Detection and Identification of Red Cell Antibodies
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
four types of unexpected antibodies
immune alloantibodies
naturally occurring alloantibodies
passively acquired antibodies
autoantibodies
immune alloantibodies are produced in responnse to
RBC stimulation
naturally occurring alloantibodies are caused by
exposure to environmental sources (ex: anti-D)
passively acquired antibodies
intravenous immunoglobulin
autoantibodies
antibodies directed against antigens expressed on one’s own RBCs
three main phase reactions occur in
immediate spin, 37C, and AHG
what is an antibody screen
pt. plasma + reagent screen cells
we use this to find unexpected antibodies in a patient’s plasma that may cause a transfusion reaction
antibody screens are preformed in which 3 areas of testing
donor blood testing
prenatal testing
compatibility testing for transplants (hematopoietic progenitor cells or hematopoietic stem cells, or bone marrow)
specimen requirements of blood bank
must be serum or plasma
need 5-10 mL aliquot of whole blood needed
when auto control is being tested in ab ID EDTA plasma is used
why is EDTA the preferred tube for bloodbank
it avoids the in vitro uptake of complement by red cells which can occur if clotted samples are used
three main methods of antibody testing
tube (traditional and gold standard)
gel
solid phase
what group type are the screener cells made of
group O
dosage meaning
you’ll have stronger reactions (3+ or 4+) when we have a homozygous antigen expression (considered double dose)
you’ll have weaker reactions (1+ or 2+) when we have hetereozygous antigen expression (considered single dose)
which antigens don’t show dosage
Kell, D, Lewis, I, and P
for the common blood group which antibodies show dosage
lutheran (Lua, Lub), kidd (Jka, Jkb), duffy (Fya, Fyb), Rh (C, E, c, e), MNS
Lutheran kids and duffy the rhesus monkey eat M and Ns
what is the purpose of enhancement reagents
it decreases incubation time and increases sensitivity (such as PEG)
3 possible enhancement reagents used in antibody detection
LISS
PEG (most common)
22% albumin (BSA, uncommon)
what are the differences between monospecific AHG and polyspecific AHG
monspecific contains only IgG, is expensive, and only works on one epitope/antigen
polyspecific contains IgG and C3d, cheaper, and works on multiple epitopes/antigens
check cells are also known as
coomb’s cells
why do we use check cells
to make sure there was adequate cell washing
to make sure AHG reagent was added
to make sure AHG reagent is functioning properly
limitation of antibody screen
the screen is designed to detect as many clinically significant antibodies as possible and avoid detecting as many clinically insignificant antibodies as possible
negative results should give great confidence that there were no clinically significant antibodies detected
what are check cells
type O Rh positive red blood cells coated with anti-D
what is auto control and its purpose
patient cells + patient plasma tested under the same conditions as reagent red cells are tested to looks for autoantibodies
should be tested as part of antiody ID but can be preformed with Absc
(do not confuse with DAT which tests for complement activation)
process of how to start the interpretation antibody screen results
negative and positive reactions are important in interpretation of panel
phase and strength of positive reactions helps suggest antibody specificity
negative reactions support the specificity suggested by positive reactions
single common alloantibody usually produces a clear pattern of positive and negative reactions
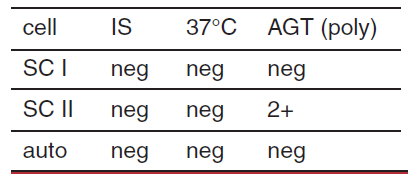
possible interpretation of antibody screen
single alloantibody
two alloantibodies, antigens only present on cell II
probably IgG alloantibody
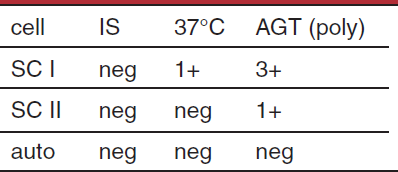
possible interpretation of antibody screen
multiple allantibodies
single alloantibody (dosage)
probable IgG alloantibody
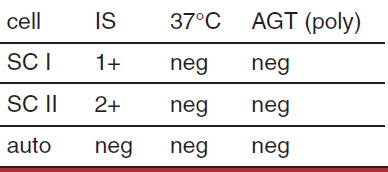
possible interpretation of antibody screen
single or multiple antibodies
probably IgM alloantibody
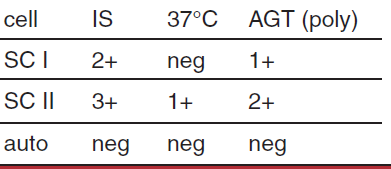
possible interpretation of antibody screen
multiple alloantibodies, warm and cold
potent cold alloantibody binding complement in AGT
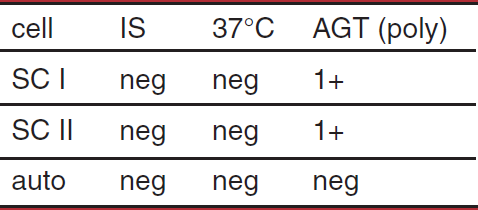
possible interpretation of antibody screen
single warm alloantibody, antigen present on both cells
antibody to high prevelence antigen
complement binding by a cold alloantibody not detected at IS

possible interpretation of antibody screen
warm alloantibodies
transfusion reaction
probable IgG alloantibody
warm autoantibody
which antibodies tend to react at immediate spin
Lea, Leb, M, N, Lua, and P
which antibodies tend to react at 37C
cold IgM antibodies (I, P1, A, B, H) and warm antibodies (D, E, and K)
which antibodies tend to react at the antiglobulin phase (AHG)
Rh antigens, Kell, Duffy, Kidd, S, s, and Lub
what does exclusion rule out mean
the process of ruling out certain antibodies as the cause of reaction
it helps narrow down the possibilities and ID the specific antibody present in the patient’s blood
list specific techniques that can be used to further ID antibodies
enzyme (common)
neutralization
elution (common)
adsorption (common)
titration
enzyme ID method
used when multiple antibodies are suspected
certain antigens are destroyed or weakened, others are enhanced, some have no effect (antigens destroyed are more likely on RBC membrane)
never used for initial panel
enzyme ID method is used for
weakly reactive antibodies present which enhance the antibody reactivity
helps differentiate between multiple antibodies present, reaction strengths, and untreated vs treated
two ways you can preform enzyme ID
one step technique (dump everything in a tube (enzyme, plasma, rbc), incubate, absc
two step proccess (preferred): RBC + enzyme then wash then add plasma
which type of ezyme treatment is preferred and why
the two step process because in babies and the elderly it gives a cleaner sample because we want to make sure everything is 100% because of transfusions and RBCs can have antigens on them
blood groups enhanced by enzymes
ABO/H, Lewis, I, P, Rh, and Kidd
blood groups decreased by enzymes
MNS, Duffy, and Lutheran
blood groups unaffected by enzymes
Kell, Diego, and Colton
neutralization ID method
soluble forms of some blood group antigens exist in body fluids (ex; plasma, urine, saliva)
this inhibits the reactivity of corresponding antibody that could mask the prescence of undelrying clinically significant, nonuetralizable antibodies
most used substances for neutralization
Lewis’s substances (most common, saliva, plasma, urine, etc)
P1 substances
Sda substances
Chido and Rogers substances
technique for neutralization
neutralizing + pts plasma then incubate
the suspected antibody should be negative (or decrease in reactivity)
the control (pt plasma + saline, incubate) should be positive
substances used for neutralization
anti-P
anti-Lewis
anti-Chido, anti-Rodgers
anti-Sda
anti-I
anti-P neutralizing substances
hydatid cyst fluid, pigeon droppings, turtledoves’ egg whites
anti-Lewis neutralizing substances
plasma or serum, saliva
anti-chido/anti-rodgers neutralizing substances
serum containing complement
anti-Sda neutralziing substances
urine
anti-I neutralizing substances
human breast milk
elution ID method
used to identify one or more antibodies attached to RBC membrane by freeing them
antibody recovered/removed is called elute
useful for removing antibodies for RBC in HDN due to ABO antibodies
how does elution work
bound antibody us reaksed from RBC antigen
this disrupts the structure of the binding site because it reverses rhe forces of attraction keep the antigen-antibody complexes together
changes thermodynamics of antigen-antibody complex
two methods for elution
lansteiner and miller heat elution
wiener’s freeze-thaw method
landsteiner and miller heat elution method is best for
cold reactive antibodies or those that have a broad temperature rnage of reactivity
weiner’s freeze-thaw method
the sample is frozen causng ice crystals to form causing hemolysis of RBCs when the sample is thawed the antibodies are released
adsorption ID method
used to remove autoantibodies
two types of adsorption techniques
autologous adsorption (using pts own RBCs)
alladsorption (using other peoples RBCs paired with elution techniques)
when picking RBCs for adsorption, the antigens that stimulate the most clinicaly significant anitbodies are
Rh, K, Duffy, S, s, and Kidd
adsorption technique
used to remove unwanted antibodies from patient serum
patient plasma (containing antibodies) is mixed with RBCs that have known antigens
unwanted antibodies in the plasma bind to the antigens on the RBCs
the RBCs with the bound antibody are removed from the serum leaving behind the rest of the other antibodies making it easier to identify the remaining ones
antibody titration ID method
measures the strength of an antibody using serial dilutions of antibody containing plasma tested against selected RBCs to determine the highest dilution casuing a positive rxn
a 4+ titer means you have a titer score of
12
a 3+ titer means you have a titer score of
10
a 2+ titer means you have a titer score of
8
a 1+ titer means you have a titer score of
5
elution and adsorption are used to detect what kind of antigens
elution is used to indentify one or more antibodies attached to the RBC membrane specifically HDFN ad HTR antigens
adsorption is used to remove autoantibodies
significance of red cell phenotyping
confirms that the antibody indentified is the correct one (its the last step of identification)
what is the number one thing MLS need to do before starting testing
check patient history (blood type, known antibodies, history of transfusion)
why is antigen typing not really preformed on a patient that hsve been transfused within 3 months
because you’ll still have circulating donor RBCs so it would cause a mixed field reaction
which method of antibody detection is useful to detect cases of HTR and HDN
elution method
what is needed on a patient label
name (spelled correctly and with first, middle inital, and last name)
DOB
time
your intials
date of draw
a unit of blood can be returned if
it’s not open
the storage temperature was maintained
it’s been within 30 minutes of the unit leaving the window
ACOS 1:1:1 ratio includes
every unit of RBCs gets one unit of FFP and one unit of PLTs
if a patient has multiple myeloma what can happen to the RBCs
agglutination mixed with rouleux
drug given for multiple myeloma
DARA
what drug causes agglutination mixed with rouleux
DARA
when you treat a patient on DARA with DTT what does it do
it wipes out the Kell blood group so you’ll have to give Kell negative blood
dolichos biflorus lectin binds with
A1 and A1B
ulex europaeus binds
H and O cells
bandeiraea simplicifolia binds
B
vicia graminea binds
N
iberis amara binds
M