Cerebral Hemispheres
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
in development, what structure constricts to form the brain regions?
the neural tube
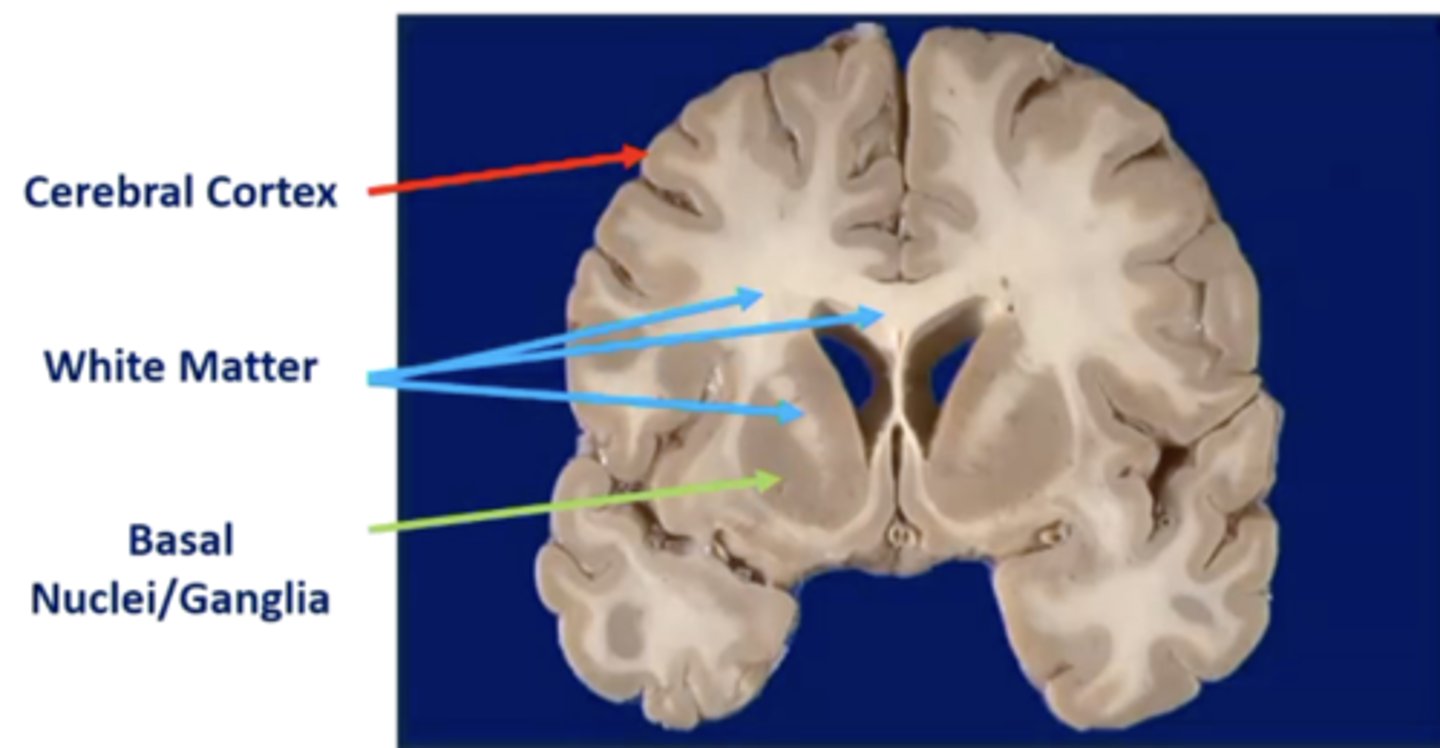
what is the cerebral cortex?
thin, wrinkled outer layer of gray matter tissue covering the brain
what are the 2 types of cortex?
1. allocortex ("other cortex)
2. neocortex ("new cortex")
list the differences between the allocortex and neocortex:
allocortex:
1. evolutionarily older (some limbic system regions) regions
2. 10% of cortex
3. 3-5 cell layers
neocortex:
1. evolutionarily newer regions
2. 90% of cortex
3. 6 cell layers
90% of the brain is (allocortex/neocortex)
neocortex
10% is allocortex
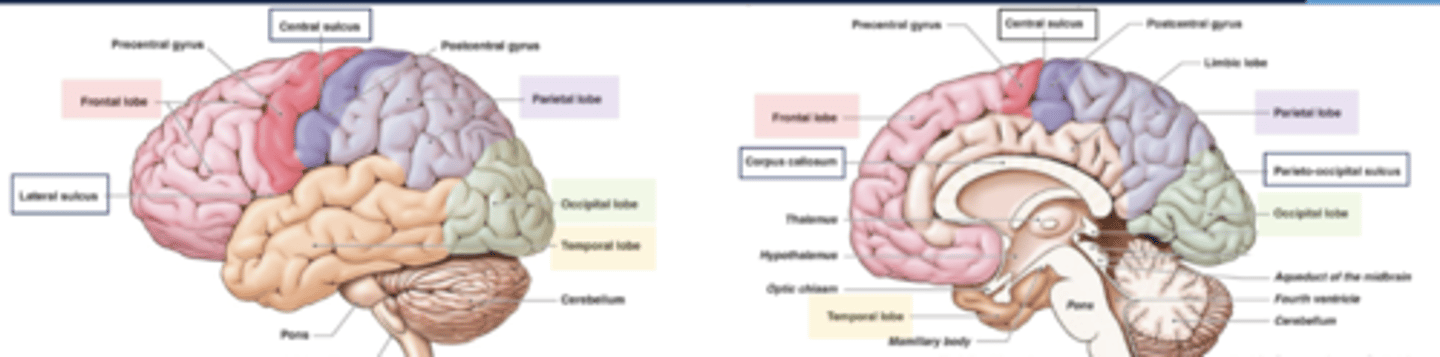
list the functions of the frontal lobe:
1. movement
2. executive functions
3. problem solving
4. reasoning/judgement
5. behaviors (emotions)
6. language production
7. memory
~primary motor cortex~
list the functions of the parietal lobe:
1. sensation
2. body orientation
3. spatial relationships
~primary somatosensory cortex~
list the functions of the temporal lobe:
1. language comprehension
2. hearing
3. behavior
4. memory
list the functions of the occipital lobe:
1. vision
2. color perception
list the functions of the cerebellum:
1. balance
2. coordination
3. fine muscle control
list the functions of the brainstem:
1. breathing
2. blood pressure
3. heartbeat
4. swallowing
5. alertness/sleep
6. body temperature
7. digestion
the primary sensory cortex is the (first/last) region in the cortex to receive sensory information
first
the primary motor cortex is the (first/last) region in the cortex before information descends to lower nervous system regions
last
what are association cortices?
integration areas for collective detailed perception
these make up the majority of the cerebral cortex
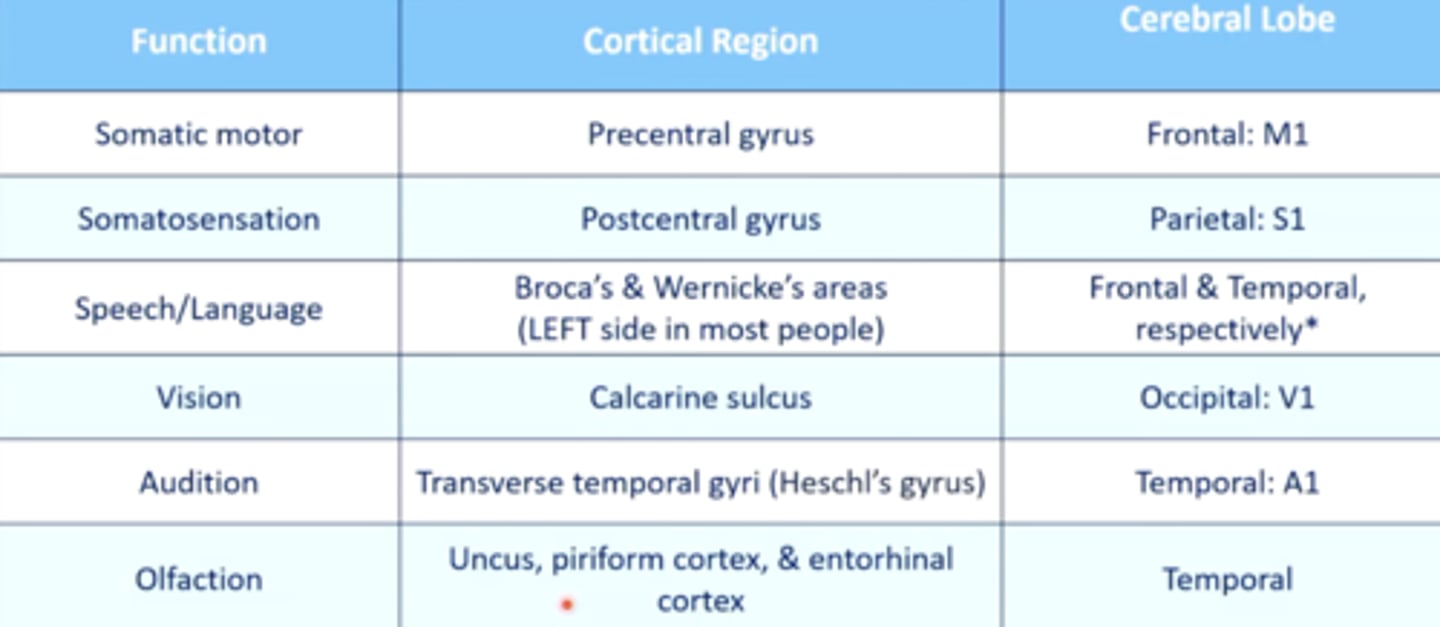
list the cortical region and cerebral lobe of the somatic motor system/primary motor cortex:
cortical region:
precentral gyrus
cerebral lobe: frontal (M1)
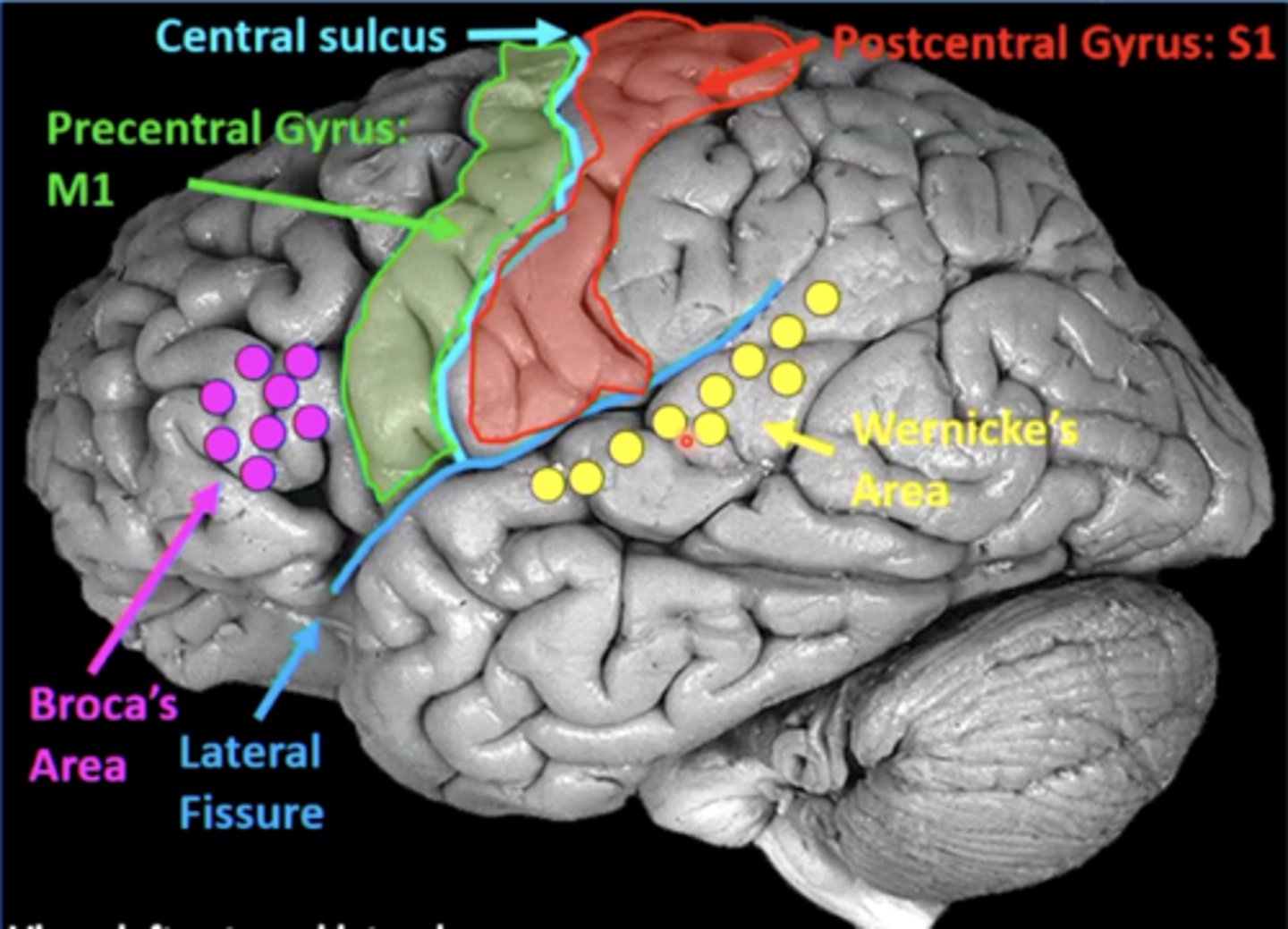
list the cortical region and cerebral lobe of the somatosensory system/primary sensory cortex:
cortical region:
postcentral gyrus
cerebral lobe: parietal (S1)
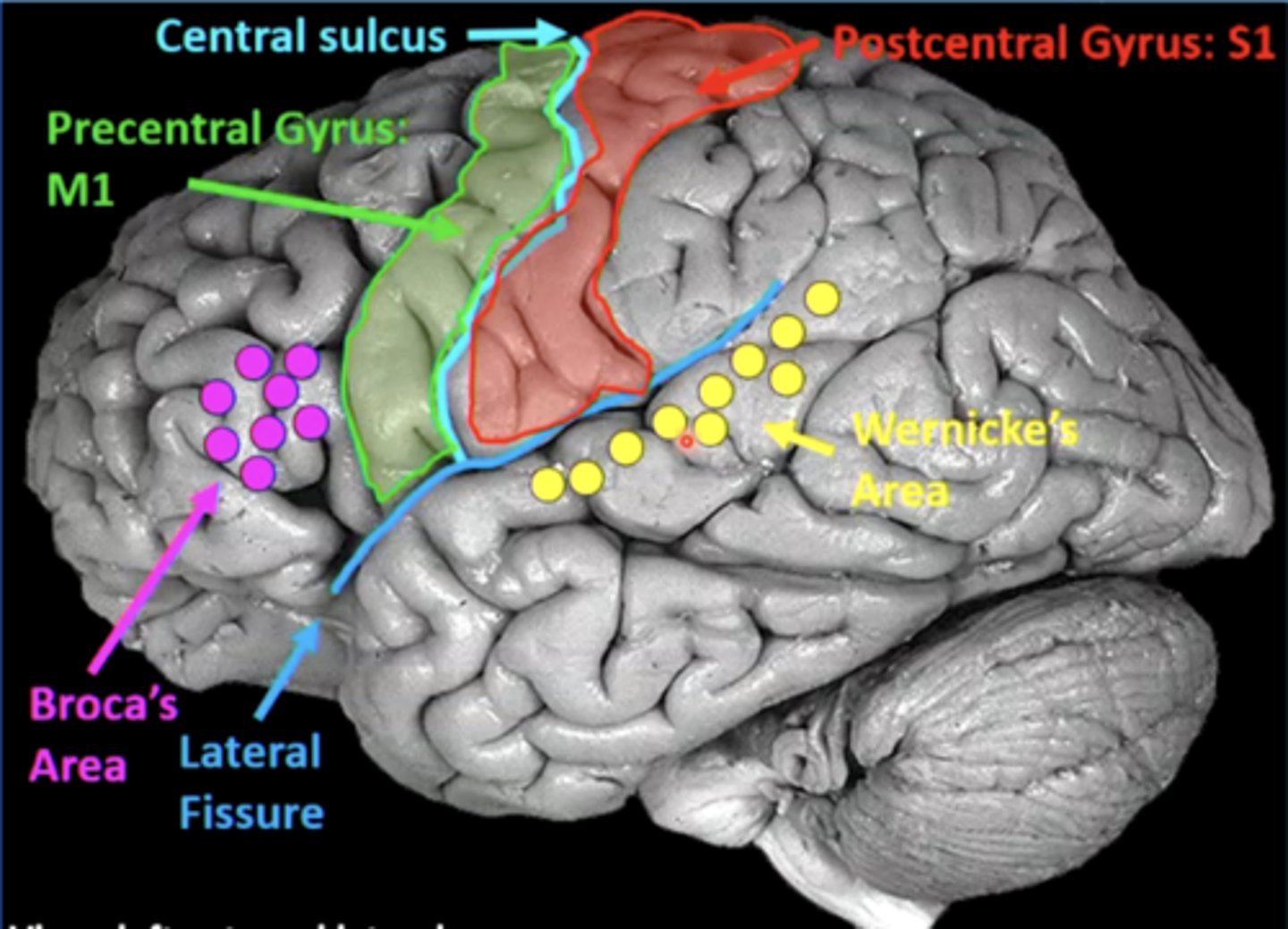
list the cortical region and cerebral lobe of the speech/language system:
cortical region:
Broca's and Wernicke's areas
cerebral lobe: frontal (Broca's) and temporal (Wernicke's)
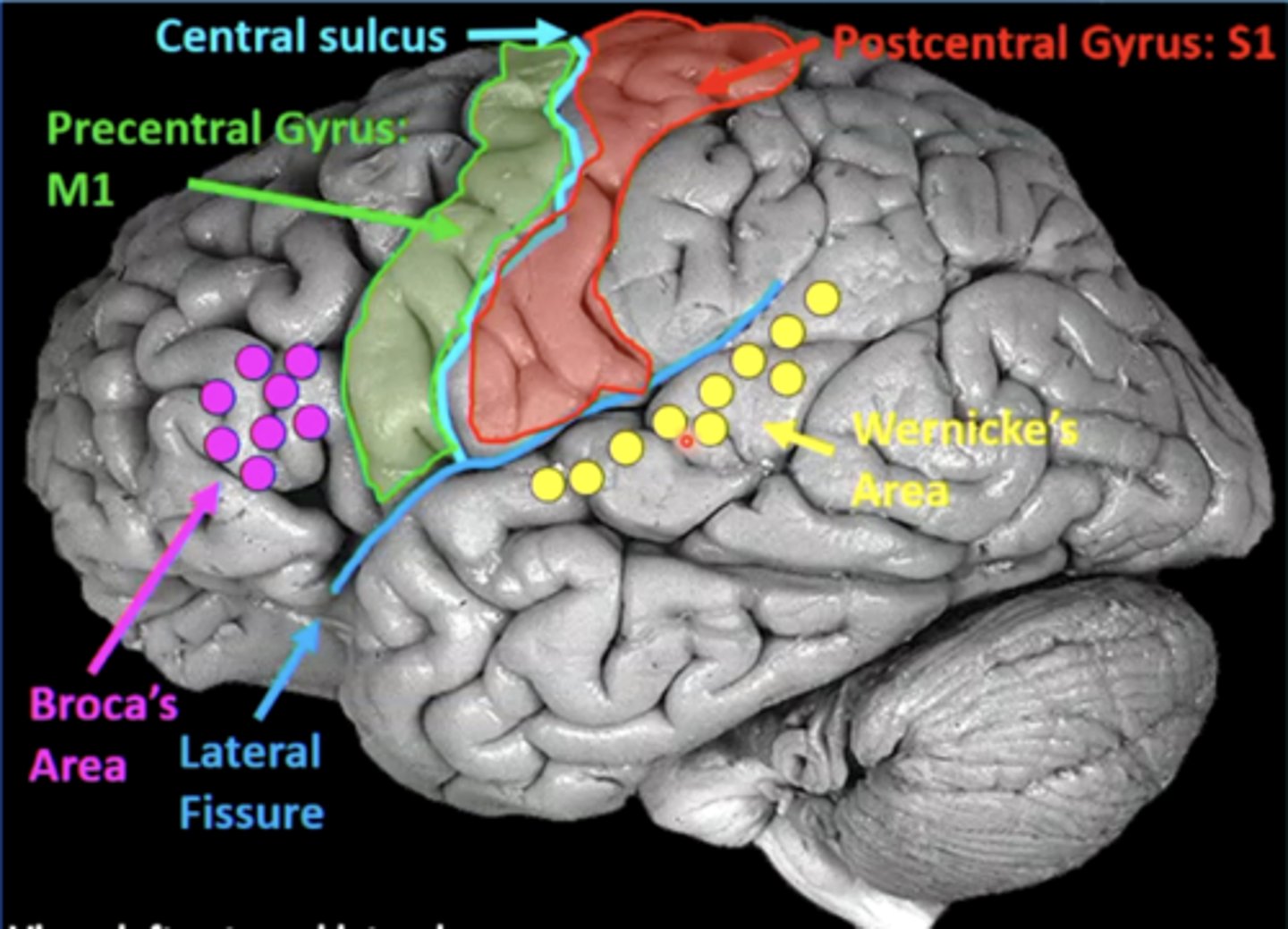
Broca's and Wernicke's areas are located on the (left/right) hemisphere of the brain in most people
left
a good guess to where the language centers are is based on your dominant hand (right hand dominant --> language centers will be in the left hemisphere)
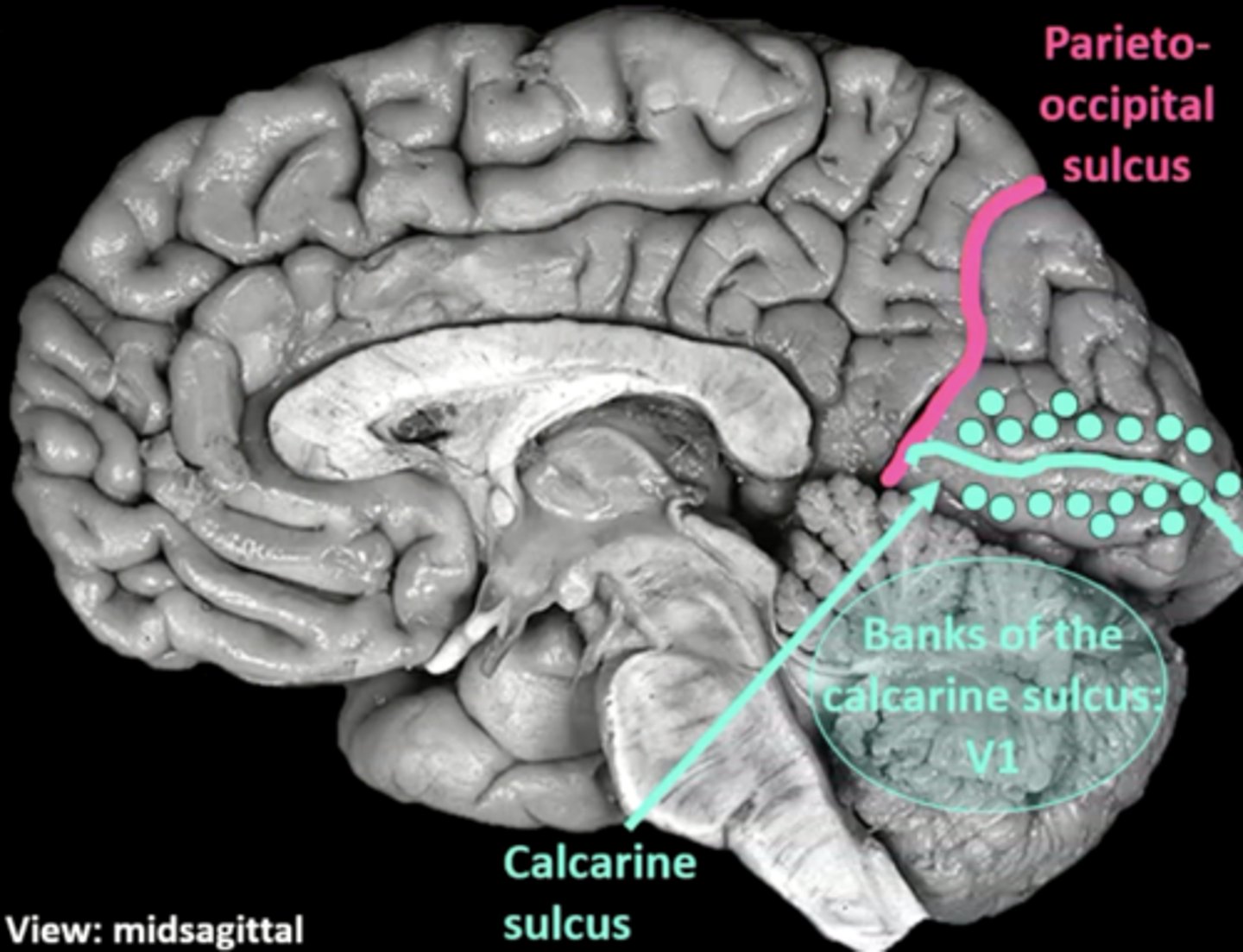
list the cortical region and cerebral lobe of the visual system:
cortical region:
calcarine sulcus
cerebral lobe: occipital (V1)
list the cortical region and cerebral lobe of the auditory system:
cortical region:
transverse temporal gyri (Heschl's gyrus)
cerebral lobe: temporal (A1)
list the cortical region and cerebral lobe of the olfactory system:
cortical region:
uncus, piriform cortex, entorhinal cortex
cerebral lobe: temporal
list the 2 "rules" of the primary motor and primary somatosensory cortices:
1. somatotopic organization (body map of contralateral side)
2. increased cortical surface area = increased receptor density/acuity
ascending sensory pathways terminate on the (ipsilateral/contralateral) primary somatosensory cortex
contralateral
descending motor pathways originate in the (ipsilateral/contralateral) primary motor cortex
contralateral
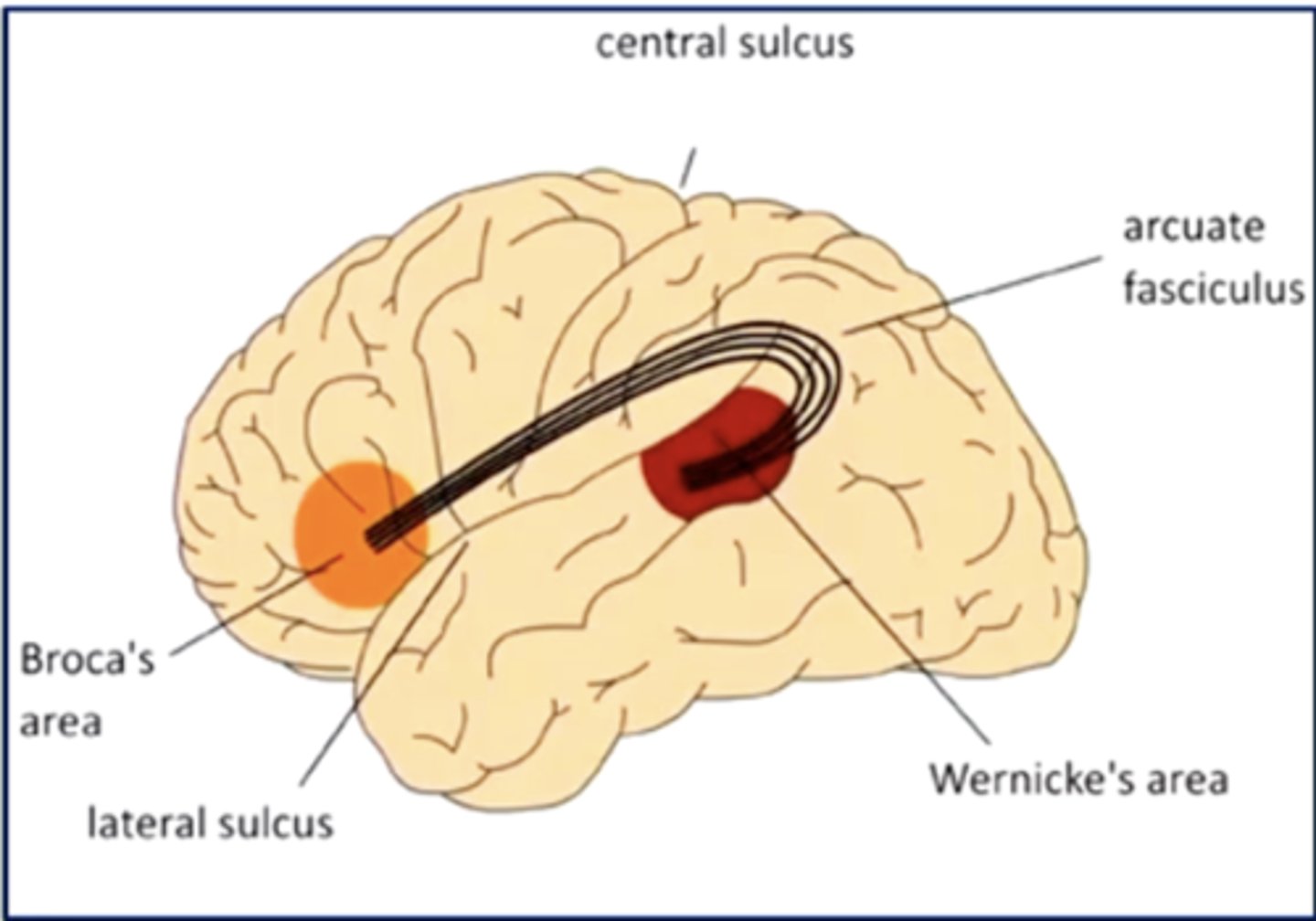
what is Broca's area?
area in the frontal lobe responsible for language production (speaking, writing, signing)
a lesion in Broca's area could result in what?
Broca's aphasia
results in slow, labored speech, agrammatism (lacking correct grammar), and anomia (inability to name objects)
understanding is good, finding/creating the words is difficult
what is Wernicke's area?
area in the temporal lobe responsible for language comprehension (speech, written language, sign language)
a lesion in Wernicke's area can result in what?
Wernicke's aphasia
person can produce fluent speech/language, but it is meaningless ("word salad")
language production is there, it just makes no sense
what is the arcuate fasciculus?
an axonal pathway that connects Wernicke's area to Broca's area
cell bodies are in Wernicke's area, and axons synapse in Broca's area
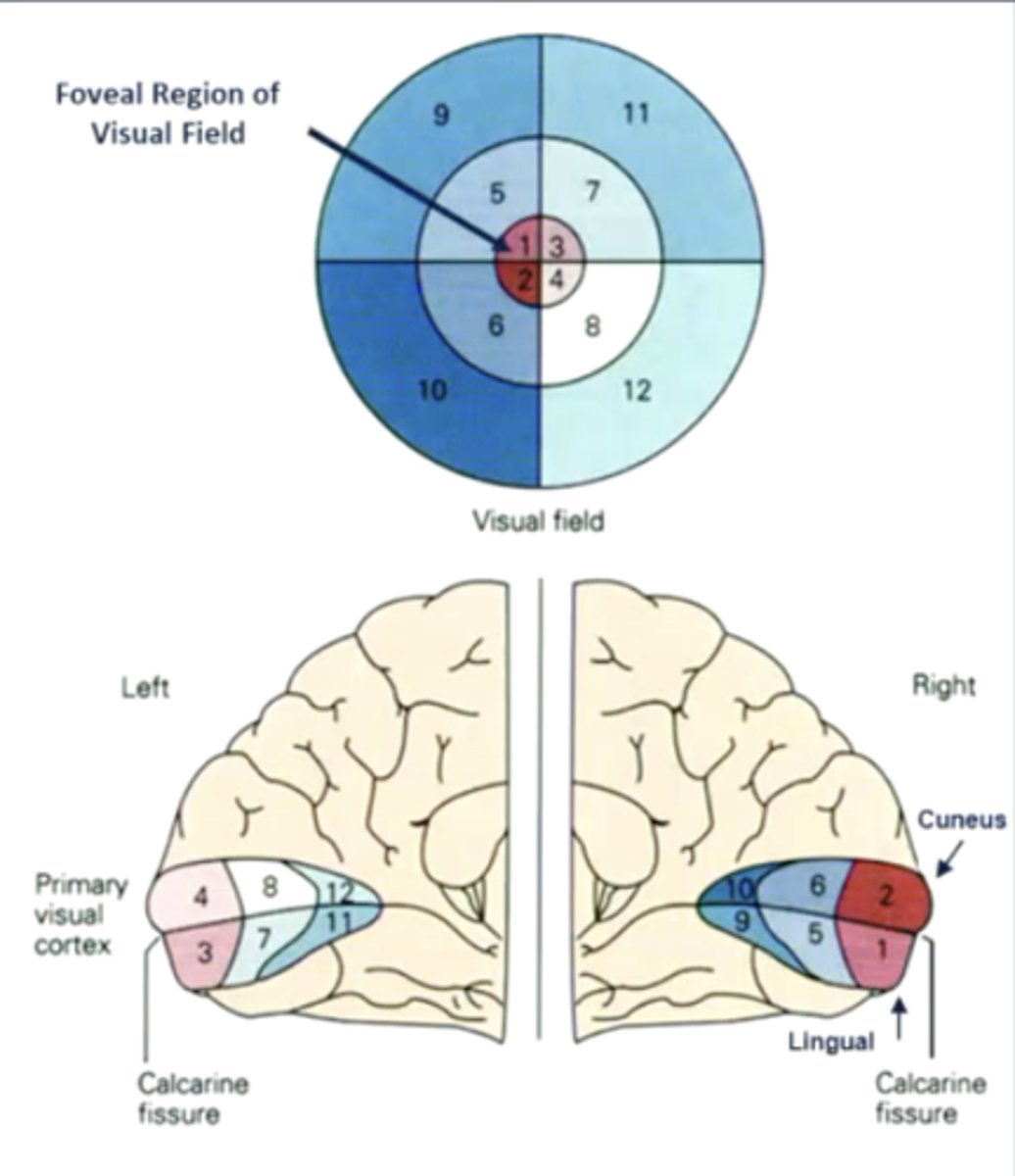
what are the 2 "rules" of the primary visual cortex?
1. retinotopic organization (contralateral visual fields)
2. increased cortical surface area = increased receptor density/visual acuity
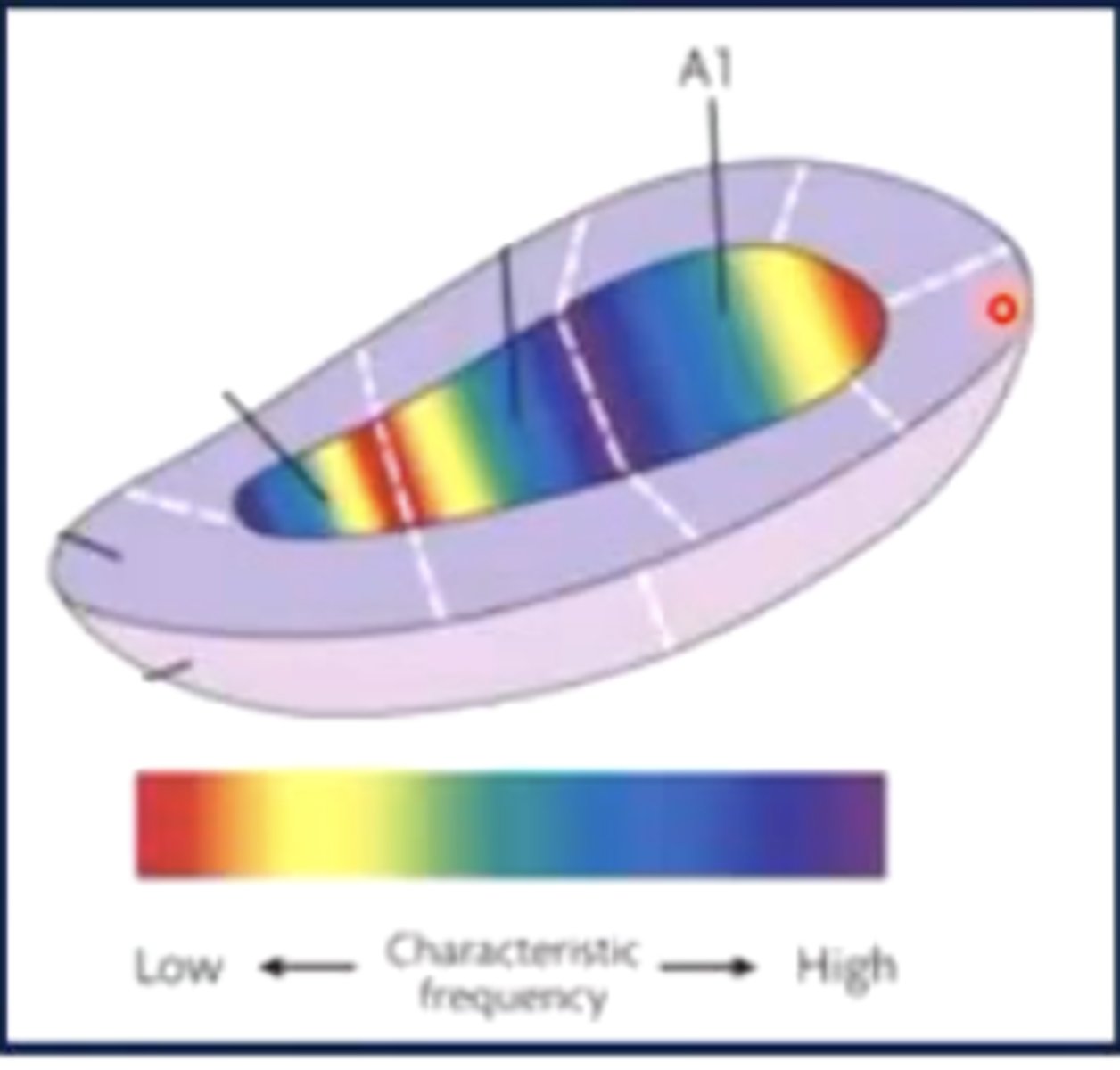
T/F: both the basilar membrane and the primary auditory cortex are tonotopically organized
true
basilar membrane = high tones at base, low tones at apex
primary auditory cortex = sound frequency map
T/F: both hemispheres process auditory information from each ear
true
sound waves arrive ipsilaterally, but quickly becomes bilateral to be processed by both sides of the brain
T/F: the olfactory system routes through the thalamus before conscious perception of smell
false
the olfactory tract goes straight back to the olfactory cortex for processing - this plays a role in memory related to smell and seizures
where is the primary gustatory cortex located?
frontoparietal operculum and insula
where is the primary vestibular cortex located?
parieto-insular vestibular cortex (PIVC) and many other areas
what is the function of the basal ganglia?
modulate movement and posture
what are the basal ganglia nuclei (5):
1. caudate nucleus
2. putamen
3. globus pallidus
4. substantia nigra
5. subthalamic nucleus
what are the boundaries of the frontal lobe?
central sulcus and lateral fissue
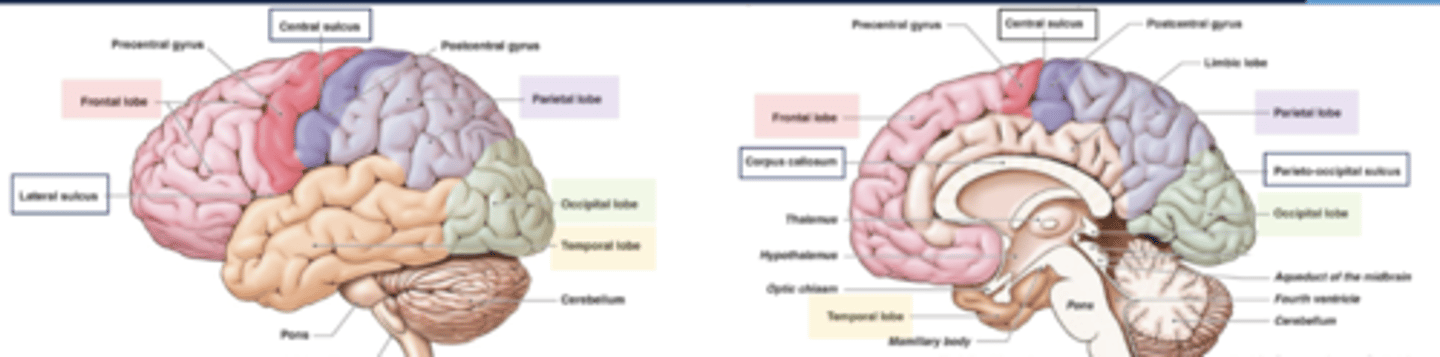
what are the boundaries of the parietal lobe?
central sulcus, lateral fissure, parieto-occipital sulcus
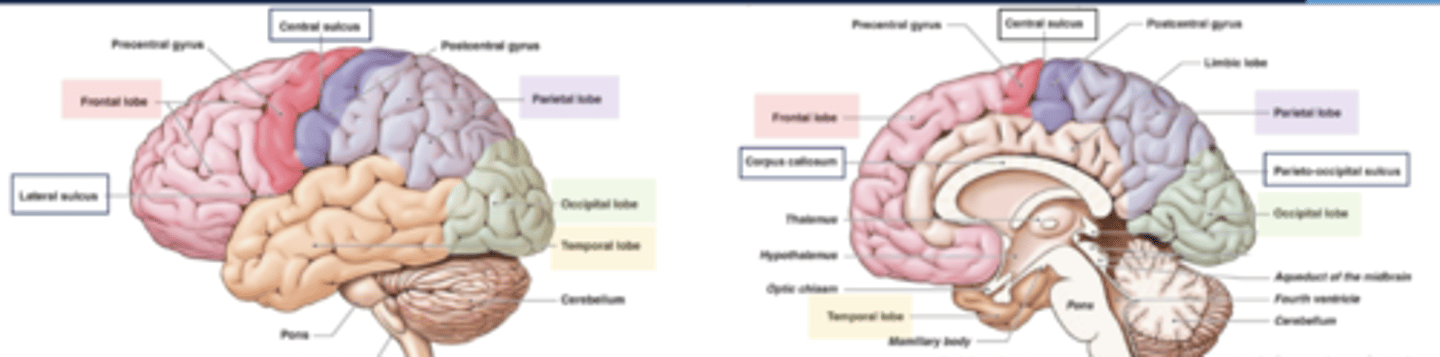
what are the boundaries of the occipital lobe?
parietal-occipital sulcus
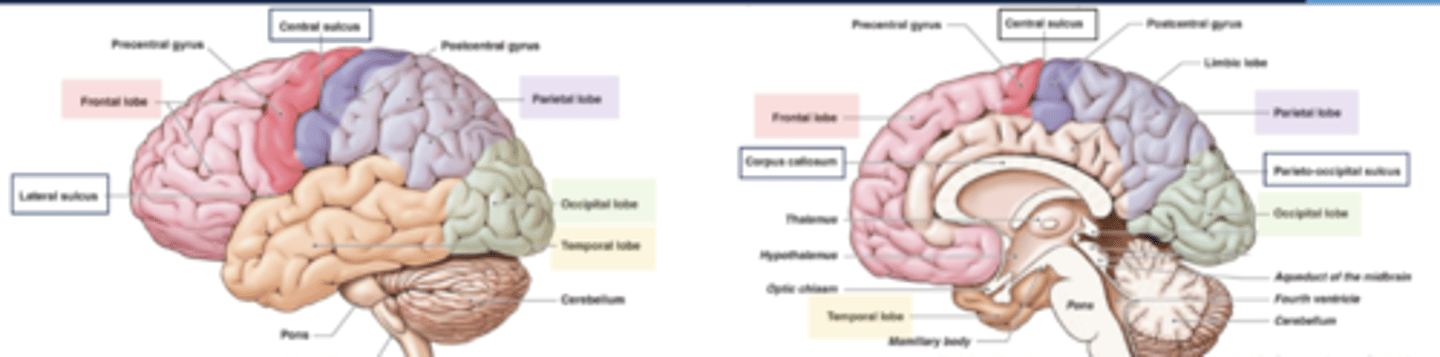
what are the boundaries of the temporal lobe?
lateral fissure