CompTIA A+ Module 4 - Comparing Local Networking Hardware
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms

What does PAN mean?
Personal Area Network

What does LAN mean?
Local Area Network

What does WLAN mean?
Wireless Local Area Network

What does MAN mean?
Metropolitan Area Network

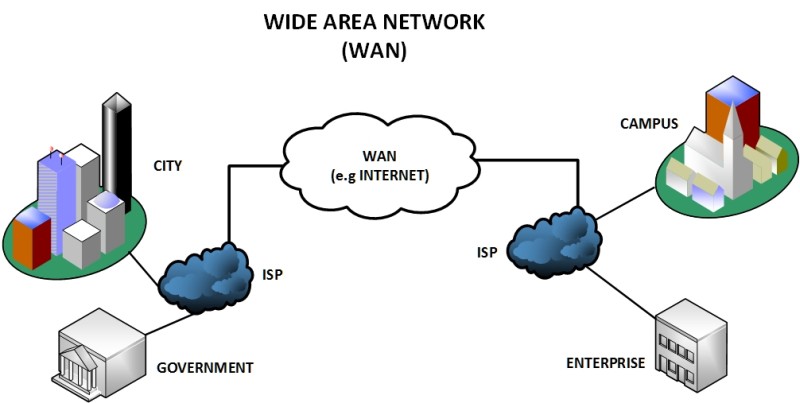
What does WAN mean?
Wide Area Network
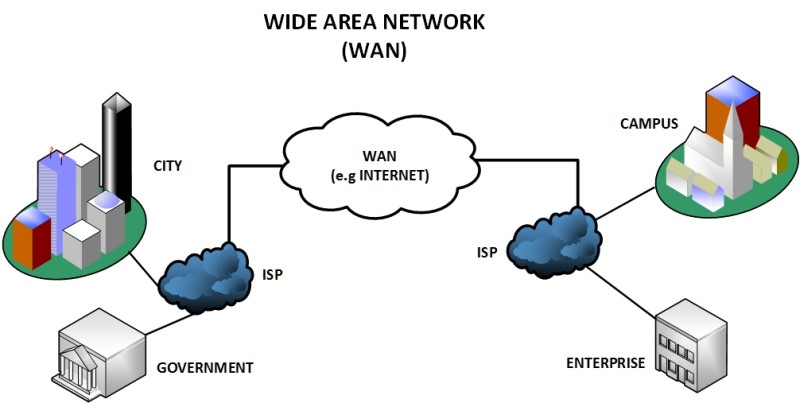
Please define a PAN.
Anything within arms reach on a desk (Computer, mouse/keyboard, monitor, headphones/microphone, etc.)
This type of network connection is very small and usually involves only 1 person.
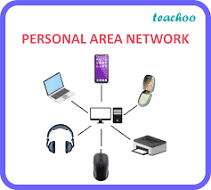
Please define LAN.
A network larger than a PAN, generally in one building (could extend to multiple buildings).
Not just limited to desktop computers and laptops: Servers, firewalls, printers/scanners, routers, etc.
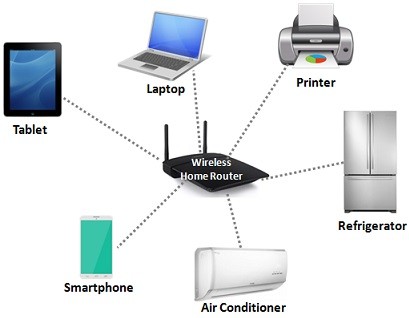
Please define WLAN.
Pretty much the same as a LAN, just using wireless devices like access points or routers.
WLAN devices typically uses 802.11 technologies.
good for hard to read areas in buildings.
Please define MAN.
A network that is larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN, usually made up of multiple LANs in multiple buildings.
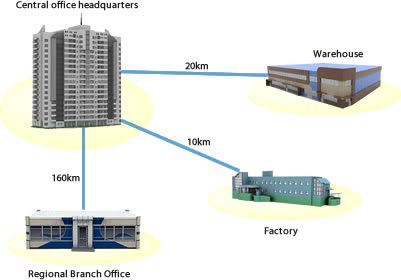
Please define WAN.
Largest of the network sizes and is generally comprised of multiple MAN networks connected together.
WAN networks can possibly extend over multiple countries.
The slowest connection of the network types.

Out of the box, how many NICs does a desktop computer come with?
Normally desktop computers come with an integrated ethernet NIC.


Out of the box, how many NICs does a laptop computer come with?
Normally laptop computers come with both a ethernet and a wireless NIC.


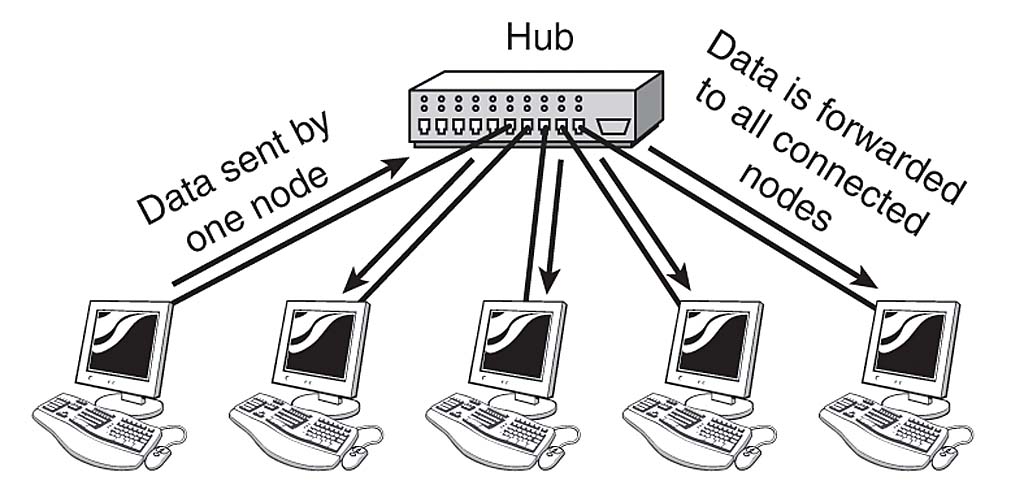
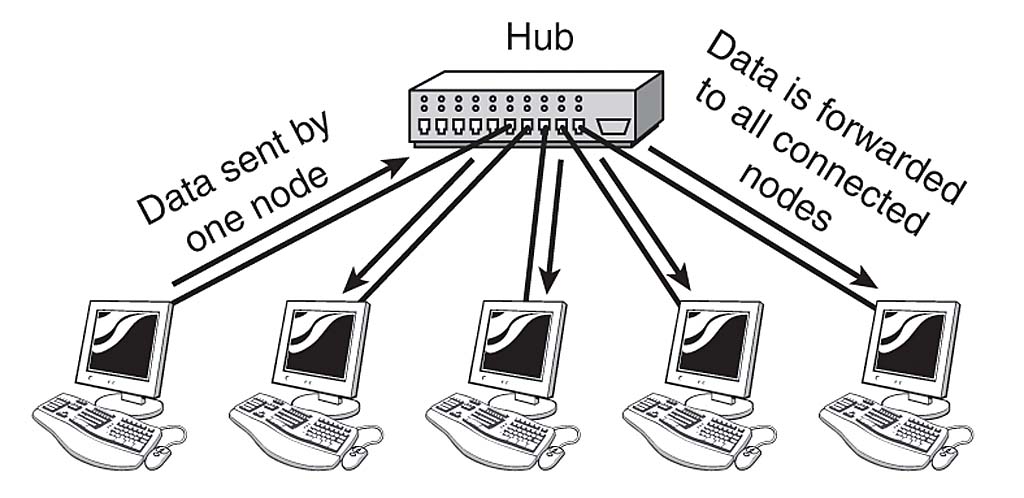
What is a dumb device?
A device that sends the input signal to all output ports to all of the connected devices.

What is a HUB?
A dumb device that’s performance is based on how many devices are connected to it,
Runs at half-duplex
More devices connected the hub, slower the output signal will become.
Has became obsolete.

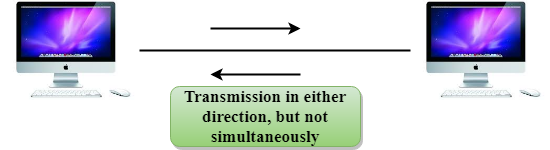
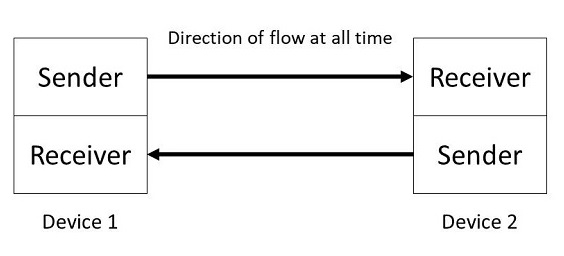
What does it mean for a device to run at half-duplex?
A communication method that allows data to be transmitted in both directions, but not at the same time.

What speeds do HUBs run at?
Half-duplex 10/100 Megabits per second (10/100Mbps) Ethernet only.

How does a network switch know where and who to send specific data to?
Network switches forwards data traffic to a specific destination port by learning each connected device’s MAC addresses.


What speeds do network switches run at?
Full-duplex 10/100/1,000/10,000 Mbps

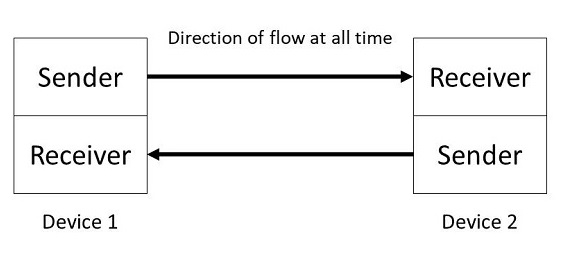
What does it mean for a device to run at full-duplex?
A communication method that allows data to be transmitted and received at the same time over one channel.
Define an unmanaged network switch.
A network switch that does not require any configuration of connected devices.
plug-and-play
usually used in small networks like in homes or very small offices.

Define a managed network switch.
A network switch that a user can log into and configure any/all devices that are connected to the network switch.


If there is a network device that is located in an area where a wall outlet is not available, what option do you have in powering this network device?
PoE (Power over Ethernet)

How can you send Power over Ethernet?
With either a PoE box or a PoE network switch.
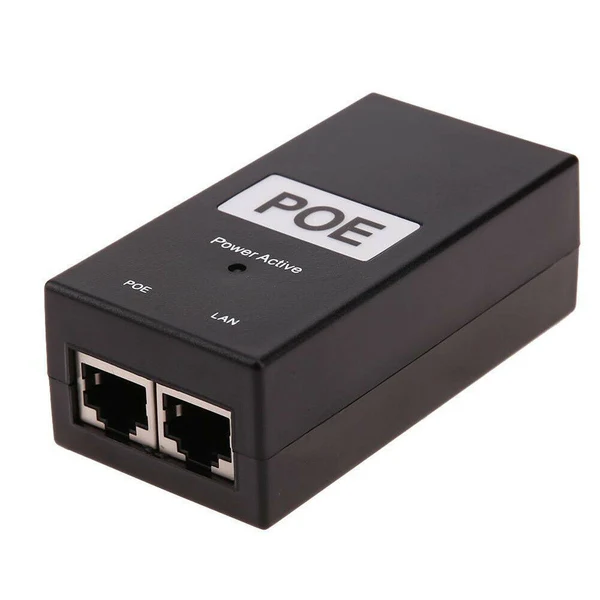


What devices benefit most from Power over Ethernet?
Access Points
VoIP Phones (Voice over Internet Protocol)

What is the most common type of network cable?
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
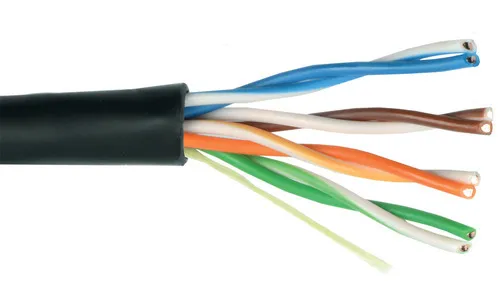

Explain the characteristics of UTP network cables.
Uses copper wires for carrying electrical signals.
Four balanced wire pairs.
Twisted wires to reduce interference.
Signal has a theoretical maximum distance of 100m or 330ft.
Realistic maximum signal between 80m to 90m or 262ft to 295ft.
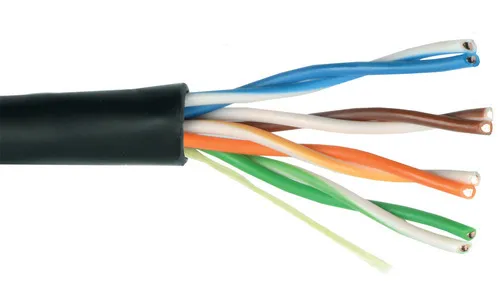

What determines the maximum length at which a network cable can function properly?
Wiring type
Location of cable

What is the difference between a shielded twisted pair (STP) and a Unshielded twisted pair (UTP)?
There is screening or shielding around the twisted wires within the cable.
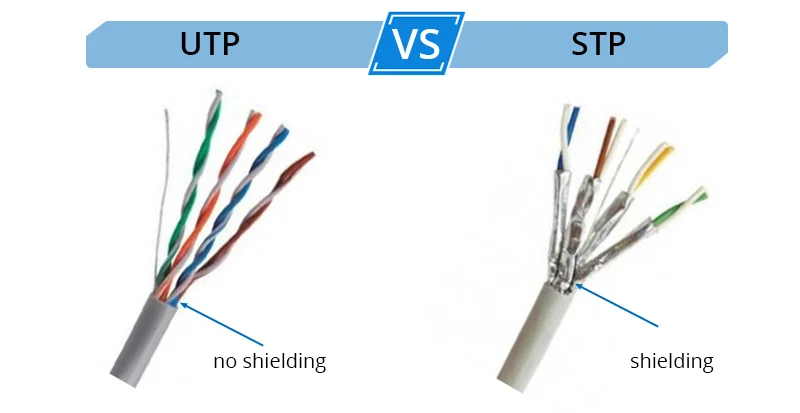

Why would a network cable need to have shielding?
To help mitigate against electric interference from near by electrical devices.

What happens if there is some electric interference on a network cable?
Slower network speed.
Limitation in cable length.
Poor connection to network.
There are two types of STP network cables: Explain a screened cable.
Has one outer foil shield around all pairs of twisted wires.

There are two types of STP network cables: Explain a fully shielded cable.
Has a braided outer screen surrounding the entire cable included foil shielding around each twisted pairs of wires.

CAT 5 Capacity
100 Megabits per second (100 Mbps)
CAT 5e Capacity
1 Gigabits per second (1 Gbps)
CAT 6 Capacity
1/10 Gigabits per second (1/10 Gbps)
CAT 6A Capacity
10 Gigabits per second (10 Gbps)

What CAT cable standard do old telephone lines use?
CAT 3 or POT (Plain-Old-Telephone)


What tool do you use to put an RJ-45 connector on the end of a UTP or STP cables?
Cable Crimper


What is a punchdown tool used for in networking?
To lock the 8 wires of the CAT cable into either a patch panel or wall box.


What is the benefit of having a CAT network cable plugged into a wall box?
If the CAT cable coming from the computer to the wall box does fail, only that cable needs to be replaced instead of the entire network cable.
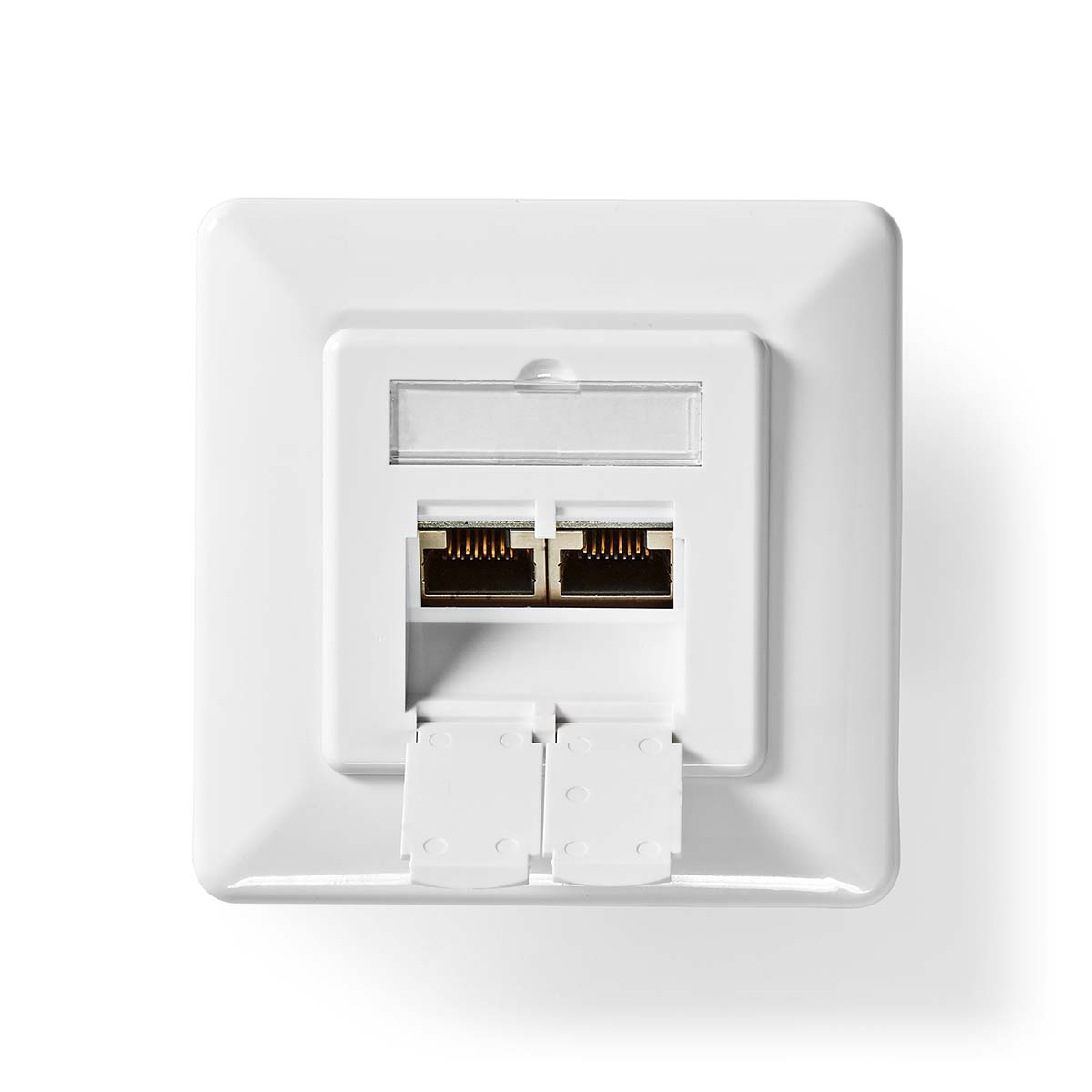


What networking tool is this?
Punchdown Tool


What networking tool is this?
Cable Crimper


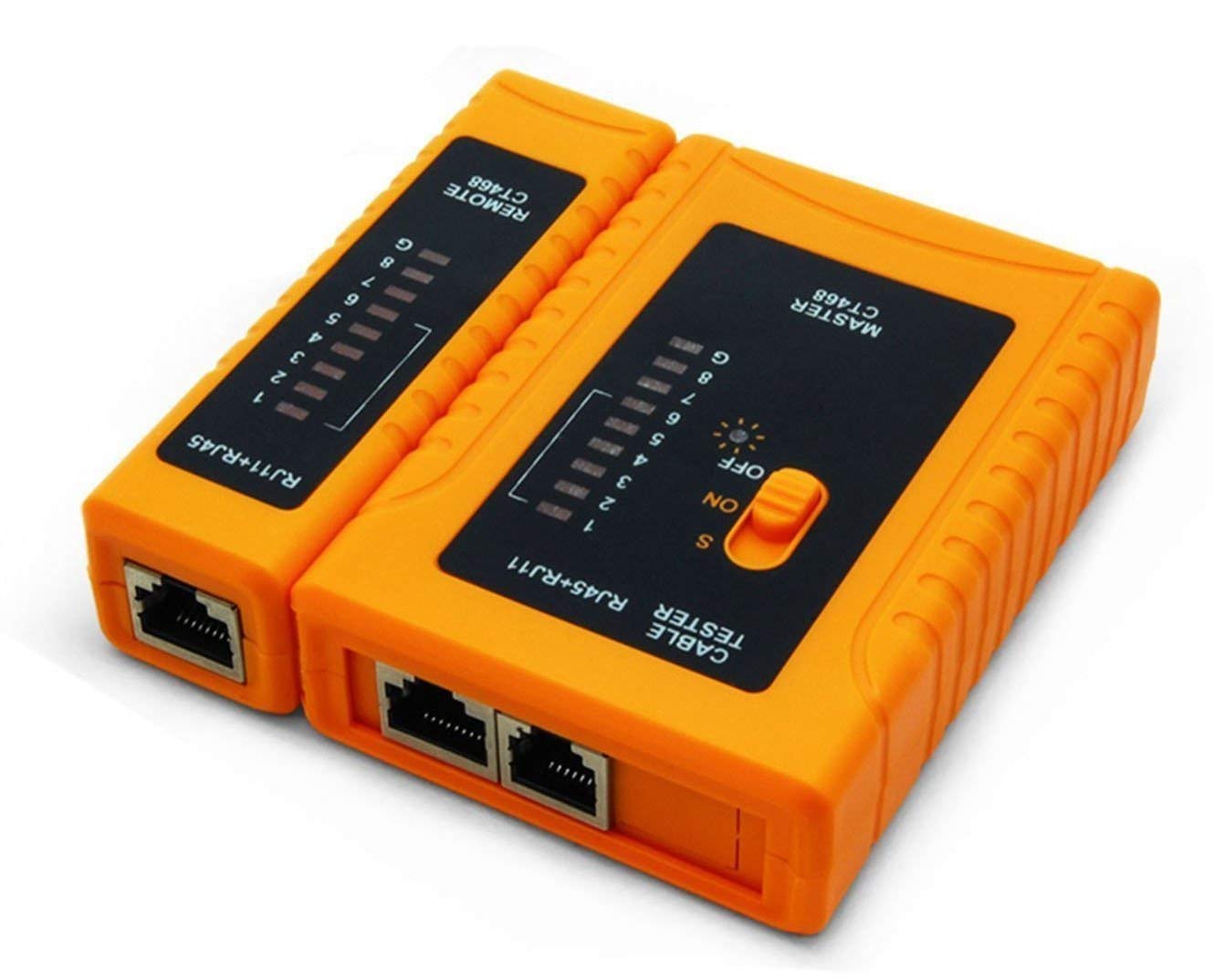
What networking tool is this?
Cable Tester

Fiber Optic Cable Types
Single-Mode Fiber
Multi-Mode Fiber
Single-Mode Fiber use cases
Used for cables that need to travel great distances outdoors.
Multi-Mode Fiber use cases
Used for cables that don’t need to travel great distances indoors.
Basic Fiber Optic Cable Connector Types
Straight Tip (ST)
Subscriber Connector (SC)
Lucent Connector (LC)

What is fiber optic cables comprised of?
Glass surrounded by rubber shielding.

What are the 4 basic IEEE wireless network standards?
802.11a
802.11b
802.11g
802.11n

What is 802.11a and 802.11g used for?
Used in home routers and access points (AP), where 802.11a and 802.11g run on different frequencies.

What is 802.11b used for?
Bluetooth devices

What is 802.11n used for?
Long range communication, requiring a direct line of sight with host.

Which of the 4 basic IEEE wireless network standards can travel through solid walls?
802.11a
802.11b
802.11g

What frequency and speed does 802.11a run at?
A frequency of 5 Gigahertz (5 GHz)
A speed of greater than 54 Megabits per second (54 Mbps)

What frequency and speed does 802.11b run at?
A frequency of 2.4 Gigahertz (2.5 GHz)
A speed of greater than 11 Megabits per second (11 Mbps)

What frequency and speed does 802.11g run at?
A frequency of 2.4 Gigahertz (2.5 GHz)
A speed of greater than 54 Megabits per second (54 Mbps)

What frequency and speed does 802.11n run at?
A frequency of either 2.4 or 5Gigahertz (2.5 or 5GHz)
Speed depends on number of open channels of the device:
1 Channel 150 Megabits per second (150 Mbps)
2 Channel 300 Megabits per second (300 Mbps)
3 Channels 450 Megabits per second (450 Mbps)
4 Channels 600 Megabits per second (600 Mbps)

What frequency to a majority of wireless devices run at?
2.4 Gigahertz (2.4 GHz)

What is the main reason behind wireless interference between wireless devices?
A majority of wireless devices use the same 2.4 Gigahertz (2.4 GHz) frequency.

What device surprisingly interferes with wireless devices?
Microwaves that are turned on.


What are access points used for?
Extending home or office network access from base router or network switch.