SCM Class 15 - Issues in Scheduling and Coordination
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Planning and control:
A set of tactical and execution-level business activities that includes:
master scheduling
material requirements planning
production activity control
vendor order management
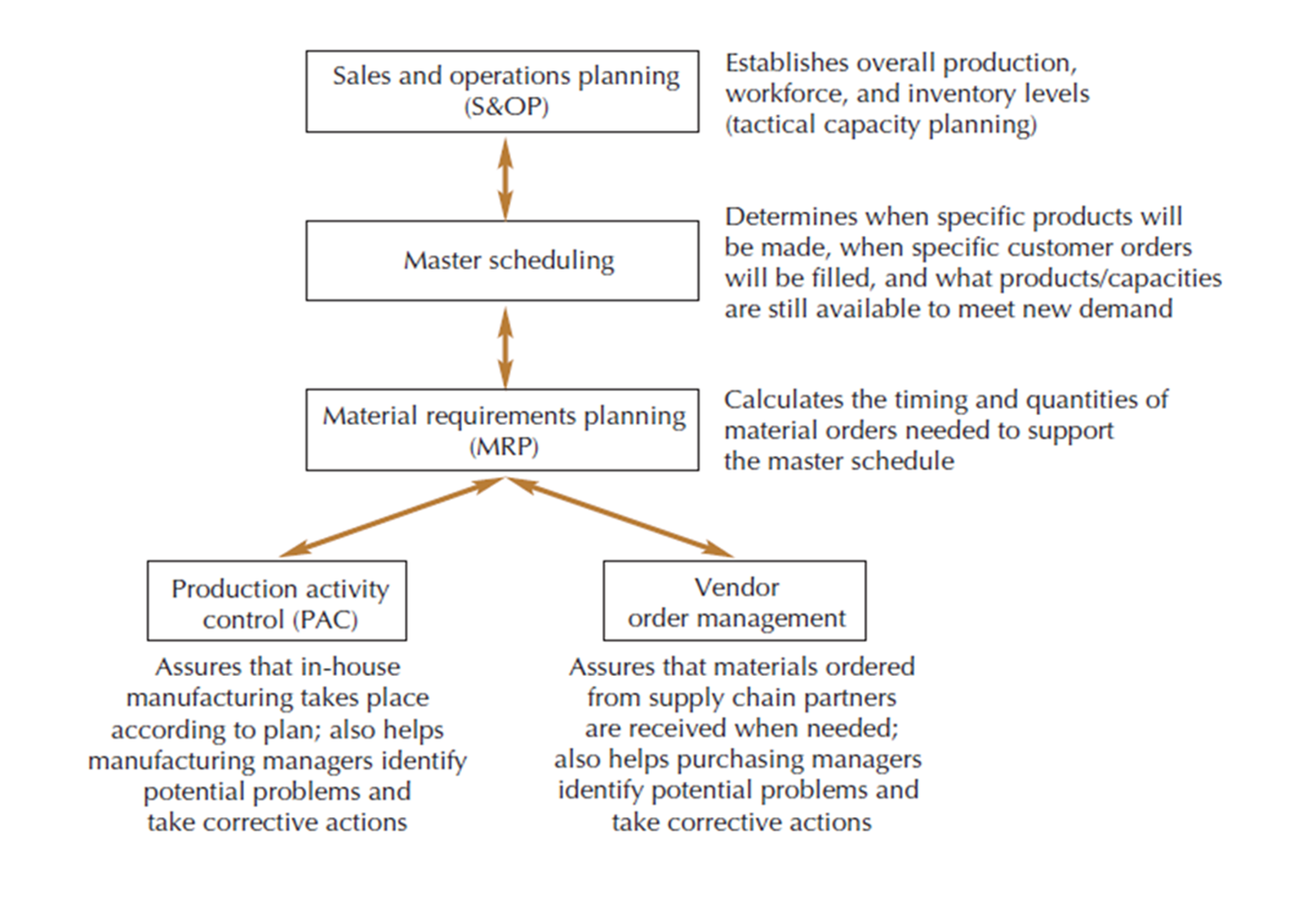
Master Schedule
a detailed planning process that tracks production output and matches this output to actual customer orders
TRACKS PRODUCTION OUTPUT AND MATCHES IT TO CUSTOMER ORDERS
makes specific the overall resource levels established by S&OP
states when and quantities products
links production with specific customer orders
Purpose:
maximize labor and equipment utilization
minimize costs
ensure adequate finished goods inventories to fill customer orders on time
match the average production rate with the average sales rate over planning horizon
Master Schedule Record
Forecasted demand: Estimate of future demand during the planning period
Booked orders: Confirmed customer orders for shipment
Projected inventory levels: Calculation of future inventory levels
Production quantities: Master Production Schedule (MPS): Planned quantity of products to be produced
Units still available to meet customer needs (Available to Promise) after filling Booked orders
Master Production Schedule (MPS)
The amount of product that will be finished and available for sale at the beginning of each week.
The MPS drives more detailed planning activities, such as Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
Planning Horizon
the amount of time the master schedule record or MRP record extends into the future
the longer the production and supplier lead times, the longer the planning horizon must be
projected ending inventory
best estimate of what inventory levels will look like at the end of each planning period
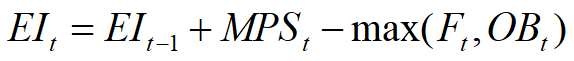

available to promise
a field in the master schedule record that indicates the number of units that are available for sale each week, given those that have already been promised to customers
First Week ATP
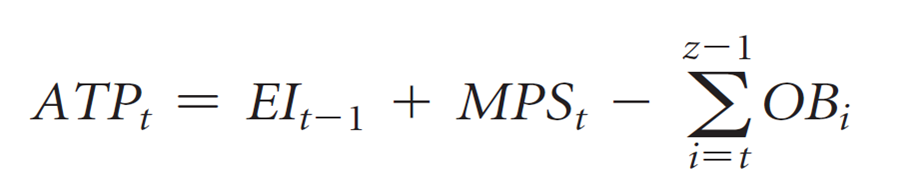
Subsequent week atp
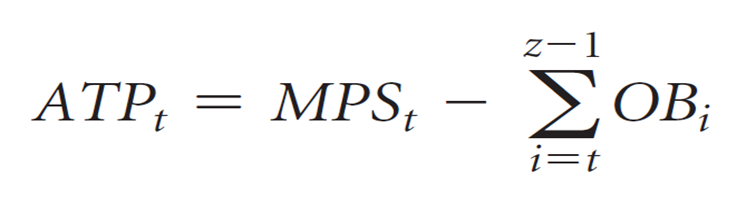
if mps=0, then there is NO ATP
Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
A planning process that translates the master production schedule (Independent Demand Items) into planned orders for the actual parts and components needed (Dependent Demand Items) to produce the master schedule.
independent demand: for finished goods - products made up of purchased or produced components and materials
dependent demand: raw materials and work in progress - components and materials used to create independent demand items
bill of materials: recipe for an independent demand item - a list of all the dependent demand items used to create the finished product
product tree structure: graphical or outline representation of all components involved in building the independent demand item
calculates future needs for components and raw materials by exploding the bill of material
planning lead time
backward scheduling
Planning Lead Time
the time from when a component is ordered (produced) until it arrives and is ready to use
Backward Scheduling
MRP calculates when dependent demand items must be ordered and when sub assembly stuff needs to be produced to complete independent demand item on schedule