Chapter 6 Homework
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What role does acetylcholine play in muscle contraction?
Stimulate muscle contraction
Which structure connects muscles to bone?
Tendons
Which muscle tissue is responsible for involuntary movements and is found in the walls of hollow internal organs?
Smooth muscle
Which condition is caused by overuse or injury to the tendons surrounding a joint, leading to inflammation?
Tendinitis
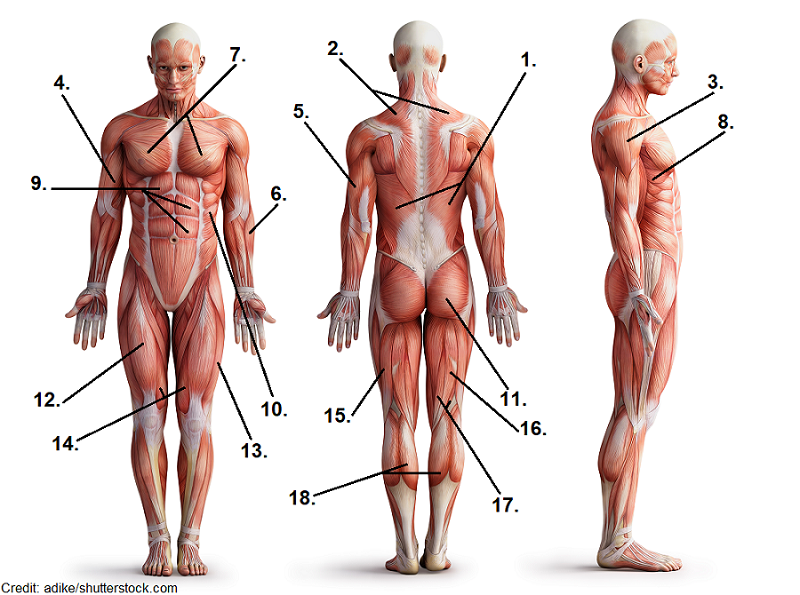
1
K.
latissimus dorsi
2
I.
trapezius
3
E.
deltoid
4
C.
biceps brachii
5
H.
triceps
7
D.
pectoralis major
10
A.
obliques
9
J.
abdominals
11
L.
gluteus maximus
12
B.
quadriceps
16
F.
hamstring
18
G.
calf muscle
What is the role of the antagonist muscle during movement?
Relaxes to allow the agonist to contract
Which of the following is a common symptom of myasthenia gravis?
Muscle weakness that worsens with activity
What kind of muscle is responsible for heart contractions, pumping blood throughout the circulatory system.
Cardiac muscle
Which neurotransmitter is affected in myasthenia gravis?
Acetylcholine
What is the term for the contractile unit of a muscle fiber?
Sarcomere
What is the primary function of skeletal muscle?
Produce movement of bones through voluntary control
Which ion is essential for muscle contraction?
Calcium
Extension
Extending the knee so the leg is straight
Flexion
Bending an elbow
Abduction
Raising your hand straight up in the air
Adduction
Moving your arm down by your side
Rotation
Turning your neck
Circumduction
Spinning your arm in a circular motion
Pronation
Turning your hand so the palm is facing down
Supination
turning your hand so the palm is facing up
Opposition
Moving your thumb across your hand (towards the pinky finger)
Inversion
Turning your foot so the sole is pointing inward
Eversion
Turning your foot so the sole is facing outward