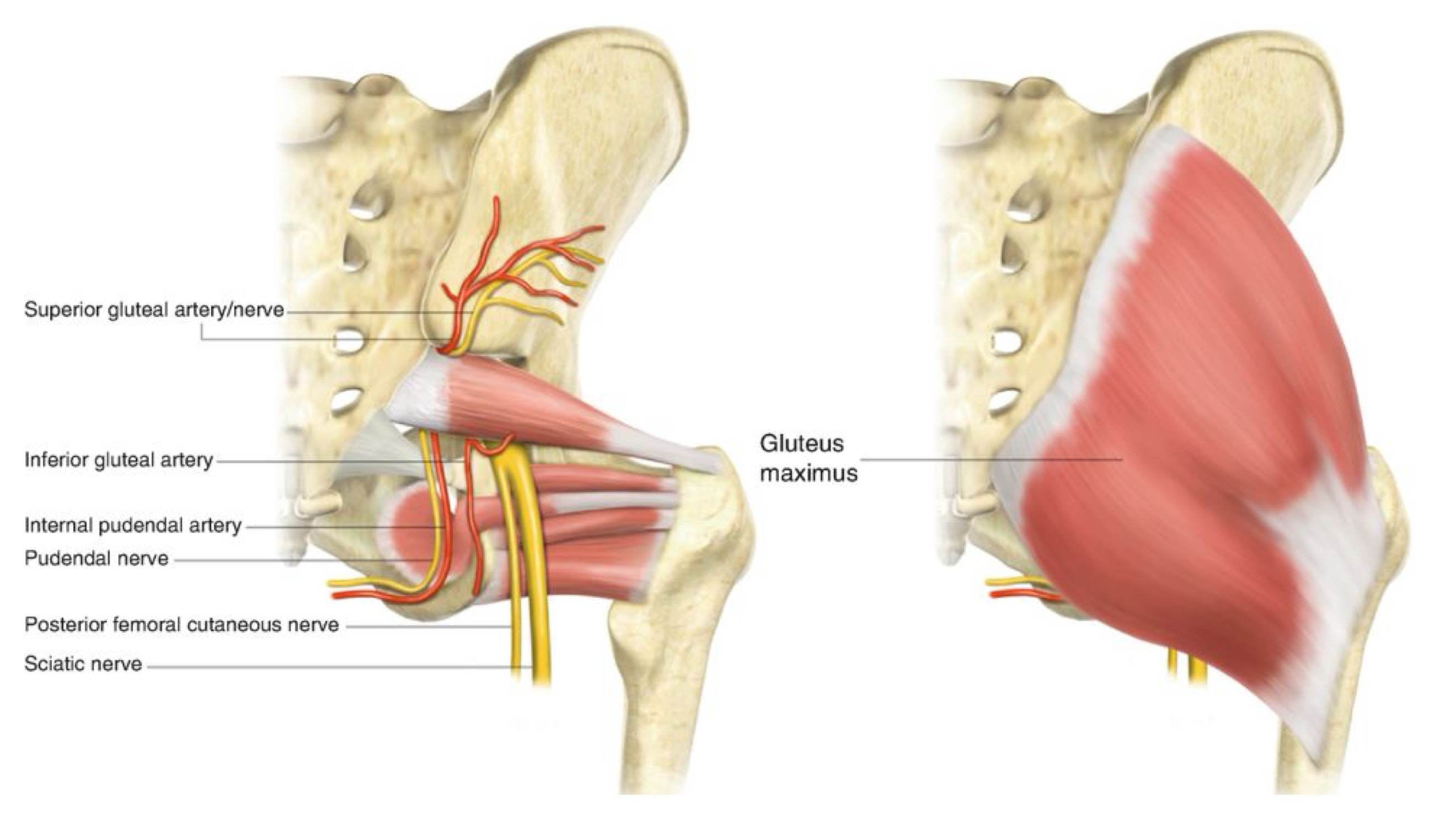
what is the greater sciatic foramen mostly filed with?
piriformis muscle (suprapiriform and infrapiriform)
what is in the lesser sciatic foramen? (PINTO)
pudendal nerve
internal pudendal artery/vein
nerve to obturator internus
TO tendon of obturator internus
where does piriformis muscle arise from/origin?
sacrum → greater sciatic foramen laterally
what is the role of the piriformis muscle?
lateral hip rotator along with obturator internus
where does piriformis muscle insert into?
greater trochanter
what is piriformis syndrome?
inflammation/scarring of piriformis muscle → compression of sciatic nerve → unilateral pain or numbness on buttock/leg
what is in the suprapiriform foramen (of the greater sciatic foramen?)
superior gluteal a/v
superior gluteal n
what is in the infrapiriform foramen (of the greater sciatic foramen?)
inferior gluteal vessels a/v
inferior pudendal a/v
nerves of sacral plexus
inferior gluteal nerve
pudendal nerve
sciatic nerve
posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
nerve to obturator internus
nerve to guadratus femoris
greater sciatic foramen
what covers the obturator foramen?
obturator internus muscle
what are the 6 muscle groups of short hip rotator muscles?
piriformis m
obturator externus m
obturator internus m
superior gemellus m
inferior gemellus m
quadratus femoris m
where do all short hip rotator muscles converge?
area back of femur medial to greater trochanter
what rotation is your short hip rotator muscles responsible for?
produce lateral rotation of hip when foot is not on the ground
when foot is on ground, rotation of trunk to opposite side
where is obturator externus arise and insert?
arise from lateral edge of ischiopubic ramus
travels bckward under femoral neck
inserts into greater trochanter
obturator internus muscle arise and inserts?
starts in pelvic cavity on ilium and ischium and travels through lesser sciatic foramen
inserts into greater trochanter
(it looks kind of fan shaped)
what is gemelli muscles?
pair of triangular muscles arising from ischium and overlaps with obturator internus muscle (inserts into greater trochanter)
what is role of gemelli muscles?
externally rotates thigh and extends hip
what is role of quadratus femoris muscle?
short and rectangular muscle, acts as external rotator and adductor
what are the 5 muscle groups of adductor muscles medially?
adductor longus m
adductor brevis m
adductor magnus m
pectineus m
gracilis m
(these also make up obturator externus)
what is adductor longus location?
arise: pubic crest
extends to femur, lower than brevis
where does the most distal aspect of adductor longus end?
edge of adductor hiatus
the adductor brevis m is ____ to longus m
deep
what is the largest of the adductor muscles and most posterior?
adductor magnus
where does the adductor magnus extend?
from outer border of pubis and ischium and extends to attach on POSTERIOR aspect of femur along linea aspera
what is the adductor hiatus?
large gap toward the distal end of femur?
what is pectineus muscle role?
adducts and flexes thigh
what is the gracilis muscle?
most medial muscle in thigh region
extends from hip joint and knee joint so affects both
adducts thigh and medially rotates and flexes knee
what are the abductor muscles?
gluteus minimus m
gluteus medius m
tensor fascia
also quadratus femoris, obturator internis, gemelli bundle, piriformis
gluteus minimus m
extends from ilium to front of greater trochanter
gluteus medium m
overlies gluteus minimus and extends from ilium to outer aspect of trochanter
tensor fascia lata m arise and extend
arise: iliac crest
extend: iliotibial tract
what is the fascia lata?
thick fibrous plane that surrounds tissue of thigh (like a casing)
iliotibial band
thickening of fascia lata and acts as area of insertion for gluteus maximus and tensor fascia lata m
what makes up the iliopsoas m?
psoas major, ilacus m, and psoas minor = primary hip flexor
what are the 3 muscles of posterior compartment of thigh?
semitendinous m
semimembranosus m
biceps femoris
what are the actions of the posterior compartment of thigh?
extend hip
flex knee
what is semitendinosus m?
MEDIAL, superficial, rope like tendon at distal attachment
sits on top of semimembranosus m
what is semimembranosus m?
MEDIAL, deeper, more membranous/flatter/wider tendon
what is biceps femoris m?
LATERAL, has two heads, long and short
what are all the hip extensor muscles/hamstring muscles?
semitendinosus m
semimembranosus m
bicep formis
what is role of gluteus maximus m?
extension when rising from squatting/seating