English 4: American culture
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
What decisions did Trump make that altered the lives of Americans?
possible answer: Trump's decisions, like tax cuts, strict immigration rules, COVID-19 handling (2020), deregulation, and trade tariffs, reshaped the economy, public health, and daily life for many Americans.
How did Trump's foreign policy differ from his predecessors?
His predecessors emphasized global coalitions, his way of treating the U.S,...
Could Trump go for a third term?
No it’s not possible to go for a third term.
What are the main themes that Trump focuses on?
Trump's key themes focus on America First:
prioritizing U.S. interests through nationalism and economic protectionism.
He supports strict immigration control, including a border wall
advocates for tariffs to protect U.S. industries, particularly against China and the EU. His EU tariffs began in 2018 with further escalations in 2019.
He renegotiated deals like USMCA and emphasized military strength, pushing NATO allies to increase defense spending.
What effects does his plan have on the rest of the world?
gas prices went down with 15%, new travel rules, start tariff fights,...
gas prices went down with 15%, new travel rules, start tariff fights,...
Trump's policies cut taxes
reduced immigration
rolled back LGBTQ+ rights, and aimed to repeal the ACA.
His tariffs caused trade disruptions
his "America First" foreign policy pulled the U.S. from global agreements.
His economic growth stalled during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Does Trump have any influence on the new pope?
No
Why does he want Greenland so badly?
It represents a key location for military presence, it also has its own airbase. He wants to expand his power. resources, its strategic location and the shipping lanes in the High North
9/11:
What hapended thatd ay?
how did it hapen?
who did it?
why did it happen?
➡ 4 planes got hijacked in the morning. Two crashed into the twin tower, one crashed into the Pentagon and one crashed somewhere in rural Pennsylvania.
➡ They took control of the planes. The pilots were very likely a part of al Qaeda. (they died, so we will never know)
➡ 19 men trained by al Qaeda, a radical islamist terrorist organisation.
➡ To send a message of destruction and fear + because they were against the American military presence in countries like Saudi Arabia.
9/11:
Why were the Twin Towers & The Pentagon targeted?
What were the consequences of this attack? Short term and long term
What impact did it have on survivors and first responders?
Could they have stopped it?
➡ World trade center = symbol of global capitalism
➡ Pentagon = symbol of American military power
➡ White house = symbol of political leadership
➡ Short term:
Patriotic feeling -> against the same enemy (al qaida)
Emotional impact (scared & no sense of security)
Mass surveillance
Rise of anti-muslim sentiment & islamophobia
Erased every trace of the attack (example: cut every scene where the twin tower were visible from the “Spider-Man” trailer)
➡ Long term:
Cultural and media legacy: the event is widely represented in literature, films, music, …
Focus on security instead of comfort in airports
Development of mass surveillance
Health problems caused by the fumes from the fire and the collapse affected first responders and people nearby
➡ Mental impact: First responders, people nearby, and witnesses were affected by the terrible sight of people jumping from the buildings, getting burned, and dying.They suffered from PTSD, anxiety and depression.
Probably not: At the time, because of the minimal security checks at the airport and the fact that the cockpit could only be opened and closed by the pilots, it would have been very unlikely that the attack could have been stopped.
How does 9/11 influence modern culture?
How does 9/11 influence modern culture?
➡ Patriot day: Every year on September 11th Americans participate in moments of silence and flags are flown half-mast.
➡ 9/11 memorials: The national September 11 Memorial & museum in New York City and the twin reflecting pools, engraved with the names of those who died.
➡ Media and documentaries: Lots of films? articles, documentaries, interviews… made about 9/11.
➡ Schools: The teaching of 9/11 is part of the official curriculum.
➡ “Never forget”: It’s a symbol of shared trauma. Never forget what happened and those we lost that day. Later it became a punchline and a meme.
How did 9/11 influence the English language (Ground Zero,..)?
➡ “9/11” became a shorthand for the attack, like “Pearl Harbor” refers to a specific date
➡ “ground zero”: Previously used for nuclear explosions, it became widely known as the site of the World Trade Center collapse.
➡ “War on terror”: Political and media term launched by the U.S. government, after the attack. It’s the international effort led by the U.S to fight terrorism.
➡ “Homeland security”: Popularized and institutionalized with the creation of the Department of Homeland Security.
What is the title of the National Anthem?
The star spangled banner
Why was the national anthem made?
→ To express patriotism and commemorate a key moment in American history, the Battle of Fort McHenry during the War of 1812.
When did it become the National Anthem?
1931
Who wrote the lyrics to the Anthem?
Francis Scott Key wrote a poem. This became the lyrics of the national anthem.
What is the message of the lyrics? (national anthem)
The message of the lyrics of "The Star-Spangled Banner" is one of patriotism, resilience, and national pride.
Why do Americans sing the national anthem at sports events?
→ "The Star-Spangled Banner" is sung at national sports events in the U.S. as a symbol of unity, patriotism, and respect for the nation. This tradition ties together American identity, pride, and national values, especially in moments where people from all walks of life come together, like at sports games.
Why do they only sing the first verses?
→ Because the first verse contains the core message. It’s also for practical reasons; singing all four would take too long, especially at public events like sports games.
Who was Martin Lutehr King?
→ Michael King Junior, born in Atlanta on January 15, 1929 and killed on April 4, 1968
What did Martin Luther King do and why?
→ Fought for civil rights, racial equality and to put an end to segregation. He himself has experienced racism as a black American man
Why did Martin Luther King organise the montgomery bus boycott?
→ After Rosa Parks got arrested when she refused to give up her place for a white man (which was back in the time expected from black people, they had to sit at the end of the bus and give up their places to white people when asked to).
What are the key ideas of the ‘I have a dream’-speech?
→ MLK gave the speech at the Lincoln Memorial. He expressed his dream to see black an white people live in harmony and peace.
Why is it difficult to define one single type of ‘US cuisine’?
Because there’s a lot of diversity in US cuisine, thanks to a mix of indigenous, immigrant, and regional influences. There is no single cuisine, it’s a fusion of different cultures.
Were any of the dishes derived from Native American cuisine?
→ Yes (e.g. three sisters stew = a vegetable medley of corn, squash and beans that are planted together so each plant can support and nourish each other. Corn, beans and squash have provided nutrition for the Chickasaw people for generations.)
Is there a direct correlation between the USA’s obese population and their cuisine?
→ Yes: FDA rules about ingredients are less strict -> unhealthy.*
What were the main influences on US cuisine?
→ Early influence: Native Americans + European settlers (Spanish, British, French)
→ Later immigration waves: Chinese, Mexican, Italian, …
Is the stereotype about obese people in America real?
→ Yes.
(*Because of the lenient rules surrounding food set up by the FDA, there’s a lot of really unhealthy ingredients in a lot of the food. Because of this there’s a high percentage of the US population that’s overweight: 30.7%)
Why doesn’t the USA have a single national dish?
→ Diversity, all states have their own dishes and traditions.
Are there State dishes?
→ Yes.
(E.g. Alaska: salmon, Connecticut: lobster roll, Georgia: peaches, …)
Why is there so much difference between the States?
→ Different cultures -> different foods
What influences from other countries are there?
→ Mexican, Chinese, Italian, African, … (much immigration = many different influences)
Where do their food related traditions come from?
→ Thanksgiving = celebration of the harvest and other blessings
How many states are there?
50
→ 13 (previously they weren’t called states yet, but ‘United Colonies’)
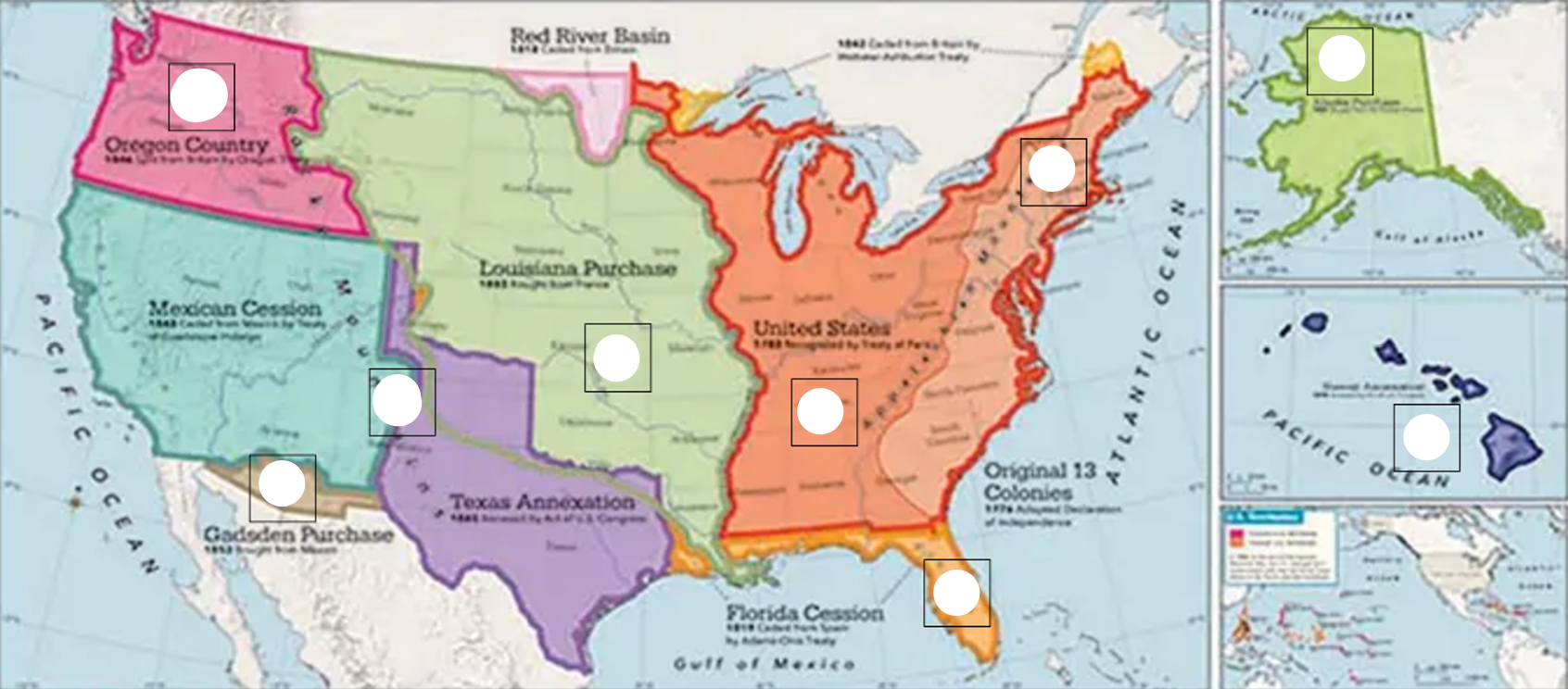
Number the different areas of land on this map in order of when they were adde
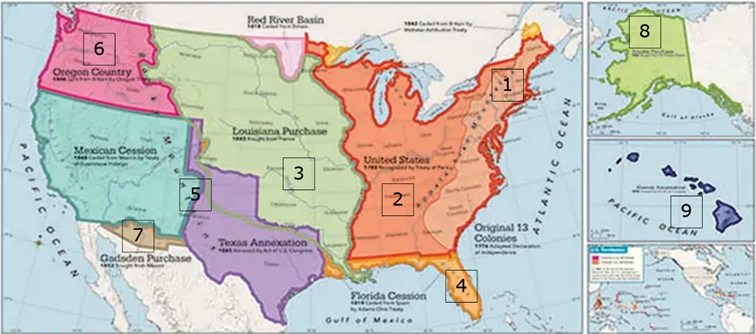
Fill-in-the-blank: historic events leading to the expansion of the US

Name the 4 (unofficial) geographical regions
Name 3 states per geographical region (+ their state abbreviations)
→ West, choose from:
Washington (WA), Oregon (OR), California (CA), Idaho (ID), Montana (MT), Wyoming (WY), Nevada (NV), Utah (UT), Colorado (CO), Arizona (AZ) or New Mexico (NM)
→ Midwest, choose from:
North Dakota (ND), South Dakota (SD), Nebraska (NE), Kansas (KS), Minnesota (MN), Iowa (IA), Missouri (MO), Wisconsin (WI), Illinois (IL), Michigan (MI), Indiana (IN) or Ohio (OH)
→ East, choose from:
Pennsylvania (PA), New York (NY), Vermont (VT), Maine (ME), New Hampshire (NH), Massachusetts (MA), Rhode Island (RI), Connecticut (CT), New Jersey (NJ) or Delaware (DE)
→ South, choose from:
Texas (TX), Oklahoma (OK), Arkansas (AR), Louisiana (LA), Mississippi (MS), Kentucky (KY), Tennessee (TN), Alabama (AL), West Virginia (WV), Delaware (DE), Maryland (MD), Virginia (VA), North Carolina (NC), South Carolina, (SC), Giorgia (GA) or Florida (FL)
→ These 48 states are all connected, but don’t forget about Alaska (AK) and Hawaii (HI). They might not be a part of the mainland, but they are a part of the USA.
Name 10 states that all start with a different letter (+ their state abbr.)
→ West, choose from:
Washington (WA), Oregon (OR), California (CA), Idaho (ID), Montana (MT), Wyoming (WY), Nevada (NV), Utah (UT), Colorado (CO), Arizona (AZ) or New Mexico (NM)
→ Midwest, choose from:
North Dakota (ND), South Dakota (SD), Nebraska (NE), Kansas (KS), Minnesota (MN), Iowa (IA), Missouri (MO), Wisconsin (WI), Illinois (IL), Michigan (MI), Indiana (IN) or Ohio (OH)
→ East, choose from:
Pennsylvania (PA), New York (NY), Vermont (VT), Maine (ME), New Hampshire (NH), Massachusetts (MA), Rhode Island (RI), Connecticut (CT), New Jersey (NJ) or Delaware (DE)
→ South, choose from:
Texas (TX), Oklahoma (OK), Arkansas (AR), Louisiana (LA), Mississippi (MS), Kentucky (KY), Tennessee (TN), Alabama (AL), West Virginia (WV), Delaware (DE), Maryland (MD), Virginia (VA), North Carolina (NC), South Carolina, (SC), Giorgia (GA) or Florida (FL)
→ These 48 states are all connected, but don’t forget about Alaska (AK) and Hawaii (HI). They might not be a part of the mainland, but they are a part of the USA.
Biggest state?
→ In land mass: Alaska (AK)
→ In population: California (CA)
Smallest state?
→ In land mass: Rhode Island (RI)
→ In population: Wyoming (WY)
What was the very first formed state?
→ Delaware (DE) was the first colony to ratify (sign) the U.S. Constitution. In doing this, DE became the first of the ‘United Colonies’, which were later renamed to the ‘United States of America’.
Why was Alaska purchased from Russia?
→ After facing catastrophic defeat in the Crimean War, Alexander II of Russia began exploring the possibility of selling the Alaskan possessions. This piece of land would be difficult to defend from the UK in any future war. The USA entered negotiations to buy Alaska, partly because the public believed that Alaska would serve as a base to expand American trade in Asia. Alaska was interesting because of all the natural resources (oil, gas, etc.).
Name one mentioned sight or fun fact for each of the 4 regions
West:
The Grand Canyon: There is a village in the Canyon where actual people live. It is called Supai Village and is home to around 208 people.
The Golden Gate Bridge in San Francisco (CA): is 1.7 miles long, or 2,7 kilometers.
Las Vegas (NV): Las Vegas is the brightest spot on Earth seen from space.
Midwest:
Mount Rushmore: no one died during the carving of the memorial
Cloud Gate: nickname = ‘The Bean’, since it has the shape of a bean
Lake Itasca: this is the source of the Mississippi River
South:
Gulf of Mexico: this is the mouth of the Mississippi River
Everglades: there are no precise dimensions of how big this subtropical swamp landscape is, since it’s constantly moving and changing. It’s estimated to be around 1.5 to 2 million acres.
Houston Space Center: Houston’s official nickname is “Space City”, because it is home to a NASA Space Center.
East:
New York City: When NYC was a colony of The Netherlands in the 1600s, it was called New Amsterdam.
Washington D.C.: the capital of the United States. Washington D.C. is not in a state or is not a state.
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: An important place, because this is seen as the ‘birthplace’ of the US because the Declaration of Independence was signed here.
Who designed the Great Seal?
→ The great seal was not created by a single person. It was created through a collaborative process of three separate committees.
→ Charles Thomson, Secretary of the Continental Congress, is largely credited for the final design.
When was The great seal designed?
→ In the year 1782 it was finally approved
Why was the great seal created?
→ to convey values and ideals
→ the new nation wanted to create a symbol that represents their values
What is the Great seal used for?
→ to authenticate official documents
→ to symbolize national identity
What is so important about the great seal?
→ The great seal of the United States is important because it serves as the ultimate symbol of national authority and legitimacy. The symbol is more than just decoration. It shows what their country stands for and it connects the modern Americans to the founders of the country.
What is the meaning behind the great seal?
→ the symbol is full of rich symbolism that reflects the ideals, values and aspirations of the nation:
a. bald eagle → strength, courage and freedom
b. olive branch → represents peace
c. arrows → symbolize the readiness for war to defend the country
d. shield → 13 red and white stripes (represents the original 13 colonies)
e. E Pluribus unum → out of many, one (symbolizes the unity of many states forming one nation)
f. unfinished pyramid → symbolizes strength and durability but also that the nation is still a work in progress
g. eye of providence → symbol of divine guidance or God watching over the nation
= it tells a story of a new, united and independent nation, committed to peace but ready for defense, grounded in divine providence and built to endure. it’s not just art, it’s a blueprint of the nation’s identity, values and purpose.
Washington Monument
Where is the Washington Monument located?
Why is the Washington Monument shaped like an obelisk?
What is so important about it?
Why was it created?
What is the meaning behind it?
On the National Mall in Washington, D.C.
It's a symbol of strength and endurance. The designers aimed to convey timelessness, power, and reverence—qualities they associated with George Washington.
It is important because it’s a national tribute to George Washington, a symbol of enduring American values, and a landmark of engineering and national pride. It reminds Americans and the world of the powerful role that leadership, unity, and principles played in building the United States.
To celebrate George Washington’s leadership
To preserve his legacy
To inspire national pride and civic values
To unify the young republic
The meaning goes deeper than just honoring a person. It symbolizes the ideals, values, and character of George Washington and the nation he helped create.
The bald Eagle
1) Why was the bald eagle called bald?
2) Are they still endangered?
3) What do they symbolize?
3) What was the pesticide called that made them endangered (in combination with hunting)?
4) What was one of the long-held superstitions (beliefs) surrounding bald eagles?
Bald used to mean white-headed.
No, they were removed from the endangered species list in 2007.
Courage, identity, and strength.
DDT (it made their eggshells brittle).
That they stole lambs and/or children.
Mount Rushmore
What does each head symbolize?
Which president represents which element?
Who’s carved into the mountainside?
Where is it located?
How was it made?
What is controversial about Mount Rushmore?
They each represent birth, growth, development, and preservation. The complete monument stands for the first 150 years of American history.
George Washington represents the birth of the United States as its first president.
Thomas Jefferson symbolizes growth through the Louisiana Purchase and westward expansion.
Theodore Roosevelt stands for development during the industrial age.
Abraham Lincoln represents preservation for keeping the nation united during the Civil War.
George Washington (1934), Thomas Jefferson (1936), Theodore Roosevelt (1939), Abraham Lincoln (1937).
South Dakota.
By blowing up 410,000 tons of rock with dynamite in a honeycomb pattern and later carving the details.
Mount Rushmore is controversial because it was built on the Black Hills, land sacred to the Lakota Sioux that was taken illegally by the U.S. government despite a treaty. The monument is viewed by many Native Americans as a symbol of colonialism and oppression, especially since it features U.S. presidents who were involved in policies harmful to Indigenous peoples.
National parcs:
Are there animals in the parks?
a. What animals live in Yosemite National Park?
b. What animals live in Yellowstone National Park?
c. What animals live in Zion National Park?
d. What animals live in Grand Canyon National Park?
e. What animals live in Everglades National Park?
8a. Yosemite National Park:
Black bears – Famous residents, often near campsites and trails
Mule deer – Common in meadows and forests
Coyotes – Frequently heard howling
Bobcats – Shy and elusive
Mountain lions (cougars) – Rare sightings
Sierra Nevada bighorn sheep – Endangered, seen in alpine regions
California ground squirrels – Abundant and easy to spot
Steller’s jays – Loud, blue birds
Great grey owls – Rare; Yosemite is a top place to spot them
8b. Yellowstone National Park:
Grizzly bears and black bears
Grey wolves – Reintroduced after being extinct in the park
Bison (buffalo) – Symbol of the park
Elk (wapiti) – Most abundant large mammal
Bighorn sheep – Found in small groups
Moose – Adapted for snow and river travel
Mountain goats – Thrive in high elevations
Coyotes – Often spotted (jokingly called “the idiot wolf-like creature” from Road Runner)
8c. Zion National Park:
Desert bighorn sheep – Seen on rocky cliffs
Mule deer – Common in meadows and riverbanks
Rock squirrels – Mistaken for chipmunks
Coyotes – Heard mostly at dawn and dusk
Mountain lions (cougars) – Rare, found in high elevations
Ringtails – Nocturnal, raccoon relatives
Zion snail (springsnail) – Tiny and unique to Zion
Golden eagles – Soar above the canyons
Turkeys – Roam the canyon floor
8d. Grand Canyon National Park:
Desert bighorn sheep
Mule deer
Mountain lions – Not true lions, more like large wild cats (pumas)
Coyotes
Grey fox
Plus many birds, reptiles, and rodents
8e. Everglades National Park:
American alligator – Iconic Everglades species
American crocodile – Rare, coexists with alligators here
Florida panther – Critically endangered and elusive
Manatee (West Indian) – Gentle sea mammals in warm waters
Bottlenose dolphins – Common in coastal areas
Roseate spoonbill – Pink bird often mistaken for flamingo
Wood stork – Large, bald-headed bird
Snail kite – Feeds mainly on apple snails
Burmese python – Invasive species damaging the ecosystem
How many national parks are there in total?
What was the first national park in the U.S.?
What’s the largest and smallest national park?
Which states have the most national parks?
There are 63 national parks in total.
10. The first national park in the U.S. was Yellowstone, established on March 1, 1872.
11.
Largest: Wrangell–St. Elias National Park (Alaska)
Smallest: Gateway Arch National Park (Missouri)
12.
California – 9 parks
Alaska – 8 parks
Utah – 5 parks
What unique geographical features can be found in specific parks?
Yosemite National Park:
El Capitan
A massive granite monolith rising about 3,000 feet (900 meters) above Yosemite Valley.
Famous worldwide for rock climbing, especially the route known as “The Nose.”
Symbolizes the park’s dramatic geology and is an icon of climbing culture.
Yosemite Falls
The tallest waterfall in Yosemite at 2,425 feet (739 meters).
Made up of three sections: Upper Fall, Middle Cascades, and Lower Fall.
Peaks during spring snowmelt, sometimes dries up in late summer.
Yellowstone National Park:
Geothermal Features (due to the Yellowstone Supervolcano):
a. GeysersOld Faithful: Famous for its regular eruptions and predictability.
Steamboat Geyser: The tallest geyser in the world when it erupts.
b. Hot SpringsNaturally heated, colorful pools of mineral-rich water.
Formed by underground volcanic activity.
Zion National Park:
Sandstone Cliffs
Towering formations in red, pink, and cream hues.
Created by erosion, uplift, and sedimentation over millions of years.
The Narrows
A narrow slot canyon carved by the Virgin River.
Walls reach up to 1,000 feet (300 meters) high, with widths as narrow as 20 feet (6 meters).
One of the most iconic hikes in the U.S.
Grand Canyon National Park:
The Grand Canyon itself
Carved by the Colorado River through millions of years of erosion.
435 km long, with a width ranging from 15 to 30 km.
The exposed rock layers date back 1.8 billion years, containing only marine fossils like tiny sea creatures.
Everglades National Park:
“River of Grass”
A slow-moving sheet of freshwater that supports diverse ecosystems.
Made up of sawgrass marshes, mangrove forests, and wetlands.
Unique Coexistence of Species
The only place in the world where American alligators and American crocodiles naturally coexist.
This occurs due to the park's blend of freshwater and saltwater environments.
What is the Liberty Bell?
Where is it located?
Why is it called that?
When was it made and by who?
What role did it play in American history?
Can people visit it?
What makes it so symbolic for the American people?
A famous symbol of the American Revolution and freedom.
Located at the Liberty Bell Center, across from Independence Hall, Philadelphia.
Originally called the State House Bell; named Liberty Bell after ringing in 1776 for the Declaration of Independence.
Made by Whitechapel Bell Foundry in London, completed in 1752.
Called citizens for the Declaration reading; now a symbol of liberty and resilience.
Yes, it is on display and open to visitors.
Symbolizes freedom and independence, inspiring despite its crack.
Where is the Statue of Liberty located?
Who designed it and when?
How did it get its name?
Why was it made?
What does it mean to the American people?
How did it become a symbol?
What's the link between the two national symbols (Liberty Bell & Statue of Liberty)?
On Liberty Island in New York Bay.
By Bartholdi (statue) and Eiffel (structure), completed in 1884.
From its original name: Liberty Enlightening the World.
A gift from France for the U.S. centennial.
It stands for freedom, hope, and welcome.
It was the first sight for many immigrants.
Both represent freedom and American values.
Do Uncle Sam and the flag have a connection?
→ Yes, Uncle Sam’s appearance is based on the American flag. His red, white, and blue clothes and the 13 stripes on his pants match the flag’s colors and stripes. Both are to represent American values, unity, and national pride.
How was the flag created?
How did they choose between different designs?
What does it symbolize for the US?
Did it change over the years?
Is there a person credited with its creation?
How many stars and stripes are on the flag?
What do the stars and stripes represent?
Why these colors?
Adopted June 14, 1777, to identify American ships and forts; 13 stars and stripes for the 13 colonies.
Congress chose stripes and stars to show unity; stars added as states joined.
Symbol of unity, freedom, pride, courage, justice, and equality.
Changed 27 times; stars added for new states, stripes always 13.
No official creator; Betsy Ross legend unproven.
50 stars and 13 stripes.
Stars = 50 states; stripes = 13 original colonies.
Red = bravery; white = purity; blue = justice and perseverance.
Who is Uncle Sam?
How did he become a national symbol?
Who created the cartoon?
Why was he created?
What makes him iconic?
What does he symbolize?
When was he created?
How is he used?
Did he change over the years?
Where did the name come from?
A cartoon figure representing the U.S. government, dressed in patriotic clothes.
Named after Samuel Wilson, a meat supplier in the War of 1812; soldiers joked “U.S.” meant “Uncle Sam.”
Artist James Montgomery Flagg created the famous WW1 recruitment poster.
To encourage patriotism and support for the government, especially during war.
Recognizable symbol of the government and American values, used in posters and cartoons.
Represents U.S. government, patriotism, and civic duty.
Name started in War of 1812; current image popularized in early 1900s.
Used in recruitment posters, political cartoons, and patriotic events.
Yes, evolved from earlier figures like Brother Jonathan; became the bearded figure we know.
From Samuel Wilson’s meat barrels stamped “U.S.”; soldiers joked it meant “Uncle Sam.”
Who started the movement?
Why did it happen?
Who were some key figures?
What was the impact on social media?
What did the movement accomplish?
Did the protests have any impact?
What are the important slogans?
When did it start?
What are they fighting against?
Alicia Garza, Patrisse Cullors, and Opal Tometi created #BlackLivesMatter.
Started after Trayvon Martin’s killer was acquitted; highlights racial injustice.
Key figure: George Floyd.
#BlackLivesMatter amplified Black voices in media and culture.
Alicia Garza, Patrisse Cullors, and Opal Tometi created #BlackLivesMatter.
Started after Trayvon Martin’s killer was acquitted; highlights racial injustice.
Key figure: George Floyd.
#BlackLivesMatter amplified Black voices in media and culture.
Made anti-racism a mainstream topic in media and entertainment.
Led to police reforms and wider awareness of racism.
“Say their names!”—honors Black victims of racism and police violence.
Began in 2013; major surge in 2020 after George Floyd’s death.
Fighting systemic racism, police reform, justice, and equality.
Led to police reforms and wider awareness of racism.
“Say their names!”—honors Black victims of racism and police violence.
Began in 2013; major surge in 2020 after George Floyd’s death.
Fighting systemic racism, police reform, justice, and equality.
Politics & US Government – Questions:
What does a lifetime appointment mean?
How many chambers are there in Congress and what are they called?
What are the characteristics of the Senate?
A lifetime appointment lasts until retirement or death.
Congress has two chambers: the Senate and the House of Representatives.
The Senate has 100 members (2 per state), serves 6-year terms, approves treaties, confirms appointments, and acts as a more deliberative body.
What are the responsibilities of:
Congress?
Executive branch?
Cabinet?
Legislative branch?
What is the role of the:
President?
Vice President?
Who does the judicial branch want to protect?
Congress: Makes laws, controls federal spending, declares war.
Executive branch: Enforces laws, leads the military as Commander-in-Chief.
Cabinet: Advises the President, manages federal agencies, helps implement laws.
Legislative branch: Same as Congress—makes laws and controls spending.
President: Head of state and chief executive, leads the executive branch, commander-in-chief, represents the US globally, oversees lawmaking.
Vice President: Supports the President and is next in line for presidency.
The judicial branch protects the rights and freedoms of all individuals in the U.S., ensuring laws are fair and constitutional.
What is the current overview of U.S. politics in the year 2025? Name at least two new regulations or social issues.
TAKE IT DOWN Act (May 2025): This bipartisan law targets the non-consensual distribution of AI-generated intimate images, commonly known as "deepfake revenge porn."
Trade Policy Shifts: The administration has reignited trade tensions by proposing a 50% tariff on all goods imported from the European Union, criticizing ongoing trade talks as unproductive
Who was Rosa Parks?
What did she do and when?
What effects did her actions have?
Why did she do it?
How is she still relevant today?
An African American civil rights activist.
In 1955, she refused to give up her bus seat and was arrested.
This sparked the 13-month Montgomery Bus Boycott.
She was tired of racial injustice and stood up for her rights.
Her actions helped advance civil rights and freedom for Black Americans.
Name 3 three differences between American and European/Belgian culture
healthcare system
→ US: mostly private healthcare system where people often need insurance to access care, and medical bills can be very high
→ Belgium: healthcare is more affordable and universal, with strong public healthcare support
2. portion sizes and eating habits
→ US: food portions are typically larger and fast food plays a bigger role in everyday life. It’s common for people to eat on the go, in their cars during the commute to work.
→ Belgium/EU: meals are smaller and eating is more about quality and tradition, mealtimes are often slower and more social
3. gun ownership
→ US: The Second Amendment protects the right to bear arms. Guns are widely available, and owning one is common for self-defense.
→ Belgium/EU: Gun laws are much stricter. You generally need a license, a valid reason (like hunting or sport shooting) and background checks.
4. Tipping vs. no tipping
How does the infrastructure of American cities affect the way people move around?
Cities are built for cars, making walking and public transport less convenient.
Why is debt (like student loans) very common in the US?
Higher education isn’t heavily subsidized like in Europe. Tuition can be very high—up to $10,000/year at public and $40,000/year at private universities—so many students take loans that may take decades to repay.
Why is tipping an expected social norm within the US?
Who relies on tips for their living wage?
What’s the standard tipping range when going to service industries?
Service workers earn low base wages and rely on tips to make a living.
Waiters, bartenders, delivery drivers, taxi drivers, salon workers, and similar roles rely on tips.
The standard tipping range is usually 15-20% of the bill.
Why is it important to build a good credit score for American citizens?
What does a high credit score mean?
A good credit score helps you qualify for loans, credit cards, housing, and sometimes jobs.
A high credit score means you’re financially responsible, pay bills on time, and are seen as a low-risk borrower.
How do different States differ in cultures?
→ Southern States (Texas, Georgia): traditional, religious, conservative laws, warm climate, heavy accent, famous for BBQ and hospitality
→ West Coast States (California, Oregon): progressive, tech-driven, environmental awareness, laid-back and creative lifestyle
→ East Coast States (New York, Massachusetts): fast-paced urban life, finance and education centers, career-focused, international cuisine, cultural institutions like Broadway
→ Midwestern States (Ohio or Iowa): family-oriented, practical and conservative laws, harsh seasons, accents like the “midwestern twang” are common, famous for comfort foods like casseroles and deep-dish pizzas
In other words, each state has its own laws, accents, climate, cuisine and lifestyle.
How much does US-culture influence Europe
→ American English slang is common among younger Europeans (e.g. 'cool,' 'slay,' 'vibe,' 'flex,' 'ghosting,' 'rizz')
→ strong influence through movies, TV, music and celebrities (e.g. Friends, Disney, Marvel franchise)
→ fast food chains like McDonald’s and Starbucks are widespread
→ Tech companies (Apple, Google, Meta) shape communication and media use (Instagram, TikTok, Youtube)
→ US pop culture sets global trends in fashion, entertainment and consumer habits (e.g. Nike, Levi’s, Black Friday sales)
How much does Europe influence the US?
Less dominant, but visible in:
→ art and architecture: Scandinavian minimalism (like IKEA)
→ classical European literature is still studied in American schools (e.g. Shakespeare, Kafka, Wolfgang von Goethe…)
→ cuisine: Italian, French and Mediterranean diets are popular
→ luxury fashion: Gucci, Chanel, Dior often featured in celebrity culture
Why do many Americans work multiple jobs at the same time?
What is “gig work” or a “side hustle”?
To cover living costs, pay off debt, or earn extra income.
Short-term, flexible jobs like driving for Uber, freelancing, or selling online.
What do American citizens use social platforms for?
Why do Americans want to build a personal brand through social media?
Networking, self-promotion, activism, community building (fundraising), and entertainment.
To attract job offers or sponsorships, grow business, or become influencers.
What are the consequences of a car-centered lifestyle in the US?
How does the US make consumerism convenient for its people?
What does consumerism mean?
Why are Big Box Stores so popular in the US?
What are Big Box Stores? Give some examples.
Why do Americans often buy in bulk?
Leads to traffic congestion, big parking lots, urban sprawl, less walkable cities, and limited public transport. Uber and Lyft provide alternatives.
24/7 stores, fast delivery, online shopping, and drive-thrus make buying quick and easy.
The belief that excessive buying boosts the economy.
They offer low prices, variety, and one-stop shopping.
Large retail stores like Walmart, Target, and Costco selling products in bulk.
Cheaper per unit and reduces shopping trips, good for suburban families.
When was basketball founded?
How many teams are in the NBA?
How many teams are in the East and West conferences?
What’s a conference?
Name 3 popular American basketball players.
How do we know basketball is big in the USA?
What does NBA stand for?
How do NBA teams get new players?
Basketball was founded in 1891.
The NBA has 30 teams.
Each conference (East and West) has 15 teams.
A conference is a group of 15 NBA teams, divided into East and West.
Popular players: LeBron James, Stephen Curry, Michael Jordan (retired).
Basketball is everywhere in the US—streets, schools, and universities—and it originated there.
NBA = National Basketball Association.
Teams get players via transfers, academies, and scholarships.
What does NFL stand for?
How do we know American football is popular in the USA?
What’s the Super Bowl?
What sports are important in the US?
Where do these sports come from?
NFL = National Football League.
American football is popular due to high viewership, polling data, and cultural impact.
The Super Bowl is the NFL championship game, deciding the league’s champion.
Important sports: Basketball, Football, Soccer, Baseball, Darts.
These sports come from the US or are adapted from the UK.
How does the president get elected?
What are the eligibility criteria to run for president?
To be president, you must be a natural-born US citizen, at least 35 years old, and a US resident for 14+ years.
If you meet these, you declare candidacy and register with the Federal Election Commission (FEC) once raising/spending over $5K.
What role does the Federal Election Commission play?
What happens in the primaries and caucuses?
What happens at the national conventions?
What is the general election?
What is the Electoral College and how does it work?
The FEC enforces finance laws and keeps foreign money out of US elections.
In primaries and caucuses, voters pick preferred candidates indirectly by choosing delegates.
At national conventions, delegates (pledged and superdelegates) choose the party’s candidate.
The final two candidates face off in the general election.
In the general election, the Electoral College votes for president, not the people directly.
Each state’s electors equal its number of Congress members; some states require electors to follow the popular vote, others don’t
→ Summary: voters choose delegates (primaries/caucuses), delegates pick candidates (conventions), electors choose president (general election).
How many presidents has America had (including the current one)?
Who was the 1st president of the US?
What is a caucus?
What is a primary?
45 presidents in 47 terms (Grover Cleveland served twice non-consecutively).
George Washington was the first president.
A caucus is a local party meeting to pick candidates and assign delegates.
A primary is a state election where voters choose candidates; can be open or closed.
What are the 3 requirements to become a presidential candidate?
What are the 4 steps to become president?
What is the Electoral College?
What does “winner takes all” mean?
How many electoral votes are needed to win?
Must be a natural-born U.S. citizen, at least 35 years old, and resident for 14+ years.
Declare candidacy, register with the Federal Election Commission, compete in primaries/caucuses, attend national conventions, then win the general election.
The Electoral College elects the president; states get votes based on congressional representation; voters actually choose electors.
Winner-take-all means the candidate who wins the popular vote in a state gets all its electoral votes.
A candidate needs 270 out of 538 electoral votes to win.
Why is the drinking age 21 in the USA, while it’s 18 in most countries like Belgium?
The US drinking age is 21 because research shows teens get drunk faster and binge more, so a higher age helps reduce accidents and protect young brains. In Belgium, teens can buy some alcohol at 16 and stronger drinks at 18.
Why is underage drinking a problem in the US?
What’s college drinking culture like?
Is there a difference in age limits for beer vs. stronger drinks?
Underage drinking happens due to curiosity, peer pressure, social norms, and marketing.
Drinking is common and accepted in college, with underage students often getting alcohol from older friends.
There is no different legal drinking age for beer versus stronger drinks; the age limit is the same.
Where could one buy alcohol?
What’s the most popular alcoholic beverage in the US?
What was the (main) reason for the prohibition?
What were the effects (dangers/problems) of people making their own alcohol?
Does the American youth drink less nowadays than they used to?
Alcohol is sold in liquor stores, grocery stores, convenience stores, and some bars/restaurants, depending on local laws.
Whiskey is the most popular alcoholic beverage.
Prohibition was mainly due to health concerns.
Homemade alcohol was often toxic and dangerous, causing serious harm.
Youth drinking has decreased over the past 20 years.
What effects did the LA Riots have (short and long term)?
What sparked the riots?
How long did the riots last?
Why didn’t the police react from the start?
Short term: 63 killed, 2,000+ injured, 1,100+ buildings destroyed, 11,000 arrested, curfews, National Guard called. Long term: police reforms, more training, body cameras, national attention on racism and police violence, inspired movements like Black Lives Matter.
The riots began after the not-guilty verdict for officers who beat Rodney King, whose assault was caught on video.
The riots lasted six days, from April 29 to May 4, 1992.
Police were overwhelmed and unprepared early on, pulling back for safety, allowing rioters to act freely until the National Guard arrived.
LA Riots:
Why didn’t the police react from the start?
How do the LA Riots link with Black Lives Matter (BLM)?
What effects did the riots have on how police work today?
Police were unprepared and overwhelmed early on, pulling back for safety, which let rioters act freely until the National Guard arrived.
The LA Riots and Rodney King case highlight police brutality, racism, and injustice—issues central to BLM protests, like after George Floyd’s death in 2020.
The riots led to police reforms like body cameras, anti-bias training, improved community trust, and better ways to investigate police misconduct.
LA Riots
What federal troops were deployed since the coast guard is also considered a federal troop?
-> The federal government deployed:
United States Army (from Fort Ord and Fort Lewis)
United States Marines (notably from Camp Pendleton)
California National Guard (activated by the governor, but they are technically a state force unless federalized
Federal law enforcement agencies like the FBI and ATF also assisted, but not in combat roles.
How many tribes were there before and after Columbus?
How many tribes are officially recognized today?
How many Native Americans live in the US today, and what percentage of the population is that?
Which Native Americans are significant in American literature?
Over 1,000 tribes before Columbus; about 500 after.
574 tribes are officially recognized by the government today.
Around 5 million Native Americans live in the US today, about 2.9% of the population.
Notable Native American writers include N. Scott Momaday and Joy Harjo.
Name 3 well-known tribes and their locations.
What does Native American culture look like today?
Why did colonizers want to get rid of Native Americans?
What challenges do Native Americans face today?
What are Native American reservations?
Cherokee (Oklahoma, North Carolina), Apache (Eastern Arizona), Navajo (Utah, New Mexico, Arizona).
Some still practice traditional rituals; most live among others or on reservations; they continue to fight for sovereignty.
Colonizers wanted their land for themselves.
Challenges include limited access to healthcare and education.
There are 326 reservations where Native Americans govern themselves, recognized by the US government.
What is a Melting Pot?
What is a Salad Bowl?
What are the differences between them?
When did it start ‘existing’?
What about America today?
Melting Pot: cultures blend into one.
Salad Bowl: cultures coexist but stay distinct.
Difference: blending vs. keeping separate.
Started early 1900s with immigration.
Today, America is more a Salad Bowl, valuing diversity.
Important dates in American history mentioned during the presentations:
1492
1607
1775 – 1783
1776
1861
1865
1929 – 1968
1955
1992
2001
201
1492, arrival of Columbus in America;
1607, Jamestown, first permanent English settlement
1776, the Declaration of Independence, declaring the 13 American colonies independent from Great Britain
1775 – 1783 The American Revolutionary War
1861, start of the Civil War
1865, end of the Civil War and abolition of slavery
1955 Rosa Parks refused to give up her seat
1929 – 1968 Martin Luther King
1992 LA Riots
2001 the 9/11 attacks
2013 Black Lives Matter