Chapter 48 | Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
The Nervous System
Information processing
CNS: Integrates information
PNS: Transmits information
Basic unit: Neuron
Information processing
Sensory input (external/internal) via sensory neurons (PNS)
Integration of information in the CNS (via interneurons)
Response (external/internal) via motor neurons (PNS)
Nerves
Neurons bundled at axons
Ganglia
Neurons clustered at their cell bodies
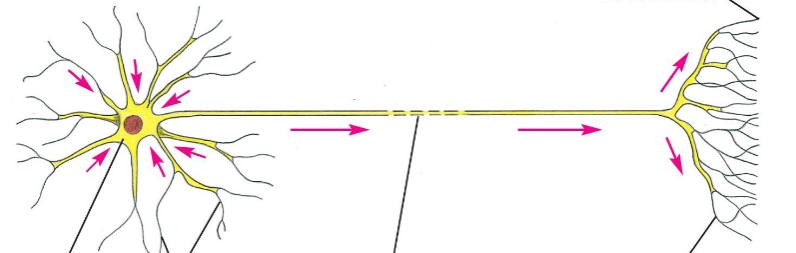
Neuron
Consists of the cell body, dendrites, axon, axon terminal, synapse, & glia

Cell body
Contains majority of organelles, nucleus, & cytoplasm
Dendrites
Extensions of the cell body; functions to receive information
Axon
Large extension from the cell body, transmits information in the form of electrical signals from dendrites/cell body to the axon terminal
Axon terminal
Branched end of axon transmitting information to the next cell (e.g. neuron, gland, organ, muscle)
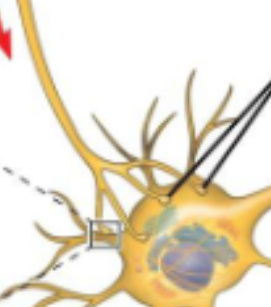
Synapse
Where information is transmitted through the end of one cell to the beginning of another cell
Glia
Support cells of the nervous system
Neuron transmission
Between neurons: signal is chemical (via neurotransmitters)
Within a neuron: signal is electrical (via ion movement)
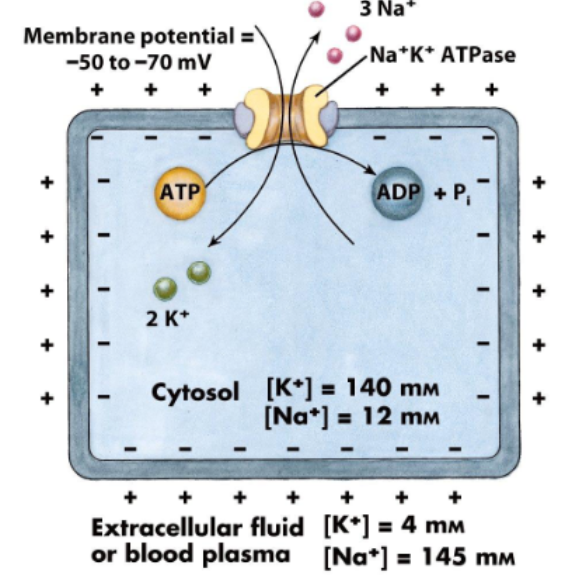
Resting state
Na⁺ high outside, K⁺ high inside the neuron
Maintained by Na⁺/K⁺ pump
Creates charge gradient:
• Outside = more positive, inside = more negative
• Resting membrane potential = -70 mVAll channels are closed
Electrochemical gradient
A gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane
Membrane potential
Measure of the charge gradient across the plasma membrane
Resting potential
The electrical potential difference (voltage) across the cell membrane of a non-excitable cell when it is not stimulated or actively transmitting signals
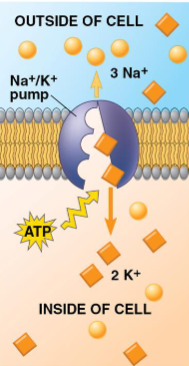
Na+/ K+ pump
Transmembrane protein that facilitates the active transport of Na+ and K+ ions across the cell membrane
Pumps 3 Na⁺ out, 2 K⁺ in
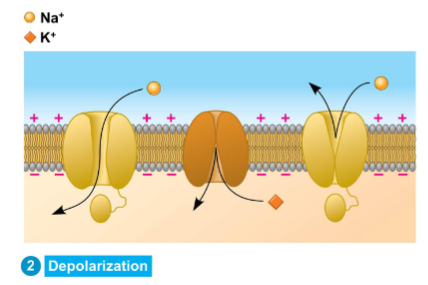
Depolarization
Presynaptic cell releases neurotransmitters via exocytosis
Neurotransmitter diffuses across synapse, binds to receptors on receiving neuron
Excitatory receptors = ligand-gated Na⁺ channels:
• Neurotransmitter = ligand
• Binding opens channel → Na⁺ floods in
Neurotransmitter
A chemical messenger that transmits signals between neurons. Made from amino acids or peptides
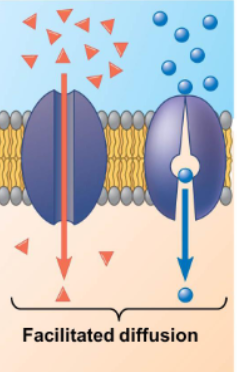
Channel proteins
Transmembrane proteins that facilitate the transport of specific ions or molecules across the cell membrane
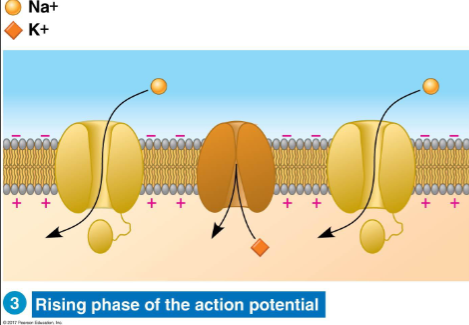
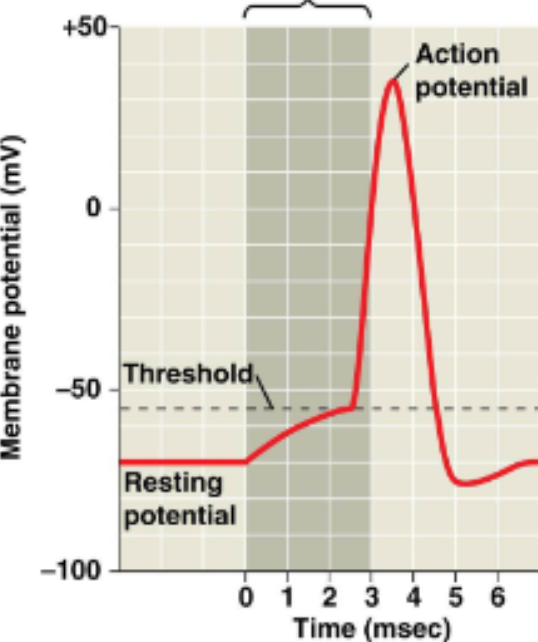
Rising phase of the action potential
If threshold is reached → voltage-gated Na⁺ channels open
Na⁺ floods in → causes depolarization
Depolarization triggers nearby Na⁺ channels to open
Action potential spreads down neuron = signal transmission
This is the "firing" of the neuron
Threshold potential
The critical membrane voltage that a neuron must reach to trigger an action potential (where the membrane is less negative enough)
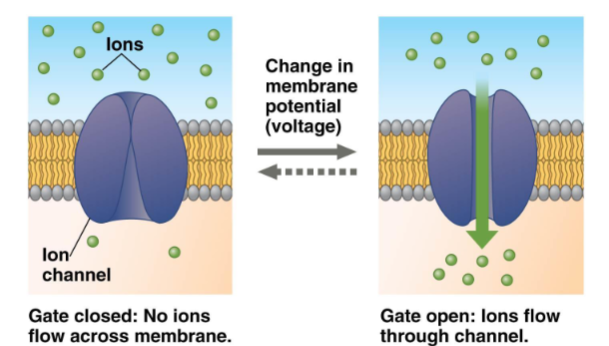
Voltage-gated channels
Channels that open when there is a change in charge
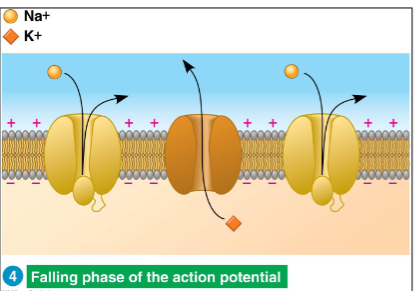
Falling phase of the membrane potential
Na⁺ channels close
K⁺ channels open
K⁺ exits the cell → inside becomes negative again; Repolarization
Repolarization of the membrane
The process where a cell membrane's electrical charge returns to its resting state after a period of depolarization
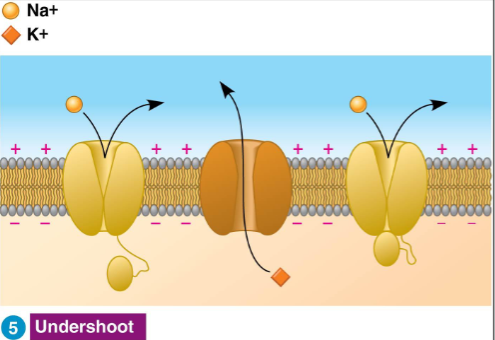
Undershoot / Hyperpolarization
Too many K+ leaving the cell, causing the membrane potential to become more negative than the resting potential
Falling phase → Resting potential
Na+ & K+ gradient is re-established using the Na+/K+ pump
Refractory period
The time taken to re-establish resting potential
At axon terminal
Action potential opens voltage-gated Ca²⁺ channels
Ca²⁺ enters the neuron, binds to vesicles with neurotransmitters
Triggers neurotransmitter release into the synapse
Signal continues to the next neuron
Excitatory Neurotransmitters
Binds to ligand-gated channels on the post-synaptic neuron, causing depolarization and moves the membrane closer to the threshold potential
Creates an Excitatory Post-Synaptic Potential (EPSP)
**Note: No threshold potential = no action potential (even if there is EPSP)
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
Binds to ligand-gated channels on the postsynaptic neuron, causing hyperpolarization by opening Cl- channels and inhibiting firing of the neuron
Creates an Inhibitory Post-Synaptic Potential (IPSP)
Summation
Sum of all EPSPs & IPSPs that either reach threshold or not
Temporal summation
All EPSPs / IPSPs either reaching threshold or not in a period of time
Spatial summation
All EPSPs / IPSPs in a certain location in close proximity
After the neuron fires / is inhibited
Enzymes break down neurotransmitters, chemically changing them so they can no longer bind to receptors
OR
Neurotransmitters are taken back into the pre-synaptic neuron via passive transporters or reuptake channels
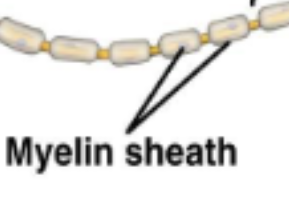
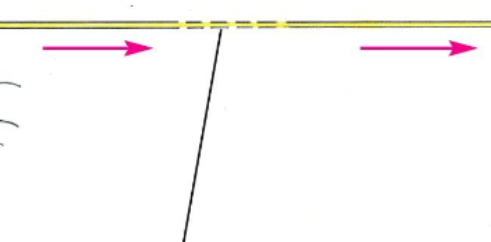
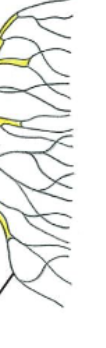
Myelin sheath
Wrapped around the axon of a neuron, an insulating coat of cell membranes from Schwann cells
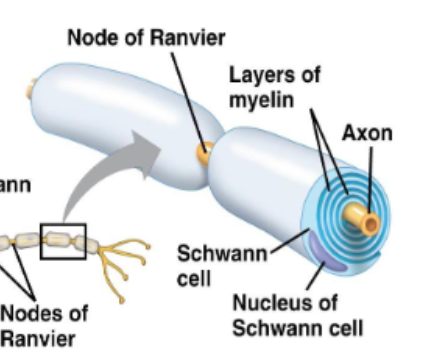
Nodes of Ranvier
Exposed areas of the axon that are not myelinated, where action potentials are generated
Saltatory Conduction
An action potential is regenerated at each node [of Ranvier], appearing to jump along the axon from node to node