Genetics 34 | Gene Therapy and Treatment
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What is precision medicine?
looks at the genetics, environment, and lifestyle of a person to select treatment that could work best for them.
What are the limitations of precision medicine?
Limited Knowledge: Only a small portion of the human genome is actively studied, leaving much unknown.
Lack of Therapies: Even if a genetic cause is identified, there may be no available treatment.
High Costs: Although sequencing costs are decreasing, the expense and time required for accurate interpretation are still high.
Technology Development: Precision medicine technologies, like gene therapy and genome editing, are still in early stages and need further exploration.
What are strategies for treating genetic disease?
Lifestyle changes (e.g., diet and avoiding risk factors for certain conditions).
Dietary restrictions (e.g., removing specific nutrients like gluten or galactose or supply the missing product).
Supplying missing products (e.g., hormone or vitamin replacements, clotting factors, or insulin).
What dietary restrictions are needed for someone with celiac disease?
Remove gluten from their diet (avoid rye, barley, and wheat).
What dietary restrictions are needed for someone with galactosemia?
Remove galactose from their diet (avoid foods containing lactose, as it breaks down into galactose).
What dietary restrictions are needed for someone with phenylketonuria?
Restrict phenylalanine intake (avoid high-protein foods and some artificial sweeteners) and, if needed, provide supplemental BH4 depending on their specific gene mutation.
What treatments are needed for someone with congenital hypothyroidism?
Provide thyroxine as treatment to replace the missing thyroid hormone.
What treatments are needed for someone with hemophilia?
Supply clotting factor concentrates (Factor VIII for hemophilia A or Factor IX for hemophilia B) to improve blood clotting.
What treatments are needed for someone with type 1 diabetes?
Replace insulin to manage blood sugar levels.
What treatments are needed for someone with vitamin D-dependent rickets?
Give vitamin D to support bone development and strength.
What is gene therapy?
A treatment that alters genes to treat or prevent disease.
What are the main approaches used in gene therapy?
Replacing faulty genes with healthy ones.
Reducing or inactivating harmful gene expression.
Introducing new genes to help fight disease.
Gene editing for permanent genetic changes.
How does gene therapy work?
Adds, removes or changes genetic material in cells to correct abnormal genes or produce beneficial proteins.
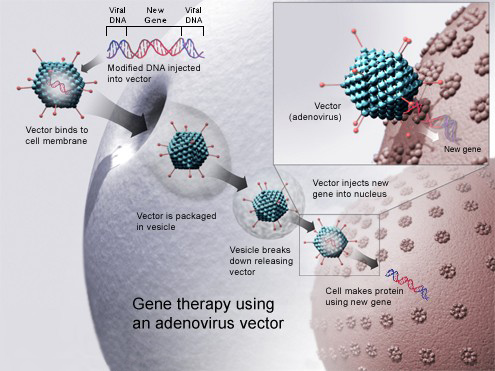
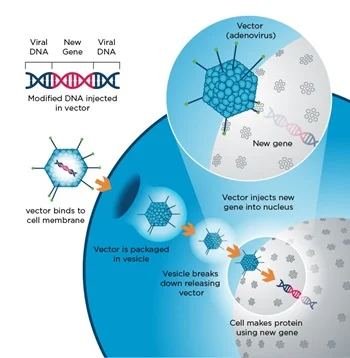
How does gene therapy deliver genetic material into cells?
Via viral vectors (modified viruses, adenoviruses) or non-viral methods (like electroporation or nanoparticles) to deliver the genetic material into the cells.
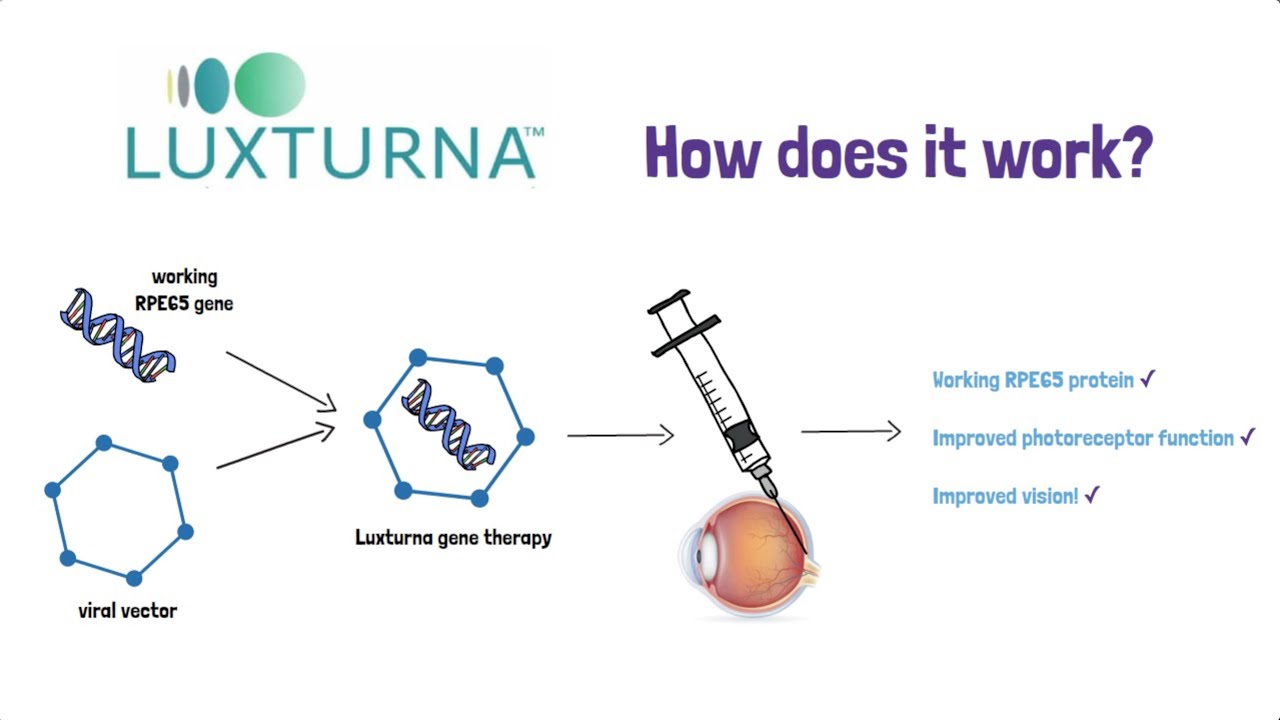
What was the first in vivo gene therapy approved by FDA?
Luxturna, used to treat Leber congenital amaurosis associated with RPE65 mutation.
Spinal Muscular Atrophy is caused by mutations in which gene?
SMN1 gene
How is Spinal Muscular Atrophy treated?
Zolgensma. Costs $2.1M (most expensive medication in the world)
What is RNAi?
a process that "knocks down" gene expression, helping to reduce or silence specific genes. This can identify therapeutic targets for diseases.
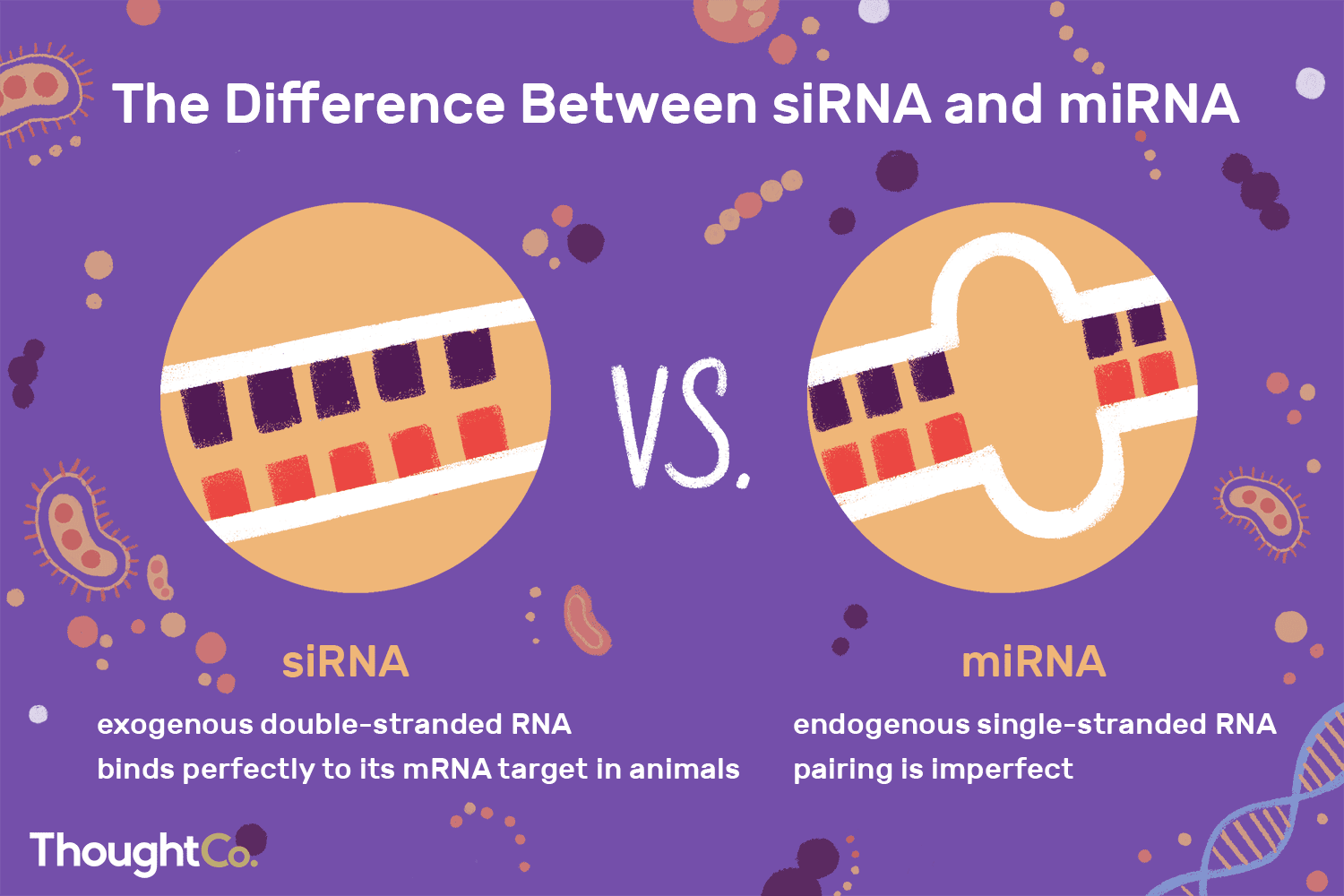
What are miRNA and siRNA?
miRNA (microRNA) and siRNA (small interfering RNA) are types of RNA involved in RNAi.
Both miRNA and siRNA are produced from double-stranded RNA, which is cut by an enzyme called Dicer.
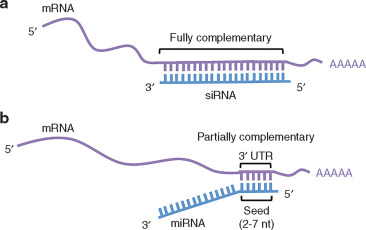
How does miRNA work?
miRNA binds imperfectly to mRNA to block its translation (protein production).
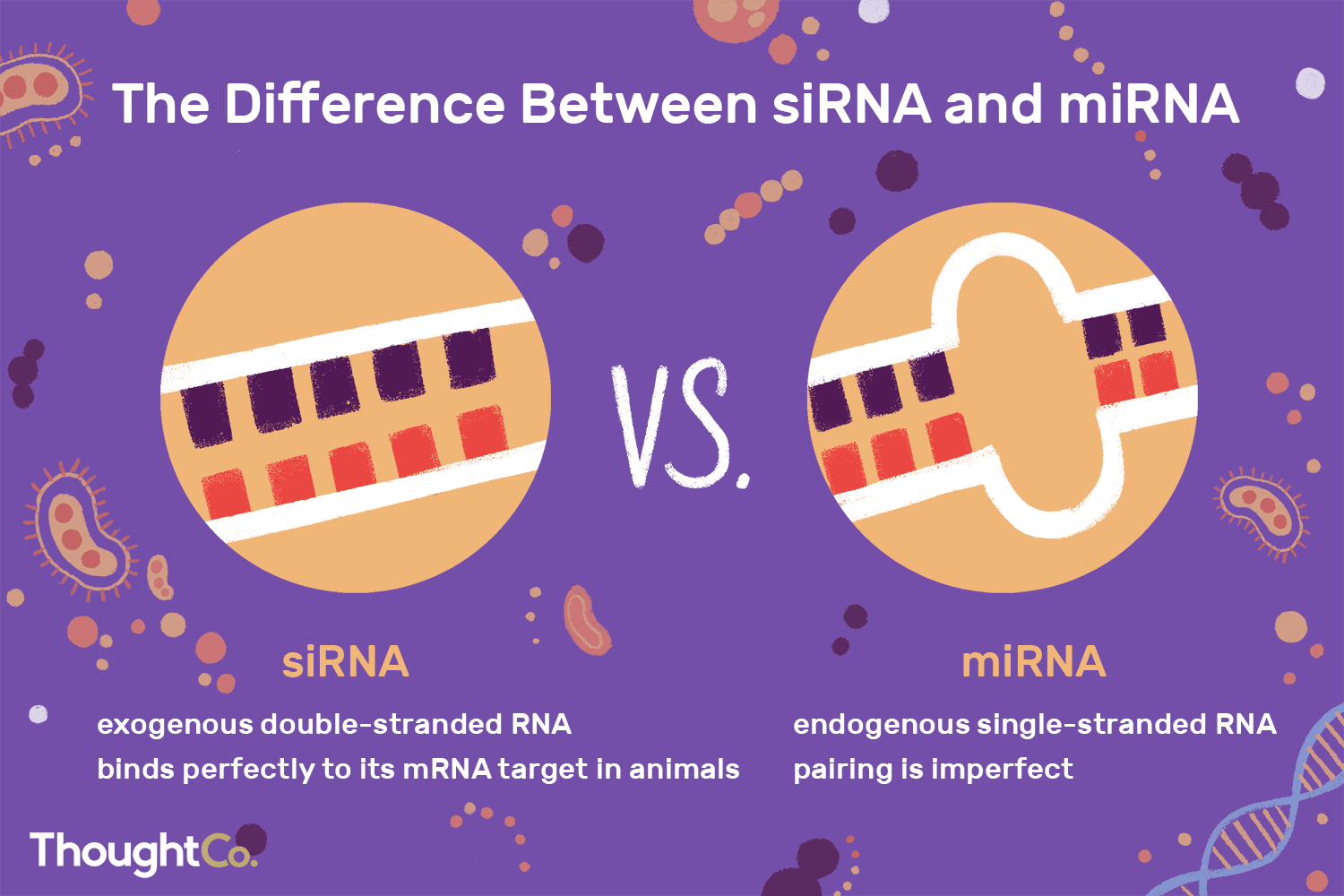
How does siRNA work?
siRNA binds perfectly to mRNA, leading to its degradation, thus preventing protein production; Knockout
What is the first siRNA-based drug approved by the FDA?
Patisiran (2018)
siRNA based therapies are only effective in the liver. Why aren’t they able to target areas outside the liver?
They have not progressed far in clinical trials.
What is genome editing?
A technique that uses "molecular scissors" to insert, delete, or replace DNA in an organism's genome.
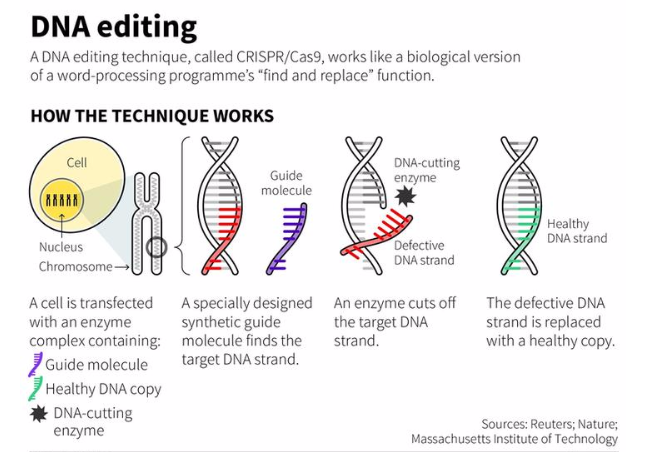
What nuclease enzyme is used in CRISPR?
CRISPR/Cas9 which creates breaks in DNA
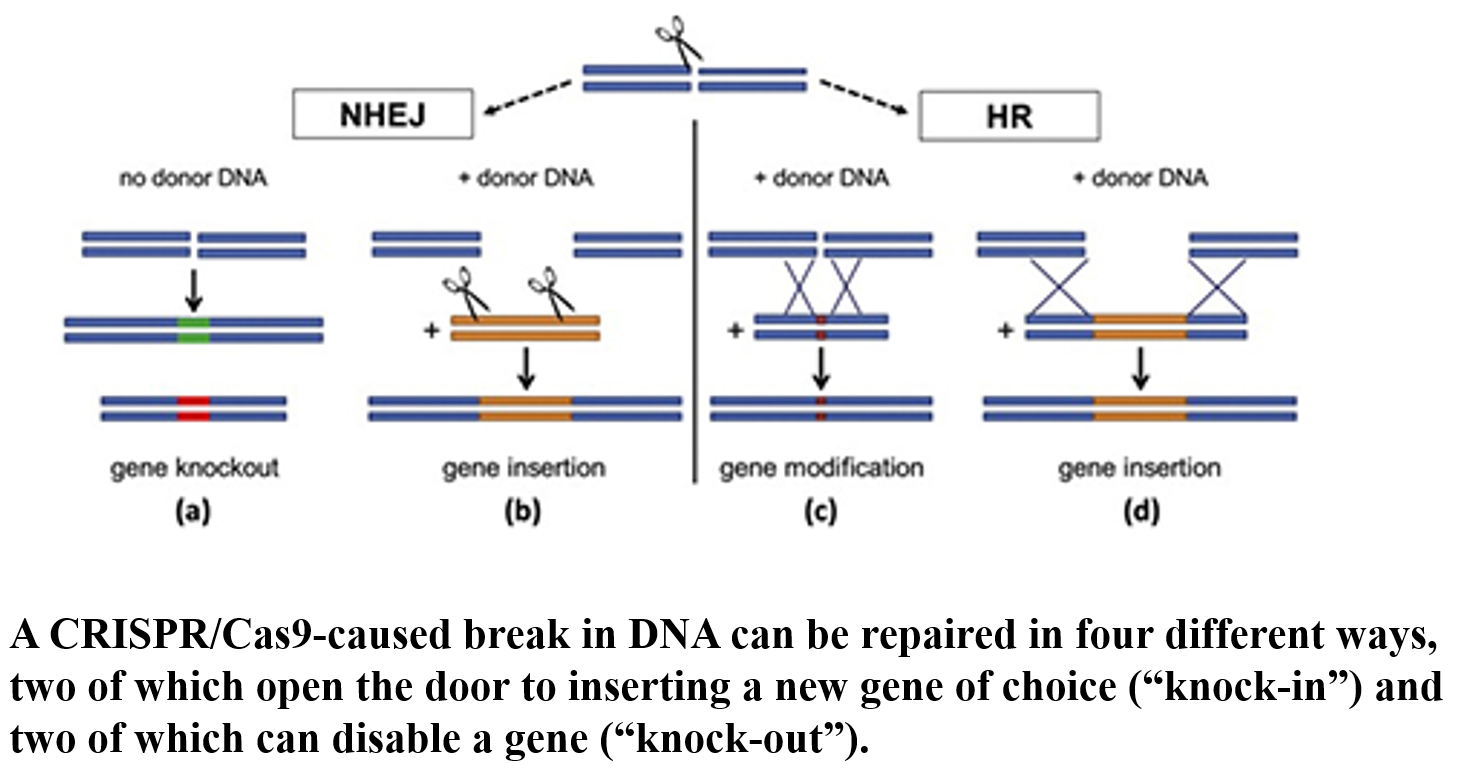
What functions can the Cas9 enzyme perform?
Knockout: Disables a gene.
Knock-in: Inserts a new gene.
Gene Modification: Alters an existing gene.
Gene Insertion: Adds additional DNA sequences.
The first human CRISPR trial was done in which country?
Chengdu, China
The first human CRISPR trial was meant to treat which condition?
Non small cell lung cancer; ex-vivo
What was the CRISPR human embryo (baby) scandal?
It was a scandal involved Chinese scientist He Jiankui, who used CRISPR technology to edit the genes of twin embryos to make them resistant to HIV.
This controversial experiment, conducted without full ethical approval, took place in China and sparked global outrage over the ethical implications of gene editing in humans.

What are the challenges of genome editing?
Not 100% accurate
Still very new
Eugenics potential
Expensive
Not regulated uniformly
Risk of unintentionally producing harmful organisms