week six kickoff
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
physical examination
first step in the diagnosis or treatment based on signs and symptoms
signs
objective information detected by the physician
symptoms
subjective information supplied by the patient
what is the role of a clinical medical assistant in the general physical exam?
interview (chief complaint/subjective)
obtain histories (subjective)
determine vital signs (objective)
measure weight and height (objective)
ensure instruments and supplies are available
help into position, ensuring patient comfort
observe for signs of distress or need for assistance
educate patients on self-examinations
perform injections, EKG, phlebotomy
what are the different positions used for a physical exam?
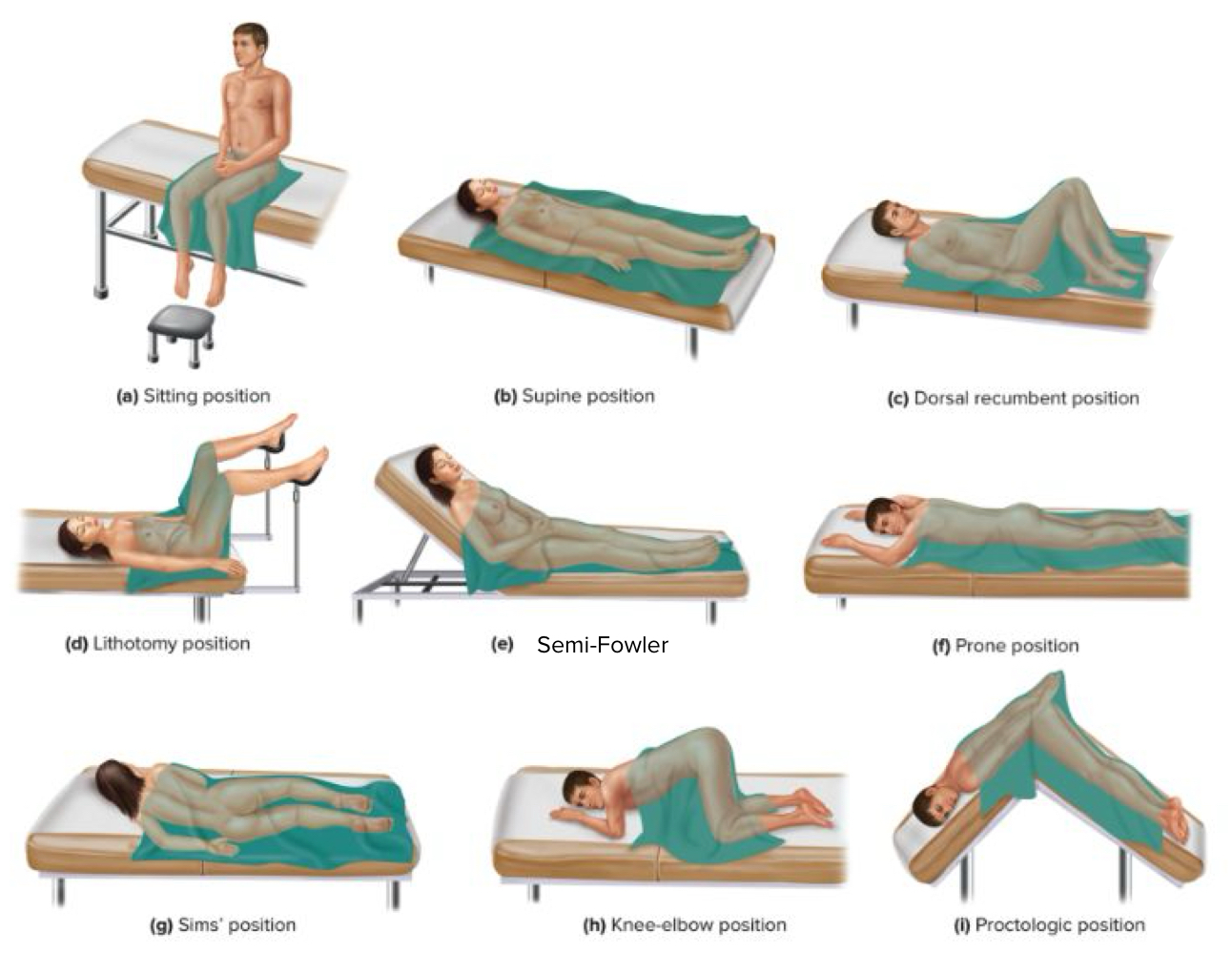
inspection
visual exam
auscultation
listening to body sounds
palpation
touch
percussion
tapping or striking the body to hear sounds or feel vibrations
mensuration
process of measuring
manipulation
moving of a patient’s body parts
range of motion of joints
which exam method is the physician using when observing the range of motion of joints?
mensuration
palpation
manipulation
inspection
manipulation
which position has the patient lying on the left side, left leg slightly flexed, with the right leg flexed at 90º angle?
lithotomy
prone
jack-knife
sim’s
sim’s
gynecologic exam
overview of a woman’s health and cancer-screening exams and tests
breast exam
examination of breasts and underarm areas to check for abnormal lumps
what is the medical assistant’s role in th gynecologic exam?
have patient empty bladder and obtain urine specimen if needed
provide a gown and interview patient
discuss gynecologic and general health
review of factors that may indicate cancer or STIs
ask questions about the patient’s menstrual cycle
check vital signs
determine the 1st day of her last menstrual period
gather supplies and assist physician
pregnancy tests
detect presence of hormone HCG
STI tests
may require bacterial and tissue cultures, examining lesions, blood tests, and patient history
ultrasound
assess organs and structures and produce pictures of a baby
hysterosalpingography
x-ray procedure used to view the inside of the uterus and fallopian tubes
hysterosalpingo-oophorectomy
removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries
assisting in urology
patient chief complaint and history: check for any changes in urination
the physical exam
palpation of the kidneys and bladder and visual inspection of the external genitalia
inspection and palpation of the penis and scrotum
the groin is examined for a hernia
in men over 40, the prostate gland is examined by digital insertion into the rectum
MA is responsible for teaching the patient to perform a regular testicular self-exam (TSE)
urinalysis
most commonly ordered test
blood testing
monitor for dysfunctions of the prostate gland and certain STIs
semen analysis
determine fertility and evaluate success of vasectomy
smears
diagnose infections
cystometry
measure bladder capacity and pressure
ectopic pregnancy
fertilized egg unable to move out of fallopian tube into uterus for implanation
fibrocystic breast disease
benign, fluid-filled cysts or nodules in breast
ovarian cysts
sacs of fluid or semisolid material
usually benign
menstrual disturbances
amenorrhea - absence of menstruation
dysmenorrhea - painful menstrual periods
menorrhagia - heavy or prolong menstrual bleeding
metrorrhagia - abnormal bleeding
kidney stones
chemical substances in the urine form crystals in the kidney, ureter, or bladder
renal calculi, nephrolithiasis, or urolithiasis
what type of organism is chlamydia?
bacteria
what type of organism is gonorrhea?
bacteria
what type of organism is syphilis?
bacteria
what type of organism is trichomoniasis?
protozoa
what type of organism is HSV (herpes simplex virus)?
virus
what type of organism is HPV (human papilloma virus)?
virus
can chlamydia be cured?
yes
can gonorrhea be cured?
yes
can syphilis be cured?
yes
can trichomoniasis be cured?
yes
can HSV (herpes simplex virus) be cured?
no, but can be managed
can HPV (human papilloma virus) be cured?
no, but can be managed
how is chlamydia transmitted?
fluids
how is gonorrhea transmitted?
fluids
how is syphilis transmitted?
skin to skin
how is trichomoniasis transmitted?
fluids
how is HSV (herpes simplex virus) transmitted?
skin to skin
how is HSV (human papilloma virus) transmitted?
skin to skin
the MA is asked to give a patient education on a procedure for nephrolithiasis. what will the MA explain to the patient about the diagnosis?
sexual dysfunction
ovarian cyst
kidney stones
excessive bleeding from the uterus
kidney stones
which STI is not caused by a bacteria?
chlamydia
gonorrhea
syphilis
herpes simplex
herpes simplex
pediatrician
specialist for children
up to the age of 18 or 21
monitors development
immuunization schedules
parent education
development milestones for each stage
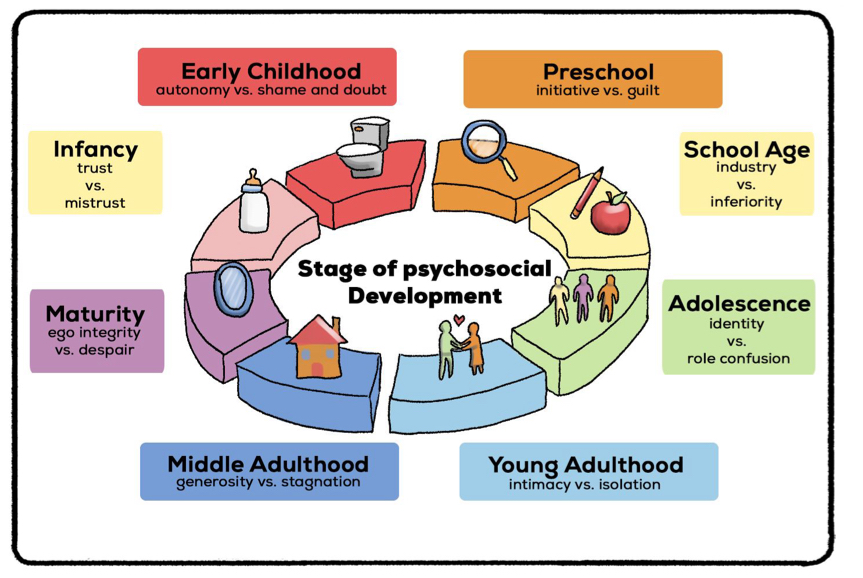
developmental stages
encompasses changes in physiological, emotional, mental, social, interactive, spiritual, and physical
erikson’s 8 stages of psychosocial development
guidelines for identifying psychosocial challenges
can have a positive or negative outcome for personality development
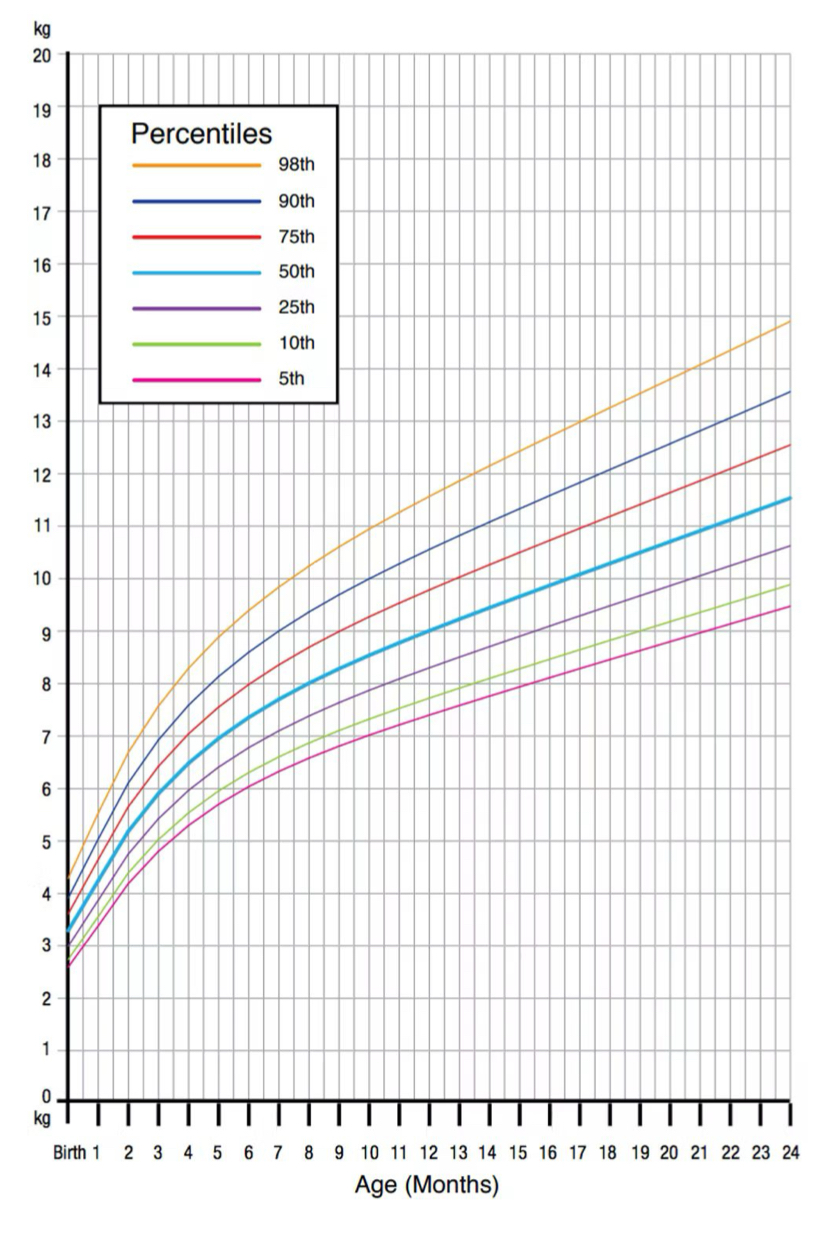
pediatric examinations
height (length), weight, head and chest circumference (up to 36 months)
temperature
use tympanic, temporal, rectal, axillary
no oral temperature in children less than five years old
pulse (apical for infants)
ear exams
blood pressure (over age 3)
use correct cuff size
do not use palpatory method
review family health history, existing conditions, current health conditions
observe child for any abnormalities that may indicate an underlying health concern
monitor growth charts, record measurements, height and weight
immunizations
check published immunization schedules found at cdc.gov
check for contraindications
ensure scope of practice when administering immunizations
informed consent for immunizations
explain the side effects of immunizations
review with the parent the vaccine information statement (VIS)
advise parents of immunity
obtain informed consent for the child’s immunization
what are common disease and disorders in pediatrics?
common cold and influenza
ear infections (otitis media/middle ear infection)
bronchitis - airways in the lungs swell and produce mucus in the lungs (viral)
respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) - mild cold-like symptoms including fever, coughing, and sneezing
hand, foot, and mouth disease (HMFD) - very contagious; symptoms include skin rash and fever
conjunctivitis - “pink eye” (redness, discharge, itchiness, and swelling in on or both eyes)
gastroenteritis - stomach flu, viral (nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea)
sinusitis - sinus infection
which of the following types of patients would be measured in length?
neonate (< 28 days)
preschool (3-5 y)
school age (6-9 y)
preadolescent (10-11 y)
neonate (< 28 days)
which is not taken on a child until the age of 3?
weight
pulse
height
blood pressure
blood pressure
what are the changes that occur in the integumentary system with age?
thinning and wrinkling skin
decreased collagen
what are the changes that occur in the musculoskeletal system with age?
osteoporosis
what are the changes that occur in the nervous system with age?
decreased blood flow to the brain due to arteriosclerosis
what are the changes that occur in the special sense with age?
impaired vision (presbyopia)
what are the changes that occur in the respiratory system with age?
increased shortness of breath
what are the changes that occur in the cardiovascular system with age?
atherosclerosis
hypertension
hypotension
assisting in geriatrics
observe for physical limitations
communicate effectively (written instructions, speak clearly with low tones)
patient may have denial or confusion
educate patient on the importance of preventative measures
ensure patient compliance with medications
which physical change happens in the elderly patient’s special senses?
presbyopia
osteoporosis
arteriosclerosis
kyphosis
presbyopia
at which age is a patient considered geriatric?
60
65
70
75
65