4.0 bile salts, fat absoprtion pathways and their role in drug absorption
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
bile
digestive fluid produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder
although mostly composed of water bile contains important substances such as
bile salts
cholesterol
bilirubin
phospholipids
the components of bile work together to emulsify fats
breaking them into smaller droplets to facilitate digestion and absorption
bile salts are derived from cholesterol,
these are the most important component for fat digestion
cholesterol excreted from the liver
in the form of bile
bilirubin
a by product of the breakdown of red blood cells, it gives bile its greenish-yellow colour
phospholipids
aid in the emulsification of fats alongside bile salts
bile salts are the most critical component of bile for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats and fat soluble vitamins
synthesised in the liver from cholesterol and stored in the gallbladder until released into the small intestine after a meal
functions of bile salts
emulsification
micelle formation
facilitation of lipase action
emulsification
bile salts emulsify large fat globules into smaller droplets increasing the surface area for fat digesting enzymes
micelle formation
they help form micelles tiny droplets that allow fats and fat soluble vitamins ADEK to be transported and absorbed
facilitation of lipase action
pancreatic lipase, the main fat digesting enzyme, requires bile salts to efficiently break down fats into free fatty acids and monoglycerides
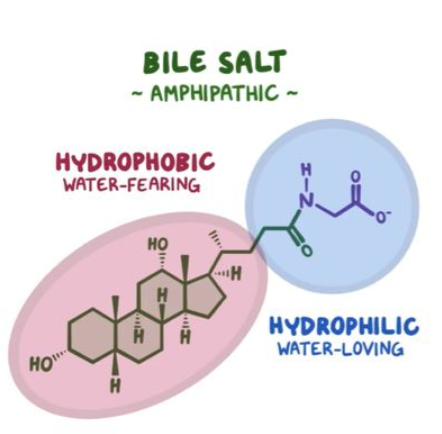
bile salts have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts
allowing them to interact with both fats AND water- this is the key to their emulsifying action
enterohepatic circulation
once bile salts have done their job in the small intestine they are reabsorbed into the ileum and returned to the liver via the portal vein for reuse, conserving resources