Surveying 1- PRELIM
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:30 PM on 11/20/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
1
New cards
Plane Surveying
the process of surveying by assuming that the earth is flat.
2
New cards
Geodetic Surveying
a process of surveying by considering the curvature or spherical shape of the earth.
3
New cards
City Survey
an extensive co-ordinated survey of the area within the limits of a municipally made for the purposes.
4
New cards
Forestry Survey
survey executed in connection with forest management and mensuration, and the production and conservation of forest land
5
New cards
Hydrographic Survey
They are of general importance in connection with navigation development of water supply and resources, flood control, irrigation and etc.
6
New cards
Topographic Survey
locates all surface features of a property, and depicts all natural and artificial features and elevations.
7
New cards
Route Survey
a data collection operation to gather information about the proposed route of a roadway, utility pipe, or railway.
8
New cards
Photogrammetric Survey
the branch of surveying in which maps are prepared from photo-graphs taken from ground or air stations.
9
New cards
Chains and tapes
measuring distances (horizontal)
10
New cards
Level
simple instrument designed to determine whether a surface is level or plumb (vertical)
11
New cards
Field notes
prepared to record all pertinent information, measurements, calculations, sketches, and observations made by the surveyor during the course of a survey
12
New cards
surveyor
professional person with the academic qualifications and technical expertise to conduct one, or more, of the following activities;
-to determine, measure and represent the land, three-dimensional objects,
point-fields, and trajectories;
-to assemble and interpret land and geographically related information;
-to determine, measure and represent the land, three-dimensional objects,
point-fields, and trajectories;
-to assemble and interpret land and geographically related information;
13
New cards
Land Information Systems (LISs) and Geographic Information Systems (GISs)
areas of activity that have rapidly assumed positions of major prominence in surveying
14
New cards
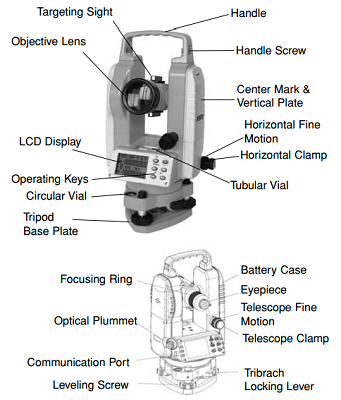
Transits and Theodolites
These tools are used to measure both horizontal and vertical angles.
15
New cards
error
difference between a measured quantity and its true value, caused by imperfection in the measuring instrument, by the method of measurement, by natural factors such as temperature, or by random variations in human observation
16
New cards
Systematic Errors
repetitive errors that are caused by imperfections in the surveying equipment
17
New cards
Accidental Errors
difference between a true quantity and a measurement of that quantity that is free from blunders or systematic errors.
18
New cards
Mistakes
a significant mistake caused by human error
19
New cards
Mistakes
it is due to the inattention or carelessness of the it is due to the inattention or carelessness of the surveyor
20
New cards
discrepancy
difference between two observed values of the same quantity
21
New cards
Precision
the degree of refinement or consistency of a group of observations and is evaluated on the basis of discrepancy size
22
New cards
Accuracy
the absolute nearness of observed quantities to their true values
23
New cards
Most Probable Value
If two or more measurements of the same quantity are made, usually different values are obtained due to random errors
24
New cards
Error of Closure
difference between a measured quantity and its true, or actual, value
25
New cards
Relative Accuracy
For horizontal distances, the ratio of the error of closure to the actual distance
26
New cards
Weights are inversely proportional to the square of the corresponding probable errors.
W∝1/e^2
27
New cards
Weights are also proportional to the number of observations.
W∝ N
28
New cards
W∝1/D
Errors are directly proportional to the square roots of distances.
29
New cards