ASTRONOMY EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Earth

the third planet from the sun; an inner planet (inside the asteroid belt); only known habitable planet; 71% of surface covered with liquid water
Pluto
previously classified as the ninth planet from the sun; usually now classified as a minor planet or dwarf planet; has five moons
Makemake
a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt
Dwarf Planet
a small planet not large enough to clear its orbit of debris
Example.
Pluto
Period (of a Comet)
the amount of time it takes for a comet to orbit the sun
Example.
Halley's Comet has a period of about 75 years
Meteor
a meteoroid that has entered Earth's atmosphere
Meteoroids
small bodies of debris from space which move into Earth's atmosphere and can then turn into meteors
Mars

the fourth planet from the sun; an inner planet (inside the asteroid belt); the "Red Planet"; home to Olympus Mons, the tallest mountain in the solar system;
Asteroid Belt
the region of space between Mars and Jupiter containing most of the solar system's asteroids
Solar System
a star, as well as the planets, satellites, asteroids, and all the other objects orbiting it, travelling together through space
Comet
a body made of ice and dust in the sun's orbit; contains a gas and dust "tail"
Example.
Halley's Comet
Jupiter

the fifth planet from the sun; an outer planet (outside the asteroid belt); largest planet; over twice as massive as all the other planets combined; has four large moons; about 90% hydrogen and 10% helium
Neptune

the eighth planet from the sun; an outer planet (outside the asteroid belt); methane in the atmosphere absorbs red light to make it appear blue; gives off over twice as much energy as it receives from the sun
Go back to previous term
reveal term definition
Go to next term
Celestial Bodies
a physical object in space which has observable characteristics
Example.
planet
Haumea
a dwarf planet with an orbit beyond Neptune
Planet
a body moving in orbit around a star; large enough to clear debris in its orbit; has enough gravity to make it round
Example.
Earth
Virgo Supercluster
a supercluster of galaxies that contains the Local Group and spans over 100 million light-years
Oort Cloud
a shell of comet bodies which orbit the sun
Nebula
a gas and dust cloud in space
Example.
Orion Nebula
Neutron Star
a small star with high density; made of closely packed neutrons
Example.
Crab Pulsar
Constellations
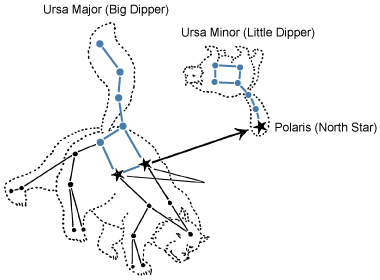
a star grouping which forms a pattern; we have ascribed images to the constellations
Example.
Orion
Saturn
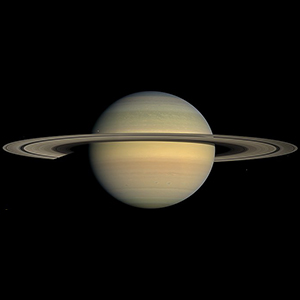
the sixth planet from the sun; an outer planet (outside the asteroid belt); the least dense planet; has a complex ring system
Planetoids
bodies that orbit the sun that are smaller than planets and larger than asteroids
Example.
dwarf planets
Friction
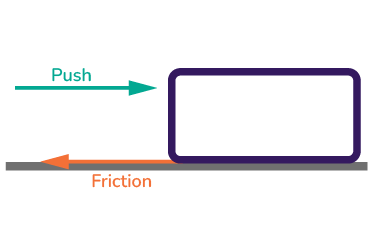
the force, in the opposite direction of motion, between two objects moving over one another
Milky Way Galaxy
the spiral galaxy in which our solar system is located
Asteroids
small, rocky bodies in the sun's orbit
Example.
Ceres
Stars
a gaseous body which produces radiant energy through nuclear fusion reactions
Example.
the sun; Sirius
Small Solar System Bodies (SSSBs)
all small bodies in the solar system except planets, dwarf planets, and satellites; name was accepted in 2006
Example.
asteroids, comets, meteors, minor planets
Shooting Star
a streak of light in the night sky caused as a meteor burns up in the atmosphere
Black Hole
an object with gravity great enough that it does not allow radiation or matter to escape
Satellite
an object or body that orbits another object or body
Example.
Earth's moon
Moons
satellites which orbit planets
Example.
Phobos
Venus

the second planet from the sun; an inner planet (inside the asteroid belt); slightly smaller than Earth; similar density and chemical composition to Earth
Kuiper Belt
a flat disc of comets, asteroids, and other small icy objects that orbit the sun at a distance beyond Neptune
Uranus

the seventh planet from the sun; an outer planet (outside the asteroid belt); composed mostly of rock and ice; has 27 named moons
Minor Planets
synonym for planetoid, also includes large asteroids
Mercury
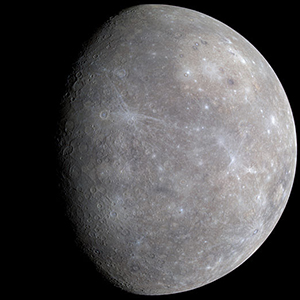
the first planet from the sun; an inner planet (inside the asteroid belt); slightly larger than Earth's moon; experiences extreme temperature variations; large iron core
Exoplanets
planets which orbit stars outside our own solar system
Example.
Proxima Centauri b
Local Group
a group of galaxies that contains the Milky Way galaxy and spans almost 10 million light-years
Galaxies
a system of stars and their systems held together by gravity
Example.
Milky Way Galaxy
Binary Stars
a two-star system; the stars rotate around a common point, or one star rotates around the other
Example.
Castor
Meteorite
what remains of a meteor after it hits the surface of the earth
Eris
the most massive and second largest dwarf planet in the solar system
Ceres
a dwarf planet located in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter