W6 Organizational behavior- Leadership: Negotiating power
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Power
Power is the capacity to influence others and control resources in an organizational setting.
Relational Power
Power is relational - It depends on interactions between people.
Situational Power
Power is situational - It shifts based on context.
Nature of Power
Power is neither inherently good nor bad - It depends on how it's used.
Influence
Power is about influence, not just authority.
Legitimate Power
Power from a formal position or authority. (CEO, manager, team leader)
Reward Power
Control over valued rewards and incentives. (Bonuses, promotions, perks)
Coercive Power
Ability to punish or impose consequences.(Disciplinary actions, firing)
Expert Power
Based on knowledge, skills, or expertise. (Subject matter experts, IT professionals)
Referent Power
Influence based on admiration or charisma. (Influential leaders, role models)
Influence Tactics- Rational Persuasion
Using logic, facts, and data.
Influence Tactics- Inspirational Appeals
Appealing to emotions, values, or ideals.
Influence Tactics- Consultation
Seeking participation and buy-in.
Influence Tactics- Ingratiation
Using flattery or praise.
Influence Tactics- Personal Appeals
Asking based on friendship or loyalty.
Influence Tactics- Exchange
Offering favors or resources in return.
Influence Tactics- Coalition Tactics
Gaining support from others to persuade someone.
Influence Tactics- Pressure
Using threats or demands.
Influence Tactics- Legitimacy
Using authority or formal rules.
Organizational Politics
Organizational politics refers to actions taken to gain and use power within a workplace.
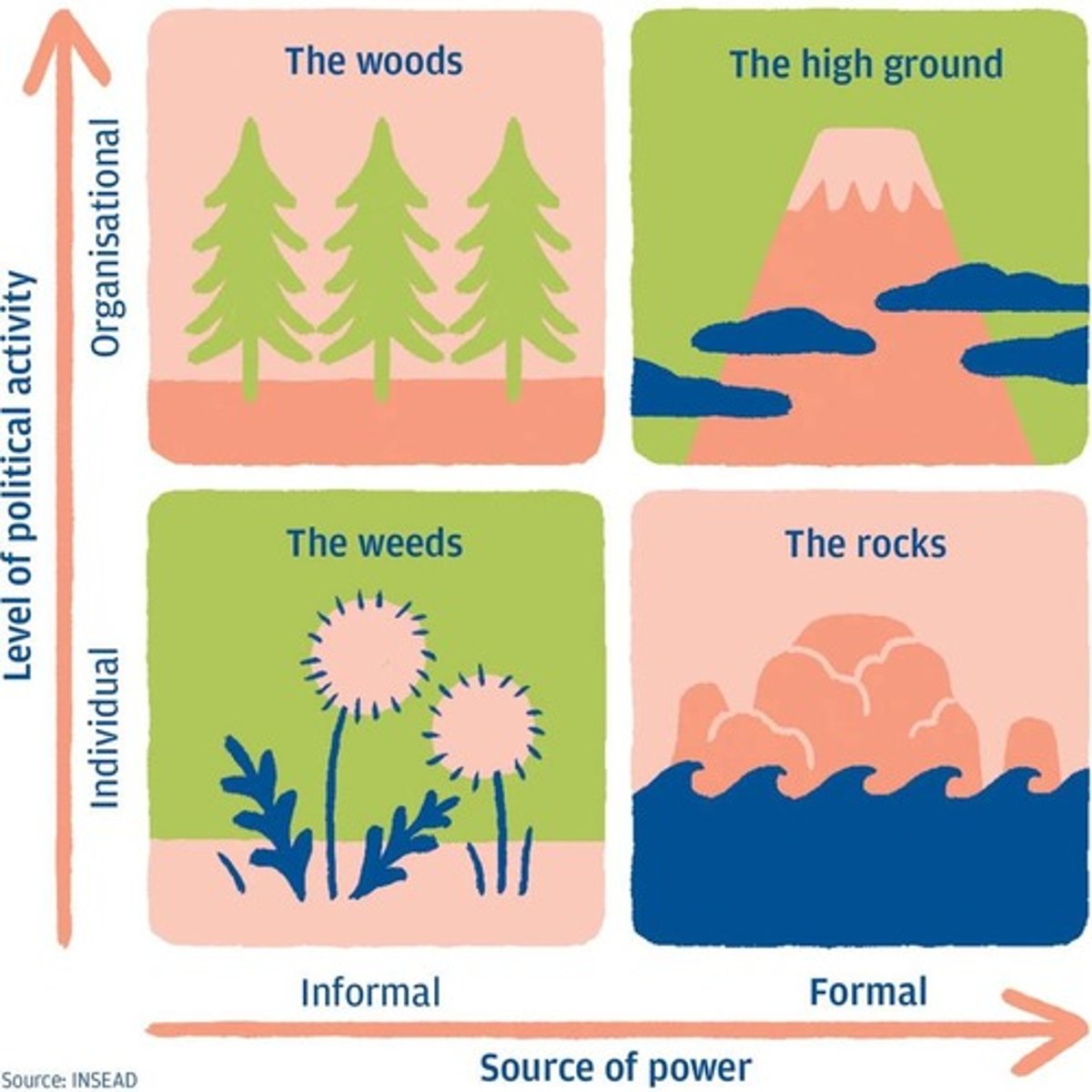
Political Behavior
Includes self-promotion, building alliances, controlling information, and lobbying for personal gain.
Political Skill in Leadership
Leaders with strong political skills are better at managing power and influence.
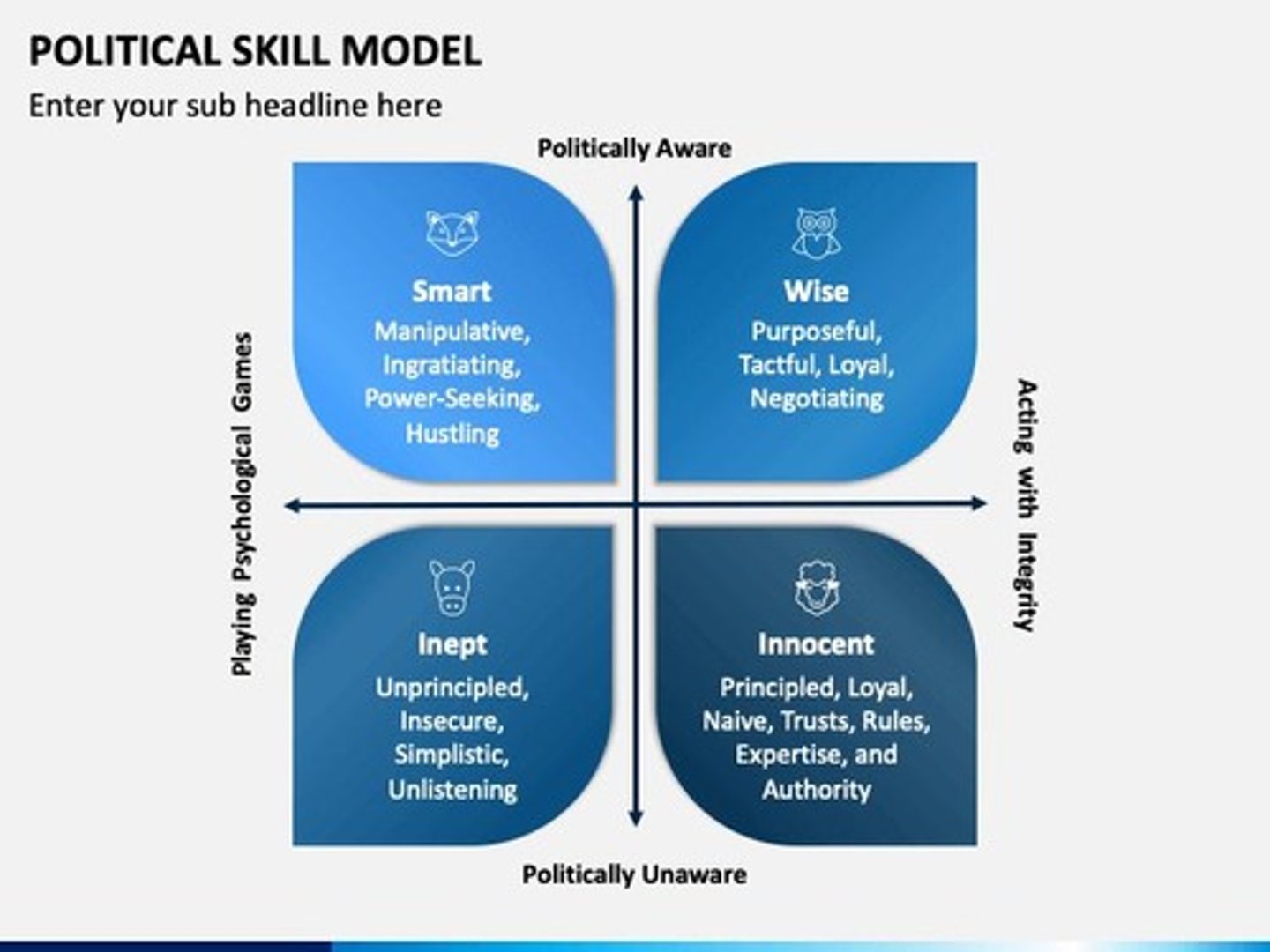
Key Traits of Politically Skilled Leaders: Social Astuteness
Understanding others' behaviors and motivations.
Key Traits of Politically Skilled Leaders: Interpersonal Influence
Adapting influence tactics to different situations.
Key Traits of Politically Skilled Leaders: Networking Ability
Building strong connections.
Key Traits of Politically Skilled Leaders: Apparent Sincerity
Appearing genuine and honest.
Ethical Power Use
Transparency, fairness, shared decision-making.
Unethical Power Use
Manipulation, coercion, deceit.
Negotiation
The process of reaching an agreement between two or more parties with different interests.
Effective Negotiation: Preparation & Planning
Define goals, research the other party.
Effective Negotiation: Definition of Ground Rules
Set guidelines for the discussion.
Effective Negotiation: Clarification & Justification
Exchange information and clarify positions.
Types of Negotiation: Distributive Bargaining
Win-lose negotiation (one side gains, the other loses).
Types of Negotiation: Integrative Bargaining
Win-win negotiation (both sides benefit).
Effective Negotiation: Closure & Implementation
Finalize the agreement.
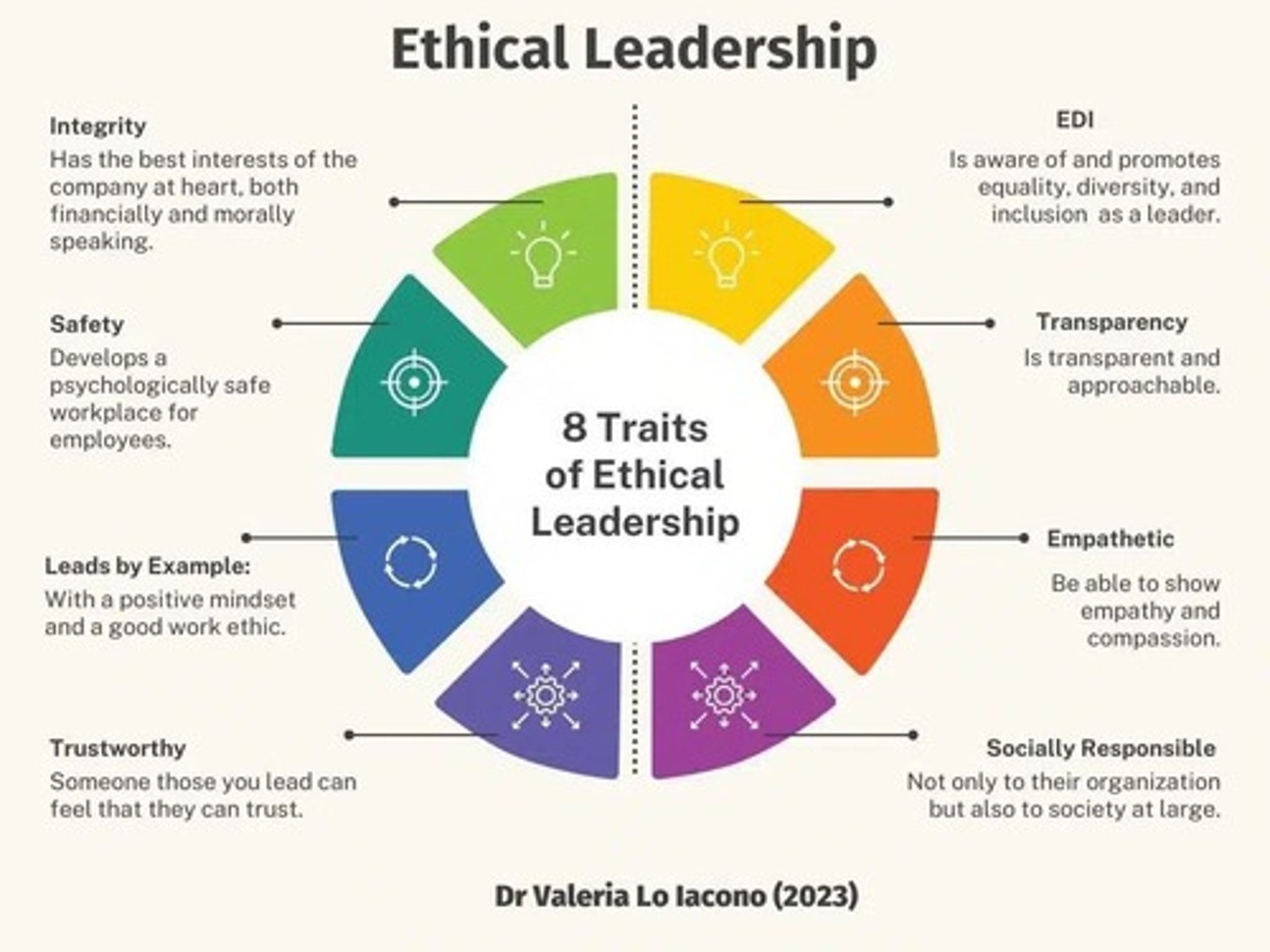
How to ensure ethical leadership
Promote transparency. Encourage accountability. Set ethical role models.
Bargaining & Problem-Solving:
Present proposals and make concessions.
Closure & Implementation:
: Finalize the agreement