Materials engineering lecture 4 polymers
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
What are macromolecules?
Very long molecules, consisting of structural units and repeating units, connected by covalent chemical bonds
What is monomer?
Many repeating complementary subunits
What is polymerization?
Monomer units bind together to form a polymer
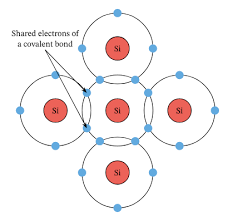
What are covalent bonds? Give ex. Draw pic.
Electrons that are shared between atoms.
Ex. Silicon has a valance of 4: four covalent bonds must be formed
Each of the two atoms contribute one electron each
Double and triple bonds and can be unsaturated
What us a double and triple bond?
Sharing of two and three pairs of electrons (between two carbon atoms)
What does unsaturated mean?
Each carbon atom is not bonded to the maximum amount of atoms (4): to get saturated hydrocarbons, all bonds need to be single to get the max number of atoms
Summed up what are polymer molecules?
Units (monomer=repeat unit) connected by covalent chemical bonds, which then create macromolecules
What is the degree of polymerization?
Number of repeating units
What are copolymers and give the 5 examples.
Polymers formed using several types of monomers
Alternating (ABABAB, poly(A-alt-B)
Random (ABBBAA), poly(A-ran-B)
Statistic (AABBAB), poly(A-co-B)
Block (AAABBB), poly(A-b-B)
Graft (AAAAA), poly(A-g-B)
What is a homopolymer and give an example
Same repeating units AAAAAAA, poly(A)
What is bifunctional?
Two active bonds that form a 2-dimensional molecule
What is trifunctional?
Three active bonds that form a three-dimensional molecule
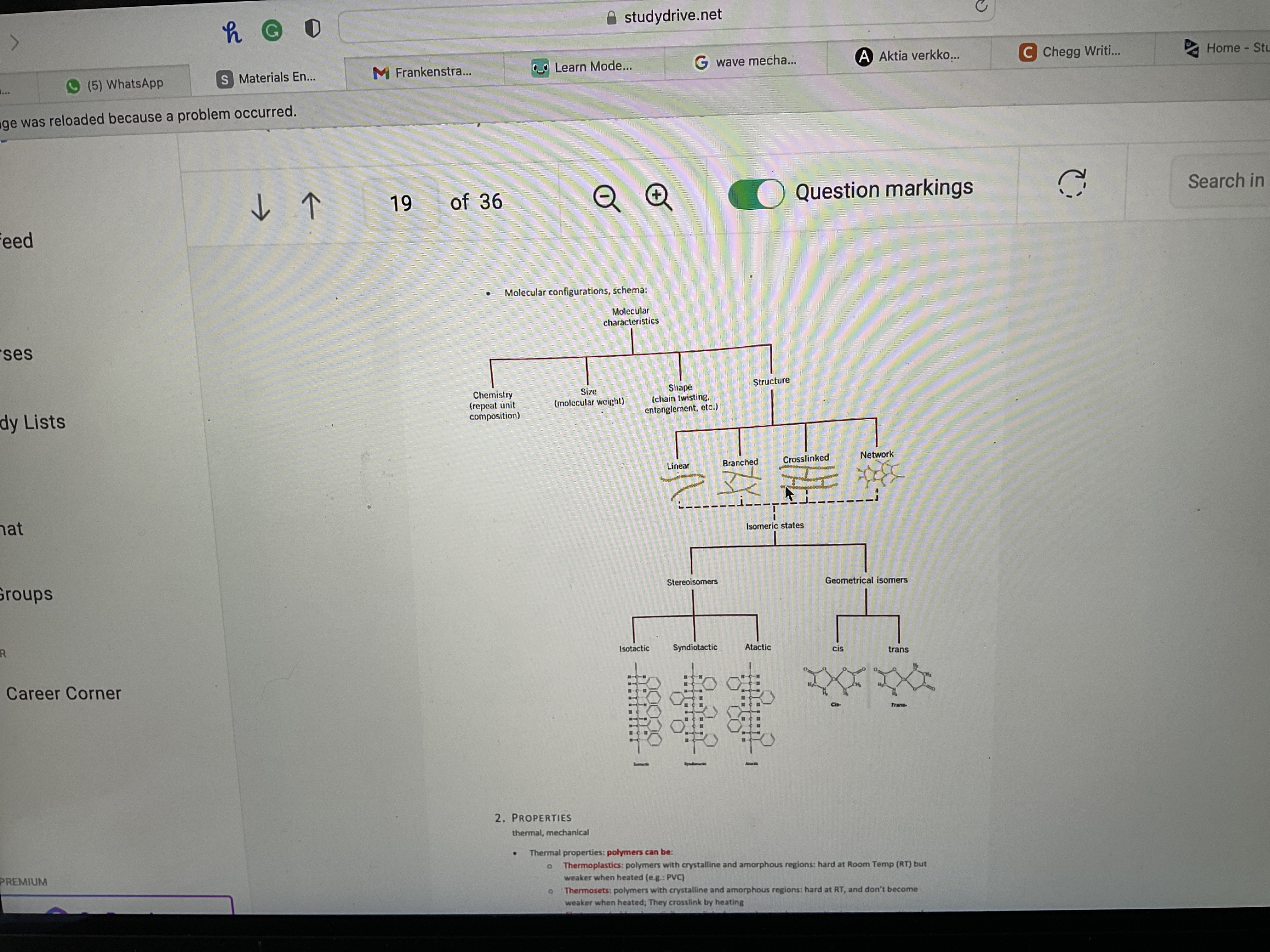
Name 4 molecular shapes
Linear, branched, cross-linked, networked
Draw linear molecular shape
A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A

Draw branched molecular shape
A-A-A-A-A-
I
A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A-A
I
. A-A-A-A-A-A
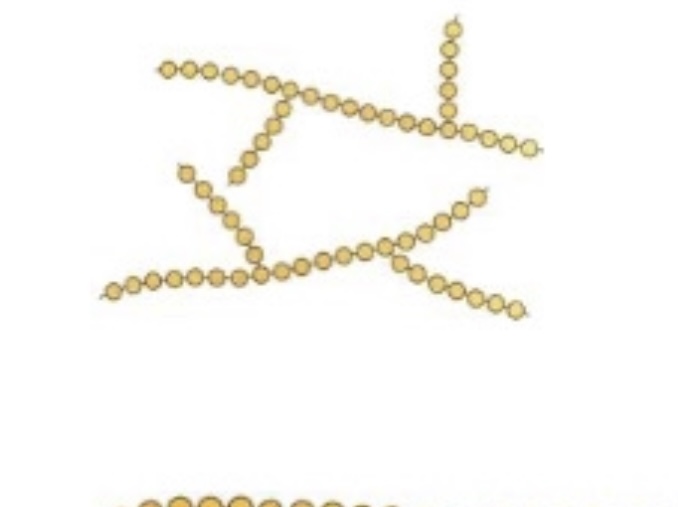

Draw cross-linked molecular shape
Draw networked molecular shape
read
What are the thermal properties of thermoplastics? Give example
Polymers with crystalline and amorphous regions: hard at room temp (RT) bur weaker when heated (e.g.: PVC)
What are the thermal properties of Thermosets?
Polymers with crystalline and amorphous regions: hard at RT, and don’t become weaker when heated; they cross-link by heating
What are the thermal properties of Elastomers (rubbers)?
Partially cross-linked, amorphous polymers: extension causes creation of crystalline regions, but vdwaal forces too weak—> no plastic deformation
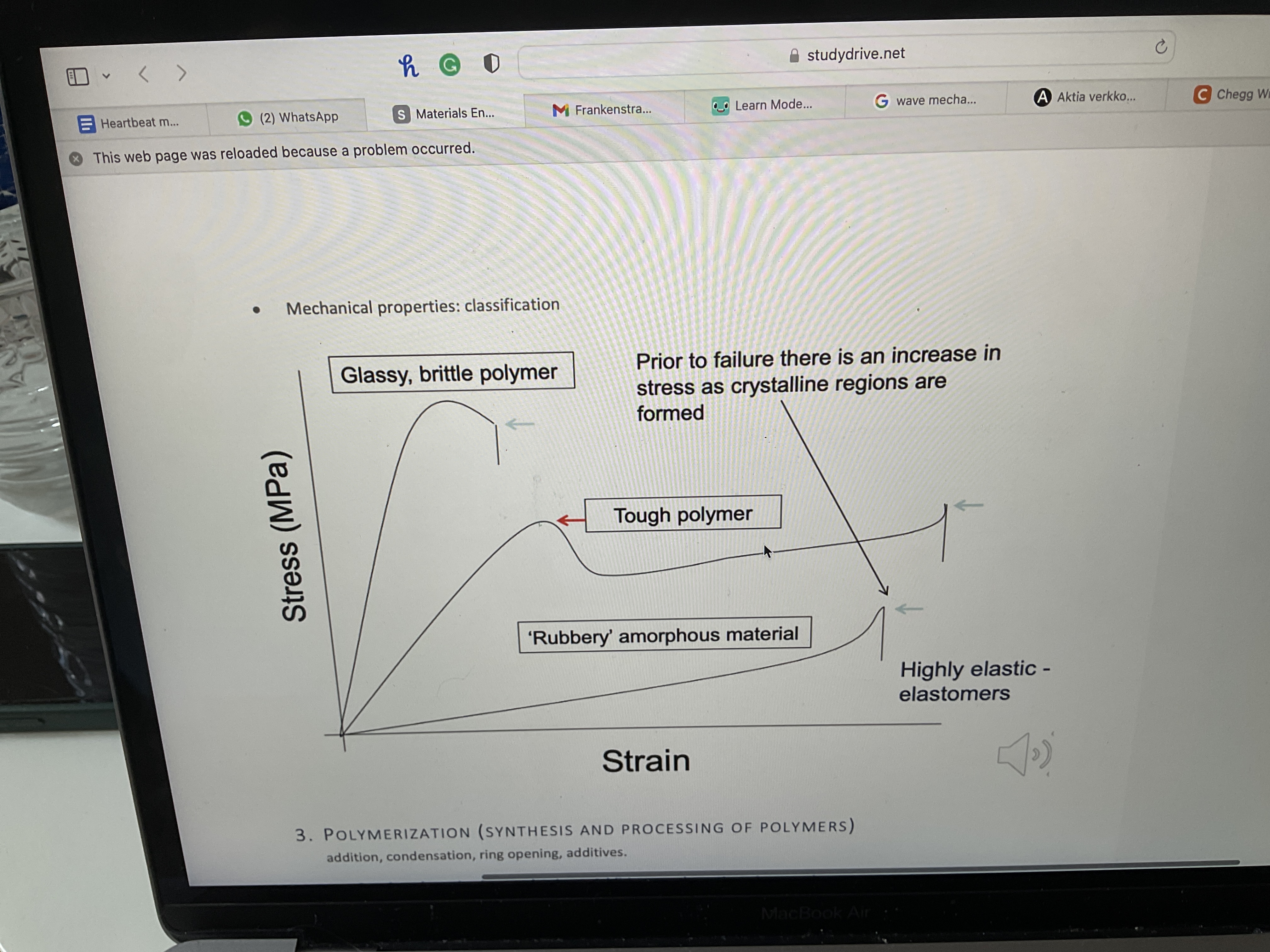
Draw mechanical properties classification
What are the main 3 polymerization mechanisms?
Addition, condensation and ring opening
What are the three stages of addition
a) +-+= Low Mw
b) -+-= High Mw
c) ++-= Medium Mw
d)- - += low or medium Mw
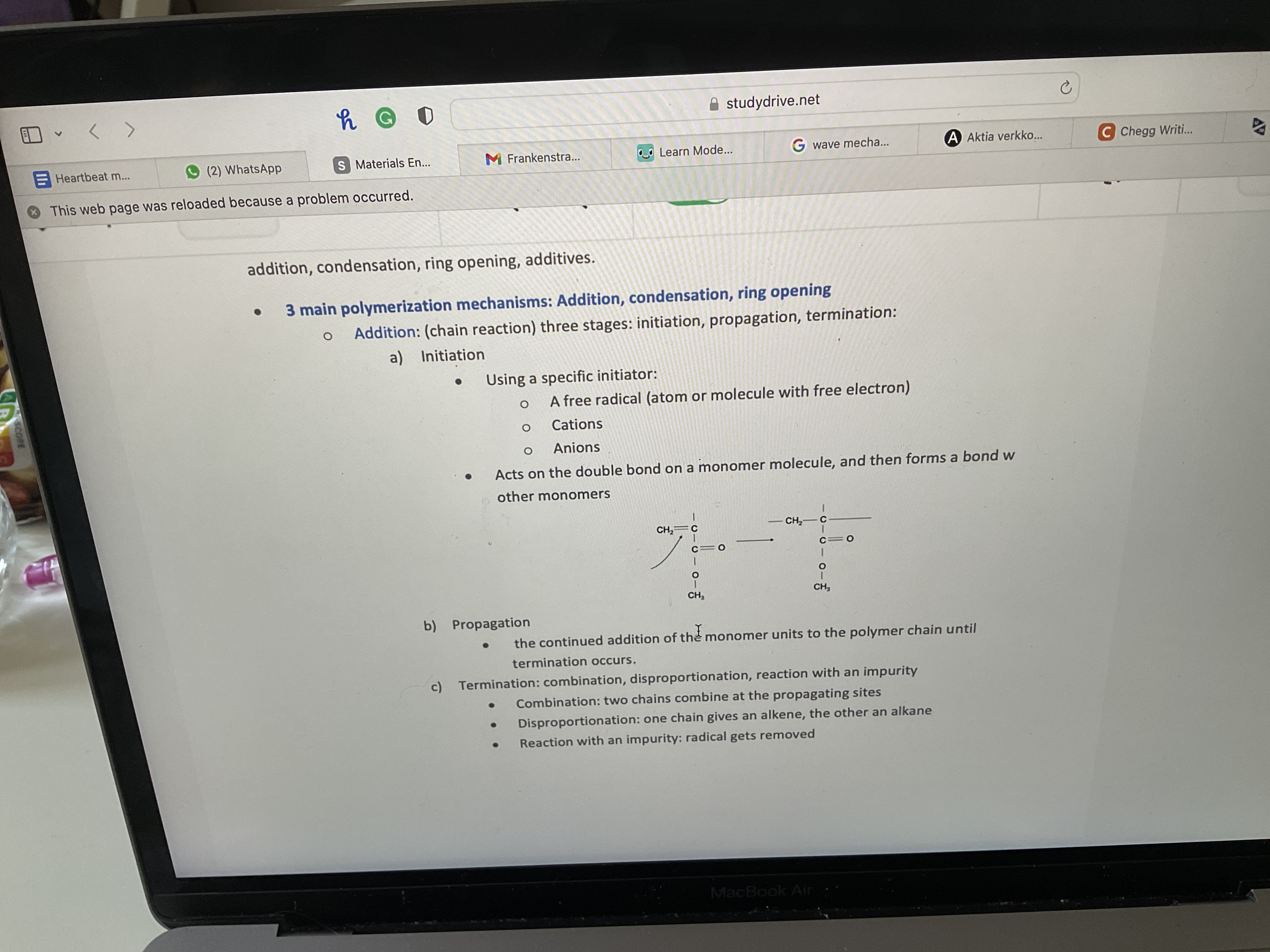
Explain what happens in condensation and draw

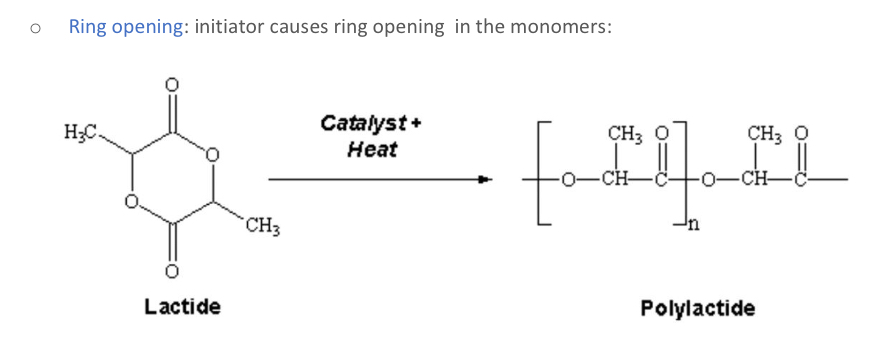
Explain ring opening and draw
What are additives? Give examples
Foreign substances, to enhance or modify a polymers properties
Ex. Filler, plasticizers, stabilizers, colorants, flame retardants
why use fillers as additives5? And give ex
Improves:
tensile and comprehensive strength
Abrasion resistance
Toughness
Dimensional stability
Thermal stability
Ex. Wood flour, glass, clay, talc, silica and sand
Why use plasticizers as additives 4? And give ex
Improve:
flexibility
Ductility
Toughness
Ex. Poly (vinyl chloride)
Why use stabilizers as additives? 2
Improve:
mechanical integrity
Prevent deterioration
Why use colorants as additives? 2 and give ex
gives a specific color to the polymer
May impact opacity
Dyes or pigments
Ex. Titanium oxide, diazo pigments
Why use flame retardants as additives? 1
Flammability resistance
T/F most natural polymers are degradable
T
T/F synthetic polymers are sometimes non-degradable
T
What needs to be true for it to be a biodegradable polymer?
Main chain of a polymer needs to contain labile bonds
What are the three steps of polymer degradation? Study pic
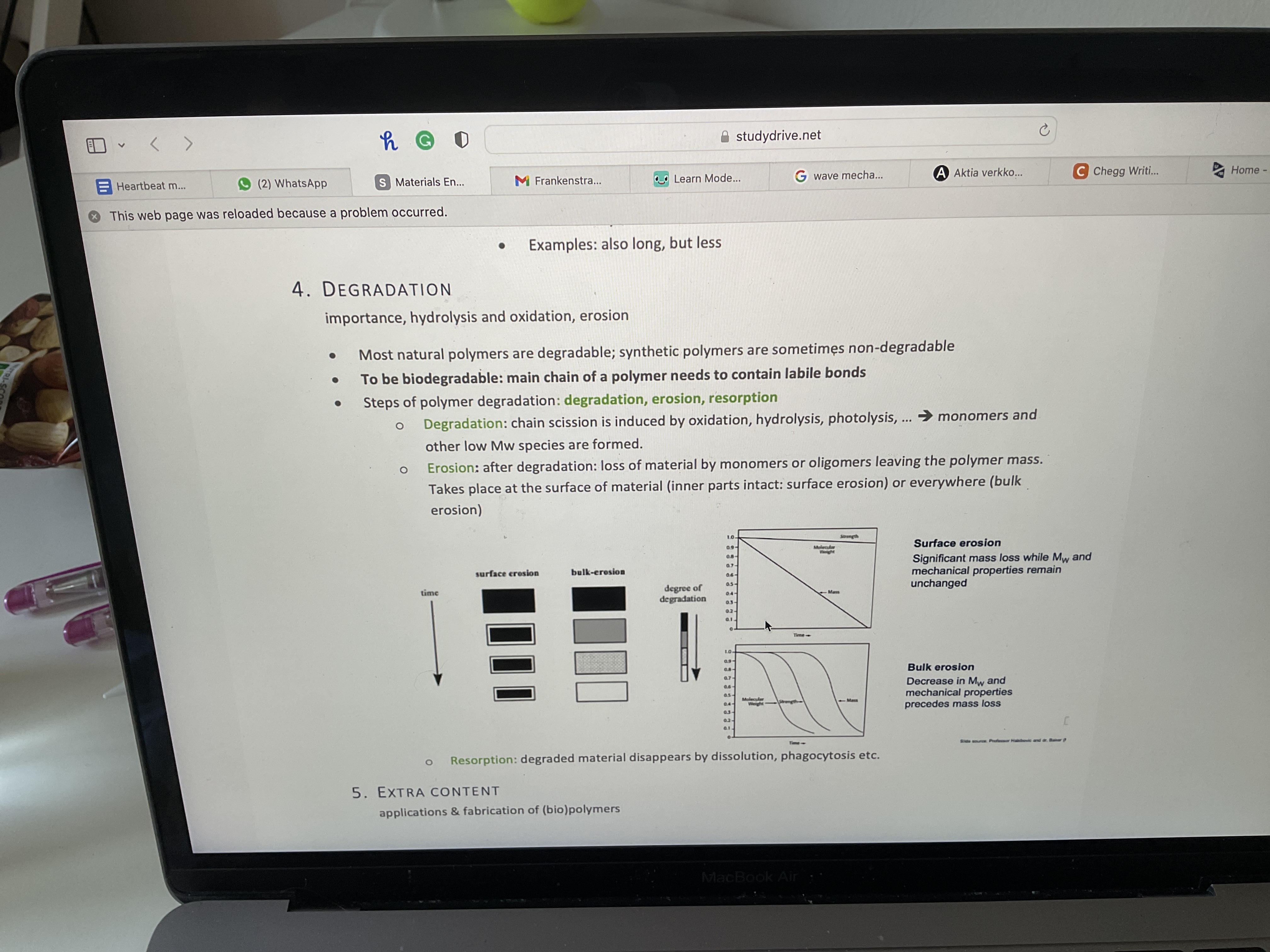
What word am i looking for: significant mass loss while Mw and mechanical properties remain unchanged?
Surface erosion
What word am I looking for: Decrease in Mw and mechanical properties precedes mass loss
Bulk erosion
What is a polymer?
A polymer is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules linked together into chains of repeating subunit

What is a plastic
A plastic contains multiple components (can be polymers) and can have additives
What is polymerization?
The process by which the monomer units bind together to form a polymer. Often by covalent bonds.
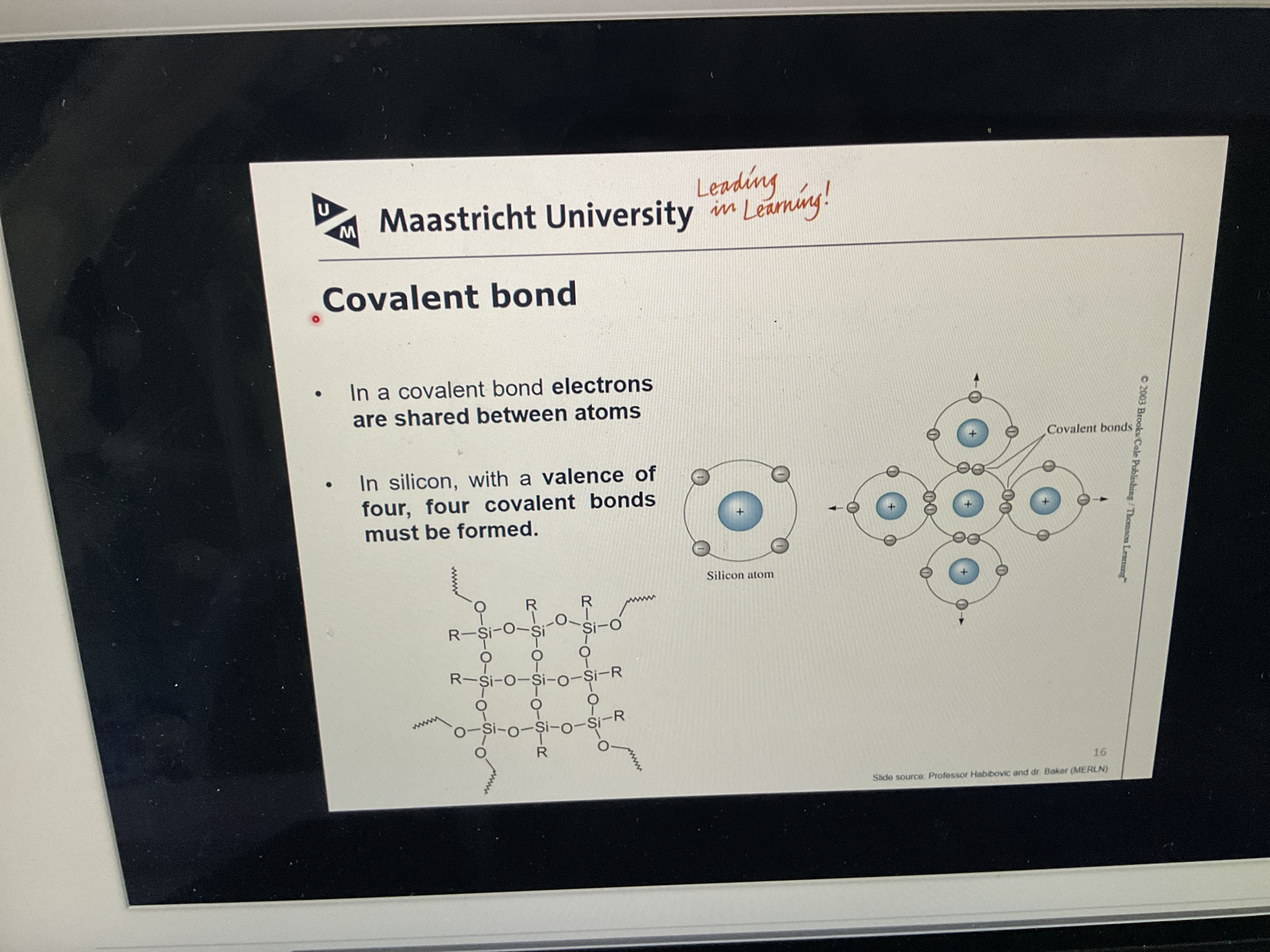
What is a covalent bond?
Outer electrons are shared between two atoms and that’s what holds the atoms together
What are double and triple bonds?
Between two atoms they share two or three pairs of electrons
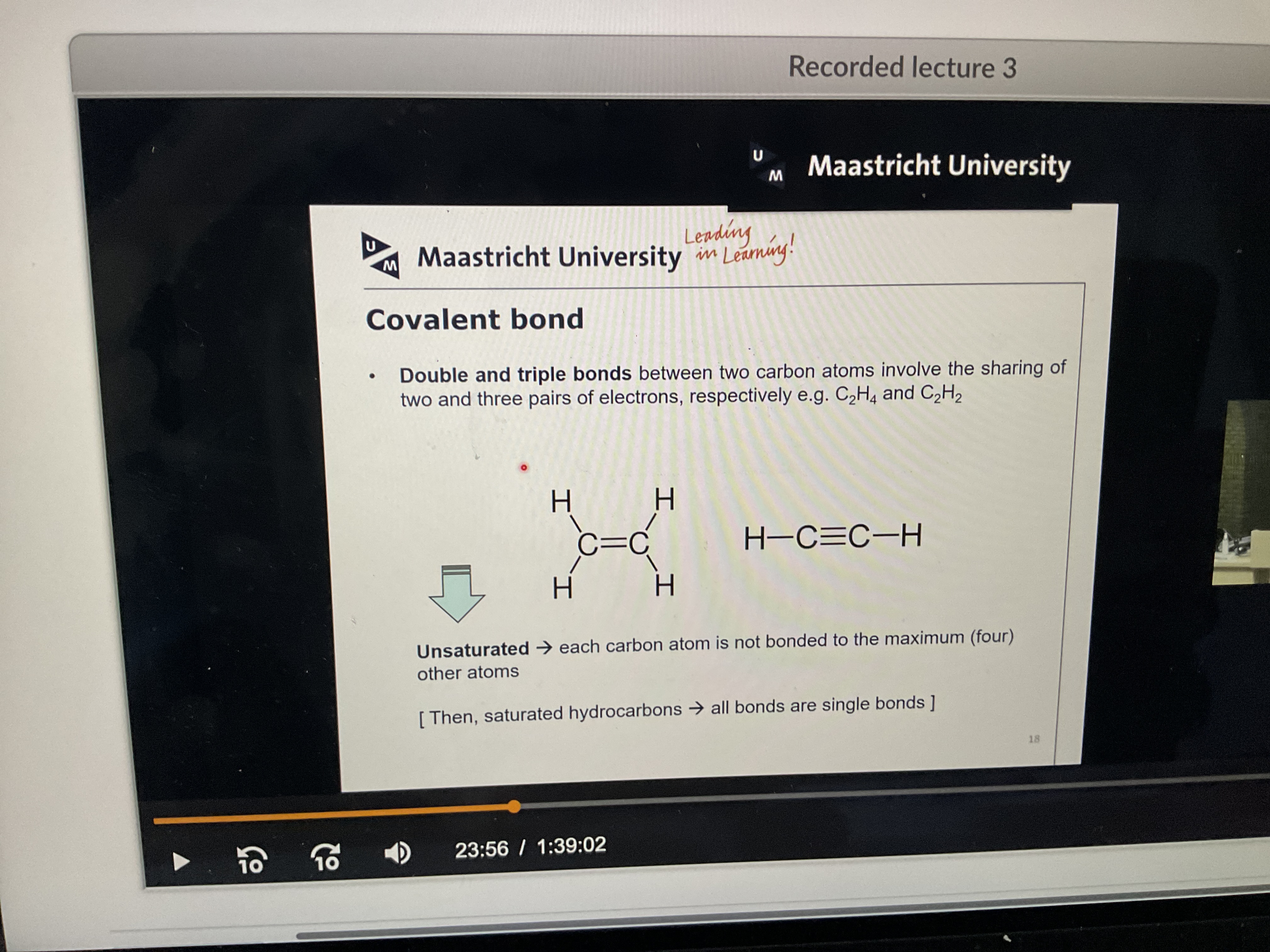
What does unsaturated mean?
Each carbon atom is not bonded to the maximum (four) other atoms
What are monomers?
Small molecule from which a polymer is synthetizised
Look at polymerization
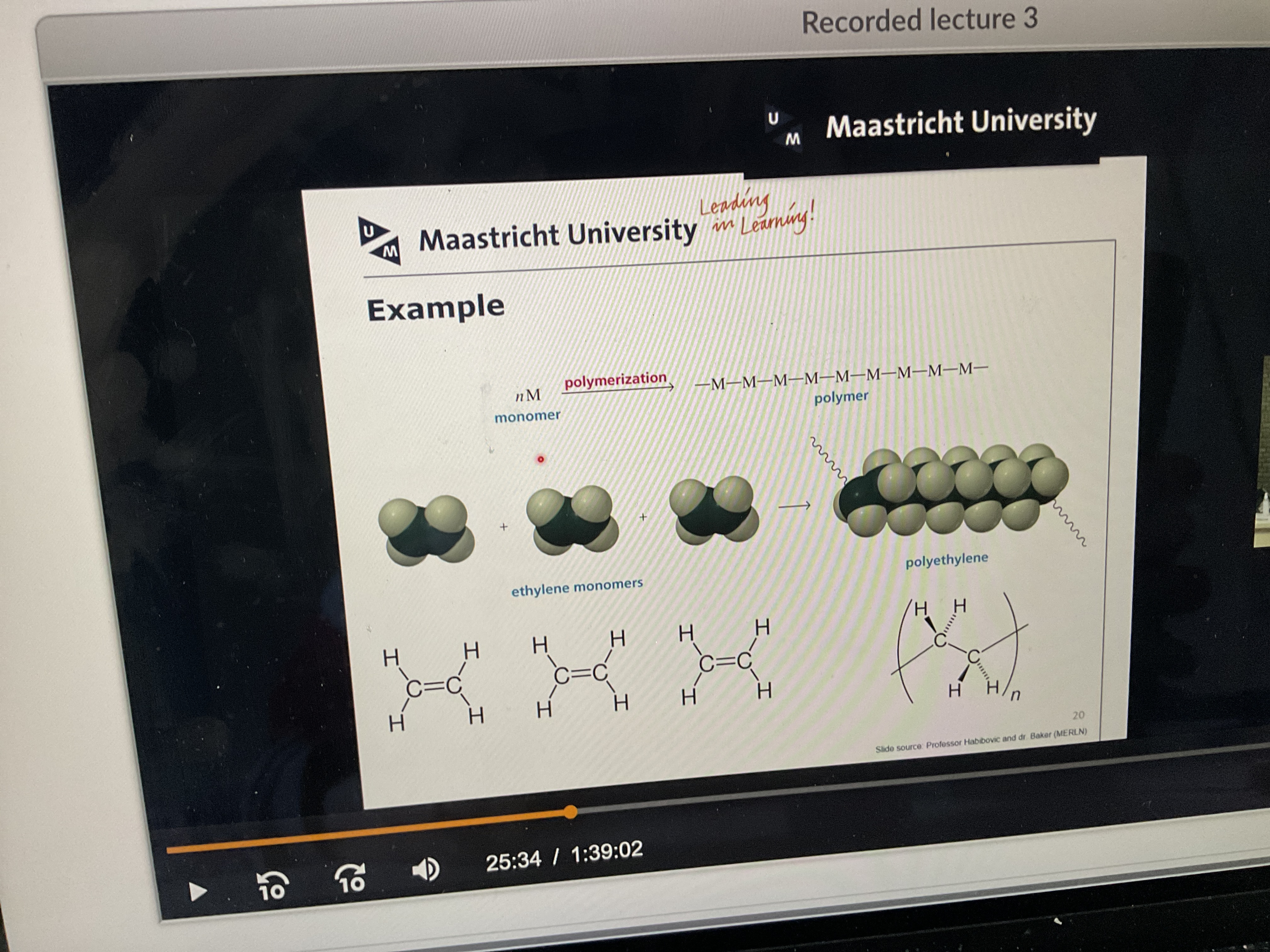
What is the degree of polymerization
N, the umber of repeating units (monomers)
What is an initiator?
Compound that starts the polymerization process by generating reactive species (free radicals, anions, cations) which then react with monomers to form polymer chains
Name two inorganic polymers
Silicones and polyphosphates
What are copolymers?
Polymers formed of several types of monomers
BBAABAB
Are polymers more often organic or inorganic
Organic
What is a homopolymer?
Repeating units along the chain are the same
AAAAAAA
What are the four types of copolymers?
Random: if the monomeric units are distributed randomly
ABABBABBAAAB poly(A-ran-B)
Block: long sequence of one polymer unit followed by another
AAAAAABBBBBB poly(a-b-B)
Graft: one polymer branching from the backbone of another
AAAAAAAAA
BBBBBBBB Poly(A-g-B)
Alternating: alternating sequence
ABABABABAB Poly(A-alt-B)
What is a bifunctional monomerunit?
Two active bonds that form one dimensional molecule —> chain
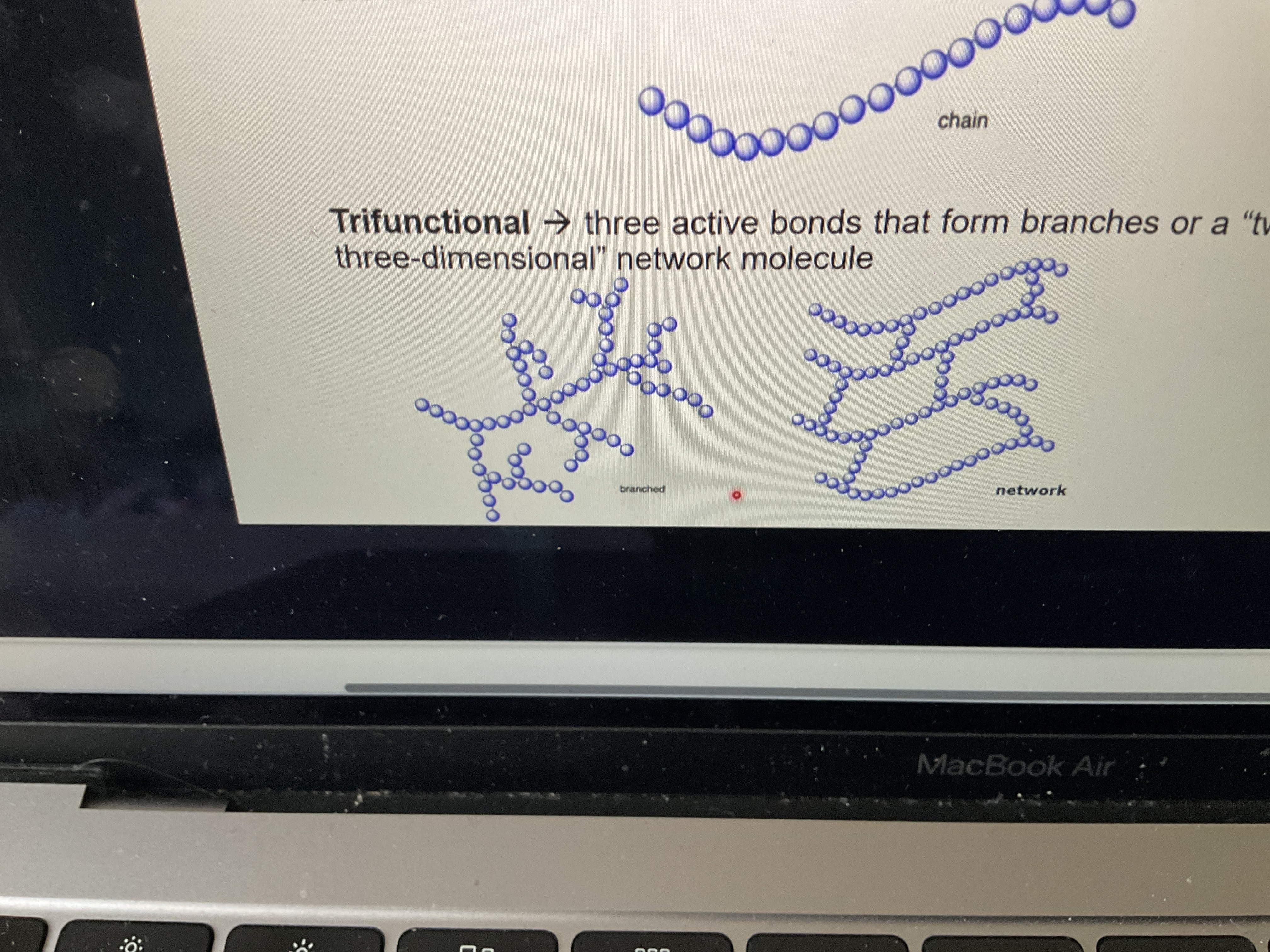
What is a trifunctional monomer unit?
Three active bonds that form branches or a two- or three-dimensional network molecule
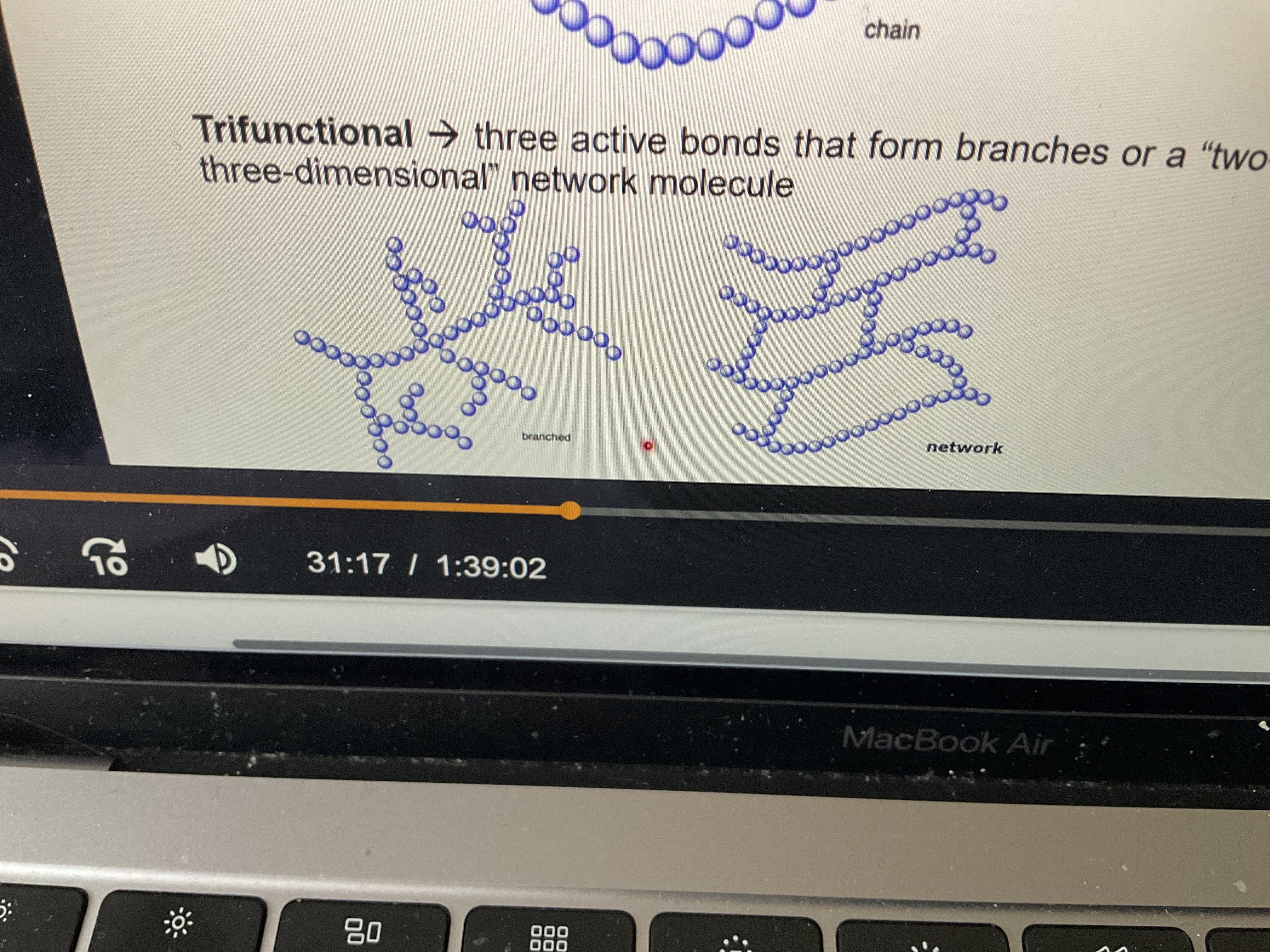
What’s difference between branching and network?
What are the differences between small molecules and polymers in terms of molecular weight?
Simple compounds have one molecular weight; polymers have a distribution
Why is it important to know the molecular weight of a polymer?
Different weight have different properties which influence fabrication
What is the difference between polydisperse and monodisperse?
Monodispersed are pure compounds with precise units and a single molecular weight. In contrast, polydispersed is a polymer mixture with an average molecular weight
What are isotopes?
Atoms that have different molecular atomic weight
What is polydispersity index?
Polydispersity index: Ratio between molecular weights. The higher the index the more diverse molecules you have in there. Closer to 1 is only a singular molecules.
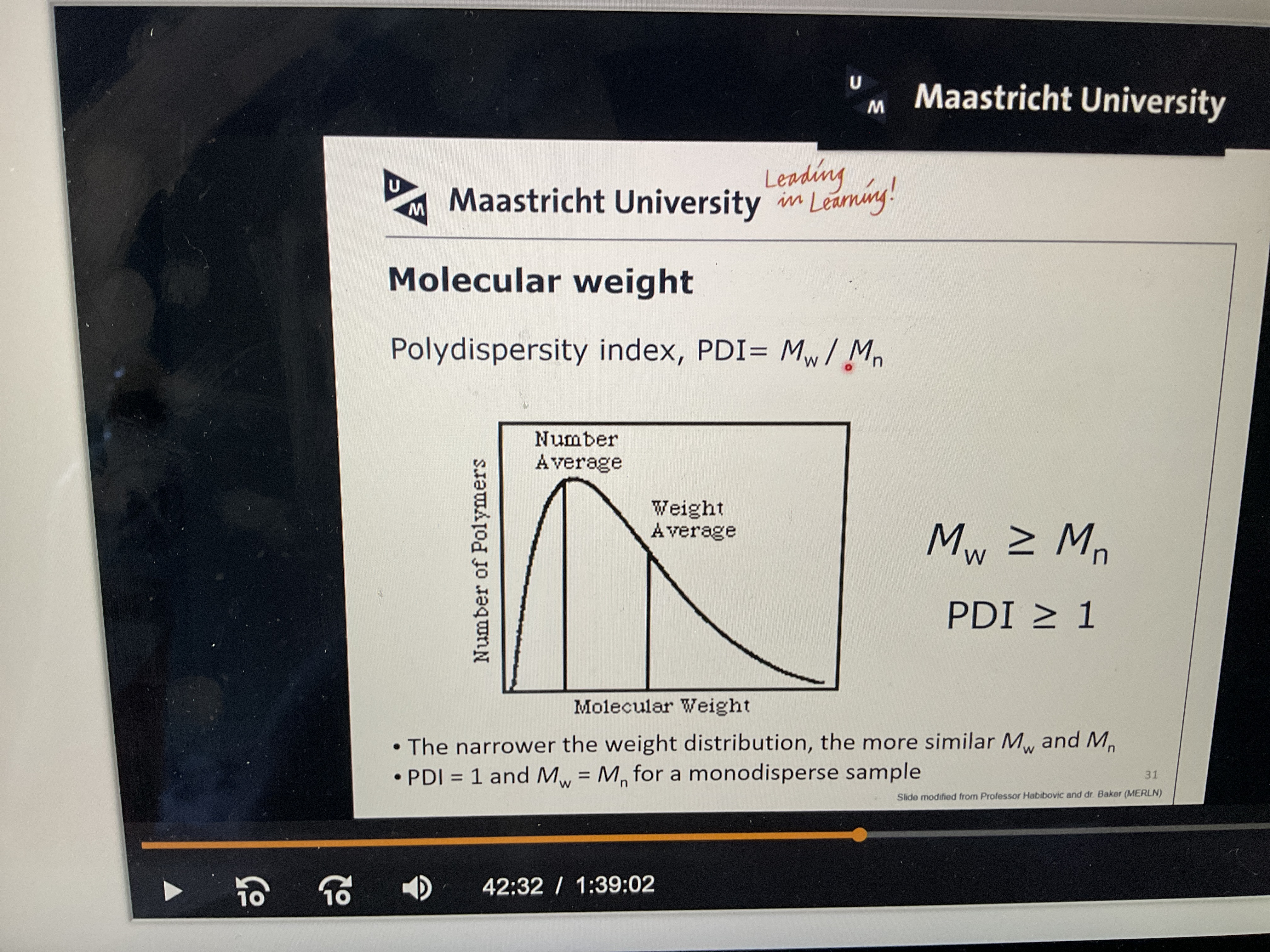
How do you calculate average chain size of a polymer?
DP=Mn/m
Mn= number of average molecular weight
M= repeating unit molecular weight
What are the four skeletal structures of polymers?

What does linear chains effect in a polymer compared to branched ones?
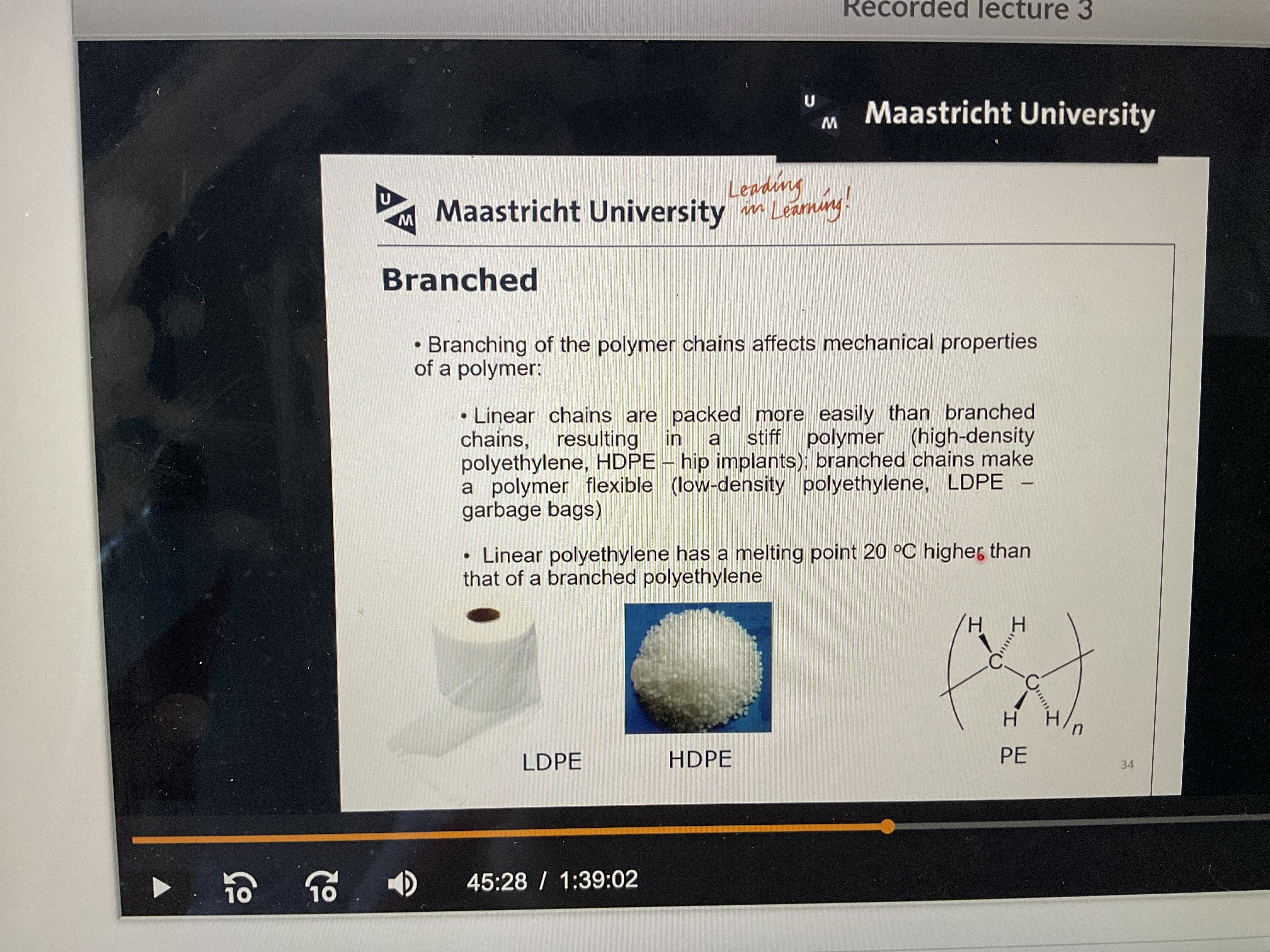
There is a variety of polyethelines. But what do they vary in?
extent and length of branching
Molecular weight and molecular weight distribution
Crystallinity
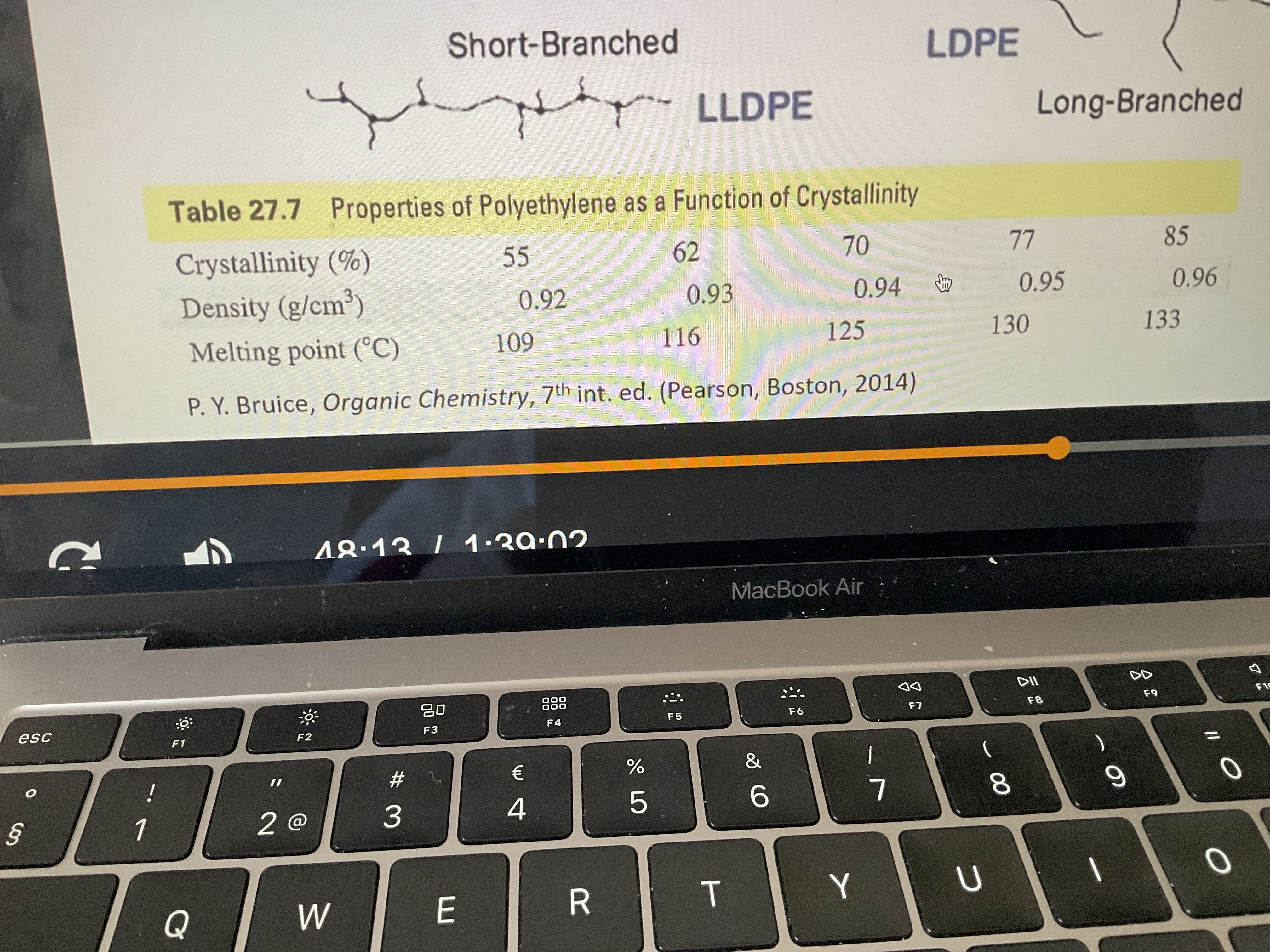
What happens?
As the percentage of crystallinity goes up in polyetheline, so that means they are more linear, the density and melting point will go up.
What is isomerism?
Molecules with Same composition (same number of atoms and types of atoms) but different atomic arrangements
What two types of isomerism are there?
Stereoisomerism and geometrical isomerism
What is stereoisomerism?
Atoms are linked together in the same order (head to tail) but differ in their spatial arrangement (tacticity)
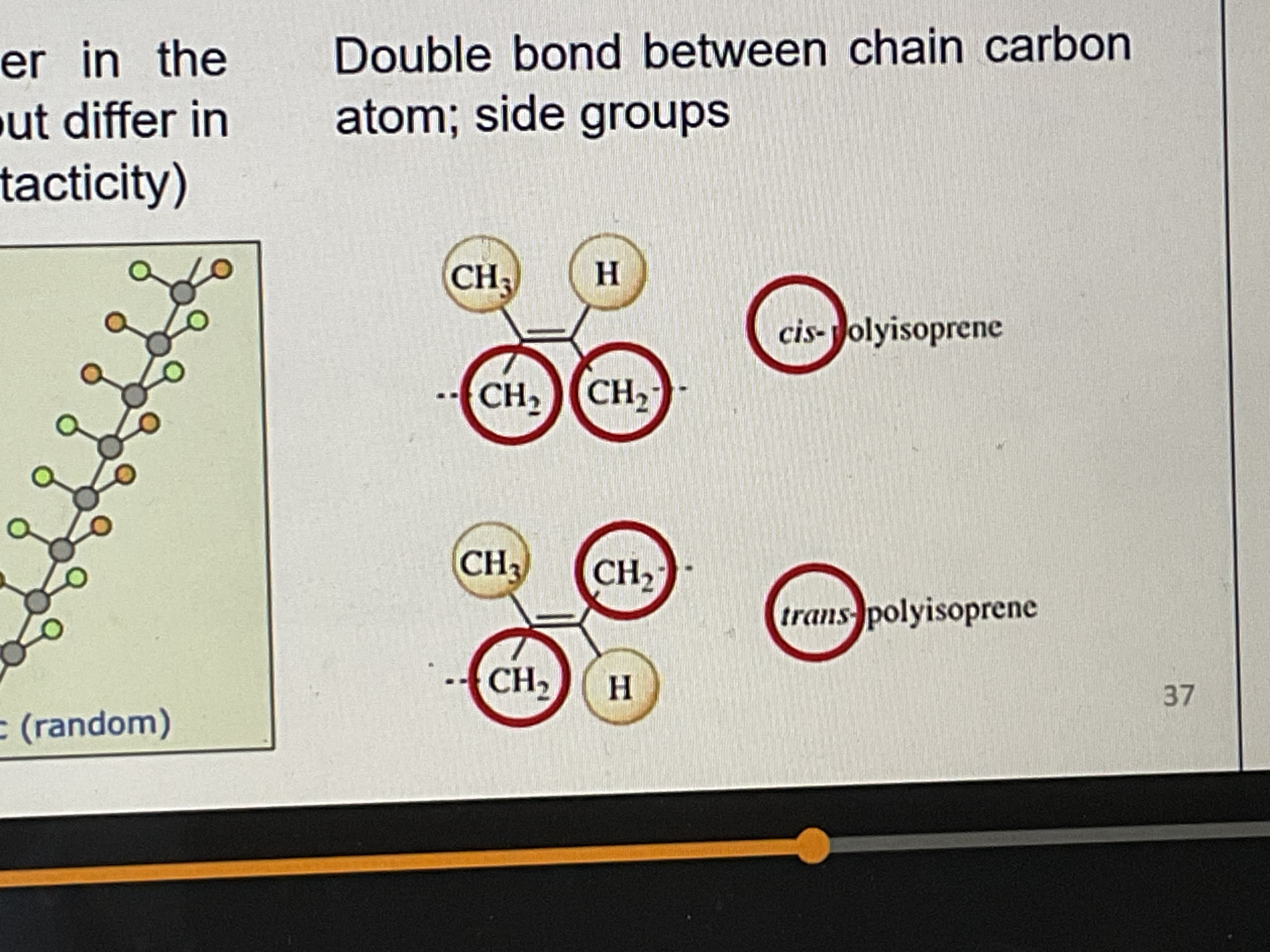
What is geometrical isomerism?
Double bond between chain carbon atom; side groups
What are the thermal properties in polymers?

What is glass transition temperature?
the temperature at which an amorphous polymer changes from a rubbery (elastomeric), viscous amorphous solid state to a glassy amorphous solid, or vice versa.
What does the melting and glass transition look like on a graph?
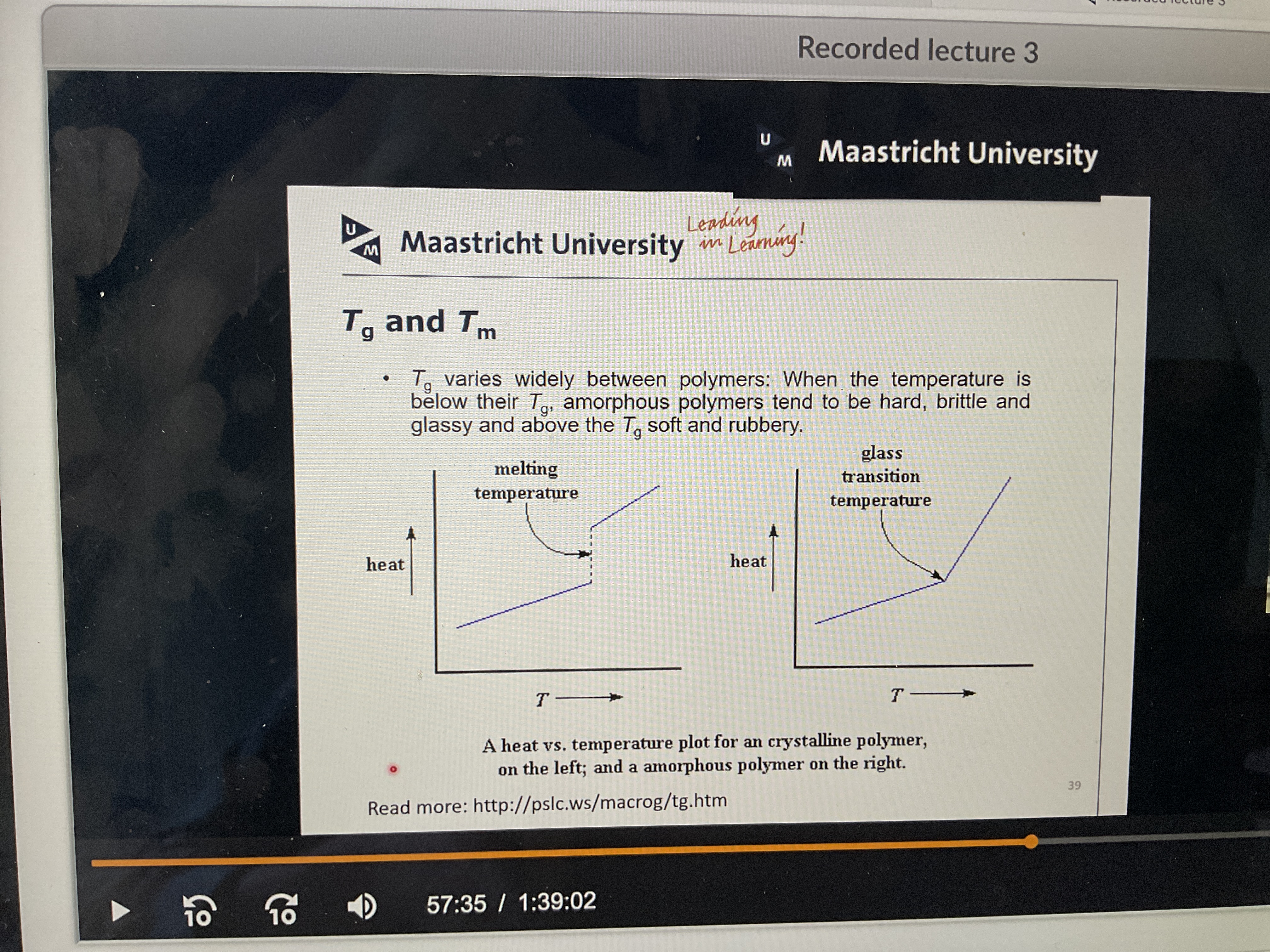
What’s the crystalline melting temperature?
Describes the temperature at which crystalline polymers undergo a phase transition from a crystalline state into a liquid
Can there at the Same time be both glass and crystalline melting temp?
Yes because different parts of the chain can look different
Why is the melting point higher than the glass transition temperature?
In a crystalline domain, that’s the part that melts, they pack really nicely and densely, so there are stronger interactions that hold the molecules together so you need more energy to break those.
In the amorphous its more disordered, less structured so weaker. This takes less energy to break.
That’s why temp of melting is always higher than glass transition !!
What are thermoplastics?
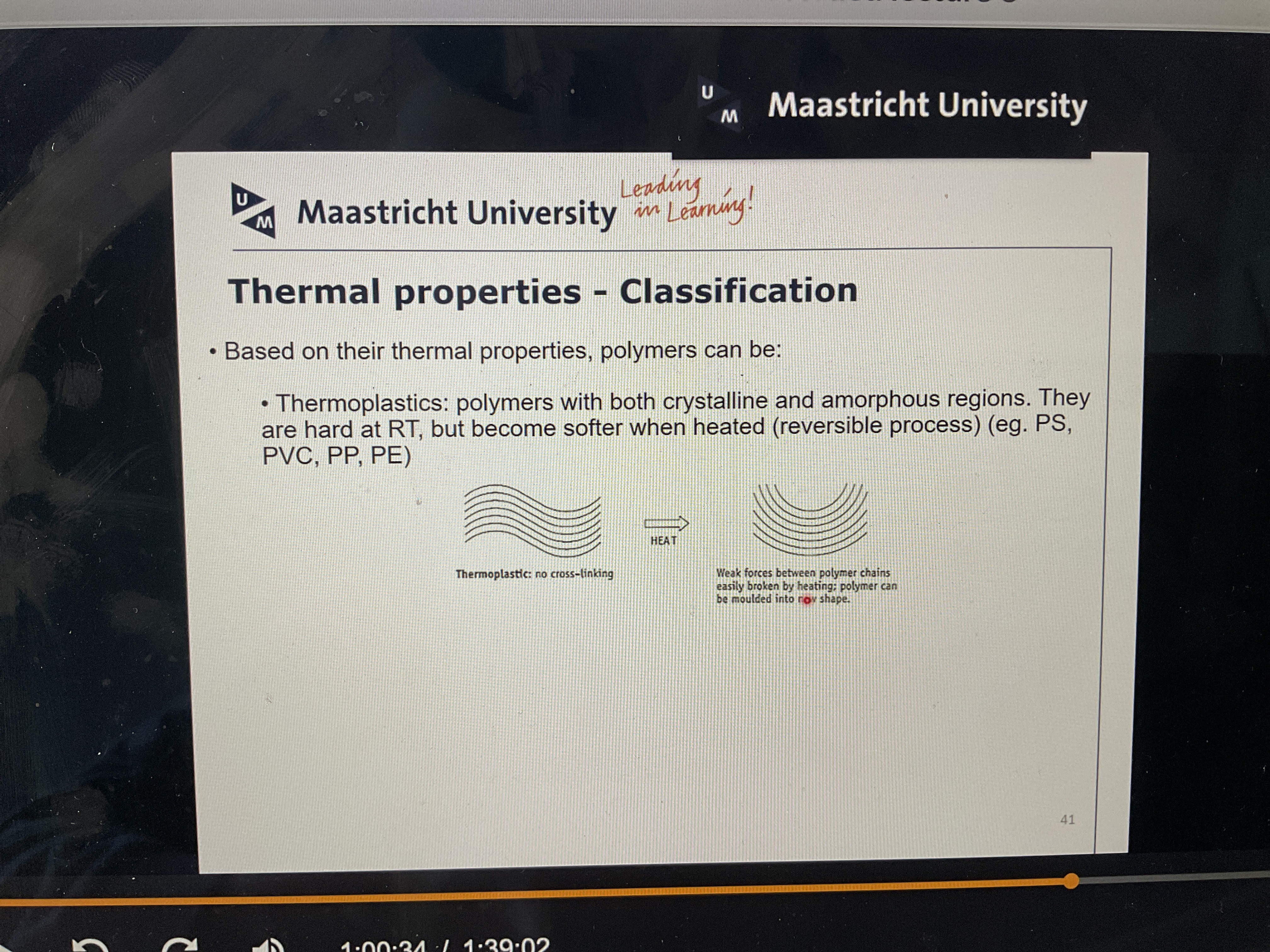
What are thermosets?

What are elastomers and rubbers?
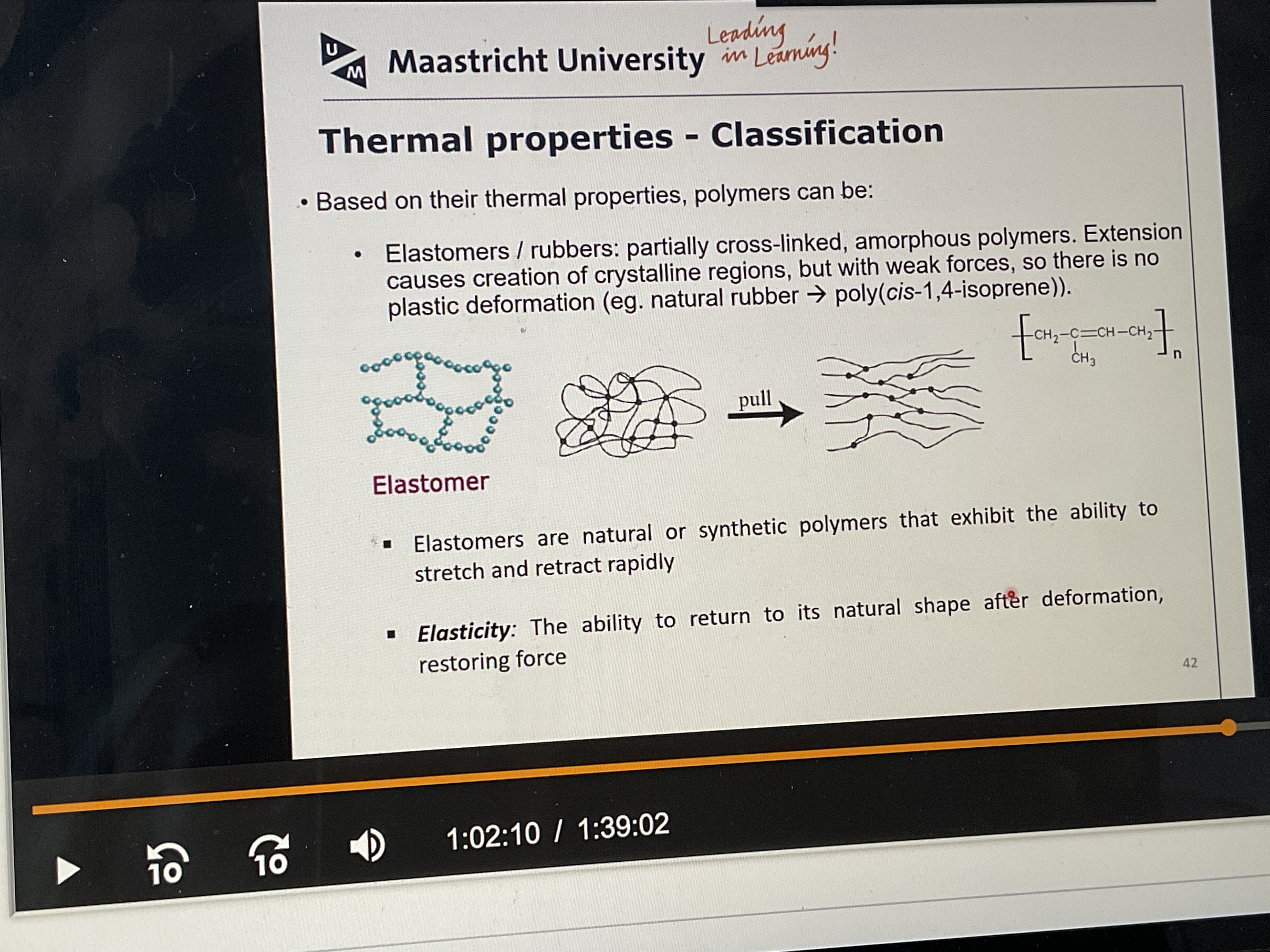
What does elasticity mean?
The ability to return to its natural shape after deformation, restoring force
Draw on a strain and stress graph: a glassy brittle polymer, a tough polymer and a rubbery amorphous material
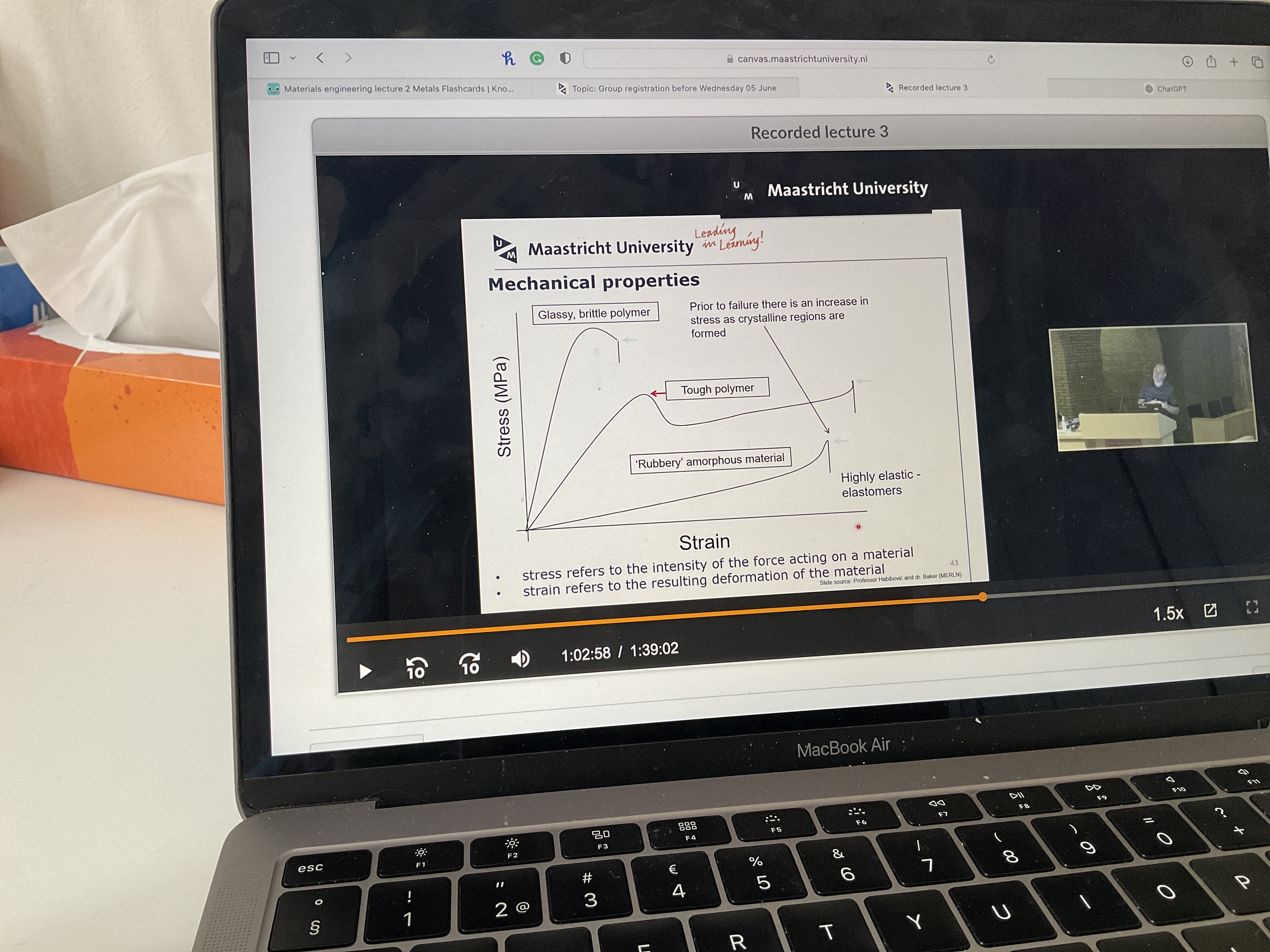
What are the three polymerization mechanisms?
Addition polymerization (chain growth)
Condensation polymerization (step growth)
Ring opening polymerization
What does addition polymerization look like? And what are the three steps called?
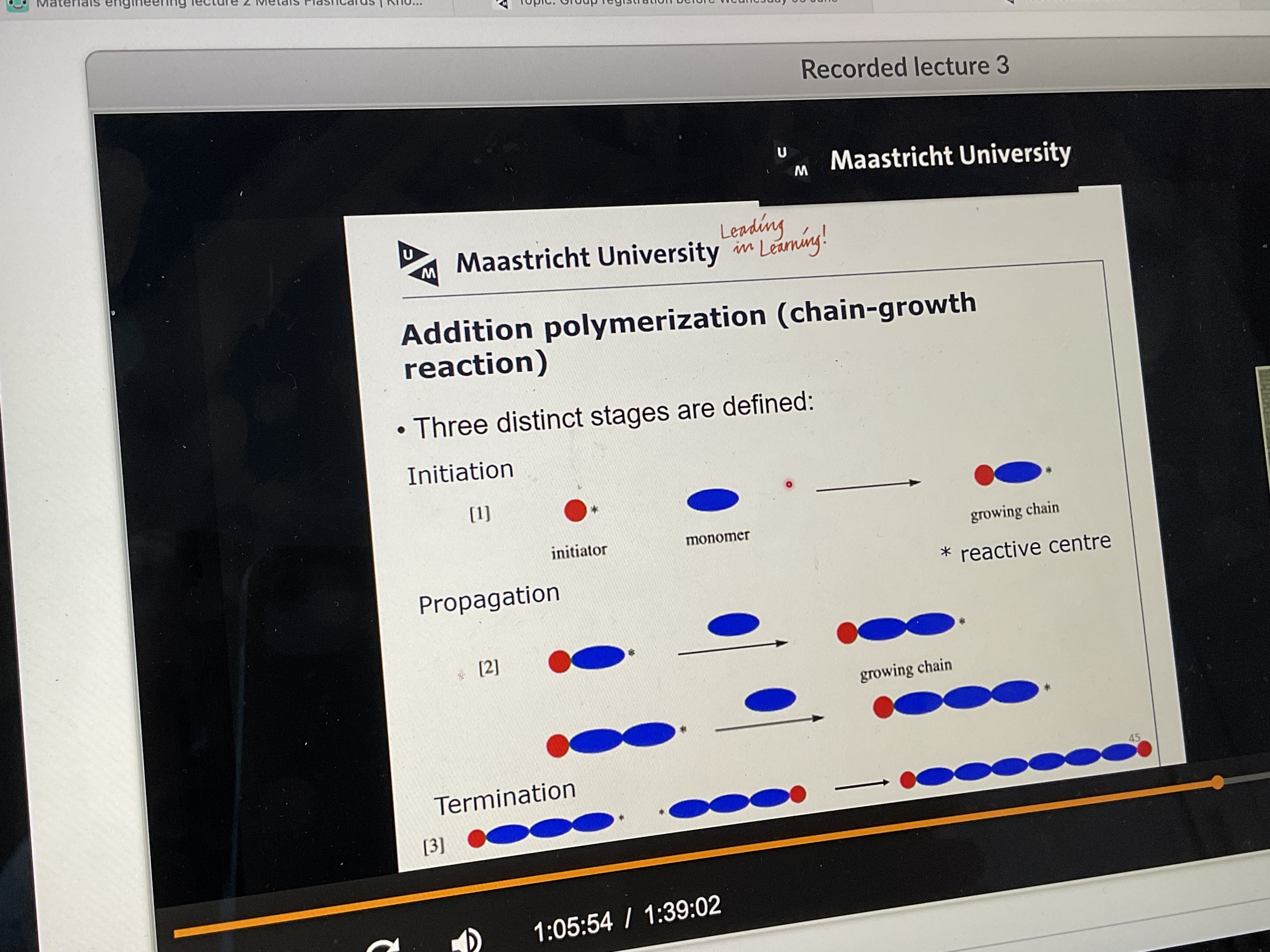
Read
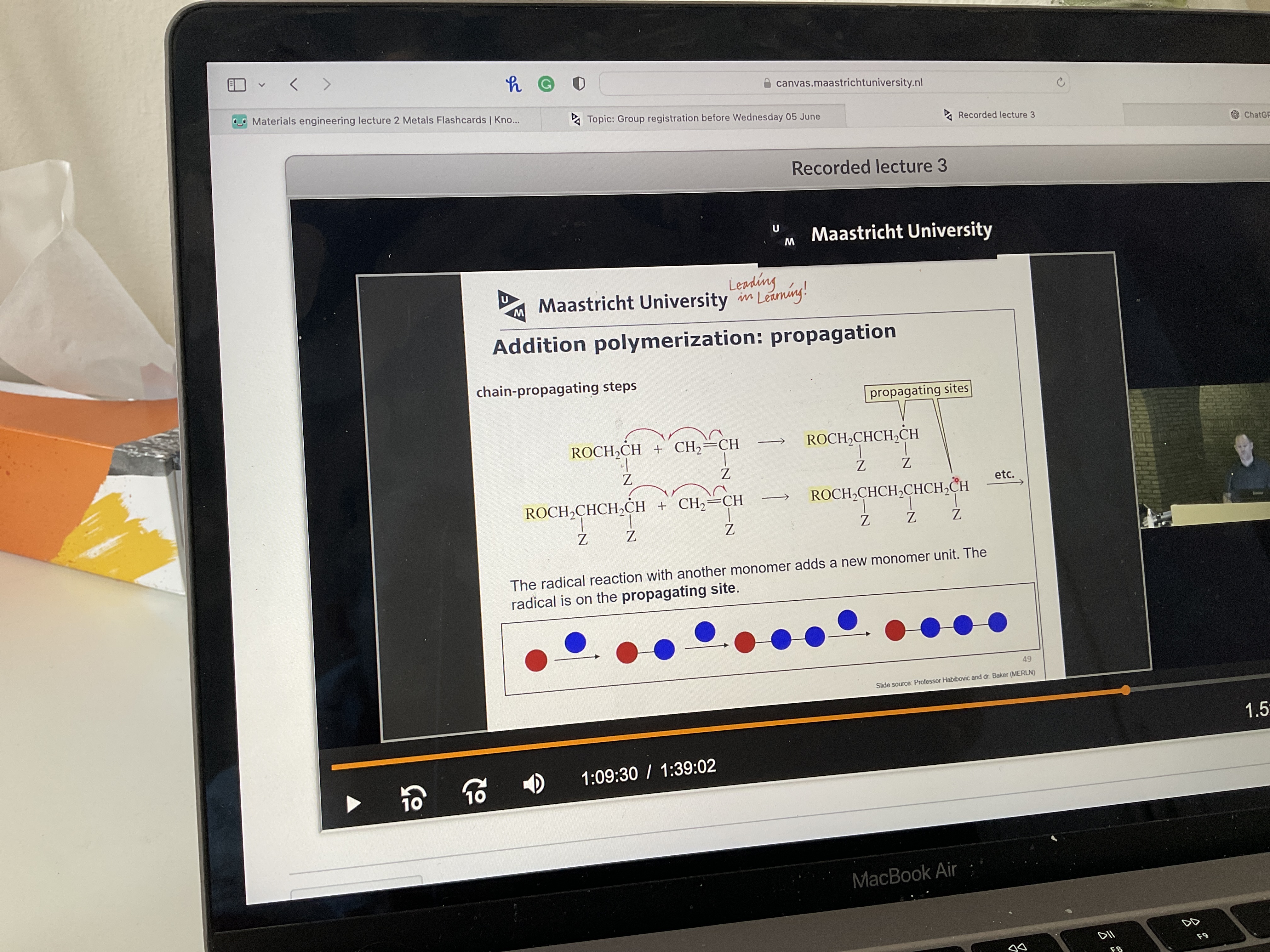
What doe combination mean in polymerization?
Two chains combine at the propagating sites
What does disporportionation mean in polymerization?
One chain gives an alkene, the other an alkine
What happens in a reaction with an impurity?
Radical is removed
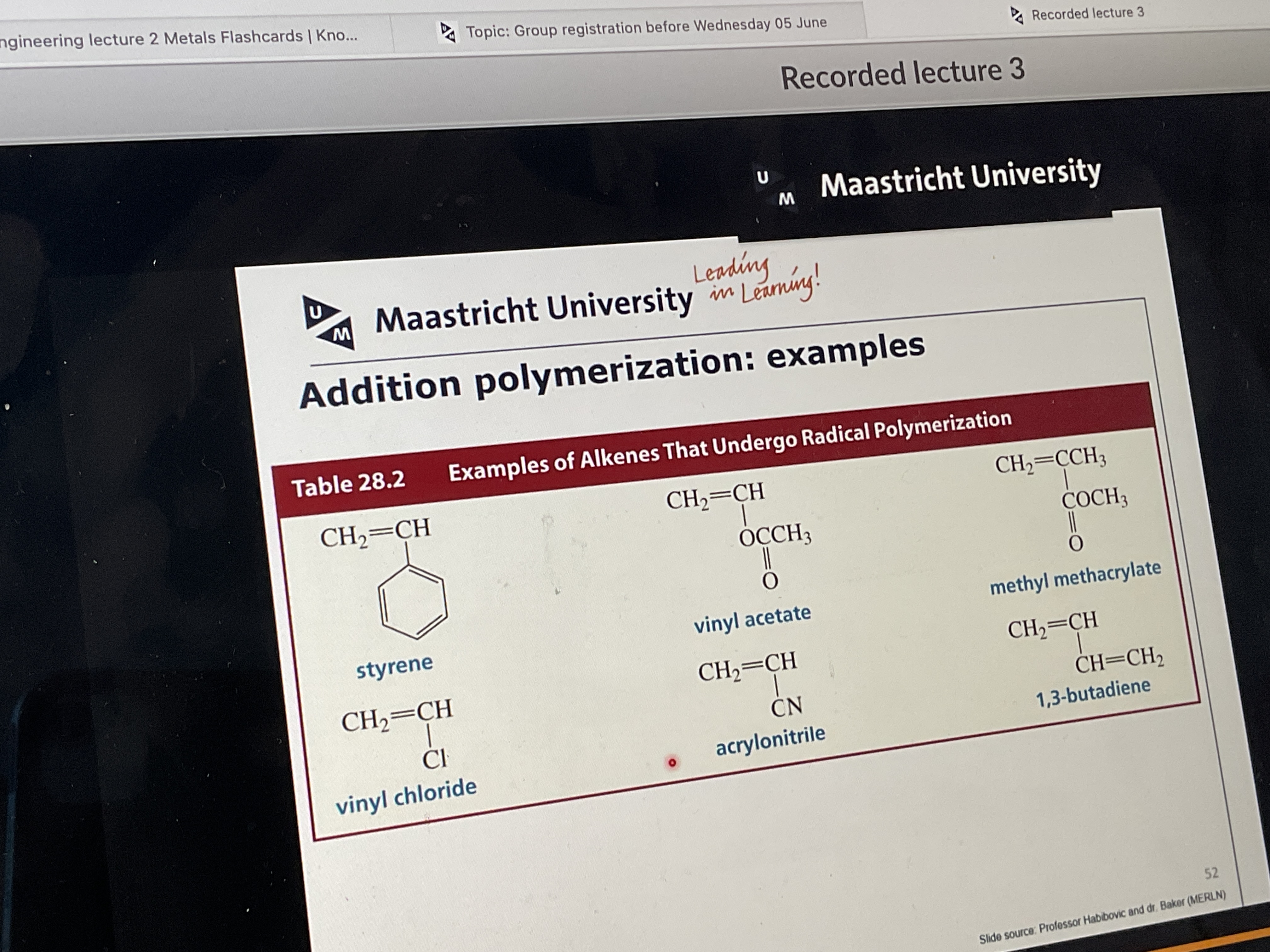
Give examples of alkenes that undergo radical polymerization
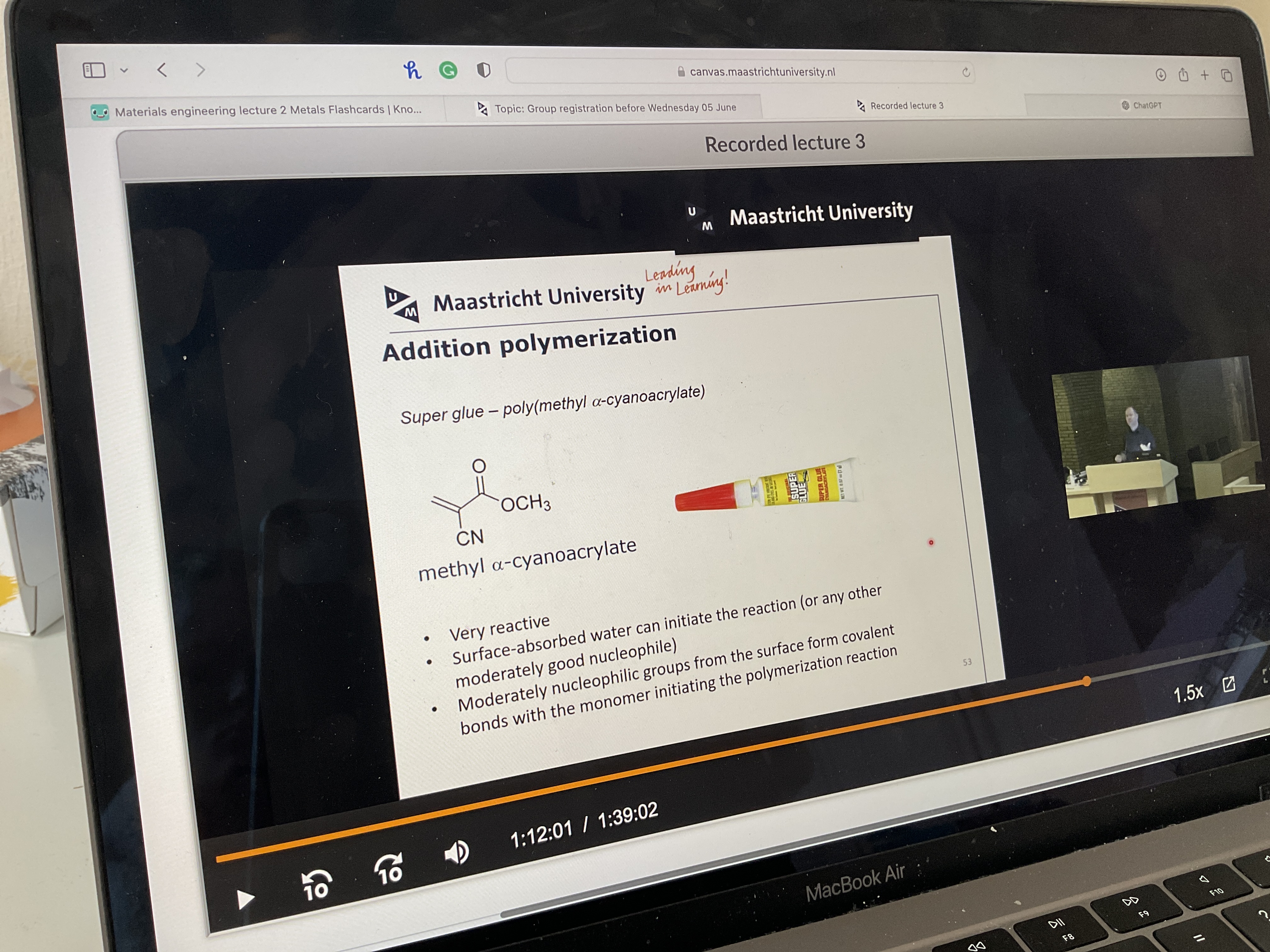
How does superglue work?
How does condensation polymerization work?
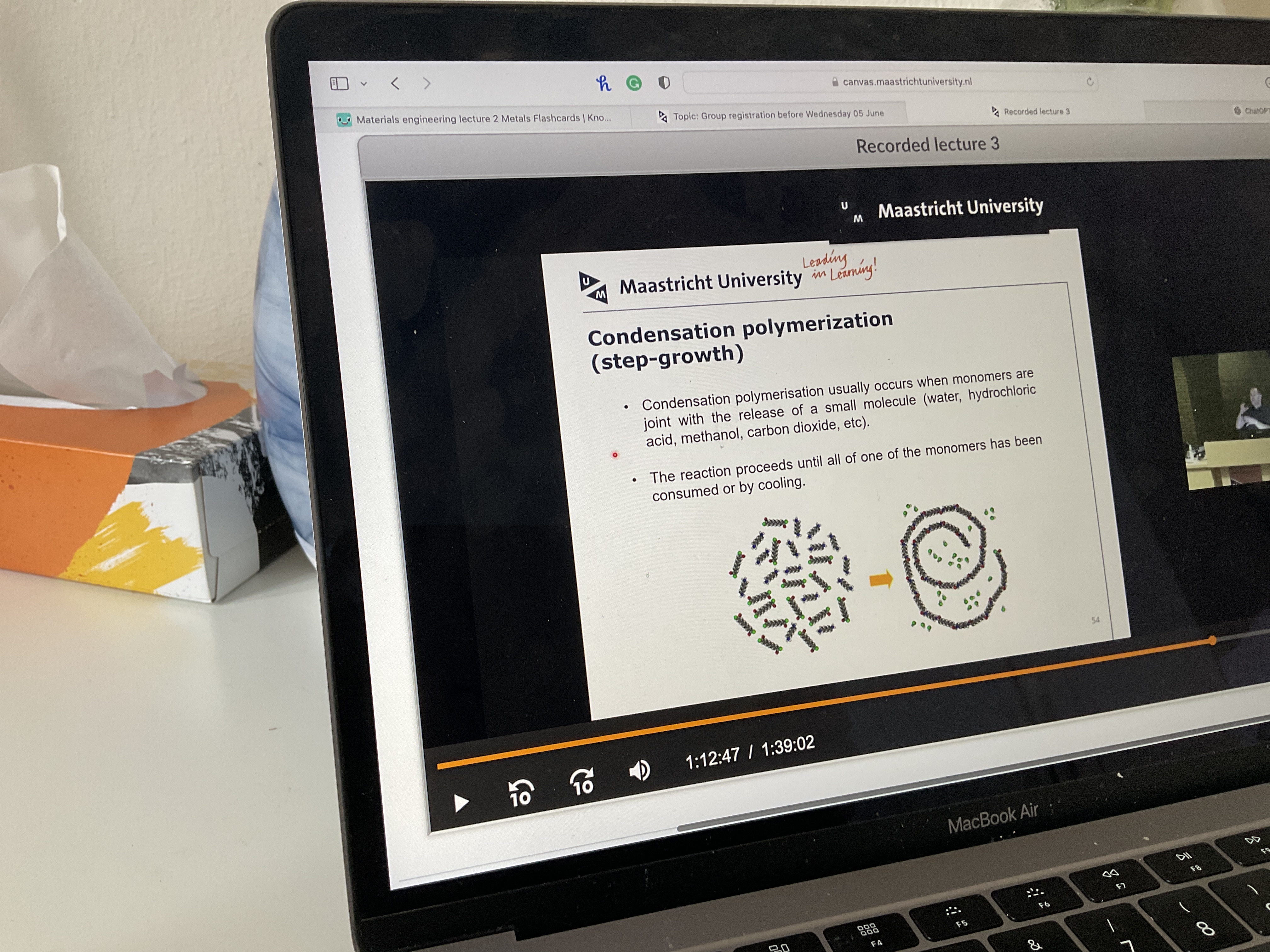
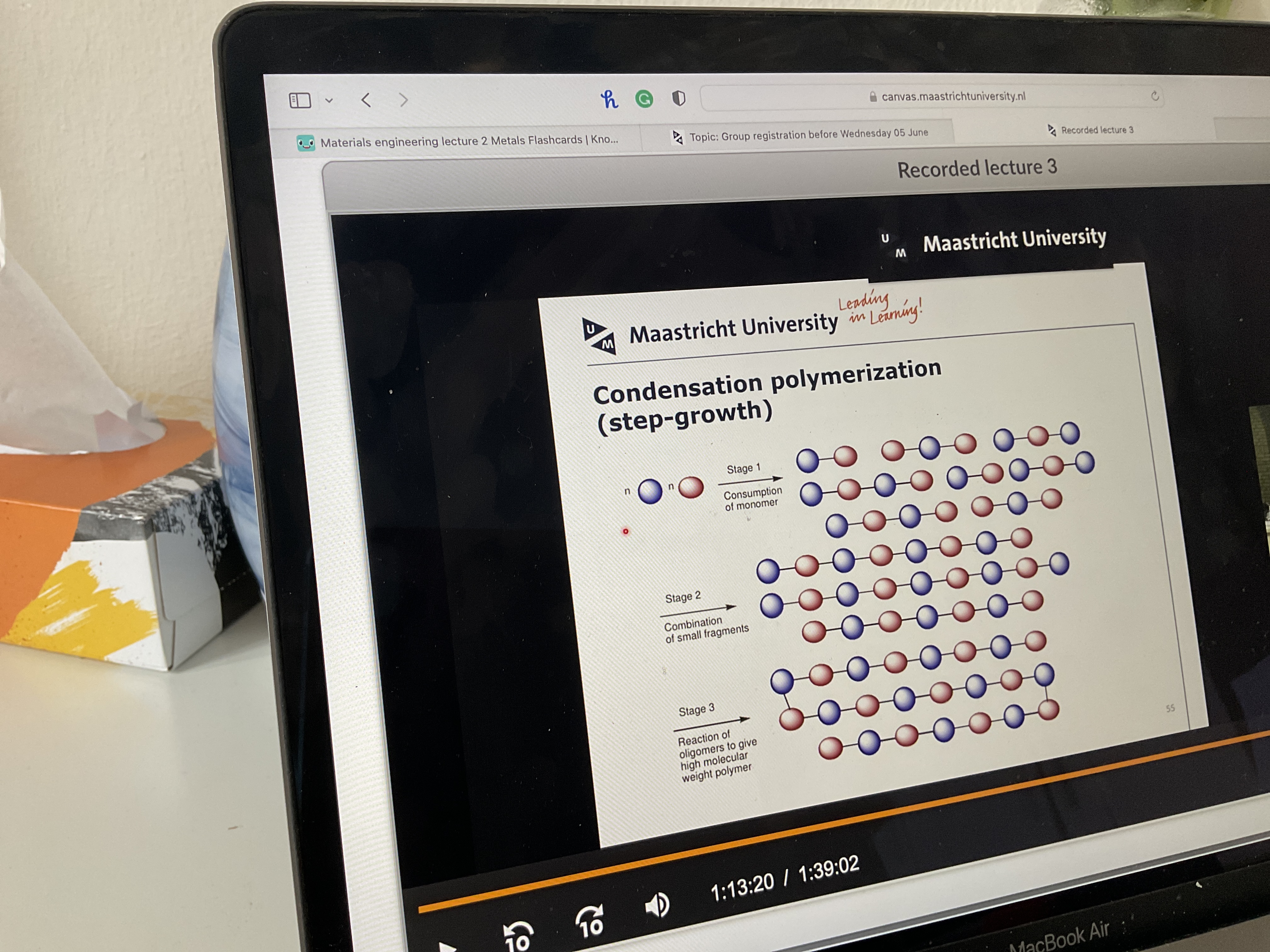
How does condensation polymerization work? Pic and steps
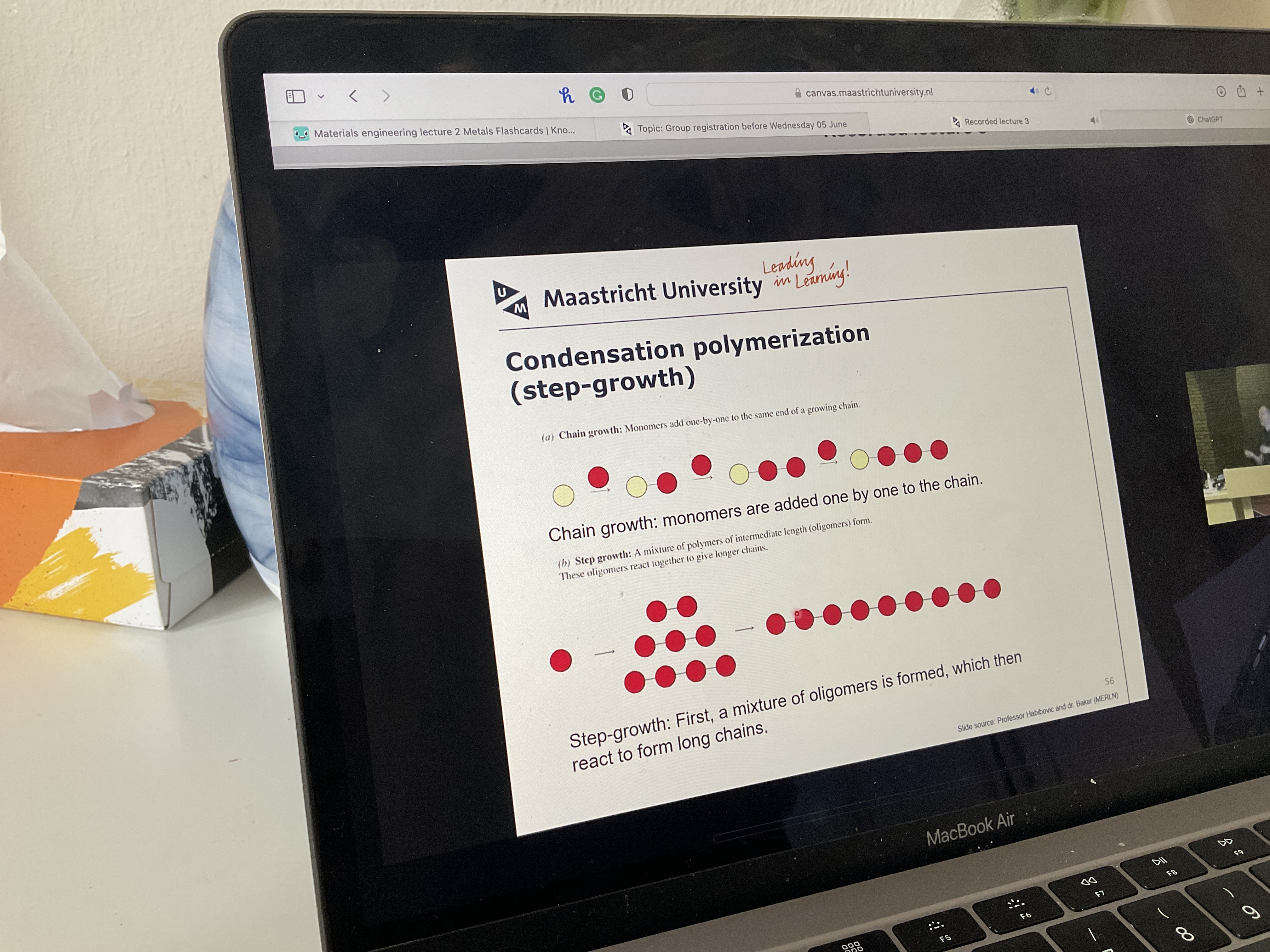
Read
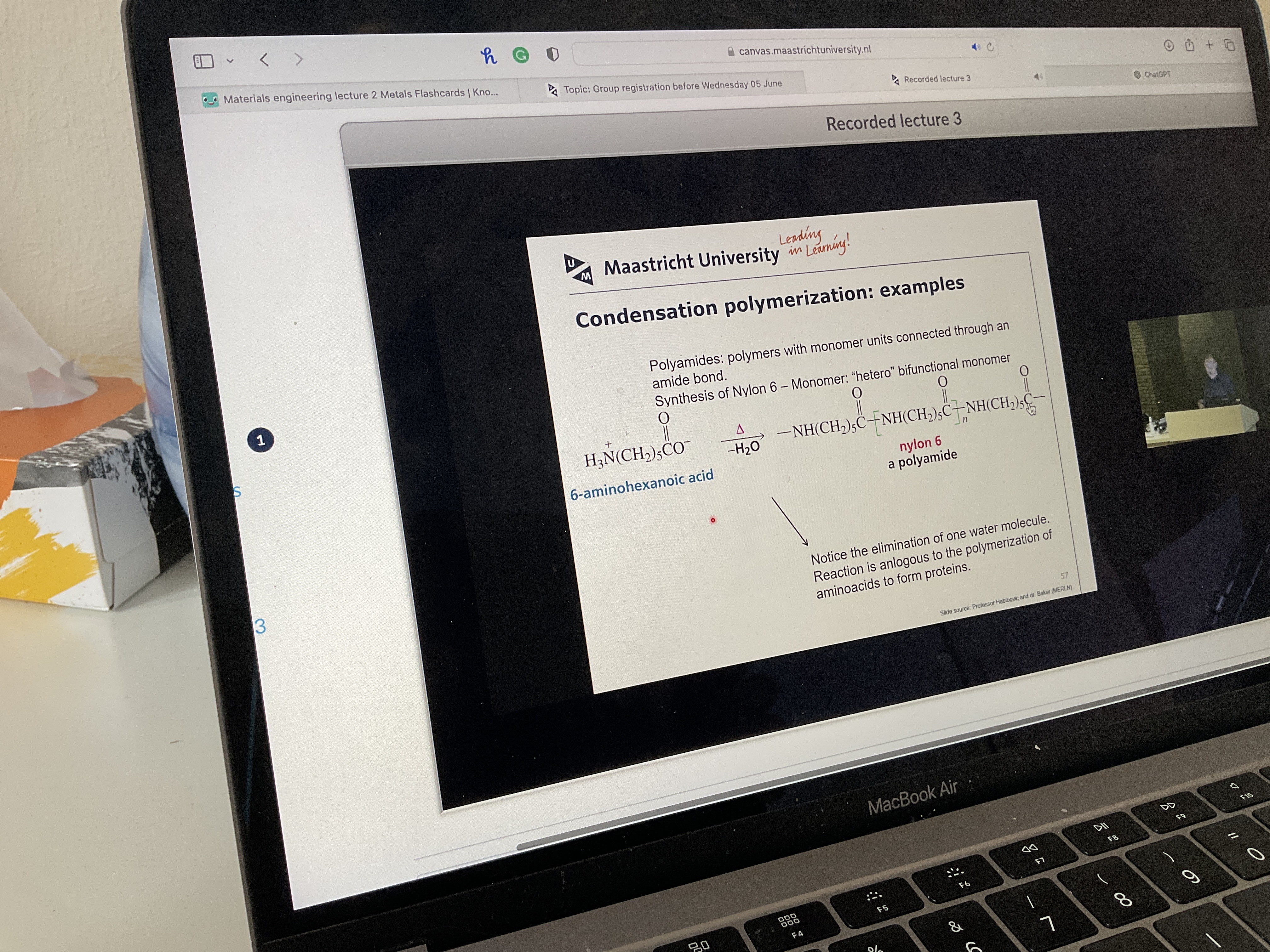
What is example of condensation polymerization?
Nylon, Kevlar, polyester, polycarbonates,
What happens in ring opening polymerization?
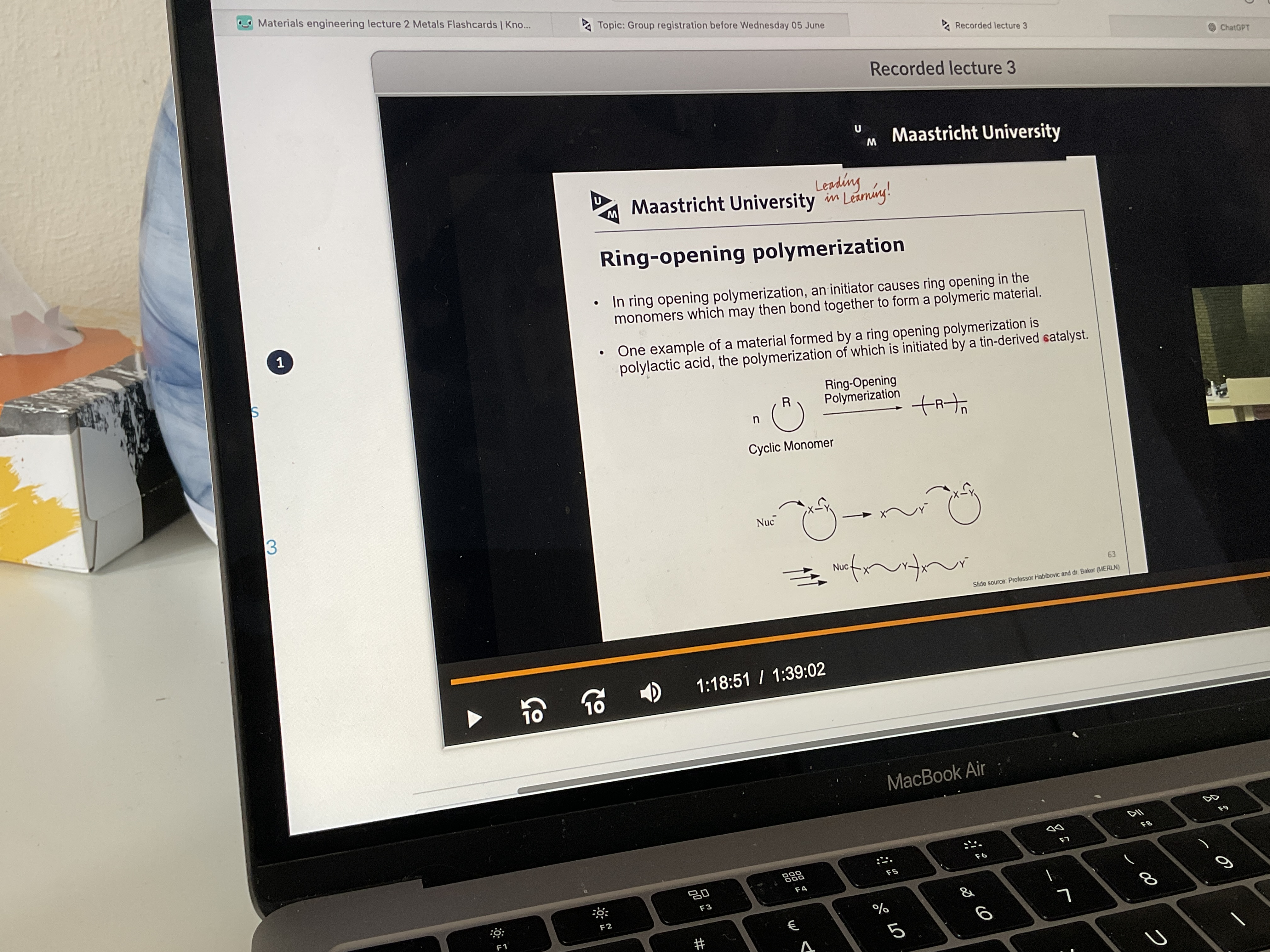
What is made by ring opening polymerization?
Polylactic acid can be used as suture material
When is polymer degredation desired and when is it not?
Yes: stitches, stuff that ends in environment like plastic bottles
No: laptop, stuff that you want to last
T/F most natural polymers are biodegradable
T
Give examples of non-degradable and degradable synthetic polymers
Yes: PLA, PGA
No: PET PMMA
What needs to be true for a polymer to be biodegradable?
The main chain of polymers needs to contain labile bonds (ester, amide, etc) where chain scission occurs to obtain compounds of lower molecular weight (most often hydrolysis)
What are the three steps of polymer degradation?
