Zoo-Lec (Sem-1) Chapter 2: Structure and Function of Animal Cells
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
plasma membrane
a selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells
phospholipid bilayer
a double layer of phospholipids that makes up plasma and organelle membranes.
two hydrophobic "tails"; hydrophilic phosphate "head"
what each phosphilipid molecule contains
cholesterol
a sterol present in plasma membranes; modulates membrane fluidity; fills in spaces between hydrocarbon chains making the membrane less permeable to very small ions and molecules
membrane proteins
transport ions and various molecules across the membrane, are points of attachment for cellular structures, form junctions between cells, serve as hormone receptors, and function as enzymes
monolayer-associated proteins
membrane protein; attach to the inner and outer membrane surfaces
transmembrane proteins
membrane protein; proteins imbedded in the membrane
glycoproteins; glycolipids
the carbohydrate layer on the outer surface of eukaryotic cells
glycoproteins
carbohydrate chains attached to proteins
glycolipids
carbohydrate chains attached to lipids
glyco; kalyx
Greek for "sugar"; "coat"
glycocalyx
a capsule made up of a fuzzy coat of sticky sugars; protection from chemical and mechanical damage; cell recognition; cell adhesion
selective permeability
a property of a plasma membrane that allows some substances to cross more easily than others.
lipid bilayer
primary barrier to movement across a membrane; hydrophobic molecules cannot permeate these fatty layers
nerve impulse
action potential; occurs when membrane channels open and close allowing sodium and potassium ions to move in specific directions
protein transporters
proteins in the cell membrane of the pre-synaptic neuron that actively pump neurotransmitters back into the pre-synaptic cell
concentration gradient
the difference in concentration of a substance between two points of reference
simple diffusion
nontransporter gradient exchanges; movement of a solute from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
osmosis
nontransporter gradient exchanges; diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
aquaporins
nontransporter gradient exchanges; channel proteins that facilitate the passage of water
aqua; porus
Latin for "river"; "tiny opening"
tonicity
nontransporter gradient exchanges; relative concentration of solutes in the water inside and outside the cell
tonus
Greek for "tension"
isotonic
nontransporter gradient exchanges; no net movement of water molecules
isos
Greek for "equal"
hypertonic
nontransporter gradient exchanges; when comparing two solutions, the solution with the greater concentration of solutes
hyper
Greek for "above"
crenation
nontransporter gradient exchanges; hypertonic; shrinking of cells
hypotonic
nontransporter gradient exchanges; when comparing two solutions, the solution with the lesser concentration of solutes
hypo
Greek for "under"
lysis
nontransporter gradient exchanges; hypotonic; swelling/bursting of cells
filtration
nontransporter gradient exchanges; a process that forces small molecules and ions across selectively permeable membranes with the aid of hydrostatic (water) pressure
facilitated diffusion
carrier-mediated transport; does not require energy; requires a concentration gradient; involves transport proteins; saturation of proteins can occur
active transport
low to high concentration; moves molecules across a selectively permeable membrane against a concentration agent; requires ATP (adenosine triphosphate) energy
uniporters
transport a single type of molecule or ion
symporters
transport two molecules or ions in the same direction
antiporters
transport two molecules or ions in the opposite direction
energy
the capacity to do work
metabolism
sum of all chemical reactions in a living organism
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
organic molecule that acts as the main energy carrier of cells
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
low-energy molecule that can be converted to ATP
ATP cycle
the bonds between the second and third phosphates are continually broken and reformed in a cycle
Inorganic Phosphate (Pi)
the phosphate used during the transfer of energy from organic molecules when ATP is formed from ADP
enzymes
mediators of metabolism; proteins; required in small amounts; not altered irreversibly in chemical reactions; remarkably adept catalyst; highly specific; activity can be regulated
substrates
the reactants of enzyme-catalyzed reactions
catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
energy of activation
the amount of energy required to start a reaction
cellular respiration
the process by which cells use oxygen to produce energy from food
aerobic cellular respiration
a metabolic process where cells convert glucose and oxygen into energy, carbon dioxide, and water; a process where oxygen is required to metabolize glucose
glycolysis; citric acid cycle; electron transport chain
key steps of cellular respiration
glycolysis
the breakdown of glucose by enzymes, releasing energy and pyruvic acid; occur at rapid rates
cytosol/cytoplasm
where glycolysis occurs
four
number of ATP molecules produced in glycolysis
two
number of ATP molecule and NADH net gain in glycolysis
lactate fermentation
anaerobic carbohydrate breakdown pathway that produces ATP and lactate
pyruvate and lactate
end products of glycolysis
substrate-level phosphorylation
occurs when a phosphate group is transferred directly to ADP from a high-energy donor
fermentation
what aerobic organisms rely on when oxygen levels are low
mitochondria
where the rest of the aerobic cellular respiration processes (citric acid cycle and electron transport chain) occur after glycolysis; double membrane-bound organelles whose inner membranes fold to form incomplete partitions called cristae
mitochondrial matrix
fluid filled area inside the inner mitochondrial membrane; it contains enzymes, coenzymes, and other molecules used in the transition step and the citric acid cycle
transition events
prepare each pyruvate molecule that was produced in glycolysis for entry into the citric acid cycle
citric acid cycle
a set of reactions that begin when acetyl-CoA donates its acetyl (C2) group to oxaloacetate (aC4), resulting in a six-carbon molecule called citric acid or citrate
eight
number of intermediate compounds in the citric acid cycle
CO2 and oxaloacetate
citric acid, when processed, results in:
NAD+ - NADH; FAD - FADH2
coenzymes reduced in citric acid cycle
four CO2 molecules; two ATP molecules; six NADH molecules; two FADH2 molecules
result of two turns of the citric acid cycle
Guanosine triphosphate (GTP)
an energy transfer molecule similar to ATP that releases free energy with the hydrolysis of its terminal phosphate group
electron transport chain
produces nearly all ATP molecules used by animals
intermembrane compartment
the space between the inner and outer mitochondrial membrane
proton pumps
specialized proteins embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane
proton gradient
a gradient formed by the difference in proton concentrations across a membrane
ATP synthase
an enzyme used to form ATP through a process called chemiosmotic phosphorylation
chemiosmotic phosphorylation
reactions that produce ATP using ATP synthase and the potential energy of a proton gradient
3 ATPs
1 NADH =
2 ATPs
1 FADH2 =
nucleus
Latin for "kernel" or "nut"; contains the DNA and is the control and information center of the eukaryotic cell; location where genetic information from DNA is transcribed into RNA
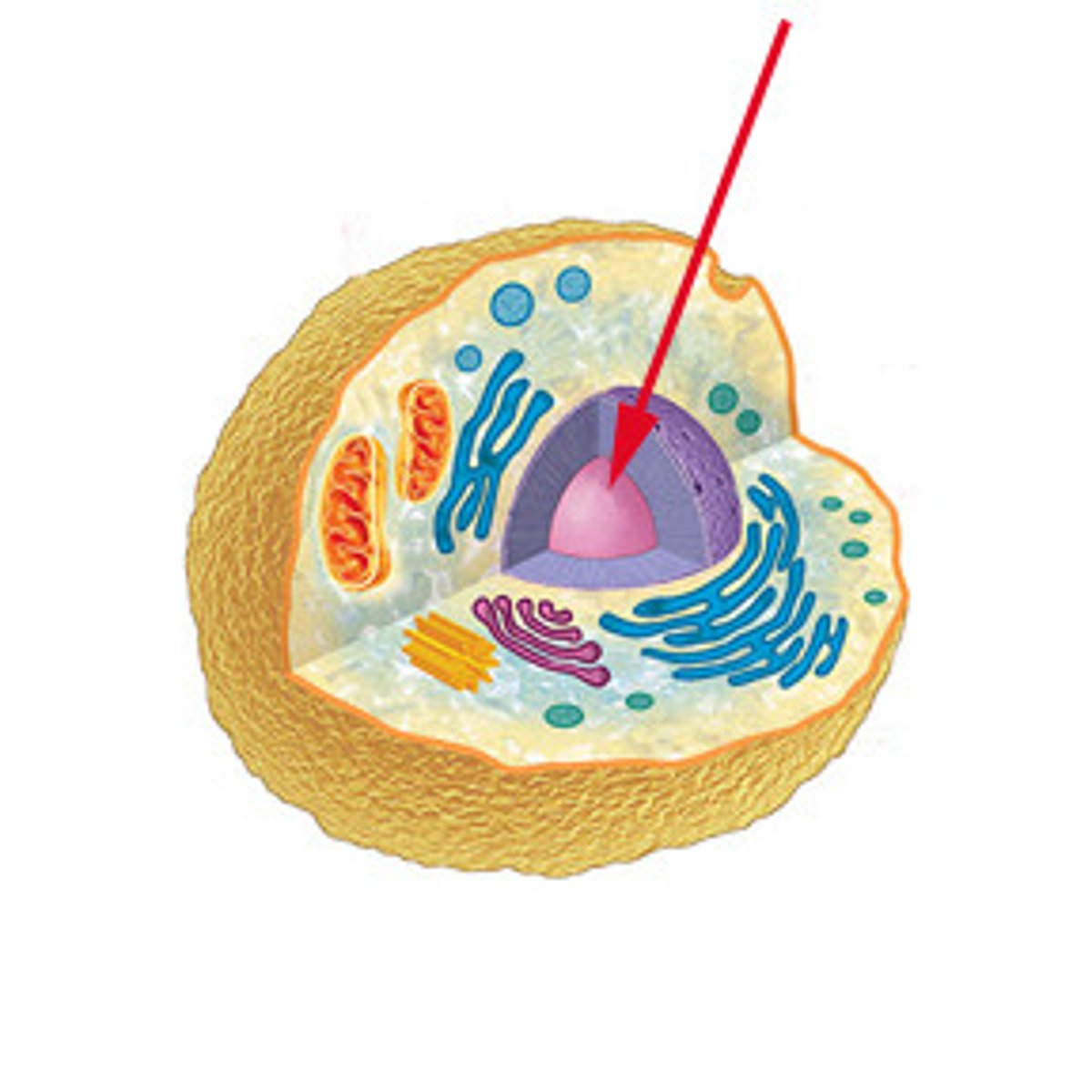
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose; then translated at ribosomes into proteins (e.g. enzymes) that determine a cell's activities
central dogma
DNA -> RNA -> Protein
nuclear envelope
a membrane that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm and is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum at a number of points
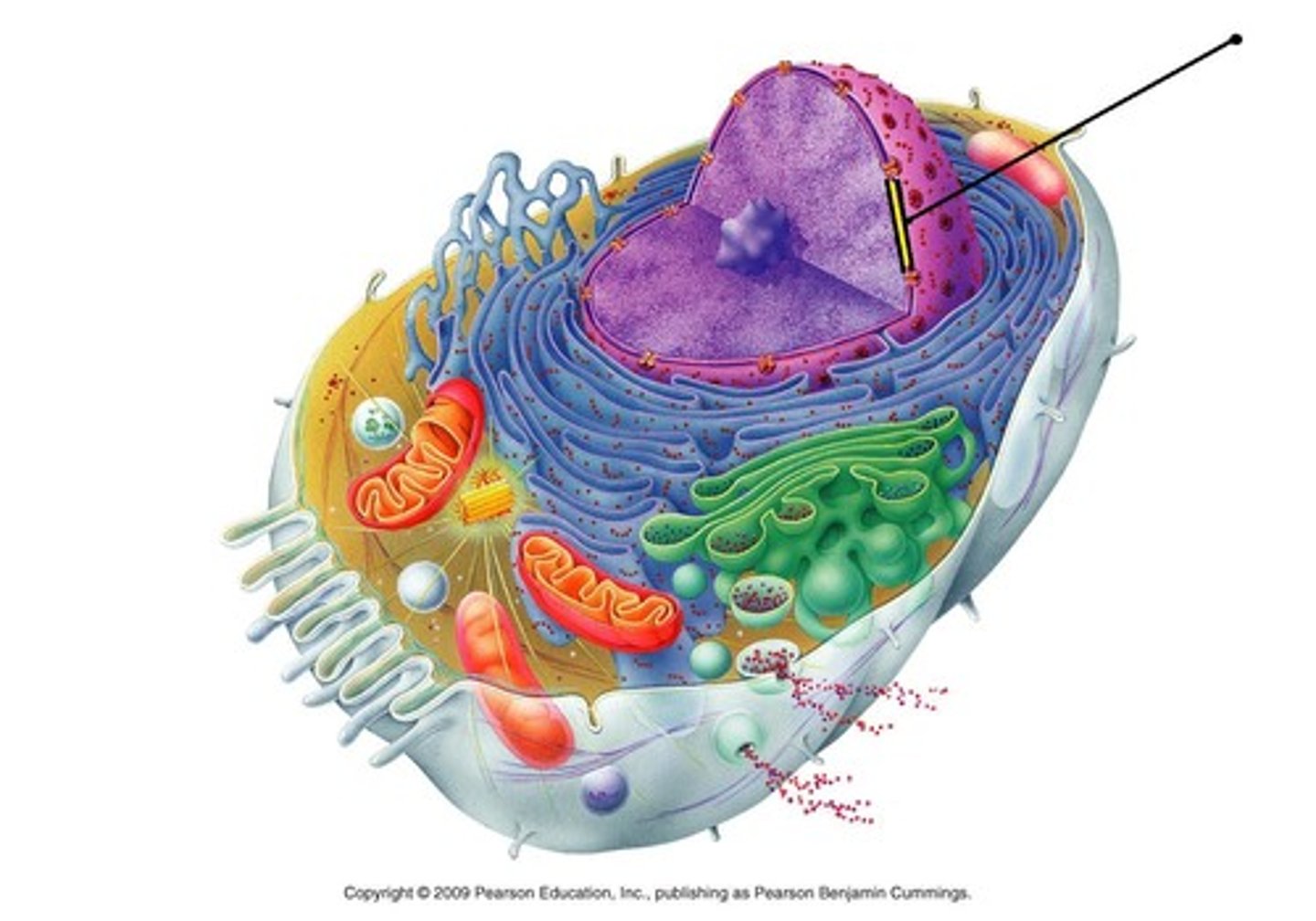
nuclear pores
holes in the nuclear envelope that are globular and filamentous proteins; they prevent DNA from leaving but permits RNA to be moved out; allow the nucleus direct contact with the endoplasmic reticulum
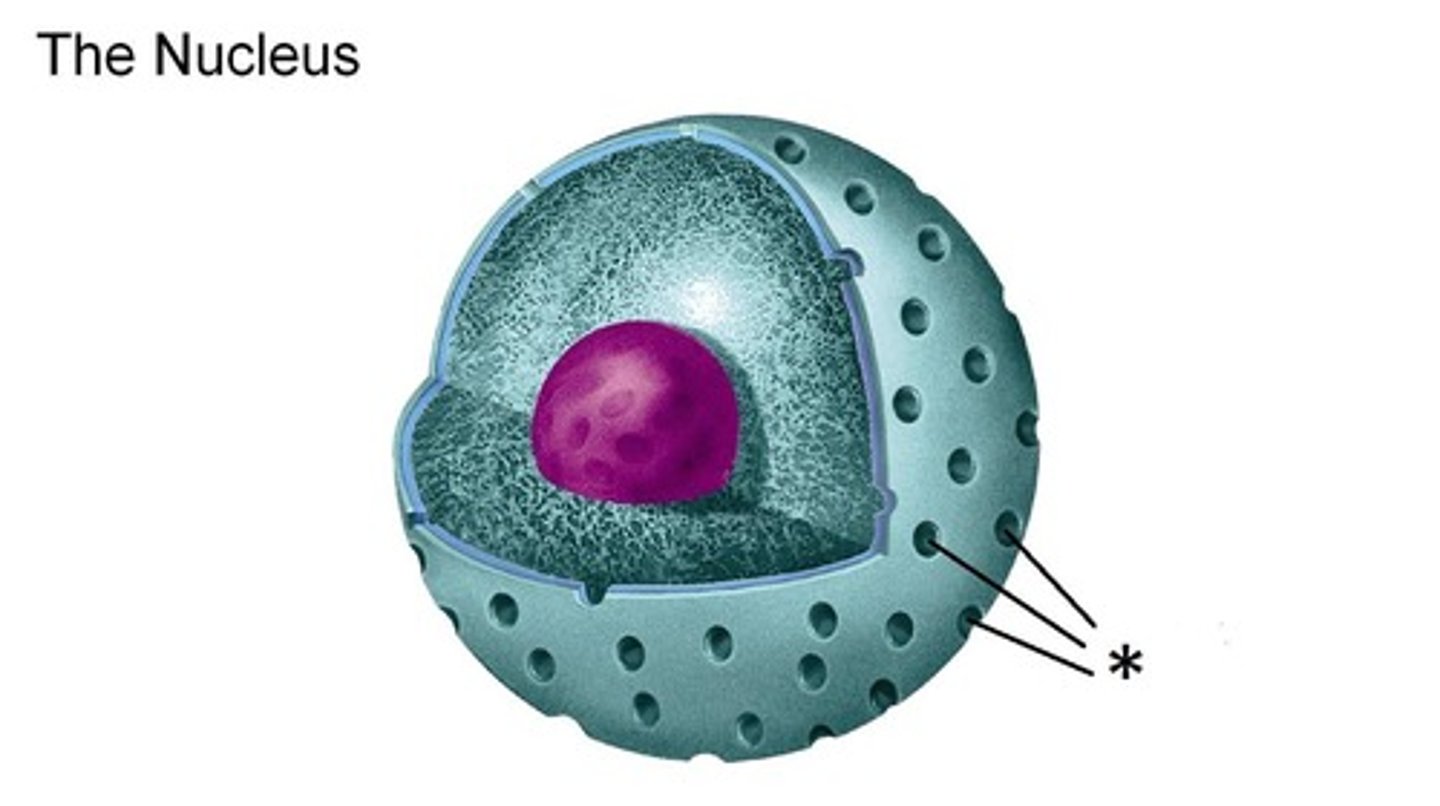
vaults
cytoplasmic ribonucleoproteins shaped like octagonal barrels; located in large numbers within the cytoplasm, associated with a cell's cytoskeleton and complexed with nuclear pores; aid in transport of RNA and other materials; involved with communication processes that regulate cellular activity (cell signaling)
nucleoli
darkly staining spherical bodies found within the nucleus; comprised of RNA and protein and is the preassembly point for ribosomes; most prominent in cells that are synthesizing large amounts of protein
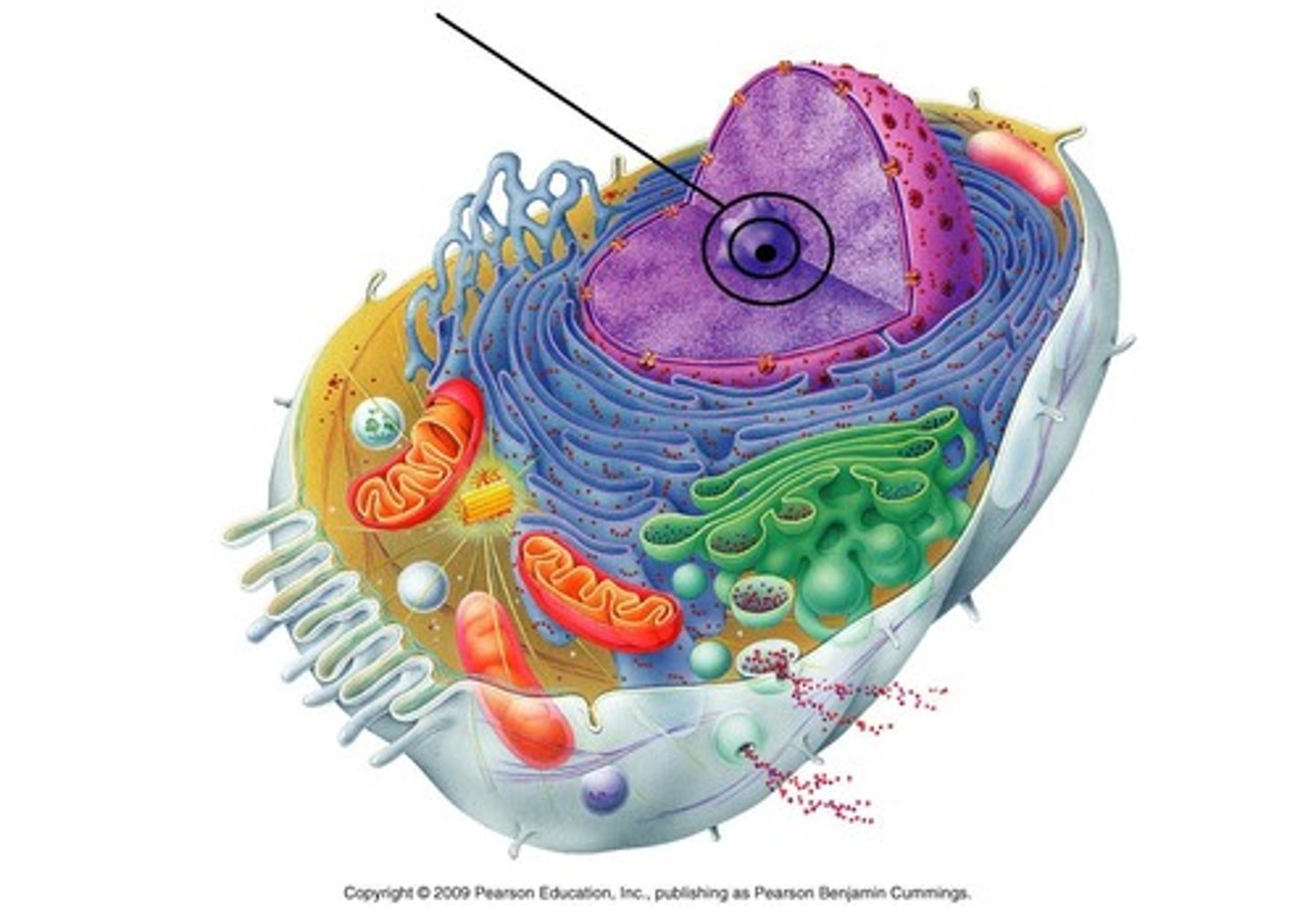
ribosome
an intercellular structure made of both RNA and protein; sites where the genetic message transcribed from DNA is translated into protein; contain almost equal amounts of protein and a special kind of RNA called ribosomal RNA (rRNA); site of protein synthesis
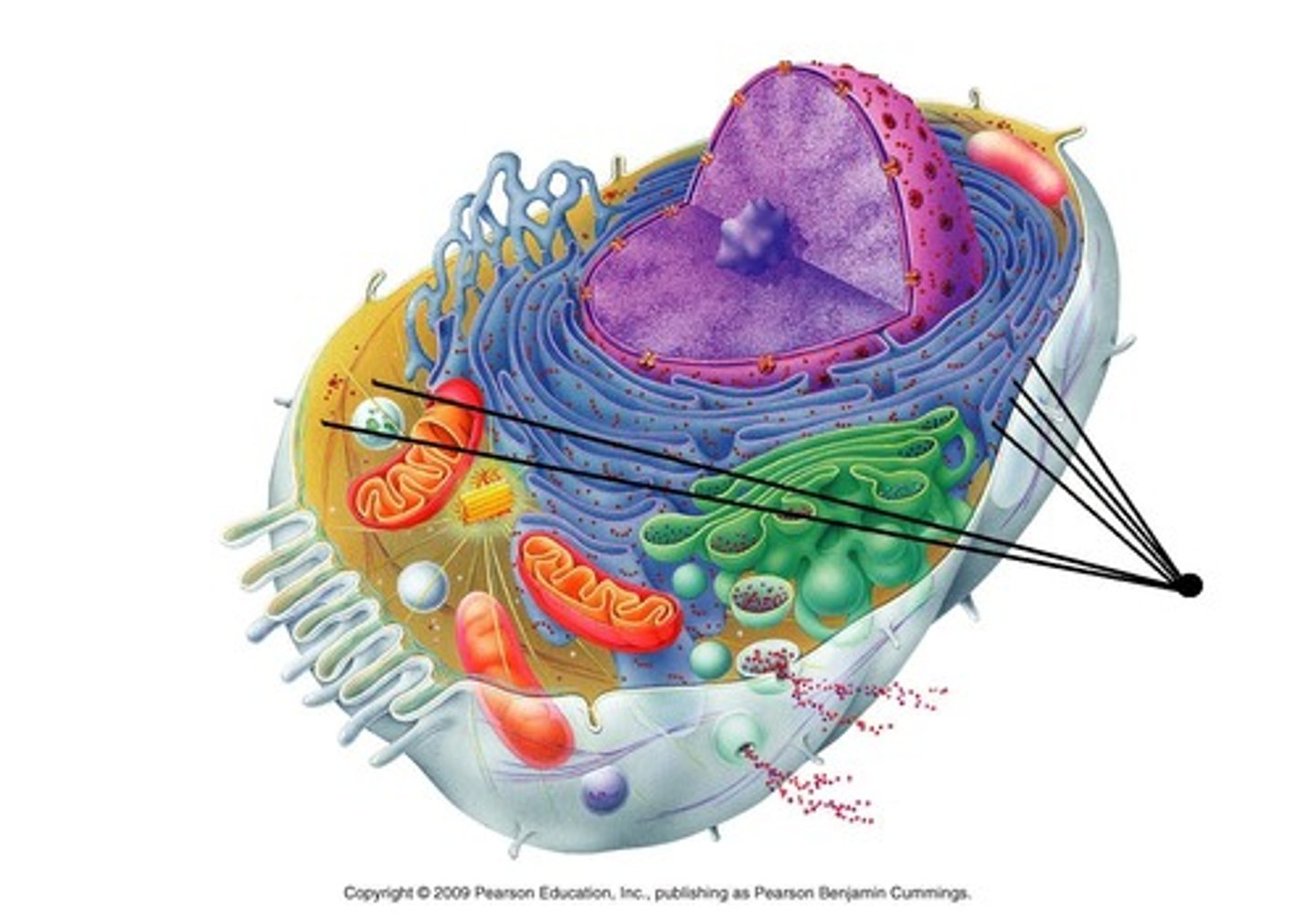
polyribosomes/polysomes
clusters of mRNA with numerous ribosomes
endomembrane system
consists of an interconnected system of membranes that includes the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, various types of vesicles, and the nuclear envelope
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
a complex, membrane-bound labyrinth of flattened sheets, sacs, and tubules that branches and spreads throughout the cytoplasm; storage unit for enzymes and other proteins
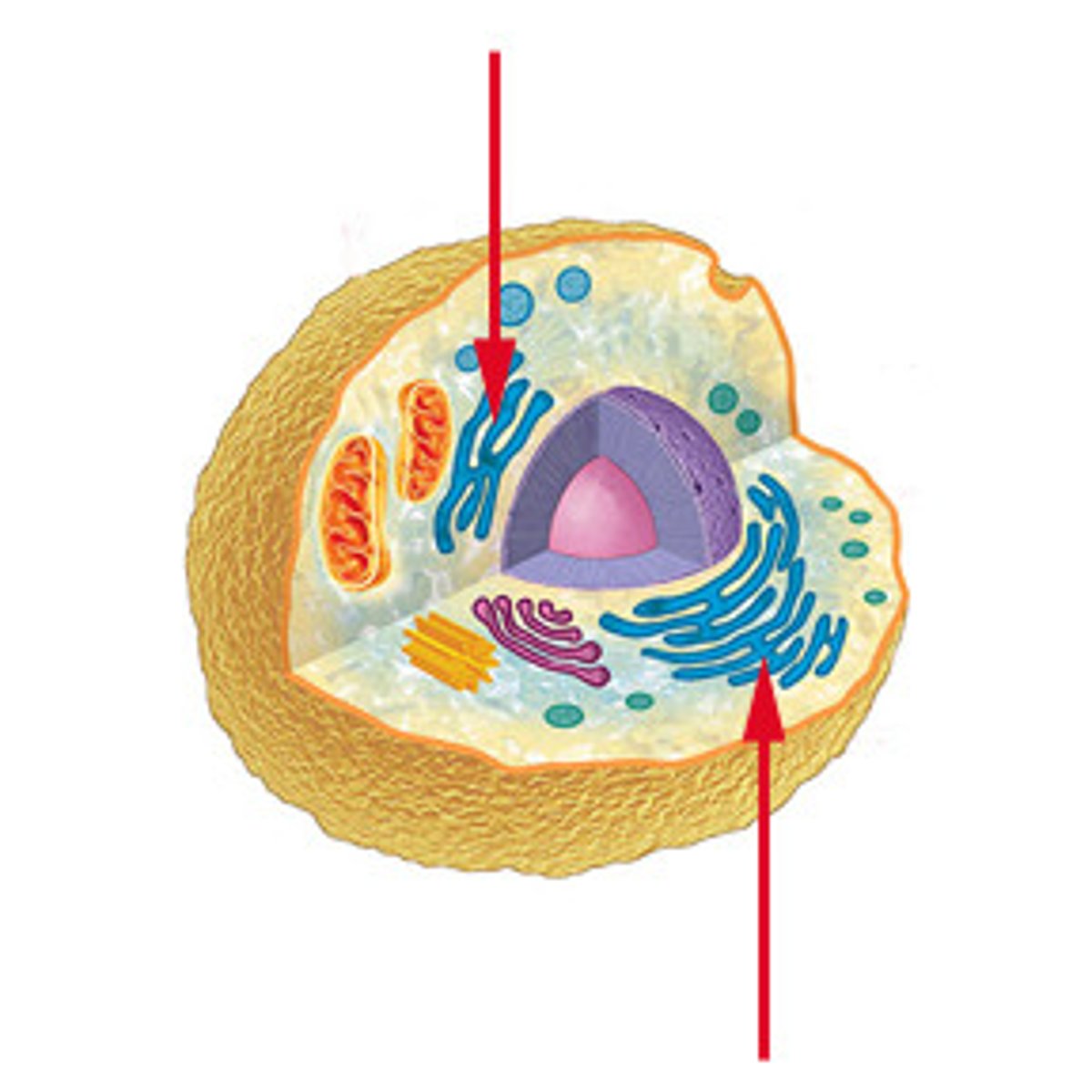
rough ER
portion of the endoplasmic reticulum studded with ribosomes; site for protein synthesis
smooth ER
portion of the endoplasmic reticulum that is free of ribosomes; the site for lipid production, detoxification of a wide variety of organic molecules, and storage of calcium ions
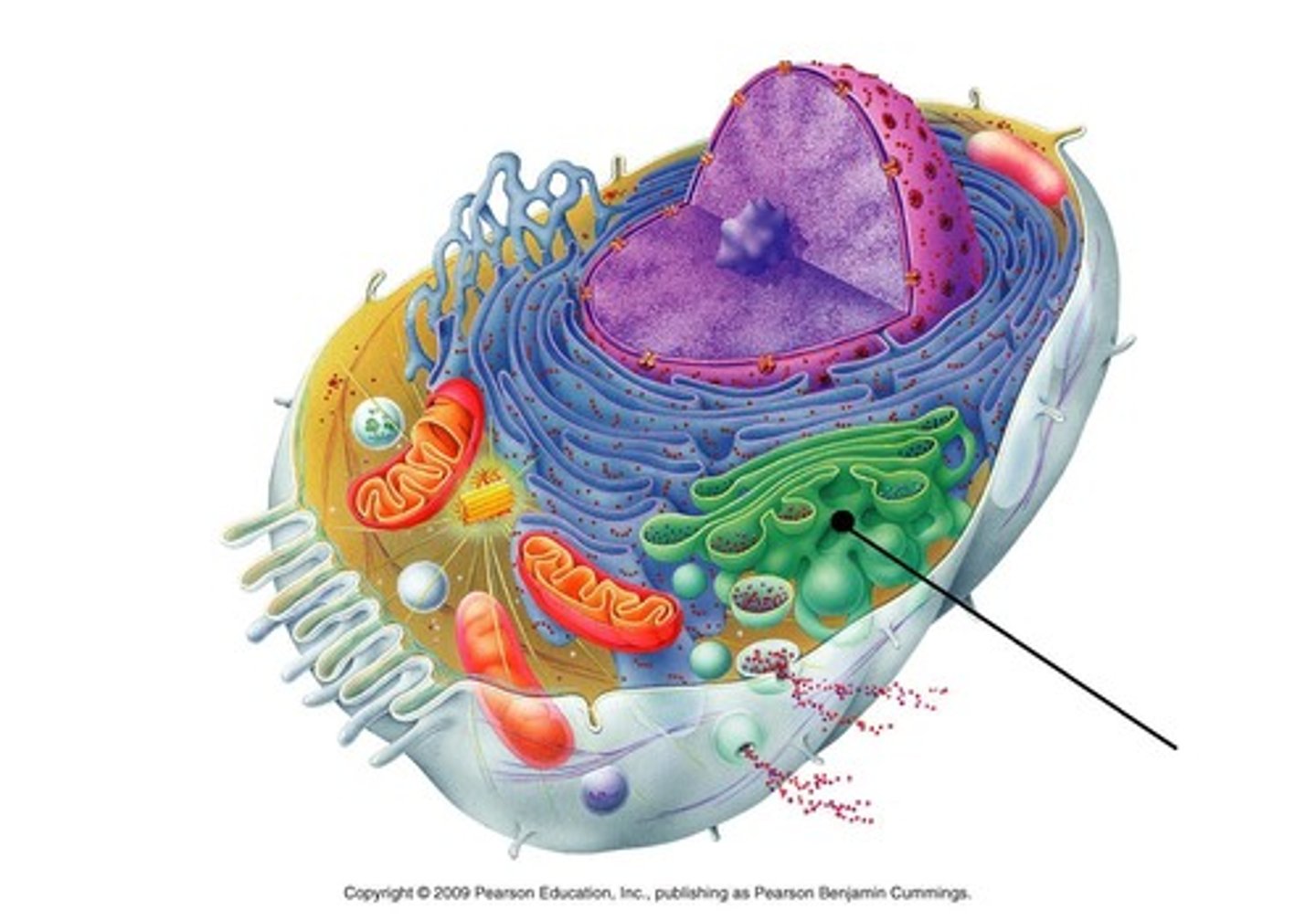
Golgi apparatus
a collection of membranes associated physically and functionally with the ER in the cytoplasm; processes and sorts protein for transport
vesicles
a part of the endomembrane system because they form from, or receive materials from, the ER or the Golgi apparatus; sacs made of membrane
transfer vesicles
proteins that ribosomes synthesize are passed into the ER and sealed off in little packets called ________ ________; pass from the ER and fuse with the Golgi apparatus
secretory vesicles
move materials to the plasma membrane for release to the outside of the cell
vacuoles
a type of vesicle used for temporary storage and transport
endosome
a vesicle created when the plasma membrane invaginates to engulf materials from the outside of the cell and pinches off and will eventually fuse with a lysosome, which is a vesicle considered next
lysosomes, plasma membrane, or secretion
destinations of proteins transported by the Golgi apparatus
secretory vesicles, vacuoles, and endosomes
transfer vesicles of the Golgi apparatus
exocytosis
a secretory vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane and releases its contents into the extracellular environment
endocytosis
the plasma membrane envelops large particles and molecules and moves them in bulk across the membrane
pinocytosis
a form of endocytosis that is small droplets; nonspecific uptake of small droplets of extracellular fluid
phagocytosis
a form of endocytosis that is solid material; similar to pinocytosis except that the cell takes in solid material rather than liquid