Lecture 57: Oestrogen and Progesterone
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
how are osteogens and progesterone synthesised?
cholesterol—>pregnenalone —→ progesterone——>androgens——> androstenediones and testosterone——→ oestrone and oestradiol
how do sex hormones bind to nuclear receptors?
steroid hormones bind to the nuclear receptors binding site in the cytoplasm
they then translocate to the nucleus
the receptors dimerise to regulate gene transcription
the receptors bind to the docking site on the DNA for the hormone response element
how do oestrogen receptors act?
oestrogen binds to the ERalpha or ERbeta
the receptor changes its conformation due to dissociation from the heat
the receptors dimerise in order to increase affinity for binding to the DNA ( binds to specific oestrogen response elements)
ERbeta receptors also produce a nongenomic response
how do progesterone receptors act?
they have 2 isoforms as they are the same gene
PR- A and PR- B
PR- B brings about the stimulatory effect of progesterone
they bind to progesterone response elements and regulate gene transcription
what does oestrogen do in the body?
stimulates endometrium, thickens vaginal mucosa and thins cervical mucus
secondary sex characteristics for women, breast duct growth
increases protein and bone production, and lowers cholesterol
decreases GnRH in hypothalamus, but increases it in ovaries, lowers LH in the pituitary
multiple effects on CNS
what does progesterone do in the body?
lowers GnRH production in the luteal phase as corpus luteum produces progesterone
stimulates the secretory phase of the endometrium
increases thickness of cervical mucus, increases glandular breast development and basal body temp
basal body temp can be used to indicate for ovulation
what are the natural and synthetic oestrogen preparations?
natural: Oestradiol, oestrone , oestriol
synthetic: ethinylestradiol
forms: oral, transdermal, IM, implant, topical
Selective oestrogen receptor modulators are used in cancer treatment and are selective due to ER-alpha/beta tissue expression
what are some of the natural and testosterone derived progesterone treatments?
natural: 17- alpha- hydroxyprogesterone
testosterone-derived: levonorgestrel
what are the features of menopause?
changes in hormone levels
due to ovarian failure, loss of sensitivity to FSH and LH
there are no more developing follicles, so no more oestrogen, no more eggs and no more progesterone
what are the phases of menopause?
perimenopause- hormone fluctuations start 2-8 years
menopause- oestrogen levels drop, official once its been 1 year since last period
postmenopause- oestrogen levels continue to decline
this can increase risk of CVD, stroke, Osteoporosis and dementia
symptoms of menopause:
hot flushes
vaginal dryness
osteoporosis
heart palpitations
what is osteoporosis and what can be taken to help once it starts?
decrease in bone density as oestrogen maintains bone density
HRT can be given to reduce fracture risk
raloxifene mimics oestrogen to maintain bone
what is HRT?
hormone replacement therapy
uses natural oestrogens
combo of oestrogens and progesterones
can be a tablet, patch, gel, spray, IUD
progesterones are given with oestrogens in HRT to counteract the stimulatory effects of oestrogen to prevent uterine cancer
what are the positive effects of HRT?
strengthens bone
lowers cholesterol
reduces menopausal symptoms
reduces osteoporosis
what are the negative effects of HRT?
increases breast and uterine cancer risk
increases blood clot risk
benefits outweigh risks
what are the contraception types?
barrier: condoms, caps
IUD: coil
oral: combined, progesterone only, emergency contraception
what are the features of combined oral contraceptives?
ethinylestradiol+ progestogen OR levonorgestrel + desogestrel
take 21/28 day cycles
oestrogen inhibits the secretion of FSH so no eggs develop
progesterone inhibits secretion of LH from pituitary leading to thickened cervical mucus and thin endometrium
what are the side effects of combined oral contraceptives?
mild: nausea, weight gain, hypertension
serious: VTE, Myocardial infarction
increases breast C risk, decreases ovarian C risk
may cause amenorrhea after stopping
what are progesterone only contraceptives?
levonorgesterol
taken continously
thickens cervical mucus, thins endometrium
may stop ovulation
useful when oestrogen is contraindicated
menstrual disorders treated with progestogens:
dysmenorrhoea- painful periods, abdominal cramps
menorrhagia- heavy periods, excessive bleeding
PMS
Endometriosis- cells behave like lining outside uterus
what are the features of occasional contraception?
high dose progesterone- levonorgesterel, within 3 days 98% effective)
ulipristal(PR modulator): within 5 days
side effects: nausea vomitting
copper IUD can cause sperm/ova toxicity
what are antiprogesterones?
medical abortion alternative to surgery
Mifepristone(PR antagonist) and misoprostol(PGE1 analogue)
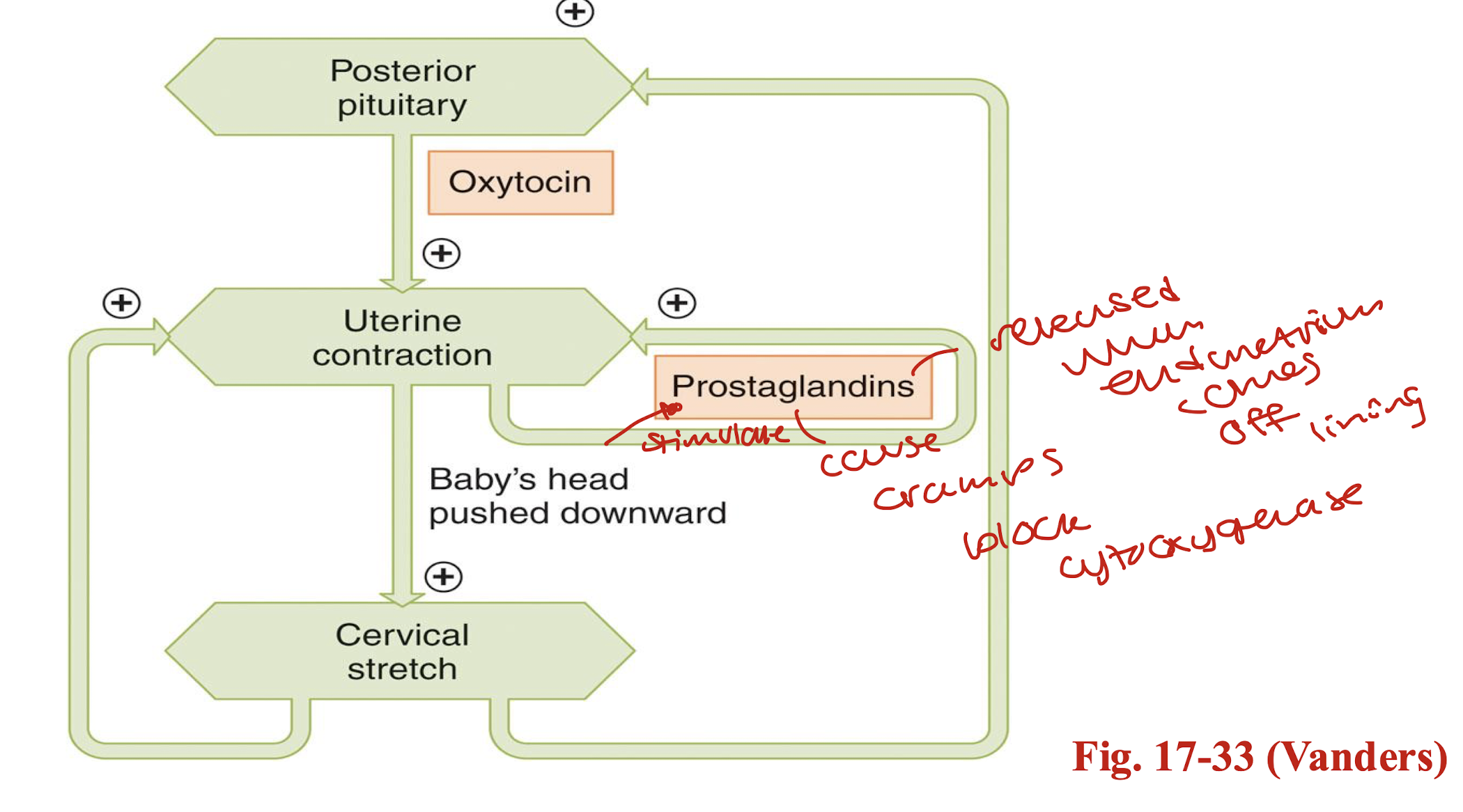
how are prostaglandins made and what do they do?
phospholipase A causes membrane phospholipid to become arachidonic acid
arachidonic acid becomes prostaglandins via cyclooxygenase
uterine contractions are stimulates by prostaglandins
how do uterine wall contractions happen?
oxytocin and PG are labour inductors
progestogens relax uterus and maintain cervix; used in habitual miscarriage and perterm labour
B2 agonists inhibit contractions