Edexcel GCSE Biology Paper 2 - Things i got wrong
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Topic 1 - Key concepts in biology, Topic 6 - Plant structures and their functions, Topic 7 - Animal coordination, control and homeostatis, Topic 8 - Exchange and transport in animals, Topic 9 - Ecosystems and material cycles
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Which indicator species indicate clean water?
Stonefly
Freshwater shrimps
Which indicator species indicate polluted water?
Bloodworm
Sludgeworm
What indicator species indicate clean air?
Blackspot fungus on roses, Bushy lichen
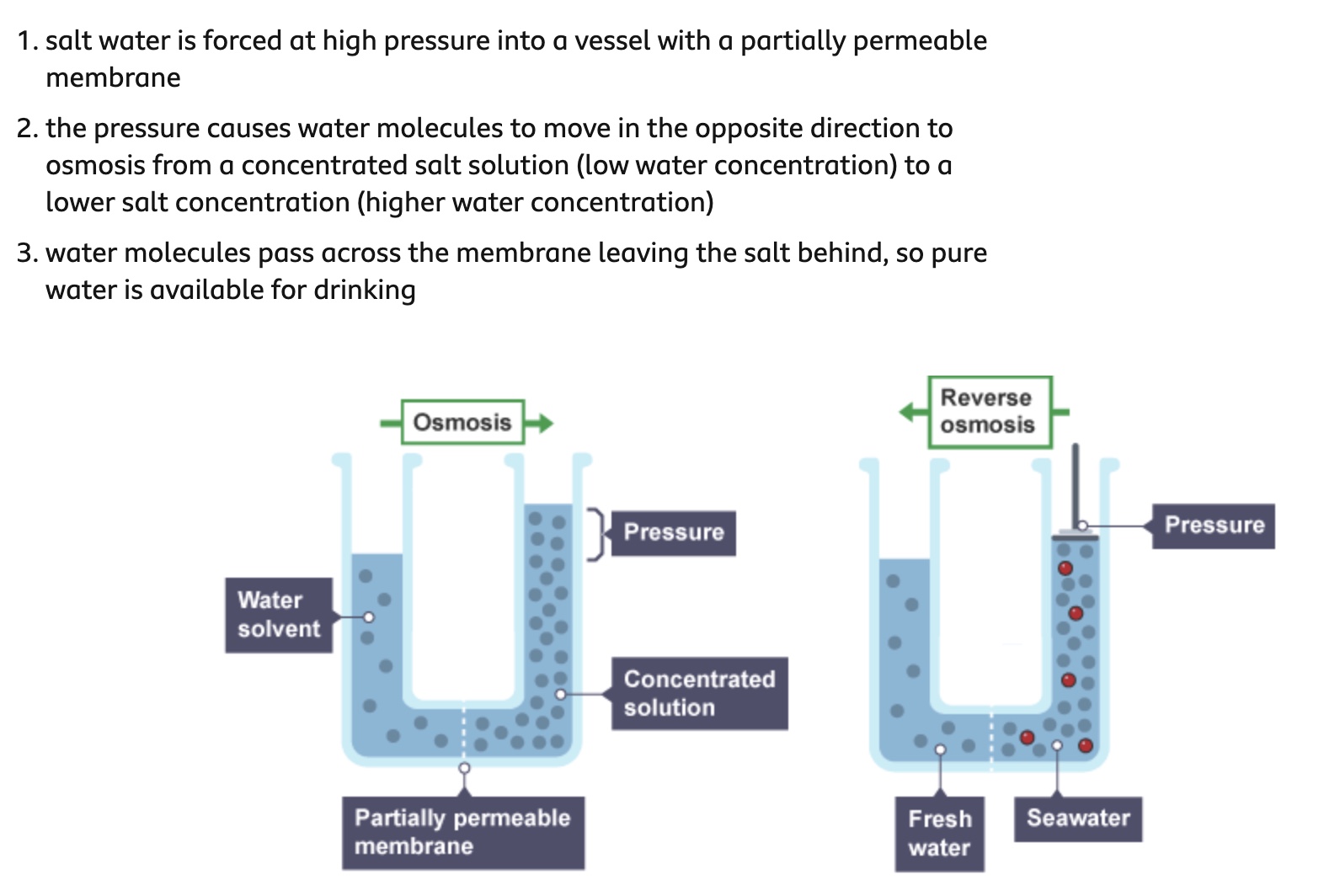
How is potable water produced?
Reverse osmosis (lower to higher concentration)
What are two features of xylem vessels?
Thick wall
One continuous hollow tube made of dead cells called lignin
What does the xylem transport and by what process does it do this?
Water and mineral ions via transpiration
What does the phloem transport and by what process does it do this?
Sugars like sucrose via translocation which is up and down the plant. The phloem contains living cells as it needs energy from respiration to transport sugars up and down the plant.
What structure is found in veins but not arteries?
Valves
Why may energy be lost between different trophic levels in a pyramid of biomass?
Energy is used for movement
Energy is transferred to the surroundings through heat loss
Respiration
What do decomposers in the soil convert?
Urea into ammonia
What does nitrifying bacteria convert?
Ammonia into nitrates
What does nitrogen fixing bacteria convert?
Nitrogen gas in the atmosphere into ammonia
How does crop rotation increase nitrate levels in the soil?
Leguminous plants contain nitrogen fixing bacteria in their root nodules which convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia which nitrifying bacteria convert into nitrates in the soil
What do plants need nitrates for?
Nitrates are needed to make proteins for growth
What are the three plant hormones?
Auxins - the growth hormone
Gibberellins - germination
Ethene - fruit ripening
What are the commercial uses of auxins?
Selective weed killers as they target broad leaf plants and kill them by causing them to overgrow while leaving the narrow leaf crops
Rooting powders as they are added to the end of plant cuttings to stimulate the growth of roots
What are the commercial uses of gibberellins?
• to stimulate germination in dormant seeds
• initiate breakdown of starch
• stimulate flower formation
• promotes fruits formation
• sprayed onto plants before pollination
• stimulate development of seedless fruits
What are the commercial uses of ethene?
Unripe fruit is harvested and ethene is sprayed on them before selling to ripen the fruit at the most desired time
Wha effect does adrenalin cause?
Adrenalin binds to receptors on liver cells
Stimulates the breakdown of glycogen into glucose to be released into the blood
Increased heart rate
increased blood flow to the muscles
Increased blood pressure
This is done to induce the fight or flight response to protect yourself when in danger
What is Fick’s Law?

What happens to excess amino acids in the blood?
They get broken down into urea in the liver
What is eutrophication?
Nitrates from fertilisers leak into nearby rivers
This causes nitrate levels in the water to increase and oxygen levels in the water to decrease
The high nitrate levels causes an overgrowth of algae
This blocks sunlight from the plants in the water
Plants in the water die as they can’t photosynthesise
and are decomposed by microorganisms/decomposers which use the oxygen in the water for respiration
What is the inverse square law?
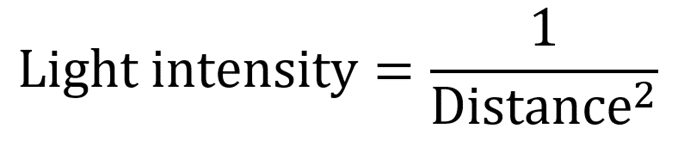
How does increased air movement affect the rate of transpiration?
Water vapour is removed from around the leaf
Increased rate of evaporation of water from leaf
Plant draws up more water to leaves from stem and root
Increased rate of transpiration
How does increased temperature affect the rate of transpiration?
Higher temperature
More evaporation of water from leaves
More water drawn up to the leaves via stem and roots
Increased rate of transpiration
How does a decrease in humidity affect the rate of transpiration?
Less humidity means lower concentration of water molecules in the air outside the leaves
This means that there is more diffusion of water from inside the leaves to outside of the leaves as the water moves via osmosis along the concentration gradient from a region of higher concentration in the leaves to a region of lower concentration outside of the leaves
More water loss from the leaves causes more water to be drawn up the plant to the leaves via the stem and roots
Increased rate of transpiration
How does an increase in light intensity affect the rate of transpiration?
Increase in light intensity means that there is an increase in the number of open stomata
This causes more water loss via evaporation from the leaves
This causes the plant to draw up more water to the leaves via the stem and roots
Increased rate of transpiration
What are the features of an atery?
Thick, muscular wall to maintain blood pressure
Narrow Lumen
What are the features of a vein?
Valves to prevent the backflow of blood
Wide lumen as lower blood pressure
What is type 1 diabetes?
When the person’s pancreas doesn’t produce any insulin
What is type 2 diabetes?
When the person doesn’t produce enough insulin or their liver has become resistant to insulin so the liver doesn’t break down glucose into glycogen
How do you calculate BMI?
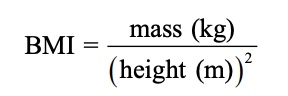
How do you calculate the cardiac output?
cardiac output = stroke volume x heart rate
What is an abiotic factor and give examples?
A non-living component of an ecosystem that influences the living organisms and ecosystems within it e.g. water, temperature, light intensity, air quality
What is a biotic factor and give examples?
A living organism that affects the population of other organisms in an ecosystem e.g. competition, predators, diseases
What is a mutualistic relationship?
A relationship where two organisms depend on each other for survival
Why is sodium hydrogen carbonate used in the pondweed photosynthesis practical?
It increases the carbon dioxide concentration in the water to provide carbon dioxide for the plant to use for photosynthesis so that carbon dioxide isn’t the limiting factor of the photosynthesis practical as it is used to measure how light intensity affects the rate of photosynthesis