HDFS Final Ch 18 Socioemotional Development in Late Adulthood
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
T/F: Although global self-esteem tends to decline in late life, most adults maintain a positive view of themselves, expressing more positive than negative self-evaluations well into old age.
T
T/F: Old (70 to 84) and very old (85 to 103) adults rate themselves more positively than negatively in a variety of areas, including hobbies, interests, family, health, and personality, and these positive self-evaluations predicted psychological well-being.
T
Older adults tend to compartmentalize their self-concept more so than younger and middle-aged adults by categorizing the positive and negative aspects of self as separate roles, whereas younger and middle-aged adults tend to
integrate them into one.
The developmental task for older adults is to
accept their weaknesses and compensate by focusing on their strengths.
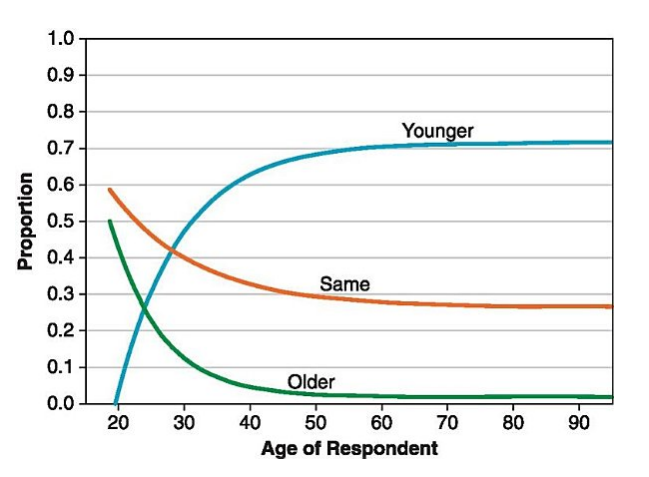
Do older adults feel younger or older?
Most older adults feel that they are younger than their years, and this tendency increases with age.
Why do older adults feel younger than their years?
One reason may have to do with avoiding the self-categorization of being old. Categorizing oneself as a member of one’s age group influences how individuals think about themselves, their competencies, and their future.
T/F: Adults with more negative self views are more likely to feel older than their years over time.
T
T/F: Even more striking, older adults who perceived themselves as younger than their real ages showed larger gray matter volume and younger predicted brain age, as assessed by MRI scans.
T
What is reminisce?
The process of telling stories from one’s past, to oneself or others.
Reminiscence, the vocal or silent recall of events in a person’s life, happens naturally in everyday conversations and serves a variety of functions.
When adults focus and ____ bitterly over difficult events, they sustain and even increase negative emotions, and show poor adjustment.
ruminate
Related to reminiscence, but more comprehensive, is
life review
What is life review?
The reflection on past experiences and one’s life, permitting greater self-understanding and the assignment of meaning to their lives.
Life review permits self-understanding and helps older adults assign ___ to their lives.
meaning
Reminiscence is fostered by encouraging _____ story telling to teach others, remember positive events, and enhance positive feelings.
autobiographical
Encouraging adults to engage in reminiscence and life review is associated with increases in
a sense of mastery, well-being, purpose in life, positive mental health (including the reduction of depressive symptoms), and social integration.
What is the last stage in Erik Erikson’s psychosocial theory?
Ego Integrity Vs Despair
What is ego integrity vs despair?
older adults find a sense of coherence in life experiences and ultimately conclude that their lives are meaningful and valuable.
Adults who achieve ego _____ can see their lives within a larger global and historical context and recognize that their own experiences, while important, are only a very small part of the big picture. Viewing one’s life within the context of humanity can make death less fearsome, more a part of life, and simply the next step in one’s path.
integrity
the alternative to developing a sense of integrity is despair, the tragedy experienced if
f the retrospective looks at one’s life is evaluated as meaningless and disappointing, emphasizing faults, mistakes, and what could have been.
The despairing older adult may ____ over lost chances and feel overwhelmed with bitterness and defeat, becoming contemptuous toward others in order to mask self-contempt.
ruminate
How does one attain ego integrity?
A sense of ego integrity relies on cognitive development, such as complexity and maturity in moral judgment and thinking style, tolerance for ambiguity, and dialectical reasoning.
The ability to realize that there are multiple solutions to problems and recognize that one’s life path may have taken many different courses is integral to developing a sense of ego integrity.
T/F: the stereotype of older adults becoming rigid and set in their ways is true.
F, it is untrue, personality traits remain stable into late adulthood as in other life periods.
Most people experience a ____-ing of personality characteristics with age.
mellowing
well-being correlates with higher levels of extroversion, agreeableness, and conscientiousness, and with lower levels of _____.
neuroticism
Fill in the blanks with the Big 5 Pers.
We have seen that well-being tends to increase over the adult years. Research from the Big 5 trait approach to personality supports this, as people in their later years tend to become happier (more ____ and less ___), more self-contented and self-centered (less ____ and __), more laid back and satisfied with what they have, and less preoccupied with productivity (less _)
more agreeable, less neurotic; less extroverted and open; conscientious
T/F: older people generally tend to NOT maintain sexual interest and do not remain sexually capable and active well into their 80s and often 90s.
F, they remain sexually capable and maintain sexual interest.
The frequency of sexual activity declines with age, but sexual satisfaction often remains _____
unchanged
T/F: The nature of sexual expression often changes in older adulthood, but most older adults remain interested in, and satisfied by, sexual activity.
T
T/F: Older adults tend to be more active participants in religion than younger people.
T
T/F: People tend to consider participation in prayer and personal religious activity as more important as they age.
T
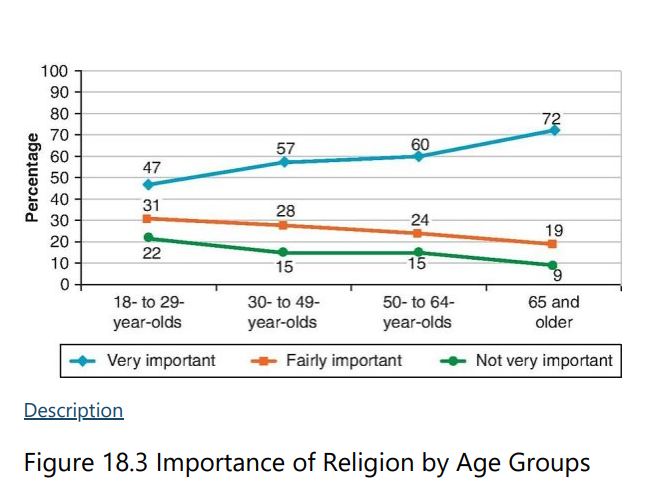
Adults are also more likely to attend religious services with age, from middle adulthood into late adulthood. Religious attendance declines in late adulthood, likely due to changes in
health, mobility, and transportation
Which type of groups in NA tend to show the highest rates of religious participation?
marginalized groups
T/F: A strong sense of religiosity can buffer stress in the face of disadvantages and stressful life events, promote resilience, and help older adults to find meaning in life
T
Religiosity is also associated with ____, a sense of self-worth, life satisfaction, and low rates of depression.
optimism
Friendships tend to improve over adulthood. In late adulthood, friendships become more important and more fulfilling, partly due to the declines in what type of responsibilities?
family and work responsibilities
With more time to devote to ____ activities, friendships become more centered on activities, such as playing card games and walking, and older adults report having more fun with their friends than do younger adults.
leisure
T/F: Older adults tend to report more meaningful relationships than younger adults.
T
Social isolation is associated with frailty and increased risk of ____ after suffering a fractured bone.
mortality
What % of older adults have a biological sibling?
85%
Older adults who have never married or who have no children rely more on ____ for support than do those who have been married or have children.
siblings
Widowed adults show increased reliance on ____.
siblings
T/F: Marriages in older adulthood are characterized by greater satisfaction, less negativity, and more positive interactions than in other developmental periods.
T
T/F: Compared with middle-aged adults, older adults perceive more positive characteristics and fewer negative characteristics in their partners. They also show greater positive sentiment override—that is, they appraise their spouse’s behavior as more positive than do outside observers. In other words, older married adults tend to view their spouses through rosecolored glasses—and viewing one’s spouse positively predicts marital satisfaction.
T
_____ provides the opportunity for couples to spend more time together.
Retirement
T/F: the empty nest, retirement, and chronic illnesses are related to divorce.
F. Contrary to popular belief, the empty nest, retirement, and chronic illnesses are not related to divorce.
T/F: Adults in long-term marriages may find it more difficult to adjust to divorce than do younger adults.
T
Social support is important for well-being throughout adulthood, but it is especially important in adjusting to ____.
divorce
Many older adults choose ______ over remarriage.
cohabitation
Many older adults enter cohabiting relationships as an alternative to ___.
marriage
Older adults may be less interested in marriage because they are past the age of ____. They also may be more interested in protecting the ___ they have accrued over their lifetime than they are in pooling economic resources.
childbearing; wealth
T/F: An older adult in a cohabiting union will be as happy as an older adult who is married.
T. In older adulthood, cohabitating unions are similar to marriages in terms of adults’ reports of emotional satisfaction, pleasure, openness, time spent together, perceived criticism and demands, and overall well-being.

Adult child-to-parent assistance most often takes the form of ____ ___ and ______, which helps older adults cope with and compensate for losses such as disabilities and widowhood.
emotional support and companionship
T/F: Overall, adult daughters tend to be closer and more involved with parents than sons, speaking with and visiting more often than sons.
T
The quality of the grandparent relationship is influenced by the degree of ____ in the grandchild’s life.
involvement
Over time, contact with grandchildren tends to decline as young and middle-aged grandchildren take on time-consuming family and work roles, but affection between grandchildren and grandparents tends to remain (weak/strong).
strong
About how many older adults experience elder maltreatment?
1 in 10 adults

What is elder maltreatment?
Acts or omissions of care that cause harm to the older person and occur within the context of a trusting relationship, such as physical, sexual, psychological, or financial abuse.
Which type of abuse is particularly common in elder maltreatment?
Financial abuse is particularly common.
Who are the most common perpetrators of elder maltreatment?
Most cases of elder maltreatment are perpetrated by caregivers, most often spouses or children, who lack social support; experience psychological, physical, or substance abuse problems; and feel overwhelmed with the task of caregiving.
Within nursing homes, institutional factors such as overcrowding and understaffing contribute to caregiver stress and can increase the likelihood of
elder maltreatment
Elder abuse is an outgrowth of what?
caregiver stress and burnout. aiding caregivers can lessen the likelihood of abuse.

What is disengagement theory?
The view that declines in social interaction in older age are due to mutual withdrawal between older adults and society as they anticipate death.

T/F: Disengagement theory is a reliable, mostly correct belief.
F. An early view, disengagement theory, is worth mentioning because it is a commonly held, though incorrect, belief.
Research has shown that the central tenet of disengagement theory is not true. Rather than disengage, most older individuals prefer to remain active and engaged with others and they benefit from social engagement.
What is activity theory, in contrast to disengagement theory?
The view that older adults want to remain active and that declines in social interaction are not a result of elders’ desires but are a function of social barriers to engagement.
AKA When older adults lose roles due to retirement or disability, they attempt to replace them in an effort to stay active and busy. (mama)
T/F: civic engagement in social and productive activities reduced mortality as much as did physical fitness.
T!
What is continuity theory?
The perspective that older adults strive to maintain continuity and consistency in self across the past and into the future; successful elders retain a sense that they are the same person they have always been despite physical, cognitive, emotional, and social changes.
Despite changing roles, people are motivated to maintain their habits, personalities, and lifestyles, adapting as needed to maintain a sense of continuity, that they are the same person they have always been. What theory does this description refer to?
Continuity theory: The perspective that older adults strive to maintain continuity and consistency in self across the past and into the future
Older adults tend to seek ____: familiar people, familiar activities, and familiar settings.
routine
What is the socioemotional selectivity theory?
The perspective that as the emotional regulation function of social interaction becomes increasingly important to older adults, they prefer to interact with familiar social partners, accounting for the narrowing of the social network with age.
Whereas young adults often turn to friends for information, older adults often have accumulated decades of knowledge. Instead, what priorities do older adults have for having friends?
the emotion-regulating function of social relationships, feeling good, that becomes more important during older adulthood.
T/F: As perceived time left diminishes, people tend to discard peripheral relationships and focus on important ones, such as those with close family members and friends.
T

It’s true that older adults have fewer relationships in comparison with young adults, but their relationships are more what?
particularly close, supportive, and reciprocal
Older adults become increasingly motivated to derive _____ meaning from life and thereby cultivate _____ (same) -ally close relationships and disengage from more peripheral social ties.
emotional; emotionally
Despite an overall decline in the number of relationships in late adulthood, this process of strengthening and pruning relationships is associated with positive well-being. It allows older adults to focus their limited time and energy on relationships that are most beneficial while avoiding those that are inconsequential or detrimental, thereby maximizing their emotional well-being. In this sense, social selectivity is what type of strategy?
an emotional regulation strategy
Older adults who live in the suburbs tend to be healthier and wealthier and show higher rates of life satisfaction than those who live in ___
cities
Which types of neighborhoods are less compact and have older adults walk less which can influence health and ability to live independently?
suburban
T/F: Generally, urban older adults have better access to transportation and health and social services than do those in suburban and rural settings, enhancing their opportunities for social participation.
T
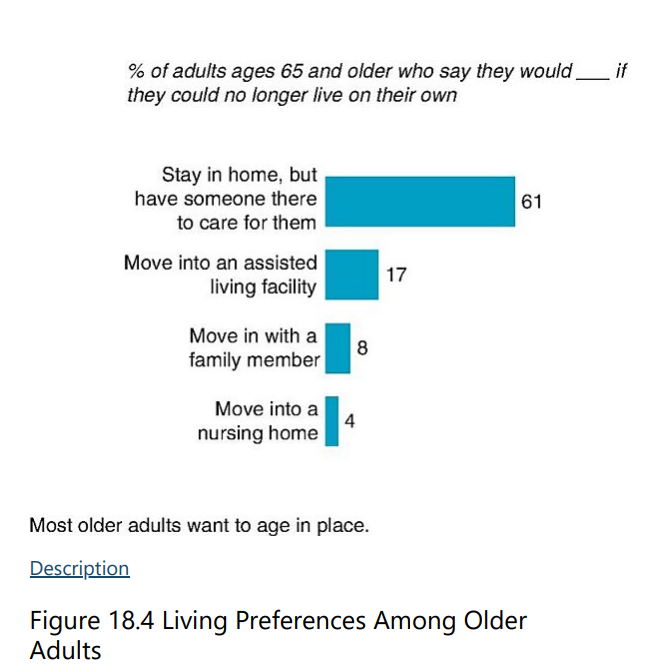
The majority of older adults prefer to age in their homes, referred to as
aging in place
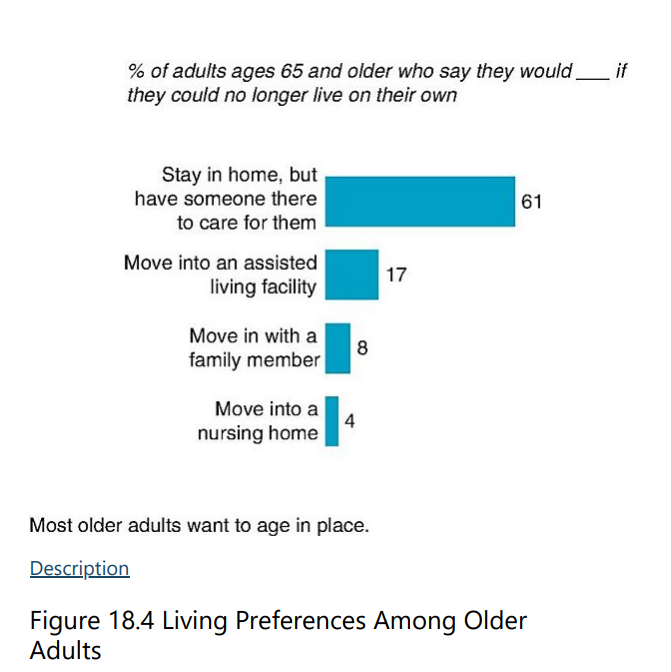
T/F: The majority of older adults prefer NOT to age in their homes.
F. They do, and this is called aging in place.
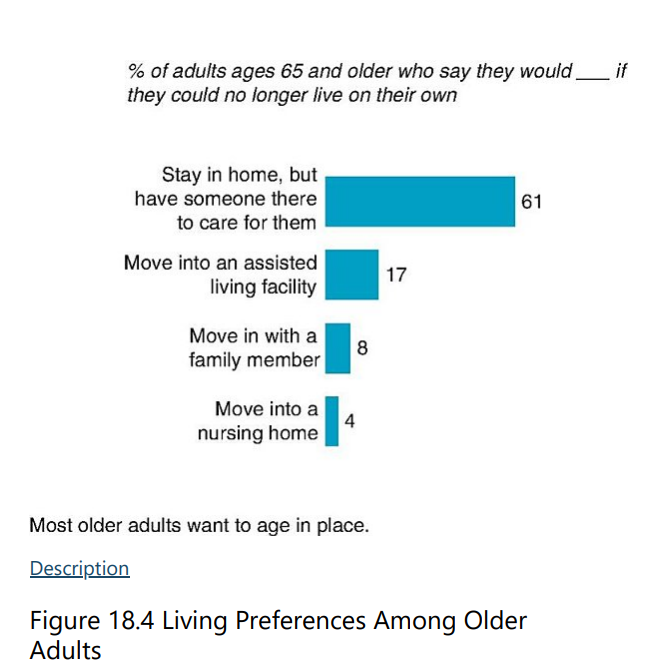
T/F: Most older adults live in or near the home they have lived in most of their lives.
T
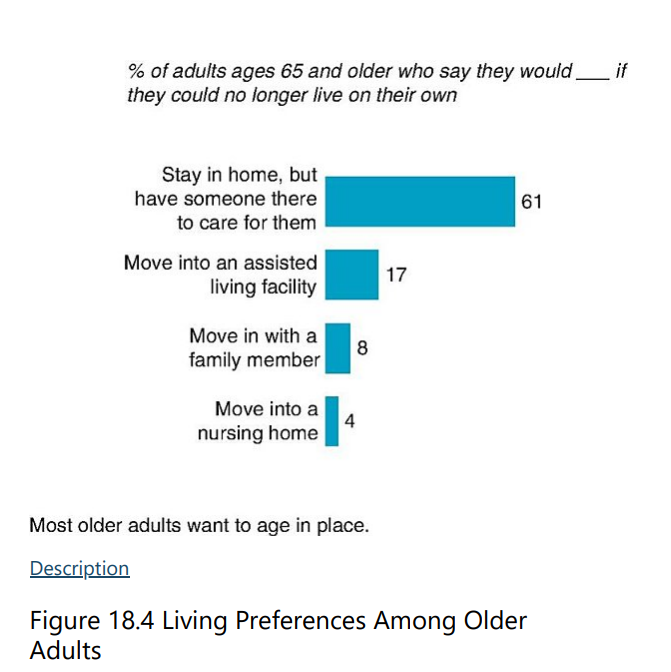
Despite the challenges, remaining in a lifelong home strengthens adults’ feelings of ____ with the past, aids their sense of identity, as well as maintains connections with the community, an important source of support.
continuity
When older adults are healthy and not physically impaired, living in their own home permits them the greatest degree of ___ over their lives, such as choosing what and when to eat.
control
Most adults prefer to age in place and retain their independence. As health declines, living alone poses physical and psychological risks, such as social isolation and loneliness. Despite the challenges, remaining in a lifelong home strengthens elders’ feelings of ____ with the past, aids their sense of identity, as well as maintains connections with the community, an important source of support.
continuity
T/F: Adults in residential settings significantly differ from those in regular homes with regard to their sense of wellbeing or feelings of loneliness.
F. Although adults in residential settings did not differ from those in regular homes with regard to their sense of wellbeing or feelings of loneliness, those in residential communities participate more frequently in social activities.
The main drawback to residential communities are
their cost, which may entail purchasing an apartment, or renting for $2,000 or more per month in the United States.
A nursing home is
a facility that provides care to older adults who require assistance with daily care and health issues
Nursing homes offer the greatest amount of care, 24 hours a day and seven days a week, but also are most restrictive of adults’ ____.
autonomy
T/F: Most older people prefer the nursing home because it provides a sense of caretaking they otherwise do not obtain from their children.
F. Most older people prefer to avoid living in nursing homes, if possible.
Encouraging social interaction in communal spaces, allowing residents to furnish and deinstitutionalize their spaces with some belongings, and modifying their environments to meet their changing needs while retaining as much autonomy as possible can help residents adapt to what type of living situation?
nursing home living.
Improved health and ____ enable adults to work many more years.
longevity
T/F: Working in late life, or retiring for that matter, are decisions that are often out of older adults’ control because of finances, health, or circumstances.
T
T/F: The reality of retirement planning is that plans may change quickly and unexpectedly.
T
What is a critical influence on the timing of retirement?
Health. Adults with poor health and visual and hearing impairments tend to retire earlier than their peers.
Retirement ages tend to vary with job conditions. Workers tend to retire early from jobs that are
stressful or hazardous.
Older adults tend to delay retirement from jobs that are
highly stimulating, take place in pleasant environments, and are a source of identity and self-esteem
Some adults cite the desire to maintain a ____ and enjoyment as reasons to work
routine
T/F: Workers in professional occupations and those who are self-employed tend to stay in their jobs shorter as compared with those in blue-collar or clerical positions.
F, longer.
Apart from health, what else is a large influence on whether and when an older adult retires?
Financial resources.
Which demographic are disproportionately at risk to live in poverty during retirement?
Black older adults