Electrical Signaling and Synaptic Transmission
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
how do neurons communicate within a neuron
using electrical signals
how do neurons communicate between neurons
using chemical signals
what encases neurons
cell membrane
what causes electrial signals in a neuron
ions moving across the membrane
ions def
particles with either a positive or negative electric charge
two types of potentials created by ions
graded potentials and propogated potentials
graded potential def
added up as ions enter the neuron and restricted ot one place in the neuron
what does a propogated potential do
travel down the neuron’s axon
what encases a neuron
cell membrane
significance of neuronal membrane
has special properites that contribute to electrical signaling
neuronal membrane composition
double layer of lipids in which proteins are embedded
what does the neuronal membrane separate
intracellular and extracellular fluids, each with their own ionic composition
structure of neuronal membrane- lipid component
double layer of phospholipids which have 2 ends, a polar head and fatty acid chain tail
properties of polar head
hydrophilic toward the intracellular and extracellular fluid
non-polar tail properties
hydrophobic, faces away from the fluid; tails face each other in the center of the membrane
2 functions of lipid part of neuronal membrane
bilayer isolates the cytoplasm of the nuron from the extracellular fluid
asle serves as a capacitator in that it is able to store charges of opposite signs that are attracted to each other but unable to cross the membrane
diffusion barrier
not permeable to ions
protein component of neuronal membrane structure
some proteins are exposed mostly on the outer or inner surface and some span the membrane
primary function protein componenet
regulate movement of ions across the membrane
active movement of ions
pumping ions across memebrane; this occurs through proteins called ion pumps
passive movement of ions across the membrane
allows ions to flow down concentration or electrical grandients (diffusion); this occurs through proteins called ion channels
ion channel def
neuronal membrane proteins with a central aqueous pore
3 main characteristics of ion channels
mutliple states
gating
selectivity
multiple states of ion channels
open or closed
ion channels gating
mechanism by which ion channel switches states
voltage gated ion channel
gate opens/closes based on chagnes in electrical membrane potential
ligand gated ion channel
gate opens/closes based on the binding of a neurotransmitter or hormone called a ligand
thermally gated ion channel
gate opens/closes based on temperature of neuron
mechanically gated ion channel
gate opens/closes based on movement
selectivity
ion channel’s ability to allow only certain ions through
channelopathies
disease caused by defective ion channels
resting membrane potentials
cellective difference in electrical potential between the inside and outside of a neuron
inside of a neuron charge at rest
negative
outside of a neuron charge at rest
positive
draw out the phospholipid bilayer

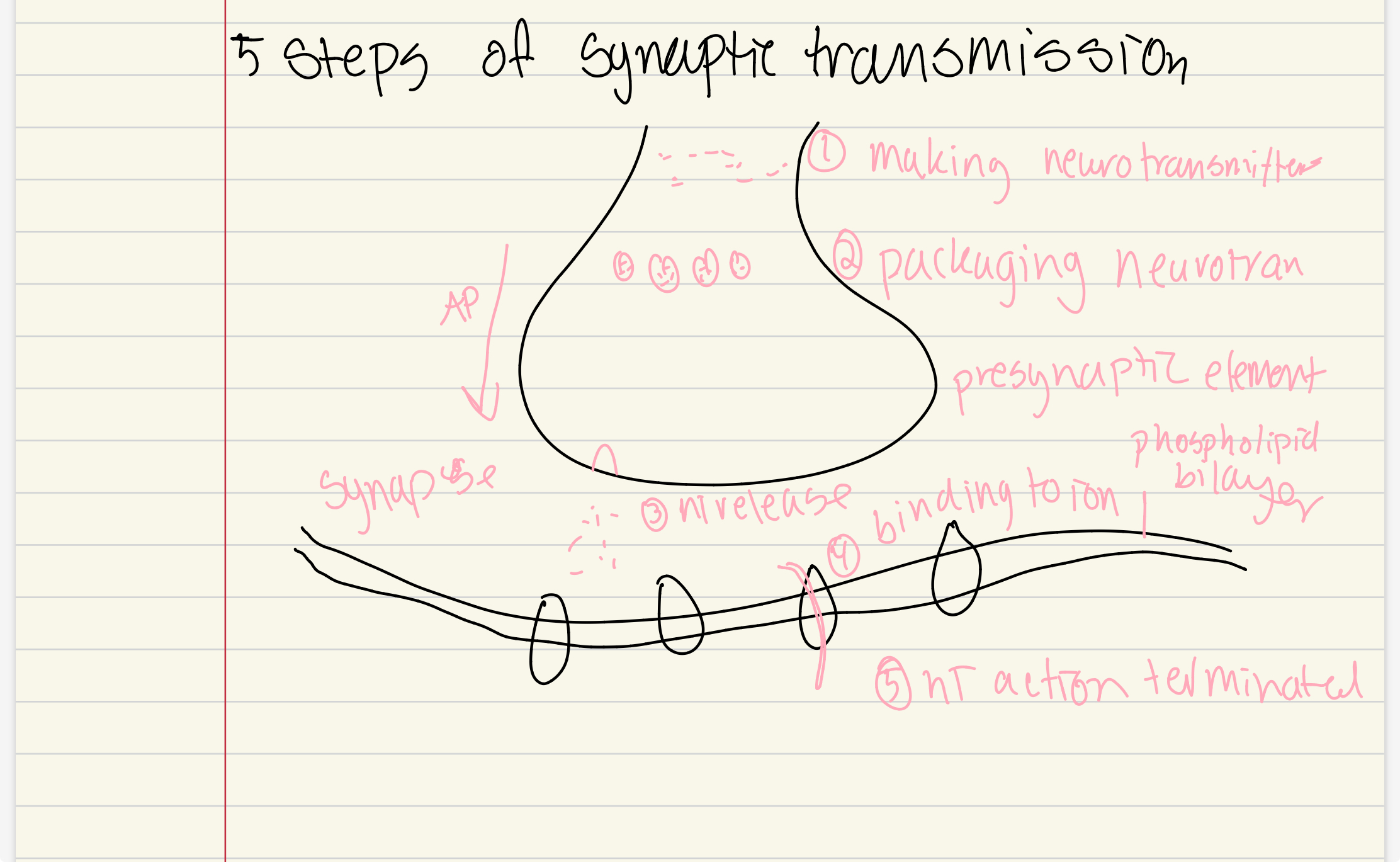
draw out the 5 steps of synaptic transmission
what is the normal resting membrane potential
-65 mV
what does the neuron imbalance at rest result in
polarization of neuron- it is ready to be fired at any second
what causes the difference in electrical potential on either side of the neuronal membrane
differences in ion concentration
where is there more Na+
extracellular
where is there more K+
intracellular
where is there more Ca2+
extracellular
where is there more Cl-
extracellular
factors that keeps resting potential at -65 mV
intracellular fluid contains many fixed anions
membrane proteins called ion pumps use active transport to maintain intracellular negativity
anions
negatively charged ions taht always stay inside the cell
active transport
energy is needed to move ions across cell membrane
classic example of ion pump using active transport
sodium potassium pump
overall concept of sodium potassium pump
pumps out Na+ from the intracellular space to the extracellular space and pumps in K+ from the extracellular space to the intracellular space
what form of energy does the sodium-potassium pump use
ATP
specifics on how sodium-potassium pump keeps the inside of the cell negative
for every 3 Na+ that go out of the cell, only 2 k+ come into the cell
temporal summation
the adding up of postsynaptic potentials generated in the same neuron at slightly different times
spatial summation
the adding up of postsynaptic potentials generated at spatially separate sites on aneurons
electronic spread (summation)
electrical inputs come at varying places in the neuron and passively spread
what happens if inputs travel too far
the electrical current leaks out of the neuron, thus it is decremental
what is the way in which neurons deal with the decremental electronic spread
action potentials
sequence of events in action potentials
resting membrane potential
local excitatory state
threshold
rising phase
peak
falling phase
hyperpolarization
resting membrane potential
Robinsons lost their retriever pray for her recovery
what is resting membrane potential
-65 mV
2 steps of local excitatory state
neuron receives and excitatory input and cell membrane depolarizes
this change in voltage in the cell cuases voltage-gated Na+ ion channels to open so Na_ start to flow into the cell
in which way do concentration gradients move ions
from areas of high concentration to low concentration
how do electrical gradients move ions
from areas of positive charge to negative charge
why does the movement of sodium change the electrical gradient
more positive ions are coming into the cell
threshold def
level of depolarization that results in an action potential 50% of the time OR the point of no return
at what mV does sufficient depolarization occur
about -55mV
what does sufficient depolarization lead to in the threshold stage
mass opening of voltage-gated sodium channels
what two things happen during the rising phase
sodium channels are in open state
sodium flows in rapidly
what is the spike peak mV
+35mV
what happens to sodium channels during peak
they close
what happens to potasium channels at peak
they open
what happens in the falling phase
potassium begins to flow out of the neuron down its concentration and electrical gradient
what happens during hyperpolarization
outward flow of K+ causes the membrane potential to dip below (and be even more neg than) resting membrane potential
what happens during resting membrane potential
APs happen rapidly in an all or none fashion
propogation of action potentials
APs propogate with full amplitude
amplitude AP
positive voltage to adjacent areas of axon causes Na+ gates to open
APs propogate with constant velocity (larger axons)
have increased velocity and less resistance
APs propogate with constant velocity (myelinated axons)
have increased velocity due to more insulation
insulated conduction
myelinated axons have bare regions called nodes of ranvier that contain many voltage-gated na+ channles
movement of voltage in axon
spreads passively down myelinated axons until it reaches a node
what happens at the node once the voltage reaches it
sodium channels opena nd another AP is produced
what is chemical communciation called
synaptic transmission
what are the chemicals used to pass along the message
neurotransmitters
5 steps of conventional chemical synaptic transmission
neurotransmitter symthesis
NT are concentrated and packaged in synaptic vesicles which are found in the presynaptic element or travel there by anterograde axonal transport
NT are released into synaptic cleft
NTs bind to ion channels in postsynaptic membrane
NT action is terminated in several ways
what happens when NTs are released into the synaptic cleft
AP traveling down axon depolarizes the presnaptic nerve terminal
volatage-gated Ca2+ causes NT-filled vesicles to bind to active zones on neuronal membrane
exocytosis- NT are released into the synaptic cleft
what happens when NTs bind to ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane
ligand-gated ion channels either open or close, thus changing the permeability of the postsynaptic cell membrane
postsynaptic potential
when ligated gated channels open or close, changing the permeabiity of the postsynaptic membrane
3 ways a NT action is termiated
NT in synaptic cleft can diffuse away
NT can be reabsorbed by presynaptic ending or by glial cells
NTs can be degraded by enzymes in the synaptic cleft
what two types of potential changes occur in the postsynaptic membrane
either a depolarizing or hyperpolarizing
depolarizing
inside of a neuron becomes more pos
hyperpolarizing
inside of a neuron becomes more negative
what is a depolarizing potential change called
excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)
what happens in an EPSP
NTs bind to ion channel on postsynaptic membrane
ion channels open cuasing an influx of positively charged ions
membrane is depolarized
process of EPSP at Neuromuscular Junction
AP is produced → influx of Ca+ → acetylcholine is released → acetylcholine binds to ion channels called acetylcholine receptors → EPSP produced (end plate potential) → muscle contraction → extra acetylcholine in synaptic cleft is removed by acetylcholinesterase
what is a hyperpolarizing potential change called
inhibitory postsynaptic potentiual
what happens in an IPSP
NTs bind to ion channel on postsynaptic membrane
ion channels open causing an influx of negatively charged ions or an efflux of pos charged ions
memebrane is hyperpolarized
IPSP inhibits generation of AP by postsynaptic cell
what determines if an IPSP or EPSP happens
postynaptic ion channels
what do postsynaptic neurons do
compare and summate all inputs to determine how to respond
what does the probability of a response depend on
amount of NT released
number of postsynaptic ion channels present.
distance from ion channel to axon hillock in postsynaptic neuron
what does it mean that neurons that fire together wire together
strength of a synapse is influenced by history of activity at the synapse
agonists
drug that promotes effects of NT
antagonists
drug that impedes the effects of the NT
Myastenia Gravis def
autoimmune disease in which body produces antibodies that bind with the ion channels in motor end plates, preventing acetylcholine from binding to these receptors