Lecture 18: Age structured populations + Life History - bio 120
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Life History
The suite of strategies that shape an organism’s lifespan, timing of reproduction, offspring number, and parental investment.
Life history strategies are shaped by trade-offs: costs of reproduction vs. future survival or fecundity.
Age structured populations
Populations broken into age classes to account for variations in fecundity and survivorship across ages. Necessary for accurate models of population growth and conservation strategies.
Life tables
Summarize key life events (age of death, timing of reproduction) for an average individual in a population.
Typically focus on females, as they often limit population growth
Life table components
Survivorship schedule (lx) Probability of surviving to age x
Fecundity schedule (mx): Number of offspring produced by a female at age x.
Survivorship curves
Graphs showing lx (survivorship) over time
Types of survivorship curves
Type I: High survival early, steep decline later (e.g., humans).
Type II: Constant survival rate (e.g., birds).
Type III: Low early survival, higher survival later (e.g., plants).
Fecundity schedules
a table or function that describes the age-specific reproductive output of an individual in a population
Trade-offs exist between reproductive output and survivorship due to the cost of reproduction.
Vary widely among species depending on life history strategies.
Net reproductive rate (R0)
Average number of daughters a female produces over her lifetime.
Net reproductive rate formula
∑lxmx
R0>1: Population growing
R0<1: Population declining.
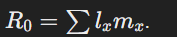
Generation Time (T)
Average age at which a female gives birth
Influences population growth rate and evolutionary fitness.
Generation Time (T) formula
∑x lx mx / R0
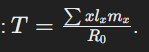
Costs of reproduction
Increased fecundity can reduce future survival or fecundity.
Trade-offs affect whether organisms favor early or delayed reproduction.
Semelparity
Single reproductive event in a lifetime (e.g., salmon, bamboo).
Often synchronized reproduction for predator satiation.
Iteroparity
Multiple reproductive events over a lifetime (e.g., elephants, humans)
Masting
Iteroparous species synchronize reproduction across populations (e.g., oak trees).
Provides benefits like predator satiation.
Reproductive value (Vx)
Expected number of future offspring an individual of age x can produce.
Important for conservation programs to focus on individuals with high reproductive value.