Q1L4 GENSCI_Philippine Ecosystems
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Ecosystem
A geographic area where a
community of living organisms
interacts with each other and with
their physical environment.
It includes both biotic (living) factors
and abiotic (nonliving) factors.
Terrestrial and aquatic
a complex web of relationships that sustain life.
What do the interactions of biotic and abiotic factors form?
Ph ecosystem components
forests
Coral reefs
Grasslands
Freshwater
Forest ecosystem
Philippine forests are incredibly biodiverse,
boasting a wide array of unique flora and fauna.
High humidity and temperature, and a large
amount of rainfall.
Tropical climate
what allows the Philippines forests to receive, absorb, and redistribute rainwater to support life.
Sierra Madre mountain range
Contains around 49% of the country’s remaining forest cover
the backbone of Luzon
shields Central Luzon from strong typhoons
Philippine eagle
Philippine mouse deer
Species of the PH in forests
cordillera mountain ranges
Zambales
Sierra Madre mountain range
Mt. Makiling
Mt. Banahaw
Where are most forests in the Ph found
Grassland
a terrestrial ecosystem dominated by grasses and herbaceous plants, with limited tree or shrub cover.
• Flora and fauna include grasses, cogon, wildflowers, rats, insects, snakes, and birds.
-Imperata cylindrica (Cogon Grass)
Mt. Pulag grassland
Lantawan Grassland in Zamboanga
Grassland examples
Generally experience moderate rainfall, but not enough to support forests.
What is the frequency of rainfall in grasslands
Overgrazing
Forest conversion
Grassland fires
Factors threatening grasslands
can lead to soil erosion in grasslands, decrease in biodiversity
What are the effects of farmers burning Cogon grass?
Freshwater
Freshwater ecosystems include lakes, rivers, swamps, and estuaries (mangroves).
Habitat for aquatic organisms (freshwater fish
and shellfish).
Lakes
Large body of water surrounded by land
Rivers
A long body of water that flows toward the sea
Swamps
Low-lying areas of land that are permanently saturated with water
Estuaries
Areas where freshwater rivers meet the Salty ocean, creating a brackish water environment
Laguna de Bay
Tall lake
Cagayan river
Candaba swamp
Ph freshwater examples
Laguna de Bay
Ph largest lake
Cagayan river
Longest and largest ph river
Sardinella tawilis
A freshwater sardine found only in the Ph, only freshwater sardine found in the world
found in the Taal lake
Illegal fishing
industrial/factory wastes
household waste
Factors threatening freshwater
Coral reefs
natural habitat of fish species and other marine organisms.
Because of such a long process, coral reefs are considered very delicate ecosystems.
Provides food, protects shorelines, attracts tourism
Owning 5% of the world’s total 617,000 sq km of coral reefs
Why is the Ph part of the world’s “Coral Triangle”
Composed of massive deposits of calcium carbonate that takes centuries to produce and develop.
Composition of coral reefs
Verde island passage in Batangas
Tubbataha reef in Sulu Sea.
Coral reefs in ph examples
Verde island passage
“Center of the Center of Marine Shorefish Biodiversity”
Tubbataha Reef
UNESCO World Heritage Site
Serves as a nesting ground for the critically endangered sea turtle
Hakwsbill Sea Turtle
Endangered sea turtle in Tubbataha Reef
Coral bleaching
Happens when sea temperatures rise, corals die
fishes or other aquatic organisms will reduce
affects fishing livelihoods
What are the effects of coral bleaching to the ecosystem
Climate change
long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns.
While there are natural causes, human activities have been the main driver of climate change
burning of fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas (Greenhouse gas emissions)
the Ozone layer has a hole, heightening temp. etc.
Causes of climate change
Burning fossil fuels
Generates greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas Emissions
act like a blanket wrapped around the Earth, trapping the sun’s heat and raising temperatures.
Ecosystem disruption
increased strong typhoons
rising sea levels
Effects of Climate change to PH
Transportation
Factorial and industrial processes
Agriculture and land
Greenhouse gas sources
Rising global temp
Ice sheets and glaciers are shrinking; snow cover is decreasing
Sea level is Rising
Extreme Weather events
Ocean warming and acidification
Climate change warning signs - already occuring now
The Philippines is vulnerable to climate change. It has accelerating environmental deterioration, unsustainable development practices, and population growth.
The PH and climate change
Forest impacts
change in forest composition
Shift geographic range of forests
Species & Natural Areas
shift on ecological zones
Loss of habitat & species
Changing temperatures disrupt species’ life cycles
Droughts and forest impact food webs
Pollinators at risk
Effects of climate change in the Ph
Ocean warming and acidification
Sea level rise destroys coastal habitats
Climate change to Ph marine ecosystem
Oceans absorb over 90% of excess heat, leading to coral bleaching.
Higher CO₂ levels make oceans more acidic, harming marine life.
w/o coral, the predator-prey balance is disturbed, leading to population declines or overgrowth of other species
Ocean warming and acidification
Loss of one habitat affects multiple species connected to it, including humans who rely on them for food and livelihood
Sea level rise destroys coastal habitats
The Philippines’ National Climate Change Action Plan (PNCCAP)
Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies in Ph
No, it is an environmental, social, and economic issue prevalent in the Philippines.
ex. Flood control supposedly used to mitigate floods and climate change effects end up to be corrupt
Is climate change just an environmental issue?
Adaptation
actions that Help cope with climate change effects (People, species, ecosystems)
Responses or measures
that directly confront climate change impacts (flood control w/ climate change)
That build resilience to current and future climate risks (I.e. Introduce climate-resilient Rice varieties)
Adaptation examples
flood control w/ climate change
Introduce climate-resilient Rice varieties
Along coastlines in order to;
protect from typhoon, tidal waves, tsunamis
Where do we plant Mangroves
Mitigation
actions that will reduce man-made climate change
This includes action to reduce GHGs or absorb GHGs in the atmosphere.
human intervention to reduce the sources or enhance the sinks of GHGs.
solving the cause!
constructing bike lanes (sustainable transportation) and green buildings
Reducing GHG emissions
Increasing GHG sequestration through reforestation.
reducing fossil fuel use and promoting green energy
Increasing GHG sequestration
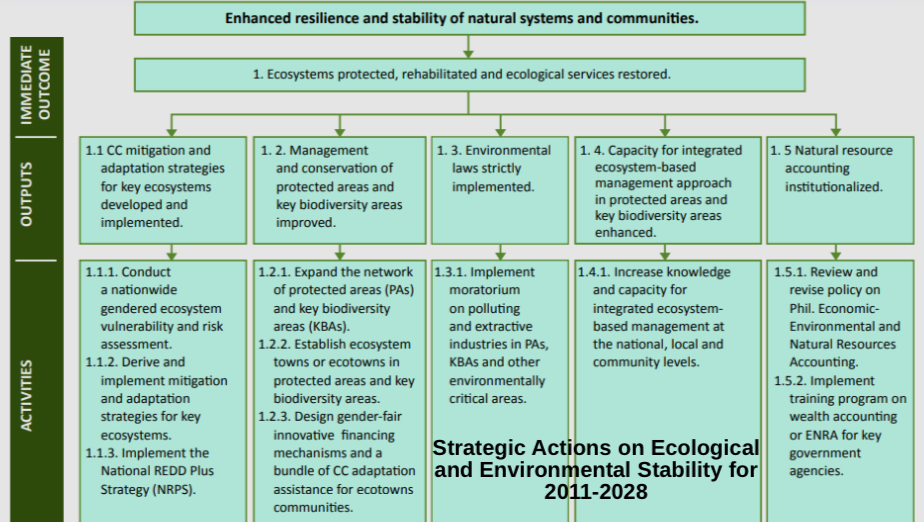
The Philippine National Climate Change Action Plan (PNCCAP)
the country’s strategic framework for addressing climate change impacts and strengthening resilience and sustainability across sectors.
It serves as the official policy guide for the government's climate change programs from 2011 to 2028, aligned with the Climate Change Act of 2009 (RA 9729).
PNCCAP legal basis
ecological and environmental stability
Increasing natural ecosystem resilience to climate change
PNCCAP priorities
PNCCAP Flow