PAEA Pediatrics EOR Topics
1/312
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
313 Terms
what is the MC conjunctivitis seen in children? what is the cause? source?
viral conjunctivitis; Adenovirus; swimming pools
Dx? preauricular lymphadenopathy, copious watery eye discharge, scanty mucoid discharge, usually unilateral with punctate staining on slit lamp examination; Tx?
dx: viral conjunctivitis
tx: supportive (cool compresses, artificial tears) +/- antihistamines for itching (Olopatadine)
Dx? bilateral eye itching, tearing, redness, string discharge, chemosis (conjunctival swelling) with cobblestone appearance to inner/upper eyelids; Tx?
dx: allergic conjunctivitis
tx: topical antihistamines (H1 blockers) (Olopatadine, Pheniramine/Naphazoline, Emedastine), topical NSAID (ketorolac), topical corticosteroids (but s/e of long term use = glaucoma, cataracts, HSV keratitis)
Dx? purulent eye discharge, lid crusting, no visual changes, absence of ciliary injection; Tx?
dx: bacterial conjunctivitis (MC S. aureus, Strep pneumo, H. influenzae)
tx: topical abx (erythromycin, fluoroquinolones, sulfonamides, aminoglycosides); if contact lens wearer cover for pseudomonas w/ fluoroquinolone or aminoglycoside
if bacterial conjunctivitis is found to be chlamydia or gonorrhea what is the tx?
admit for IV and topical abx (ophtho emergency)
-gonoccoccal: IV ceftriaxone + topical
-chlamydia: IV azithromycin
neonatal conjunctivitis is aka? if left untreated can develop what?
ophthalmia neonatorum; corneal ulceration, opacification/scarring, visual impairment/blindness
standard prophylaxis given immediately after birth to prevent ophthalmia neonatorum (neonatal conjunctivitis) includes:
erythromycin ointment, tetracycline ointment, silver nitrate, or povidone-iodine
if ophthalmia neonatorum (neonatal conjunctivitis) develops on day 1 after birth what is the most likely cause? day 2-5? day 5-7? day 7-11?
day 1: silver nitrate (chemical cause- prophylaxis is what can cause the condition)
day 2-5: gonococcal
day 5-7: chlamydia
day 7-11: HSV
orbital (septal) cellulitis is usually secondary to _________ infection in most commonly what age group?
sinus; 7-12y; other causes include dental/facial infxns or bacteremia
what is the most common sinus infection (90%) that causes secondary orbital cellulitis? what organisms are the cause?
ethmoid; S. aureus, Strep. pneumo, GABHS (Strep. pyogenes), H. influenzae
work up/Dx? decreased vision, pain w/ ocular movement, proptosis (bulging eye), eyelid erythema and edema; tx?
dx: orbital cellulitis
work up: CT scan (showing infxn of fat & ocular muscles) or MRI
tx: IV antibiotics (Vanc, Clinda, Cefotaxime, Ampicillin/Sulbactam)
what is the difference b/t orbital (septal) cellulitis and preseptal cellulitis?
preseptal may still have ocular pain, redness and swelling but NO visual changes or pain w/ ocular mvmt (hasn't affected the muscles)
misalignment of the eyes is aka? when does stable ocular alignment present in infants?
strabismus; 2-3 mos
convergent strabismus is aka? divergent strabismus is aka?
convergent: esotropia (deviated inward "cross eyed")
divergent: exotropia (deviated ouward)
a + Hirschberg corneal light reflex test, diplopia, scotomas (blind spots), or amblyopia (lazy eye) are clinical manifestations of what condition? what other tests can be performed?
strabismus; cover-uncover test to determine the angle of strabismus, cover test, convergence testing
how can strabismus be treated?
-patch therapy: normal eye is covered to stimulate and strengthen the affected eye
-eyeglasses
-corrective therapy: if severe or unresponsive to conservative therapy
if not treated before 2 y/o, amblyopia may occur and cause decreased visual acuity that is not correctable
Dx? 1-2 days of ear pain, pruritis in the ear canal, auricular discharge, pressure/fullness, hearing usually preserved, pain with tug test and tragus pressure, auditory canal erythema/edema/debris, recent swimming pool use; MC organisms? Tx?
Dx: otitis externa
MC organisms: pseudomonas, proteus, s. aureus, s. epidermis, GABHS, anaerobes (peptostreptococcus), aspergillus
Tx: 1. protect ear against moisture (isopropyl alcohol and acetic acid) 2. ciprofloxacin/dexamethasone (ofloxacin safe if there is an associated TM perf) 3. Aminoglycoside combo (neomycin/polytrim-B/hydrocortisone -BUT not used if perf suspected bc ototoxic 4. amphotericin B if fungal
malignant otitis externa is osteomyelitis at the skull base secondary to ___________ infxn; MC seen in what pt populations; Tx?
pseudomonas; MC in DM and immunocompromised pts; Tx w/ IV Ceftazidime or Piperacillin + FQ or Aminoglycoside
acute otitis media is an infection of the middle ear, temporal bone and mastoid air cells that is MC preceded by
a viral URI that causes edema of eustachian tube, negative pressure, transudation of fluid and mucus in middle ear that allows for bacterial growth
what are the 4 MC organisms seen in acute otitis media?
Strep pneumo, H. influenza, Moraxella catarrhalis, Strep pyogenes (same as seen in acute sinusitis)
Dx: fever, otalgia, ear tugging in infants, conductive hearing loss, stuffiness, possible drainage from ear, bulging/erythematous TM w/ effusion, dec TM mobility on pneumatic otoscopy; Tx?
dx: acute otitis media
tx: 1st line- amoxicillin, 2nd line- augmentin (amoxicillin-clavulate); if PCN allergy- azithromycin, clarithromycin, erythromycin-sulfisoxazole, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, if PCN adverse effect but not allergy- ceftriaxone, cefdinir, cefixine
don't forget to treat pain as well (ibuprofen or tylenol); can also perform myringotomy (surgical drainage) to relieve pain
tympanostomy if recurrent >4 times in 1 yr
if bullae are seen on the TM of a pt with AOM what should you suspect?
mycoplasma pneumoniae
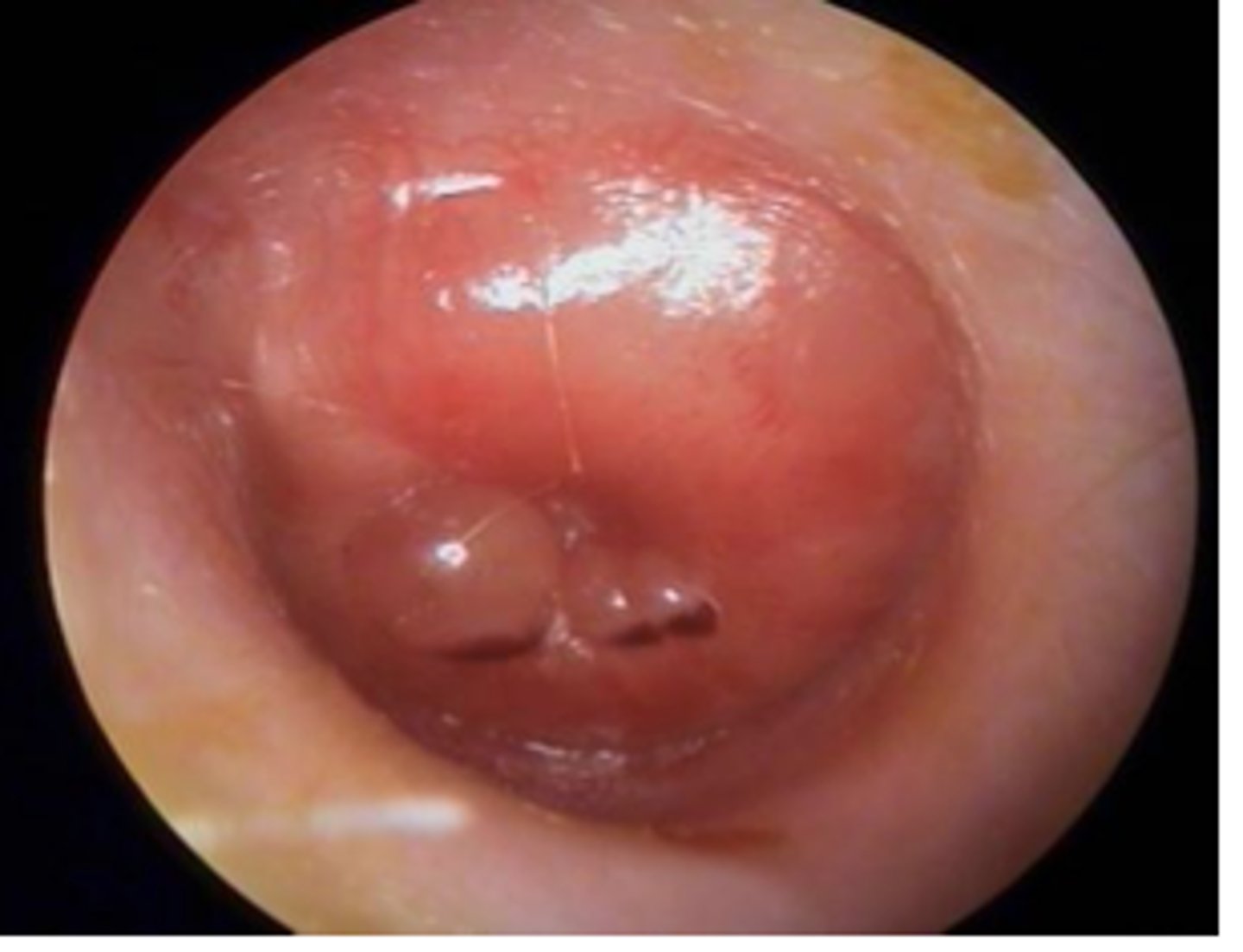
Dx? deep ear pain (worse at night), fever, mastoid tenderness and possibly fluctuance (abscess), following AOM infxn; complications?
-dx: mastoiditis (inflammation of the mastoid air cells of the temporal bone- mastoid and middle ear are connected)
-complications: hearing loss, labyrinthitis, vertigo, CN VII paralysis, brain abscess
how is mastoiditis diagnosed and treated?
dx: by CT scan is 1st line test
tx: IV abx (same as w/ AOM- amoxicillin 1st line, augmentin 2nd line, azithromycin for allergy to PCN, ceftriaxone for ADR to PCN) + middle ear/mastoid drainage (myringotomy +/- tympanostomy tube placement- can obtain Cx)
if mastoiditis refractory to tx or complicated = mastoidectomy
what are the 2 auditory examination tests (and what order do you perform them in)?
1st Weber (tuning fork placed on top of head)
2nd Rinne (tuning fork placed on mastoid bone by ear)
if a child has conductive hearing loss in their L ear what will the Weber and Rinne tests show?
Weber: lateralizes to L ear
Rinne: BC > AC
if a child has sensorineural hearing loss in the R ear what will the Weber and Rinne tests show?
Weber: lateralizes to L ear (the normal one)
Rinne: AC > BC (shows normal L ear)
what are the causes of conductive vs sensorineural hearing loss?
conductive: cerumen impaction MC, damage to ossicles (otosclerosis, cholesteatoma), mastoiditis, otitis media
sensorineural: presbyacusis MC (age-related hearing loss), chronic loud noise exposure, CNS lesions (acoustic neuroma), labyrinthitis, meniere syndrome
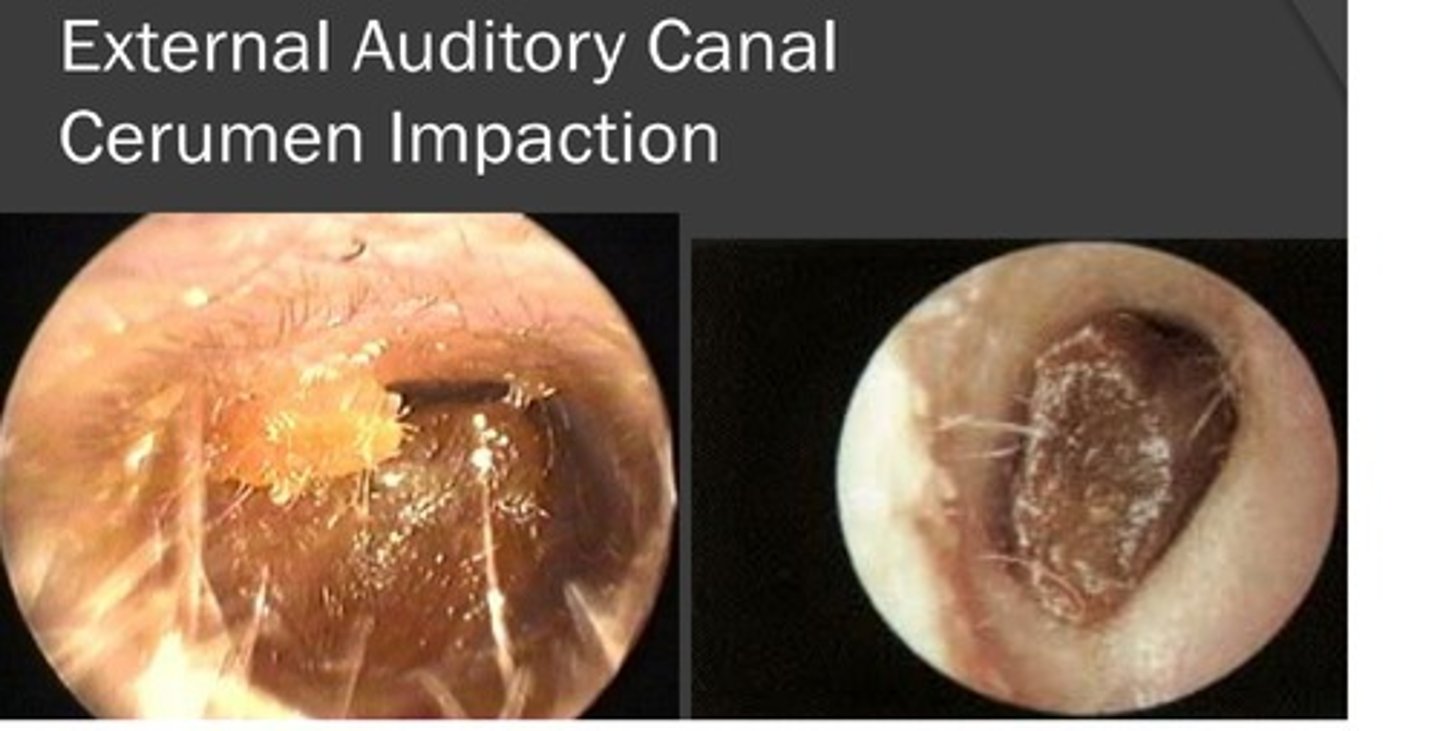
how is cerumen impaction treated?
1. cerumen softening: hydrogen peroxide 3% or carbamide peroxide (Debrox)
2. aural toilet: irrigation (as long as no TM perf- H2O must be at body temp to prevent vertigo), curette removal, suction
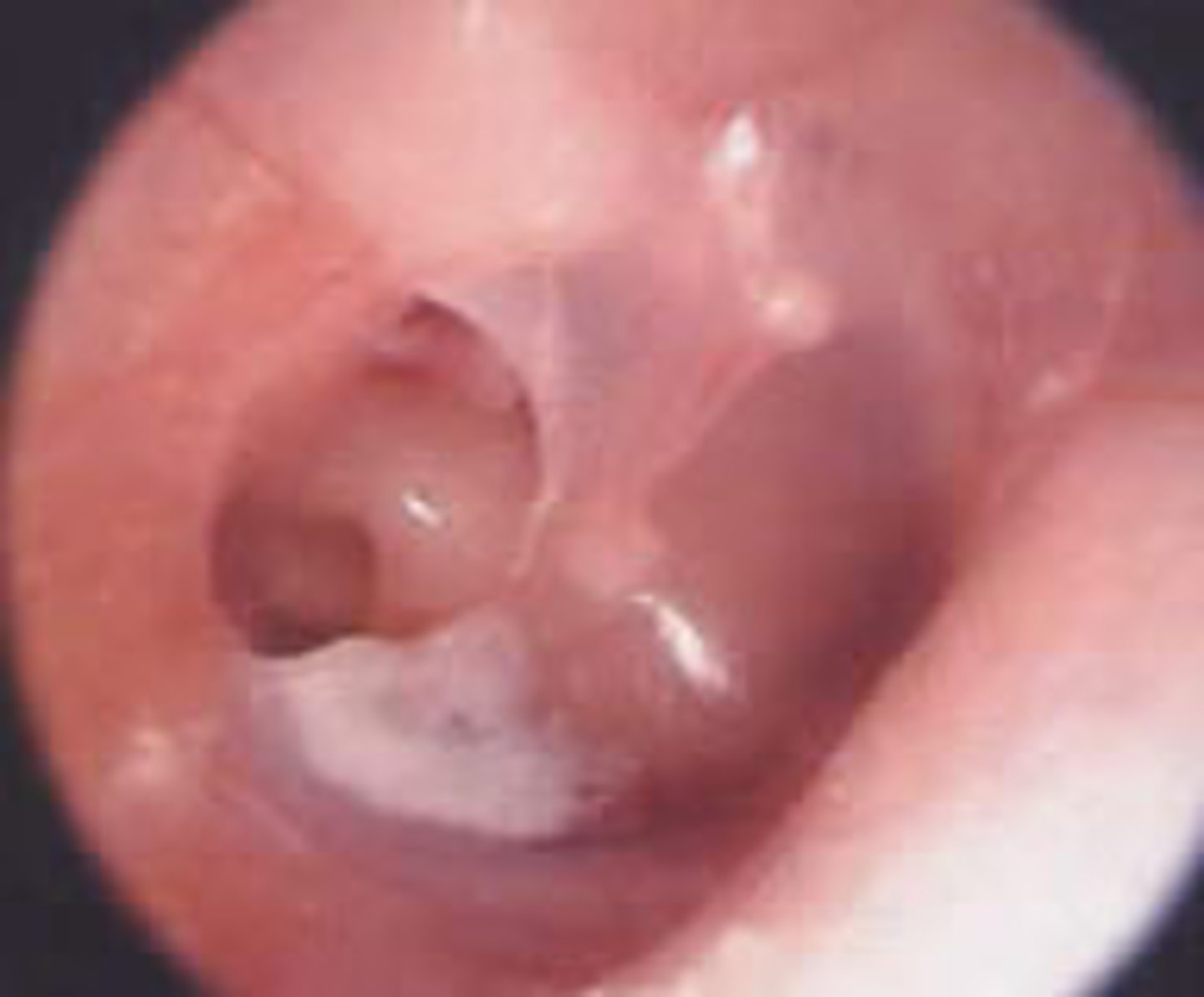
Dx? acute ear pain, hearing loss, break in the tympanic membrane, +/- conductive hearing loss, +/- bloody otorrhea, +/- tinnitus & vertigo; Tx?
dx: tympanic membrane perforation
tx: observation (most heal spontaneously) but can do surgical repair; avoid water/moisture/topical aminoglycoside (ototoxic) in ear
Dx: sneezing, nasal congestion/itching, clear rhinorrhea, worse in the morning, pale/blue turbinates, +/- nasal polyps, +/- eye, ear, throat involvement; Tx?
dx: allergic rhinitis
tx: 1st line intranasal steroids, oral antihistamines, mast cell stabilizers (cromolyn, nedocromil)
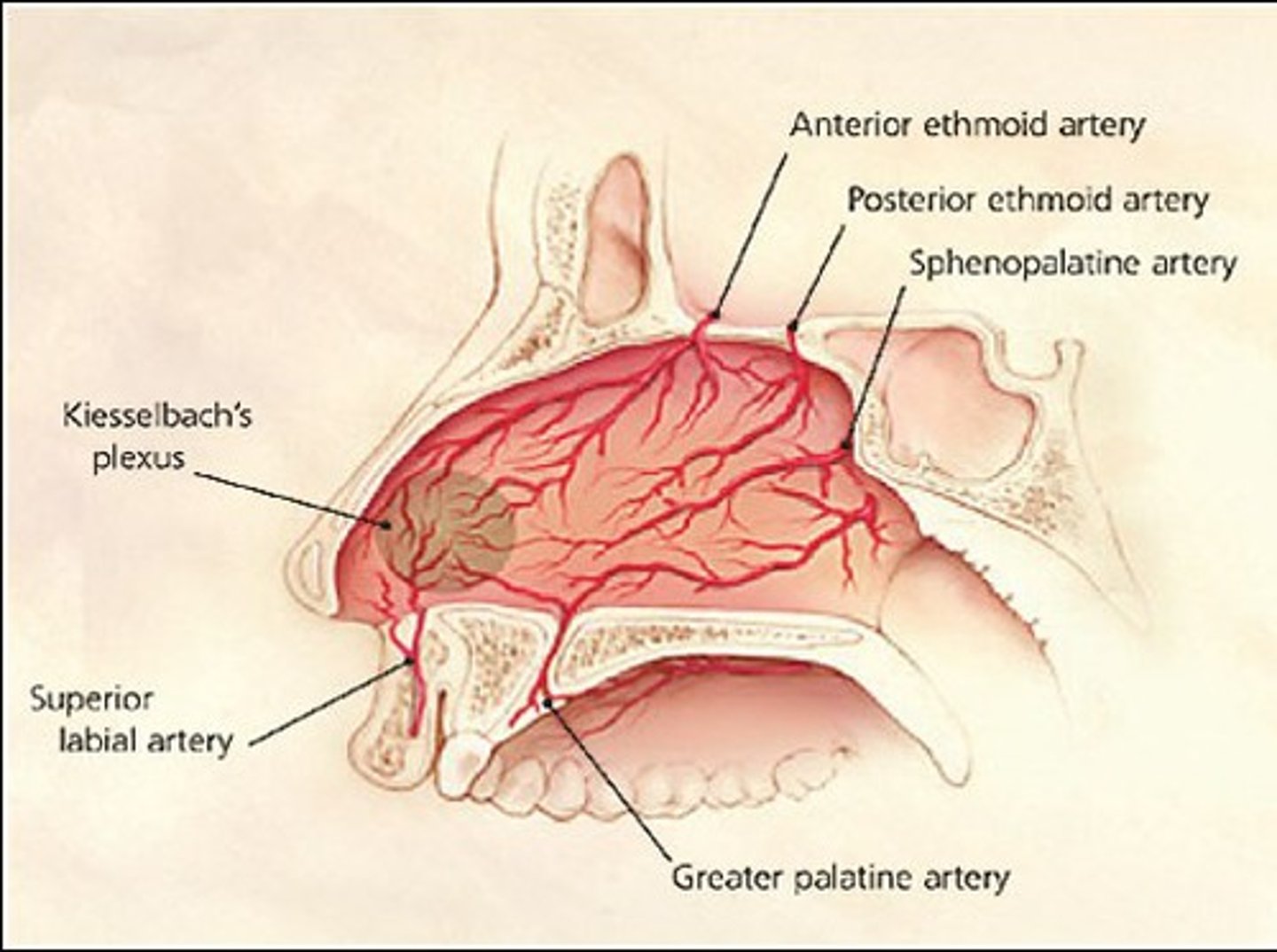
what are the blood vessels involved in anterior vs posterior epistaxis? which is MC involved?
anterior: Kiesselbach's plexus MC type of epistaxis
posterior: palatine artery- this one may cause bleeding in both nares and posterior pharynx
tx for anterior epstaxis?
-1st line is direct pressure 10-15 min in seated position leaning forward (to reduce vessel pressure)
-topical decongestants/vasocontrictors: phenylephrine, oxymetazoline (afrin)
-cauterization: silver nitrate if cannot control bleeding and site can be seen
-nasal packing: + abx (cephalexin or clindamycin) to prevent toxic shock syndrome
-adjunct therapy: avoid exercise, spicy foods (vasodilation), moisten membranes w/ bacitracin and humidifiers
acute pharyngitis/tonsillitis is MC caused by? other causes?
-viral is MC: adenovirus, rhinovirus, enterovirus, EBV, RSV, influenza A/B, herpes zoster
-bacterial: GABHS (strep. pyogenes "strep throat")
tx for acute viral pharyngitis/tonsillitis
1. fever control: ibuprofen or tylenol
2. hydration
3. bed rest
Dx? pt w/ sore throat, fever >100.4F/38C, pharyngotonsillar exudates, tender anterior cervical LAD, absence of cough and gram stain showing G+ cocci in chains
"strep throat" streptococcal pharyngitis (strep pyogenes)
what are the Centor criteria for diagnosing strep throat?
0-1 pts: no abx or throat Cx (unless 3-14y get Cx anyway)
2-3 pts: Cx
4-5 pts: abx
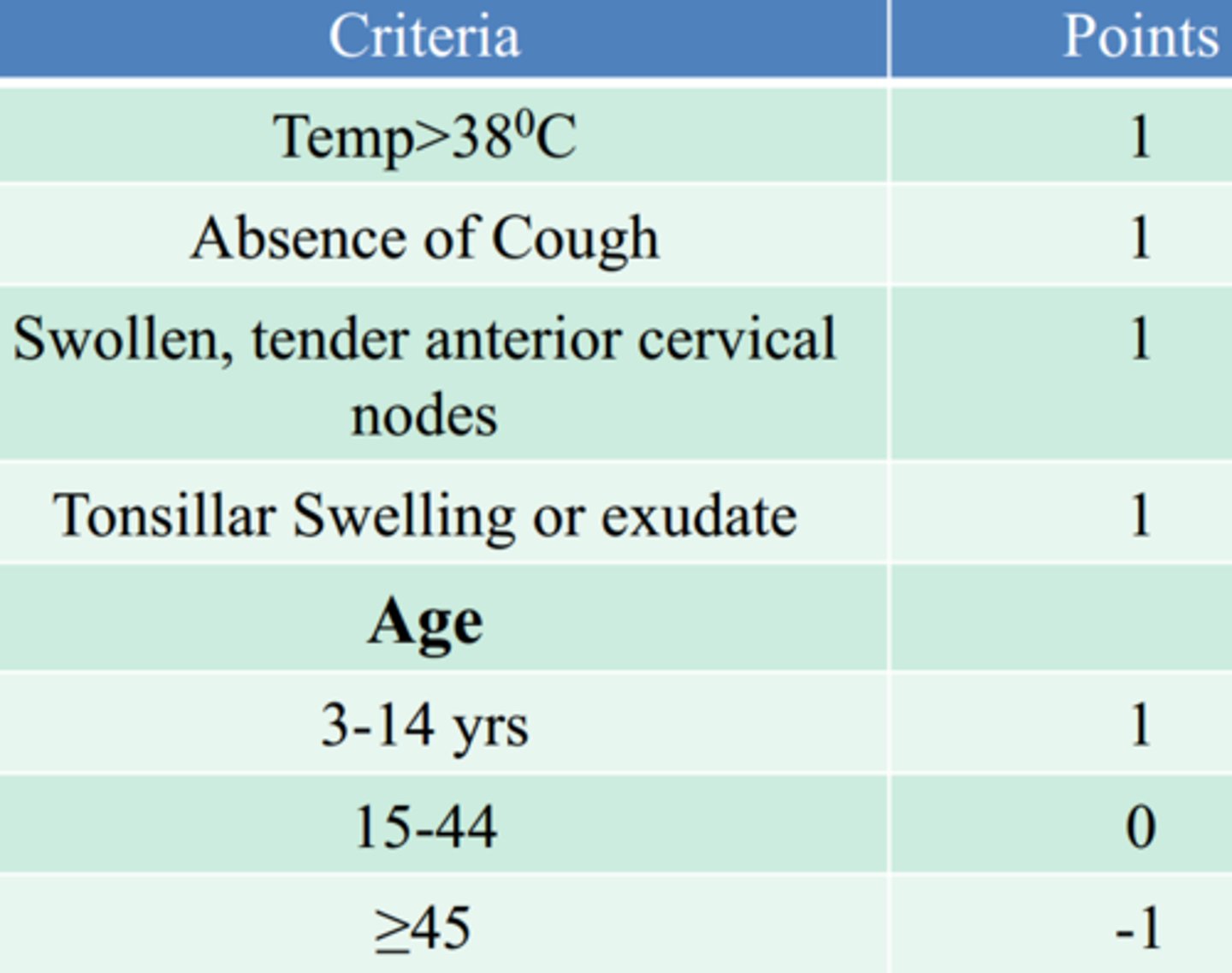
what is the tx for strep throat?
-1st line: PCN G or VK; others include: amoxicillin, augmentin
-if PCN allergic = macrolides (azithromycin, erythromycin, clarithromycin) or if ADR = cephalosporins or clindamycin
what are some complications from strep throat?
-rheumatic fever (preventable w/ abx)
-glomerulonerphritis (not preventable w/ abx)
-peritonsillar abscess, cellulitis
peritonsillar abscess is aka _______ that occurs after
quinsy; tonsillitis -> cellulitis -> abscess formation
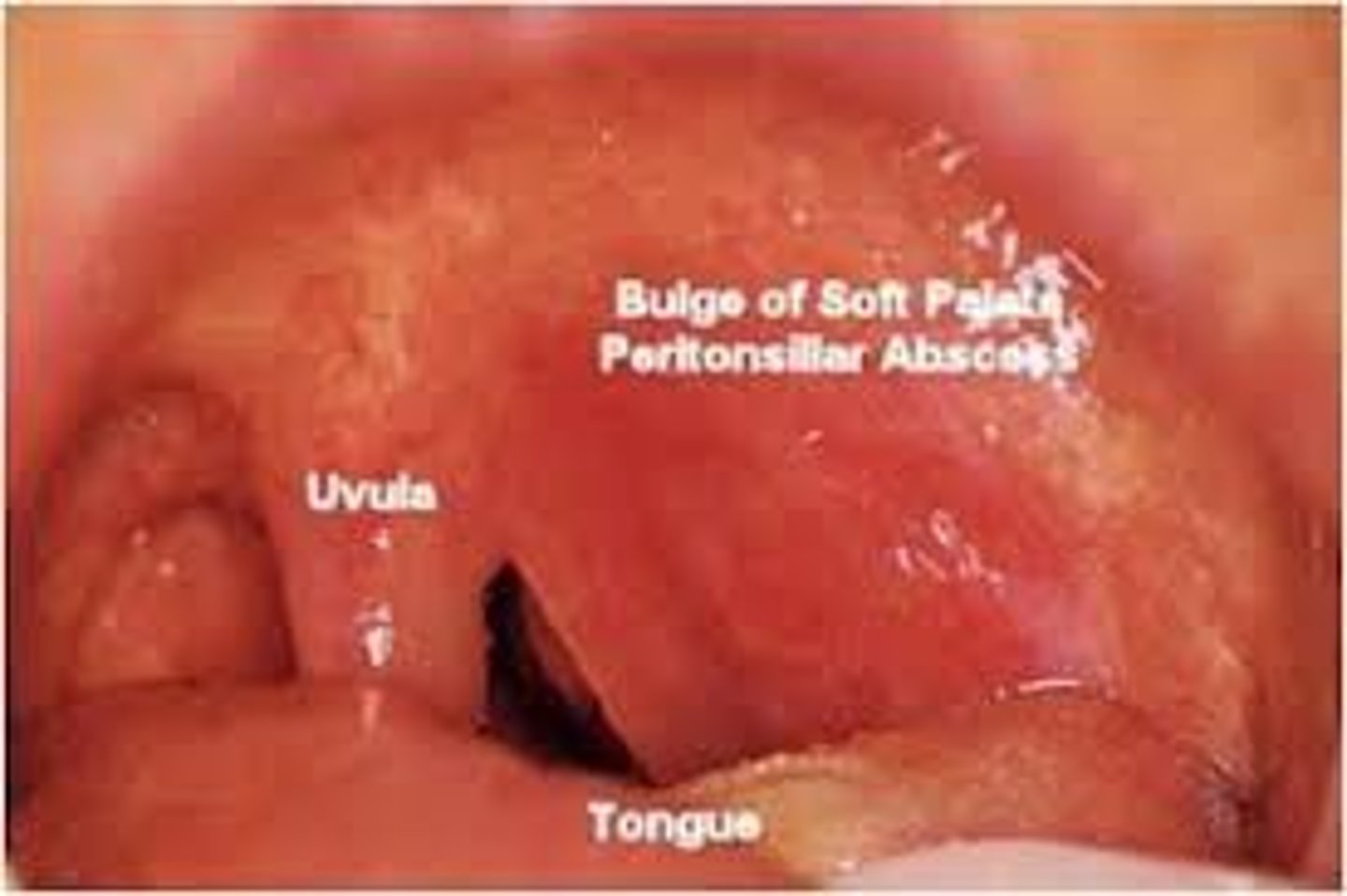
Dx? dysphagia, pharyngitis, muffled "hot potato voice," drooling, trismus (lock jaw), uvula deviation to contralateral side, tonsillitis, anterior cervical LAD
peritonsillar abscess but need CT scan to differentiate b/t cellulitis vs abscess
how is peritonsillar abscess treated?
-abx (ampicillin/sulbactam (Unasyn), clindamycin, PCN G + metronidazole) + aspiration or I&D
-tonsillectomy if recurrent strep infxns, peritonsillar infxns, or chronic tonsillitis
thrush is caused by? tx w/?
candida albicans; tx is w/ nystatin mouthwash, clotrimazole troaches or oral fluconazole
what is the most common cause of acute epiglottitis?
H. influenzae type B infxn (incidence has gone down d/t vaccination); other rare causes are strep pneumo, s. aureus, GABHS (strep pyogenes)
Dx? dysphagia, drooling, distress, fever, odynophagia, inspiratory stridor, dyspnea, hoarseness, muffled voice, tripod position, thumbprint sign on lateral XR, laryngoscopy gold standard showing cherry-red edematous epiglottis; Tx?
dx: acute epiglottitis
tx: maintain airway (comfort and keep child calm, dexamethasone to reduce airway edema, tracheal intubation for severe cases) and supportive mgmt
if bacterial cause is suspected can start on 2nd/3rd gen cephalosporin ceftriaxone or cefotaxime
diaper rash is MC caused by? tx?
candida albicans
tx: topical antifungals, frequent diaper changes to reduce dampness in that area
can also be a contact dermatitis d/t prolonged exposure to urine/feces; tx w/ freq diaper changes, petroleum or zinc oxide
an immediate drug reaction such as urticaria or angioedema that is Ig-E mediated is a type ___ hypersensitivity rxn
type I
a cytotoxic, Ab-mediated drug reaction is a type ___ hypersensitivity rxn
type II
a drug reaction caused by immune antibody-antigen complex deposition is a type ___ hypersensitivity rxn
type III
a delayed (cell mediated) drug reaction like erythema multiforme is a type ___ hypersensitivity rxn
type IV
what is the most common type of cutaneous drug eruption? tx?
exanthematous/morbiliform rash- generalized distribution of "bright-red" macules & papules that coalesce to form plaques- usually begins 2-14 days after medication initiation (abx, NSAIDs, allopurinol, thiazide diuretics)
tx: oral antihistamines
what is the 2nd Mc type of cutaneous drug eruption that occurs w/i minutes to hrs after drug administration? tx?
urticarial or angioedema (type I)- triggers include abx, NSAIDs, opiates, radiocontrast media
tx: systemic corticosteroids, antihistamines
what is the 3rd MC cutaneous drug eruption that is characterized by target lesions? tx?
erythema multiforme (type IV)- triggered by sulfonamines, PCNs, phenobarbital, dilantin
tx: symptomatic therapy
in regards to urticaria, local pinpoint pressure that results in the skin to wheal in that area is called? local rubbing causing urticaria is called?
dermatographism
Darier's sign
how is urticaria treated?
removal of offending agent, antihistamines (H1 blockers), corticosteroids, or H2 blockers as adjuvant therapy (cimetidine, ranitidine, famoidine)
erythema multiforme is MC associated with
HSV, mycoplasma, s. pneumo, sulfa drugs, beta-lactams, phenytoin, phenobarbital, malignancies, autoimmune
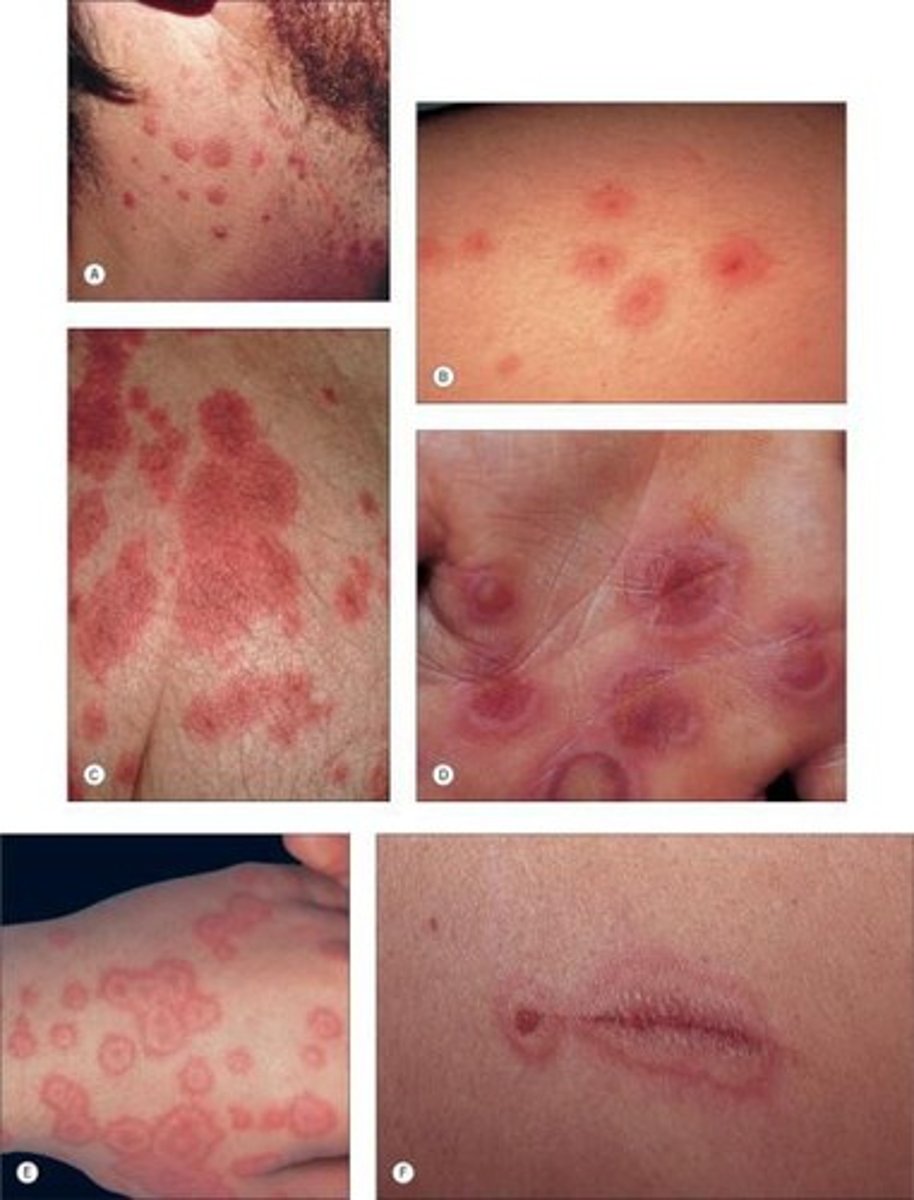
red purpuric papules and macules with a hypopigmented rim around the center and a erythematous halo around that span the palms and soles of the feet? same lesions but involving 1 or more mucous membranes (oral, genital, or ocular mucosa) and <10% BSA with no epidermal detachment.
erythema multiforme minor; major
what is the treatment for erythema multiforme?
symptomatic- d/c offending drug, antihistamines, analgesics, steroid/lidocaine/diphenhydramine mouthwash for oral lesions, and systemic steroids if severe
Steven-Johnson Syndrome and TEN are usually due to what offending agents?
MC d/t drug eruptions from sulfa, anticonvulsants, NSAIDs, allopurinol, abx, infxns like mycoplasma, HIV, HSV, malignancy, or idiopathtic
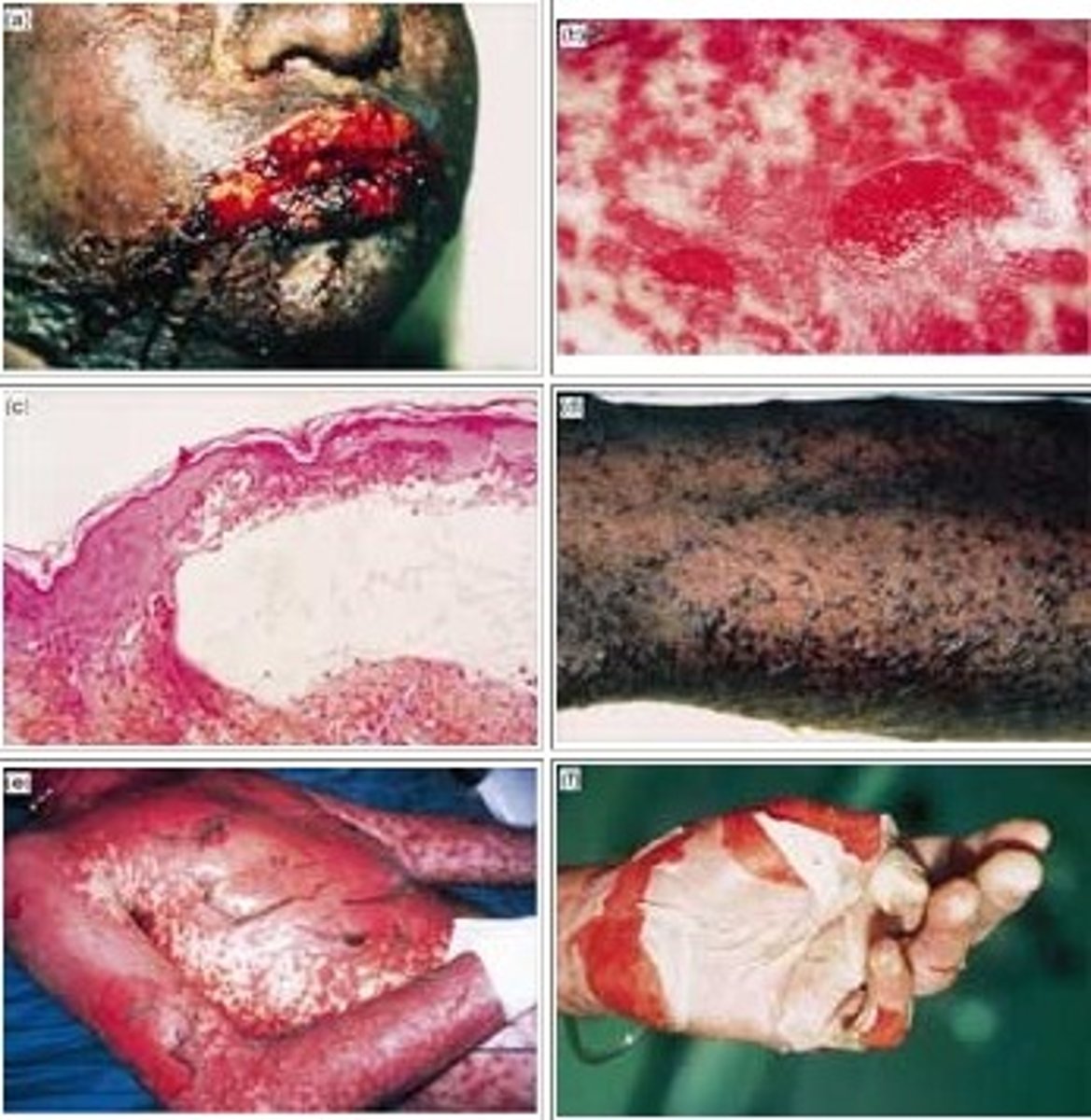
SJS is defined as sloughing of ____% BSA where are TEN is defined as sloughing of ____% BSA
SJS <10%
TEN >30%
Dx? fever, URI, widespread blisters, erythematous/pruritic papules with 1 or more mucous membranes involved with epidermal detachment (+ Nikolsky sign), <10% BSA; tx?
dx: SJS (if >30% = TEN)
tx: treat like severe burn- admit to burn unit, pain control, withdrawal of offending meds, fluid & electrolyte replacement, wound care
+ Nikolsky sign is when rubbing of skin exfoliates the outer layer
what is the pathophysiology behind the 4 causes of acne vulgaris?
1. inc sebum production (d/t inc androgens)
2. clogged sebaceous glands
3. propionibacterium acne overgrowth (nml flora that overgrows in blocked pores and causes an inflammatory response)
4. inflammatory response
what type of acne are blackheads? whiteheads? papules/pustules? cystic/nodular?
blackheads- open comedones (incomplete blockage)
whiteheads- closed comedones (complete blockage)
papules/pustules- inflammatory
cystic/nodular- severe and often heals with scarring
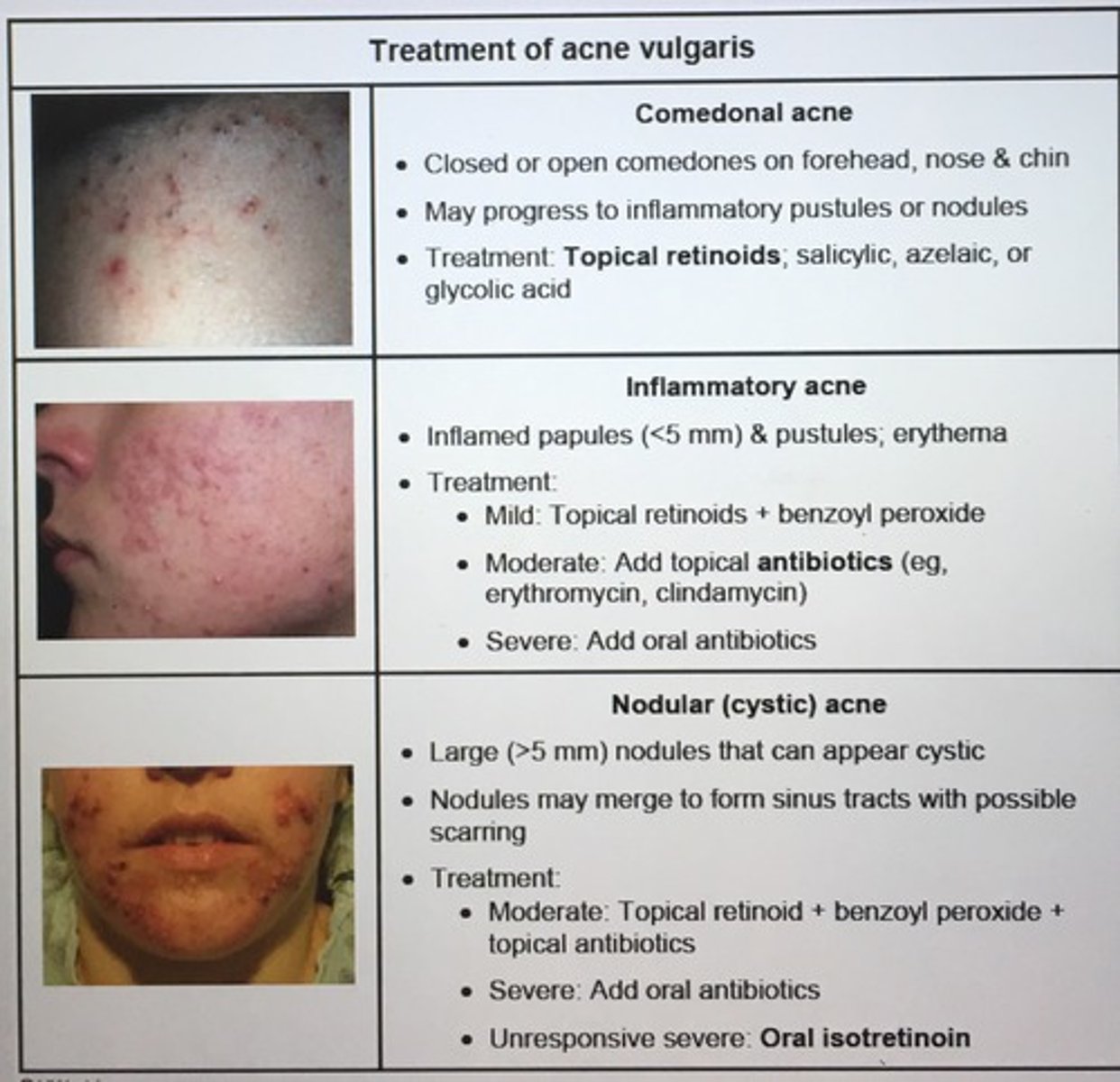
what are tx options for mild, moderate, and severe acne vulgaris?
-mild: topical retinoids (for comedone and inflammatory acne), benzoyl peroxide (decreases p. acne growth), topical abx (clindamycin), OCPs (dec androgen production reducing sebum production)
-mod: " + oral abx (tetracyclines such as doxycycline and minocycline), spironolactone (dec androgen production)
-severe: isotretinoin (accutane) works on all 4 pathophys routes. SEs include psych, hepatitis, inc TG/chol, arthralgias, leukopenia, premature long bone closure, dry skin, and highly teratogenic (so have to have 2 - preg tests before starting and then monthly thereafter + 2 forms of birth control while on it)
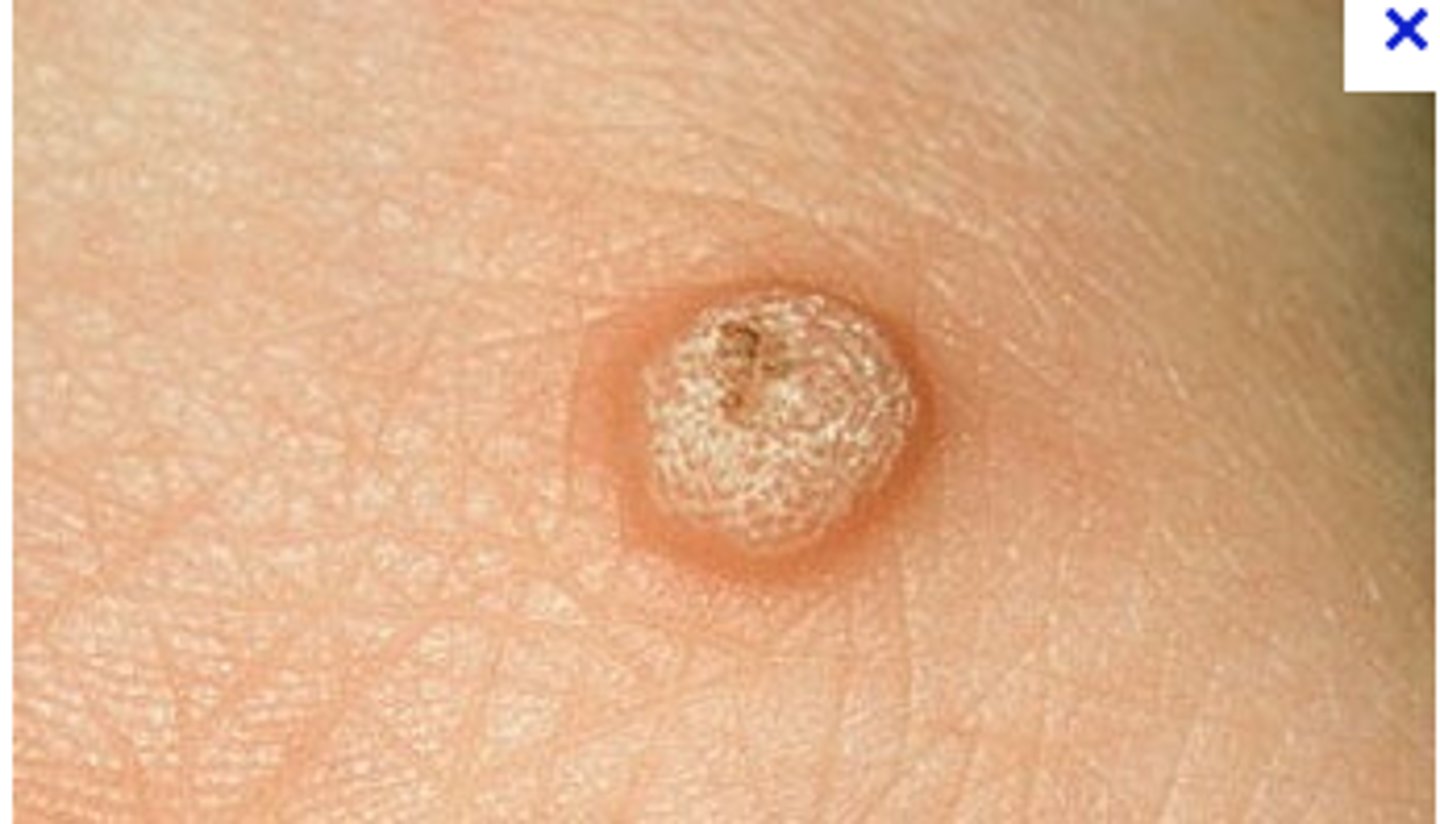
verruca are caused by _____ and commonly seen on the hands appearing as firm, hyperkeratotic papules b/t 1-10mm with red-brown punctations (thrombosed capillaries that are pathognomonic) with reg or irregular borders; tx?
HPV
tx: cryotherapy (liquid nitrogen), electrocautery, OTC salicylic acid, CO2, laser, intralesional bleomycin, intralesional candida albicans to trigger immune response to area
Dx? papulopustules on erythematous base around mouth sparing ther vermillion border which may become confluent into plaques with scales; tx?
dx: perioral dermatitis- MC in young women, may have h/o topical corticosteroid use
tx: metronidazole or erythromycin topically, tetracyclines orally (doxy, minocycline), and avoidance of topical steroids
what does the atopic triad of conditions include?
asthma, atopic dermatitis/eczema, and allergic rhinitis - usually people with one of these have another if not all
Dx? erythematous, ill-defined papules/blisters/plaques that later dry and crust over with scales most commonly in flexor creases; tx?
dx: atopic dermatitis (aka eczema)
tx: topical corticosteroids + antihistamines for itching w/ daily application of non-scented lotions/emollients and switching to gentle detergent, topical calcineurin inhibitors another option (tacrolimus, pimecrolimus alternative to steroids but can cause irritation and possible lymphoma/skin cancer risk)
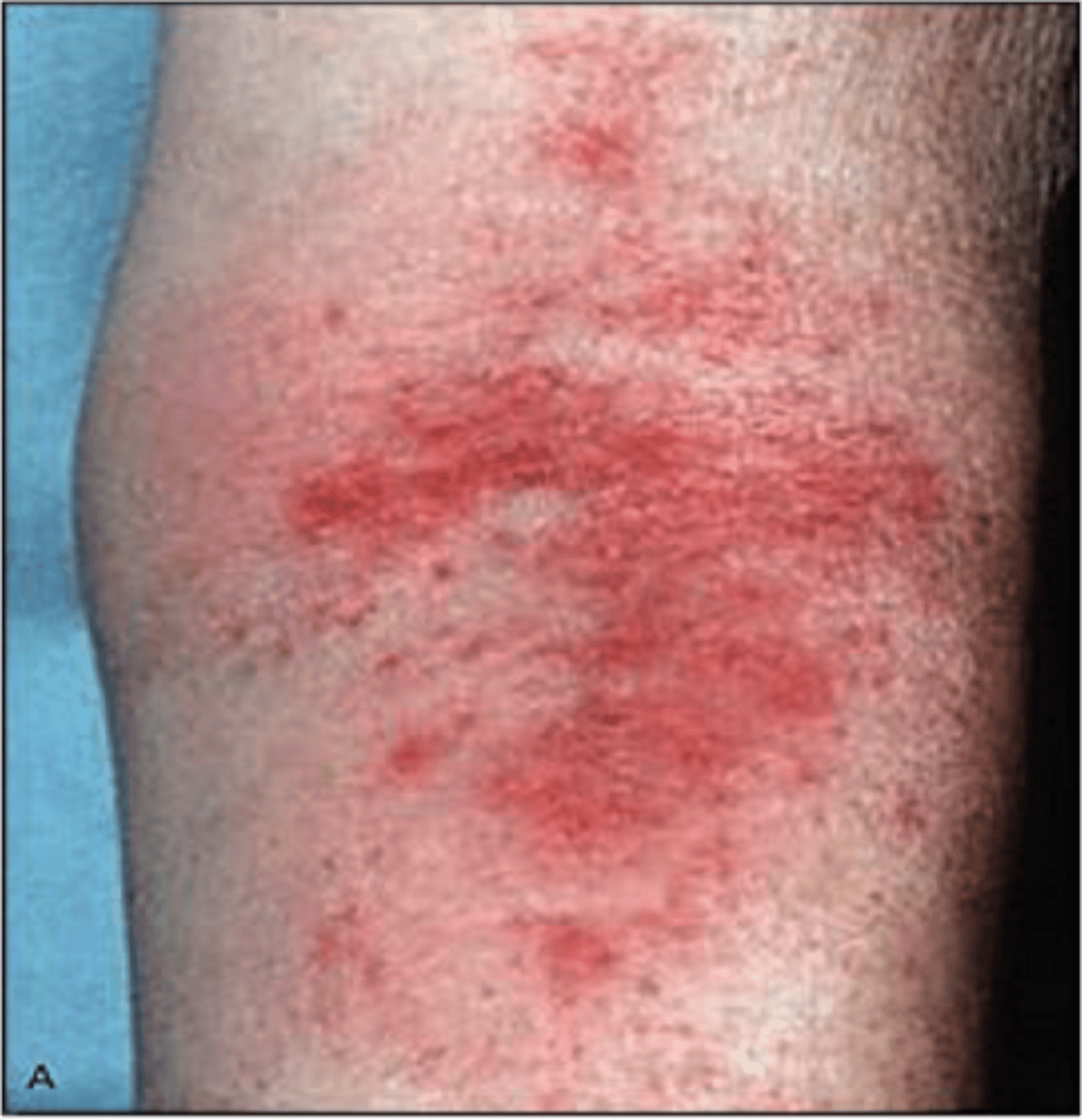
Dx? sharply defined discoid/coin-shaped lesions of dried patches/plaques of skin commonly seen on dorsum of hands, feet and extensor surfaces; tx?
dx: nummular eczema
tx: same as atopic dermatitis (topical corticosteroids, antihistamines for itching, and hydrating skin techniques)

poison ivy rash is a type of ________ dermatitis; tx?
contact dermatitis- irritant (others include detergent, chemicals, cleaners, acids, metals) tx is avoidance of irritants & topical corticosteroids
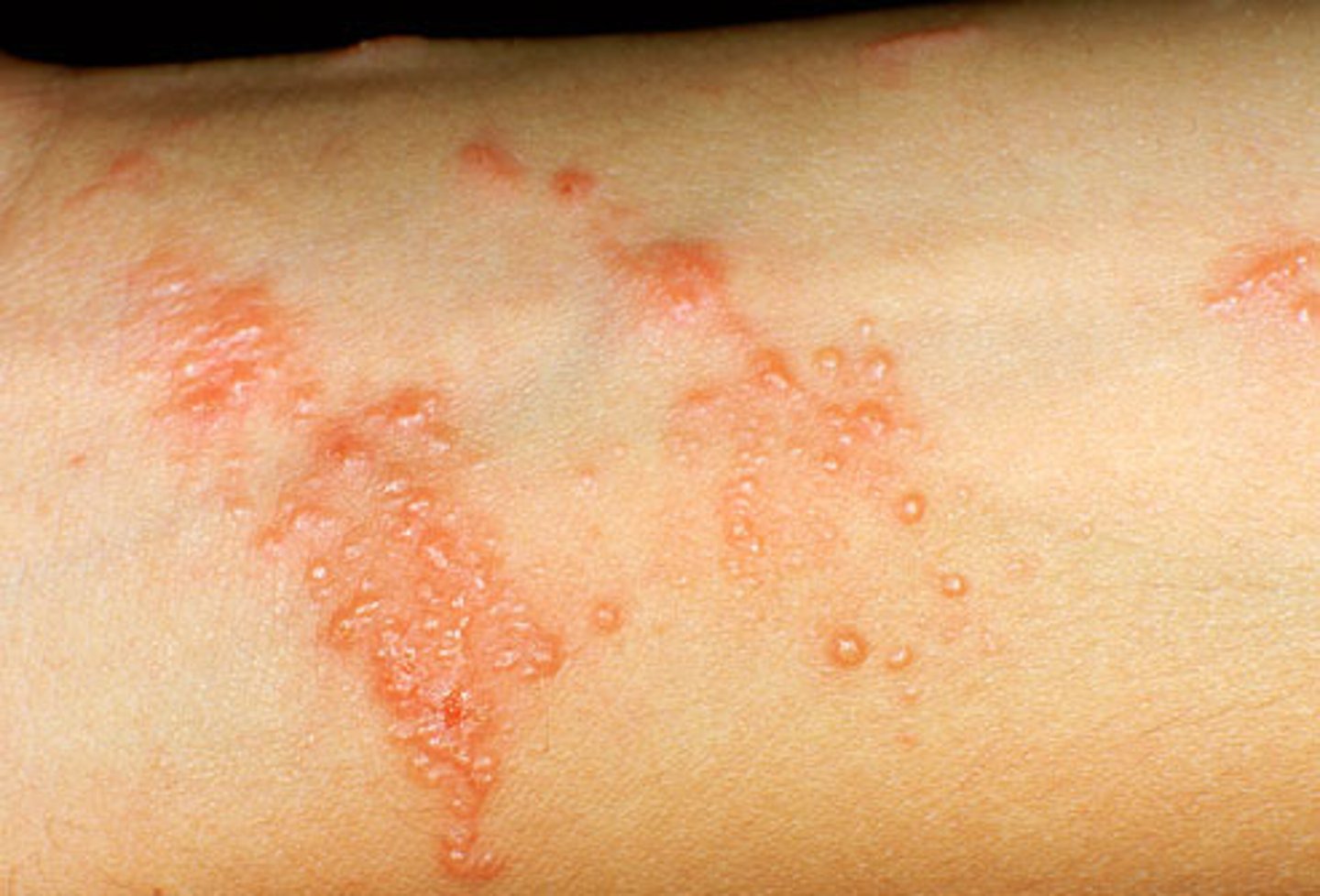
Dx? an idiopathic cell-mediated immune response with inc incidence with HepC that manifests as purple, polygonal, planar, pruritic papules with fine scales and irregular borders most commonly on flexor surfaces of extremities and skin, mouth, scalp, genitals, nails and mucous membranes that usually resolves in 8-12 mos; tx?
dx: lichen planus
tx: 1st line topical corticosteroids + antihistamines for itching; 2nd line po steroids, UVB therapy, retinoids
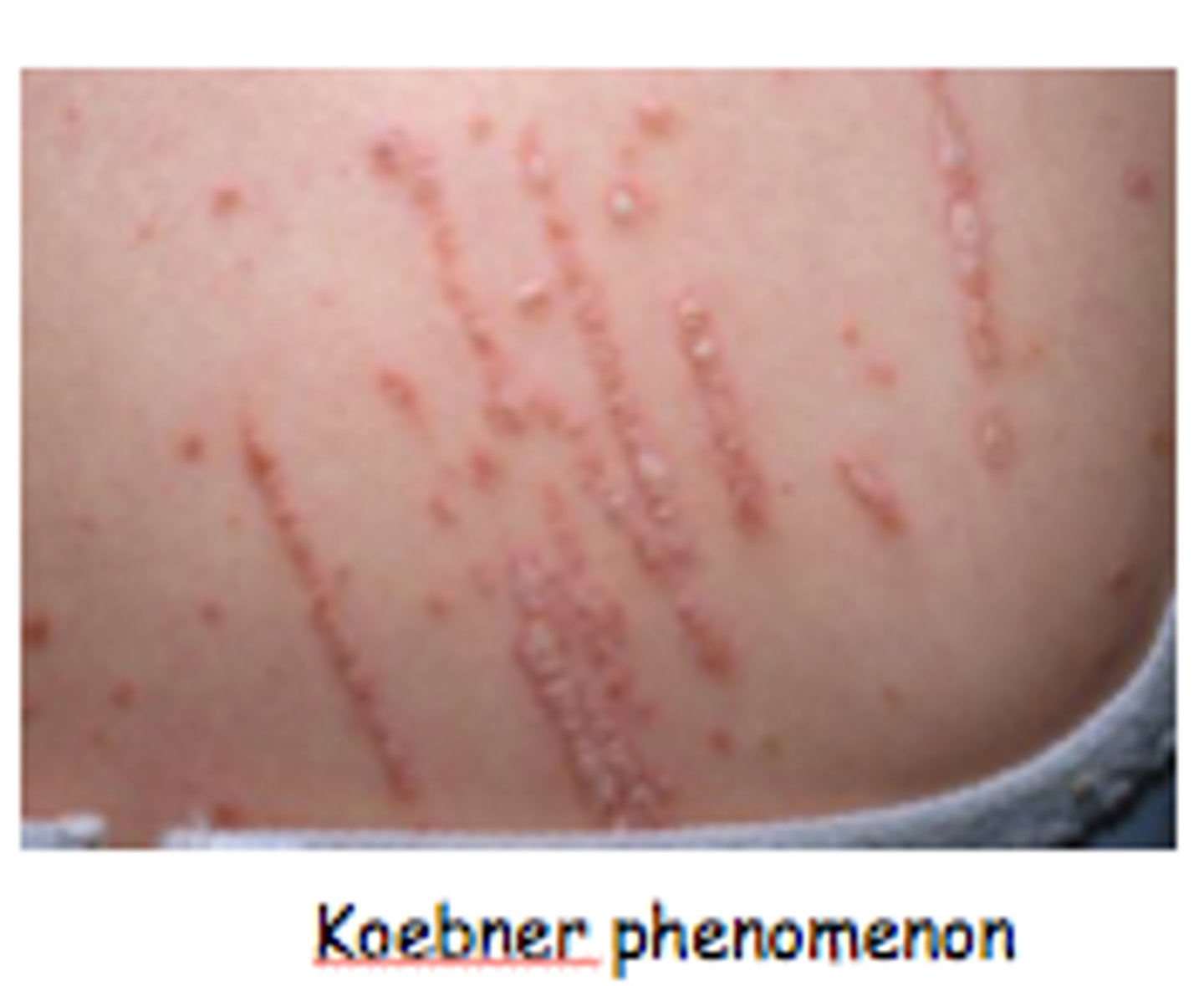
when new skin lesions appear at sites of trauma as seen in lichen planus and psoriasis, what is this called?
Koebner's phenomenon
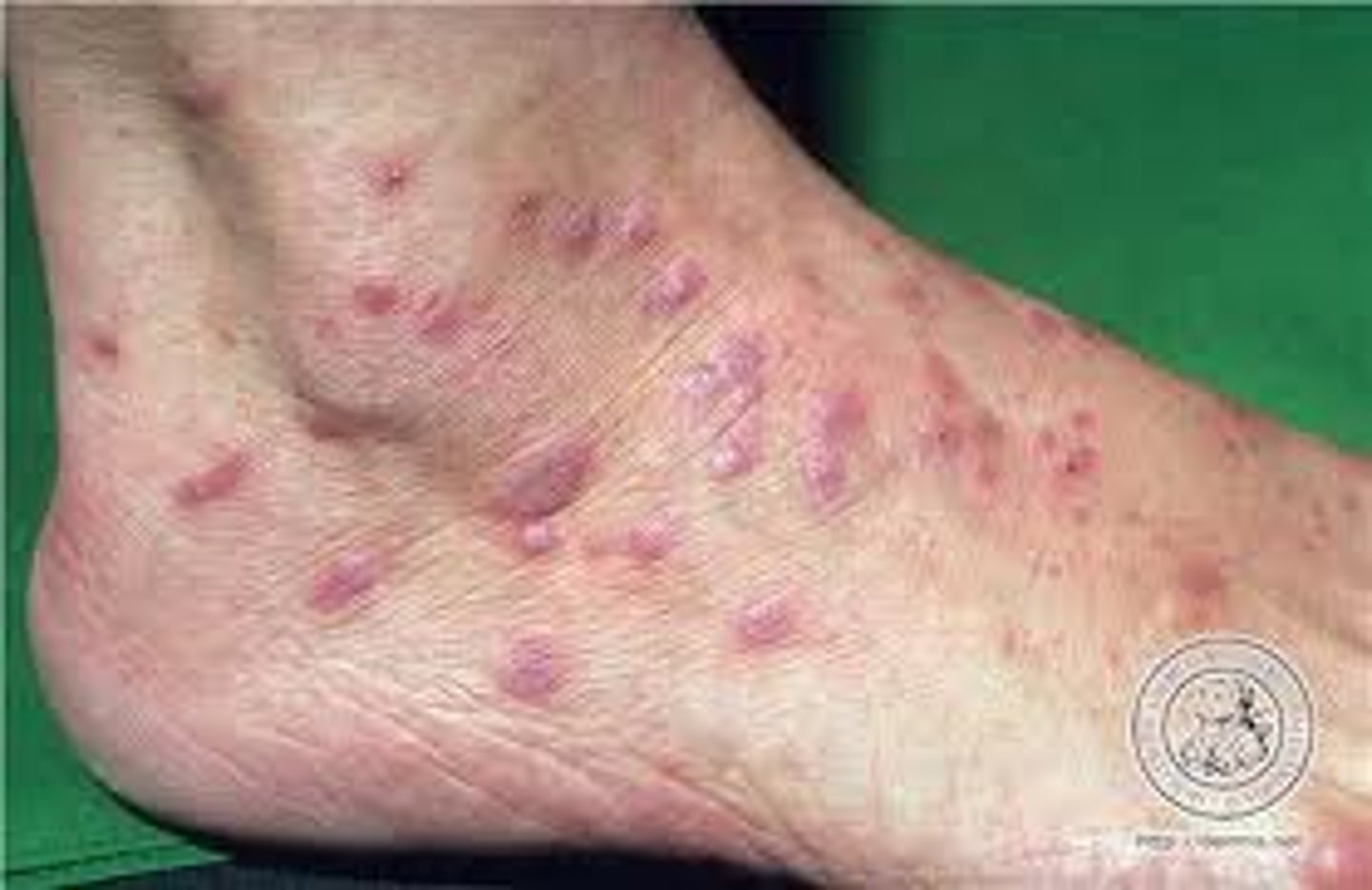
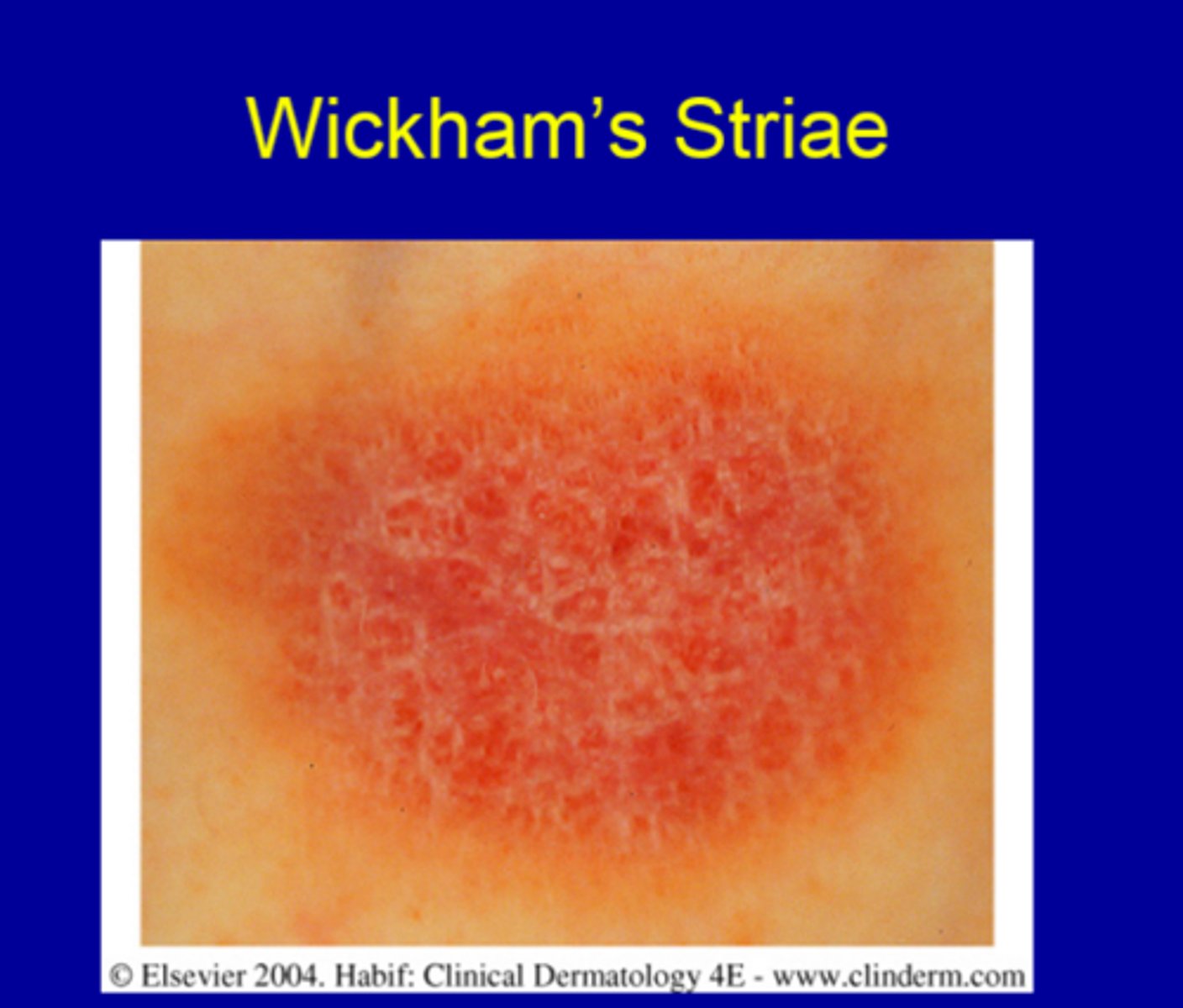
fine white lines on the skin lesions or oral mucosa seen in lichen planus is aka
Wickham striae
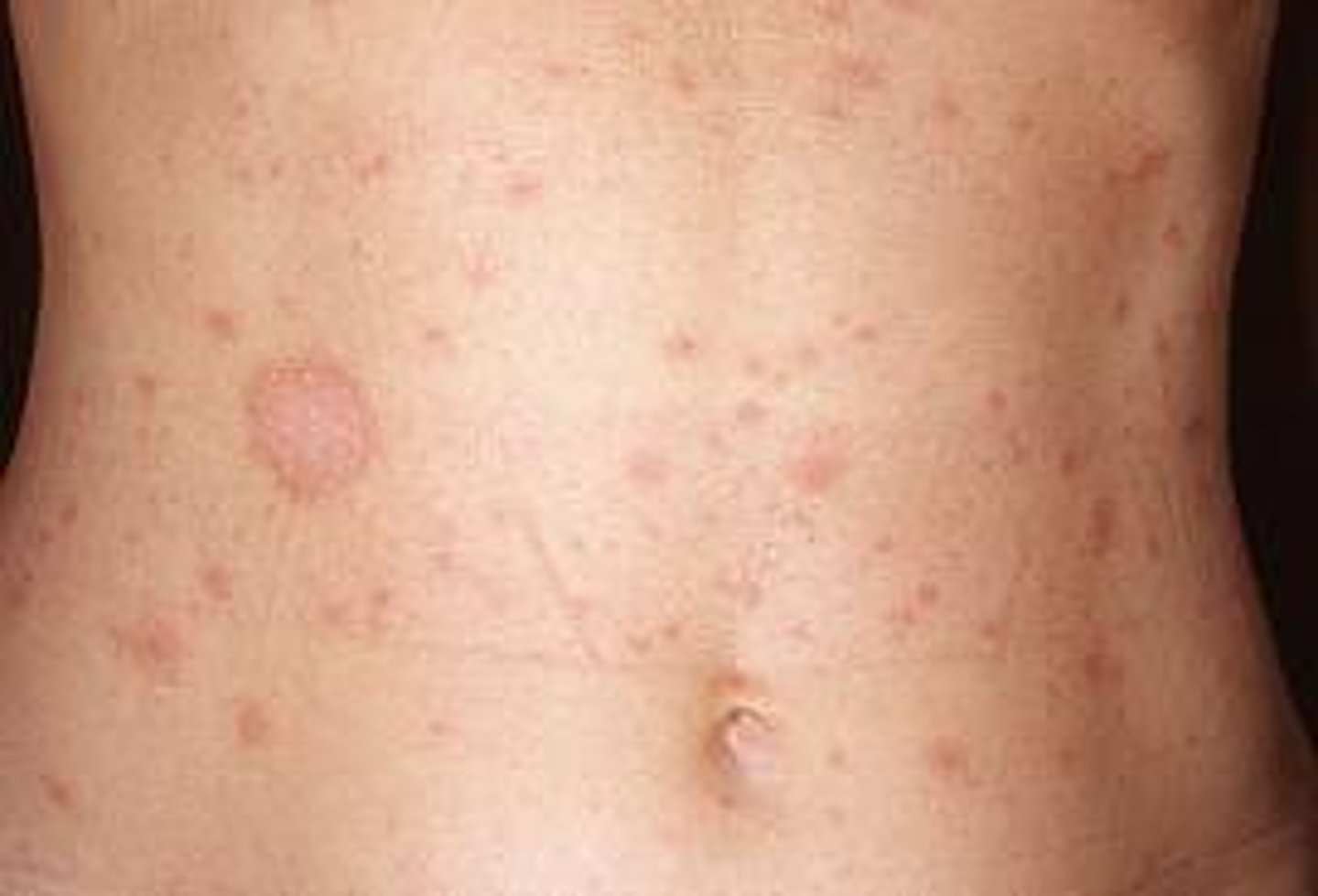
Dx? a rash that starts as a solitary salmon-colored macule on the trunk that is 2-6 cm in diameter and progresses to smaller, very pruritic 1cm round/oval salmon-colored papules with white circular (collarette) scaling along cleavage lines in a Christmas tree pattern that is confined to trunk and proximal extremities (sparing face) and usually resolved in 6-12 weeks; tx?
dx: pityriasis rosea
tx: symptomatic only: antihistamines for itching, topical corticosteroids, oatmeal baths, UVB if severe and initiated early on
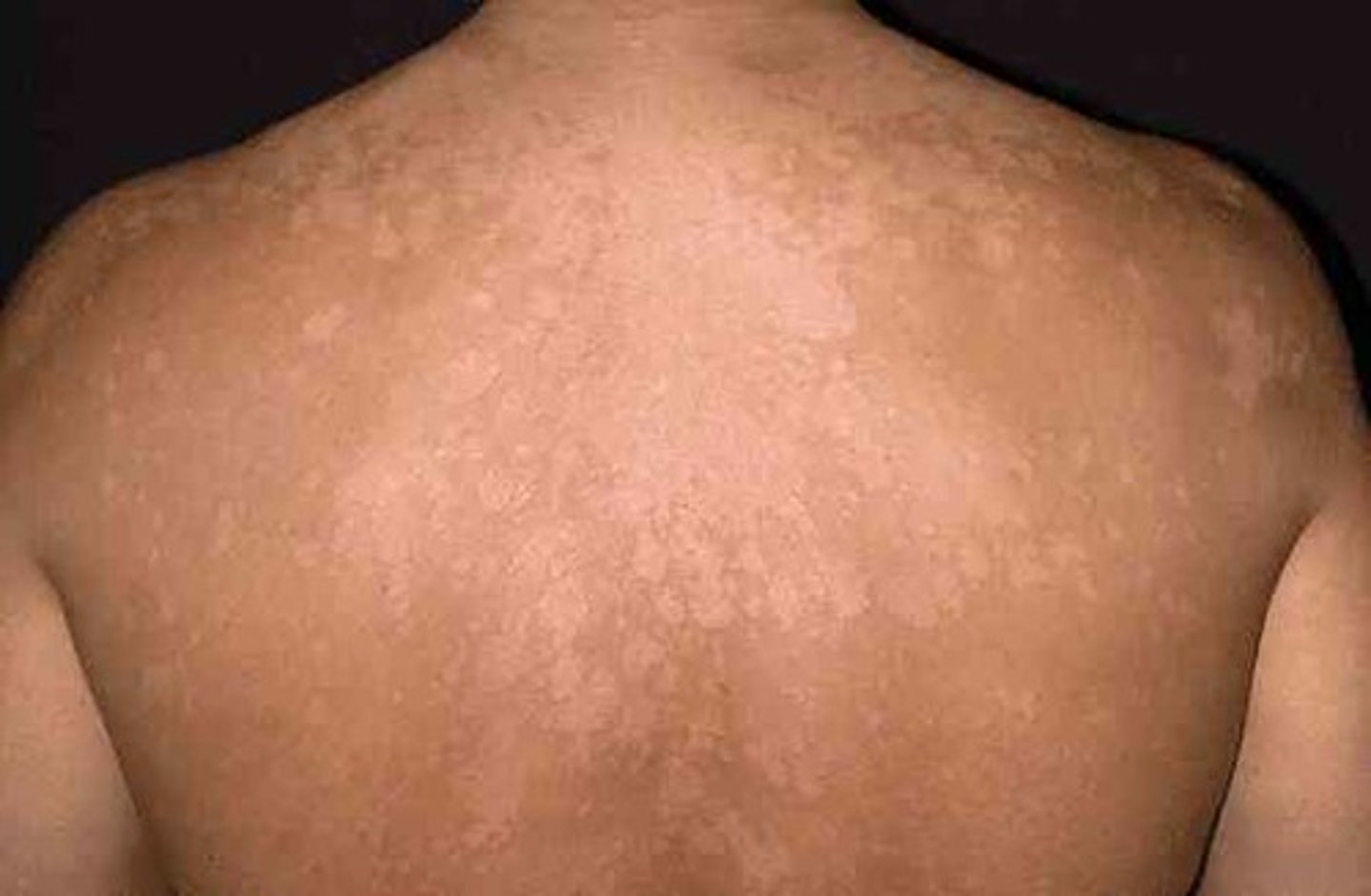
tinea versicolor is caused by an overgrowth of normal skin flora, a yeast called __________ that causes hypopigmented scaly patches to appear on trunk, face and extremities.
Malassezia furfur
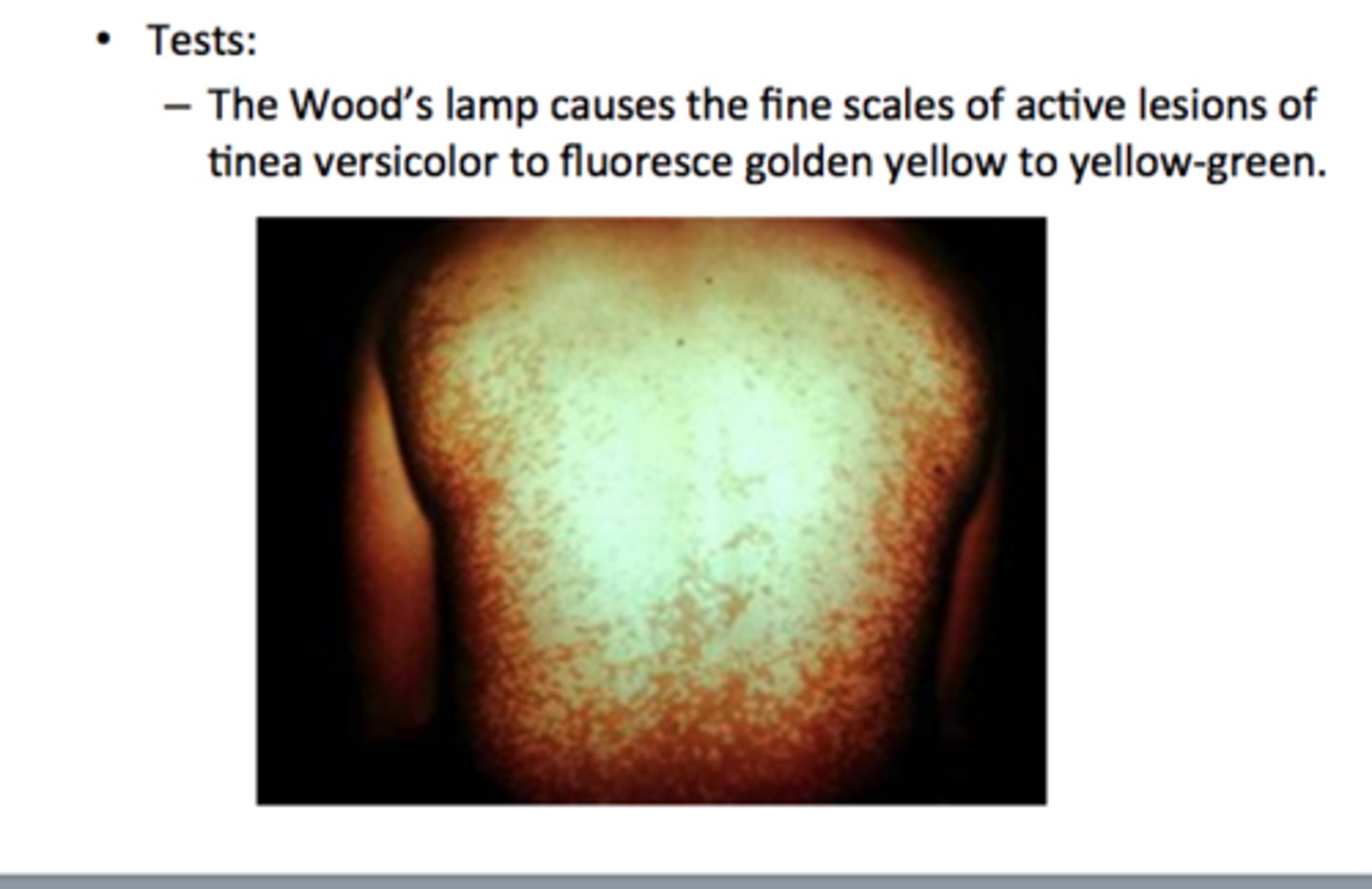
how is tinea versicolor worked up and diagnosed (besides PE) and treated?
-KOH prep from skin scraping showing hyphae and spores
-Woods lamp showing yellow-green fluorescence over affected spots
tx: topical antifungals: selenium sulfide, sodium sulfacetamide, zinc pyruthione, and "azoles"
if failed topicals: systemic antifungal therapy with itraconazole or fluconazole
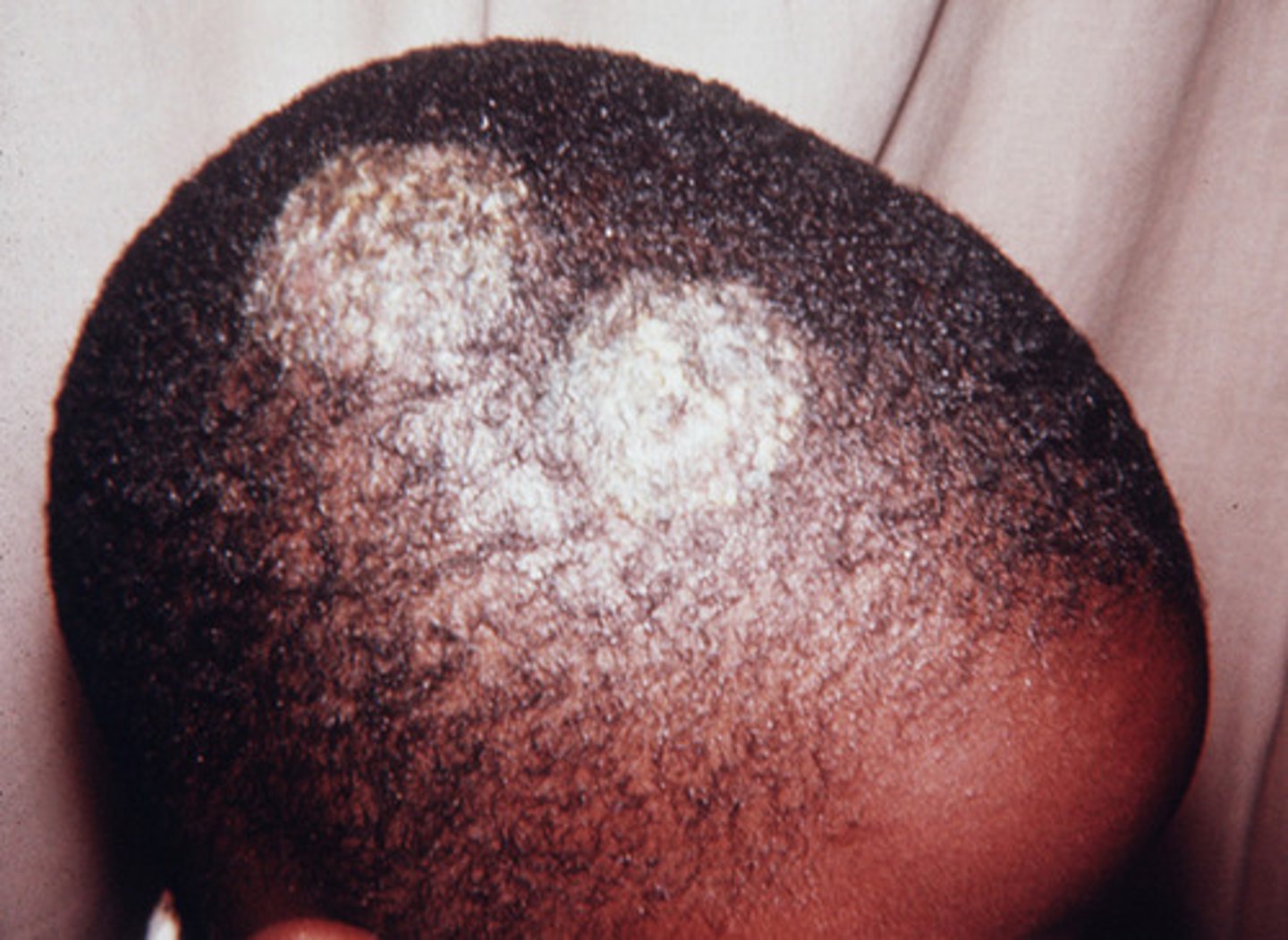
what is the 1st line tx for tinea capitis?
capitis: po griseofulvin (or terbinafine, itraconazole or fluconazole 2nd line)
all other tinea/dermatophytosis infxns are treated with topical antifungals unless failed then po antifungals (EXCEPT for onychomycosis- nail fungus)
what are the 3 types of impetigo? which is the MC type?
1. nonbullous- MC - characteristics "honey colored crust" - vesicles and pustules - MC cause is s. aureus, 2nd MC GABHS (strep. pyogenes)
2. bullous- vesciles turn into bullae then rupture into thin crusts - accompanying fever and diarrhea - s. aureus MC cause but rare and if seen will be in newborn/infants
3. ecthyma- ulcerative pyoderma caused by GABHS that will scar with healing - also rare
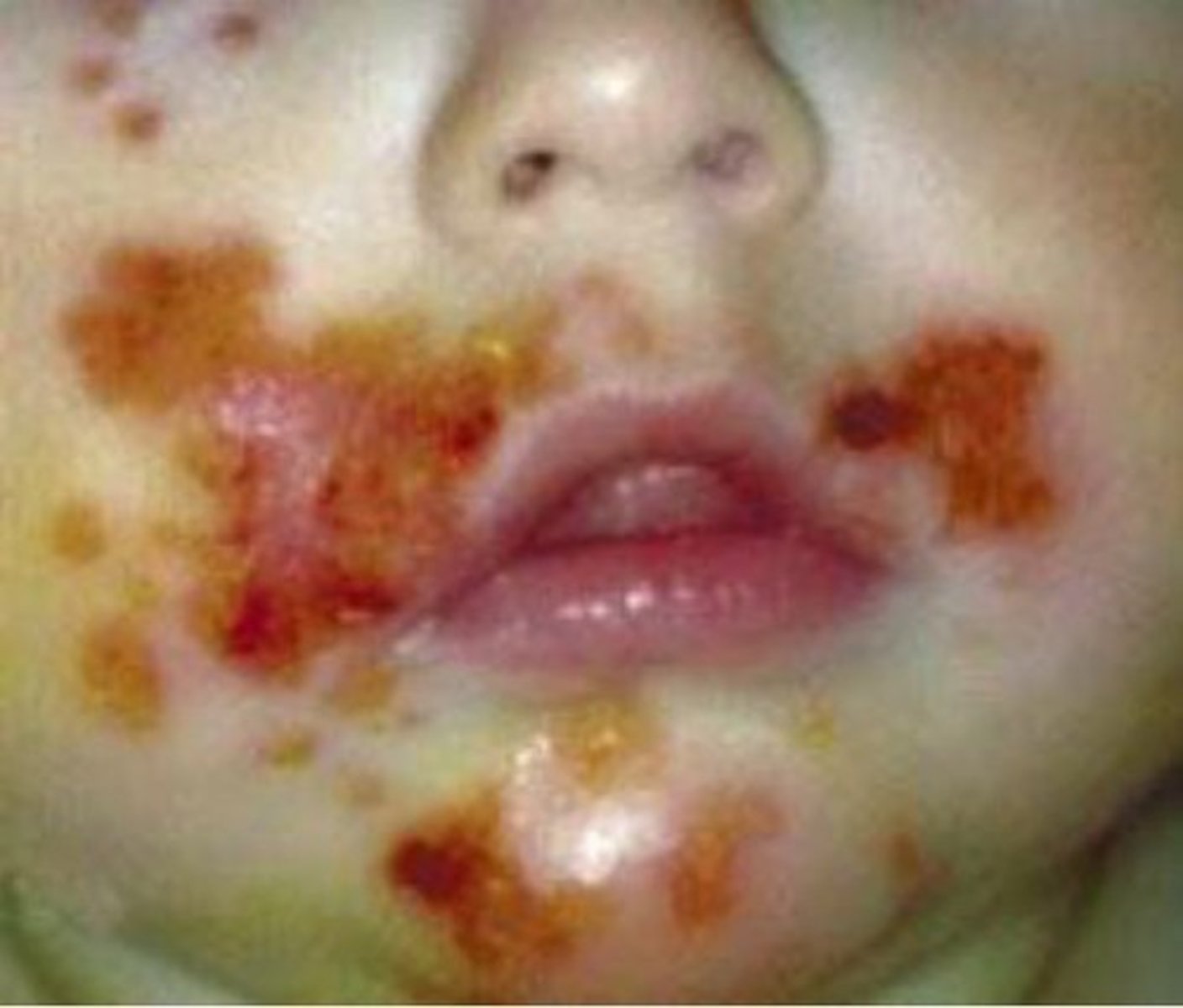
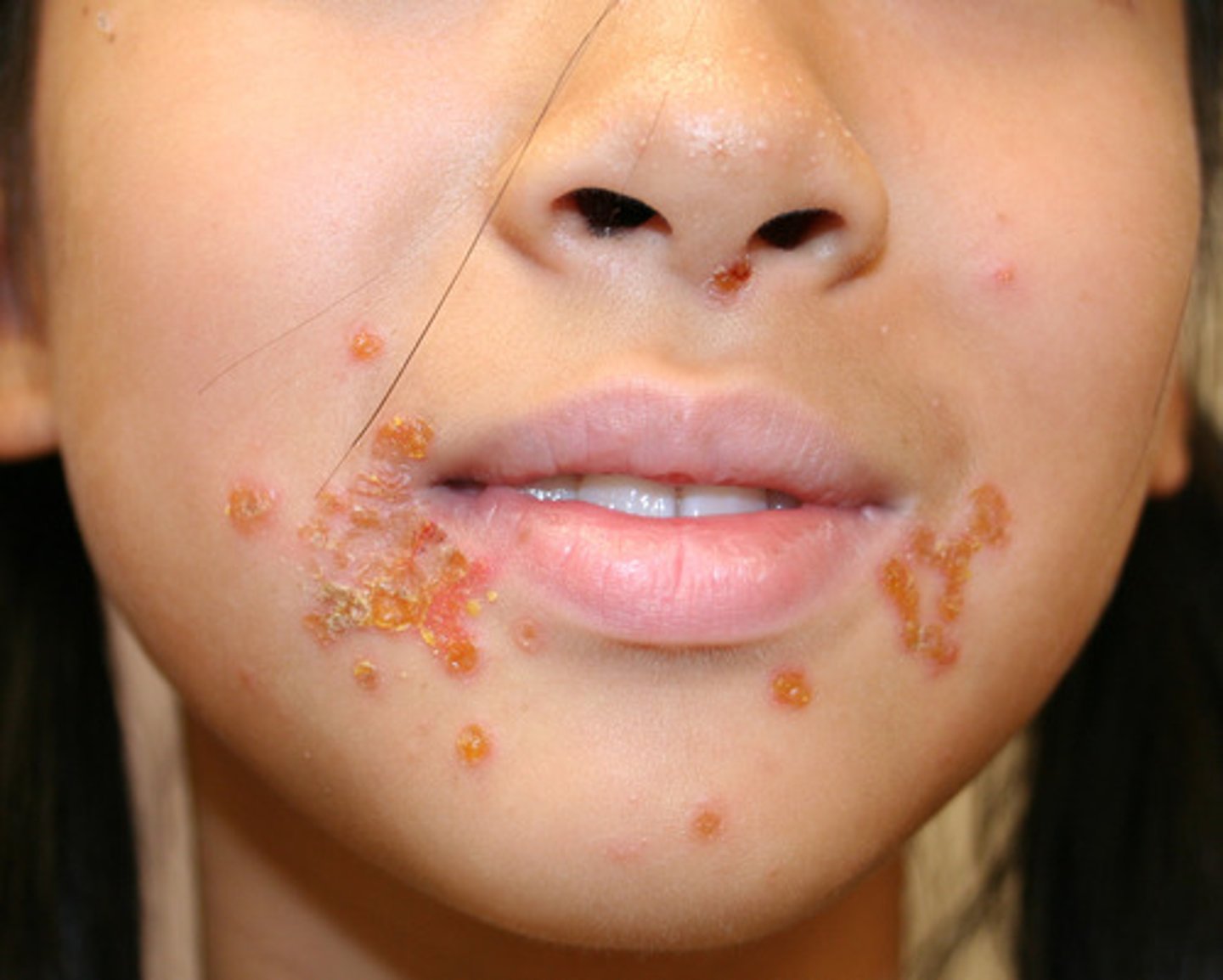
how is impetigo treated?
-topical mupirocin DOC TID x 10 days - can substitute for Bacitracin too
-if severe or systemic sxs (fever) give systemic antibiotics (cephalexin, dicloxacillin, clindamycin, erythromycin, azithromycin, clarithromycin)
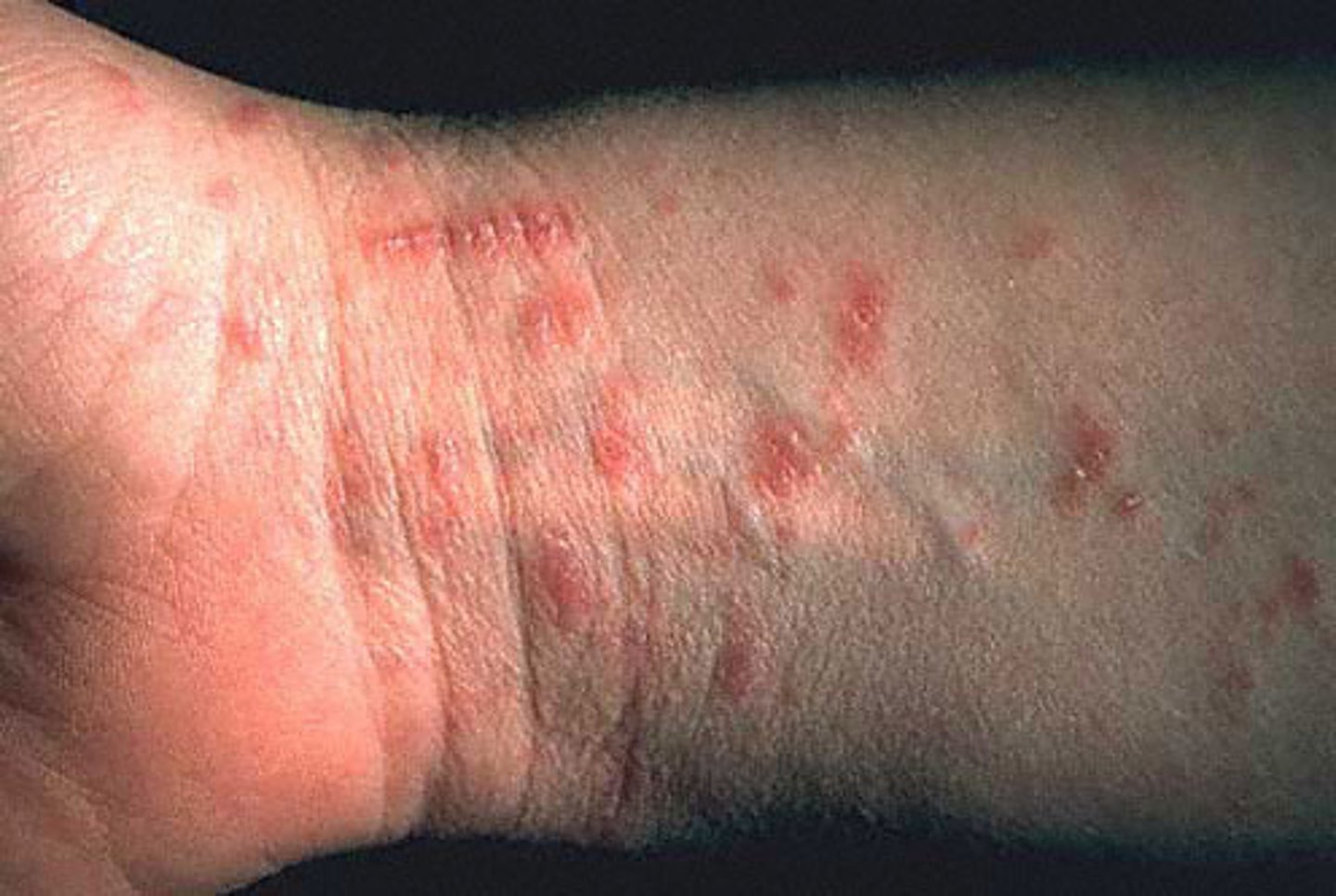
Dx? intensely pruritic papules, vesicles, and linear burrows commonly found in the intertrigous zones (between folds) including web spaces between fingers/toes, and scalp with increased itching at night- in males on scrotum, glans, or penile shaft; tx?
dx: scabies (caused by sarcoptes scabiei) - possible to see eggs/mites on scraping/microscopy w/ mineral oil
tx: DOC Permethrin cream applied from neck down and left on for 8-14 hrs before showing with repeat tx in 1 week + washing all bedding after storing in a bag for at least 72h; Lindane also indicated but more SE of seizure, teratogenic, etc; for pregnant women and infants 6-10% sulfur in petroleum jelly; oral ivermectin if extensive
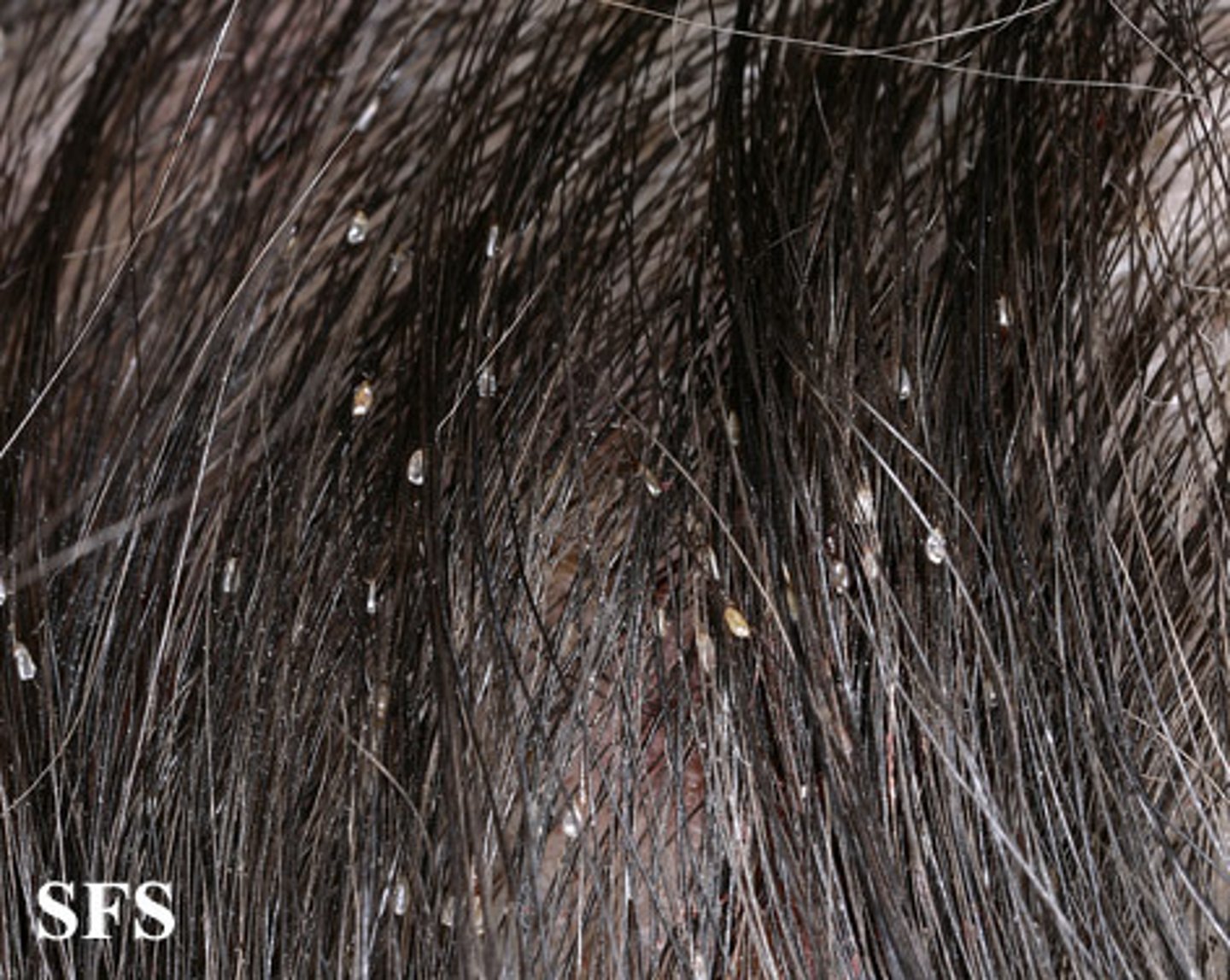
Dx? intense itching of the scalp, papular urticaria on scalp, white oval-shaped capsules at base of hair shafts; tx?
dx: lice (pediculosis)
tx: permethrin cream x 10 min unless infected elsewhere besides head then 8-10 hrs; Lindane cream 2nd line but neurotoxic; oral Ivermectin in refractory cases; wash all bedding/clothes & seal toys in plastic bag x 14 days
Dx? hair loss that occurs at temporal, mid-frontal, or vertex areas of scalp d/t dihydrotestosterone (DHT); tx?
dx: androgenetic alopecia
tx: minoxidil (rogaine) for recent onset and smaller area & oral finasteride (5-alpha reductase inhibitor aka androgen inhibitor)
I think they meant to put alopecia areata on the topic list instead of this which is autoimmune causing patchy hairloss seen in kids, MC in girls- treated w/ intralesional/topical corticosteroids or topical immunotherapy w/ allergen like squaric acid
what are the burn BSA percentages of infants/children?
18% entire head, 9% entire arm x 2, 36% entire trunk, 14% entire leg x 2
(in adults, 9% head, 9% arm x 2, 36% trunk, 18% leg x 2, genitalia 1%)
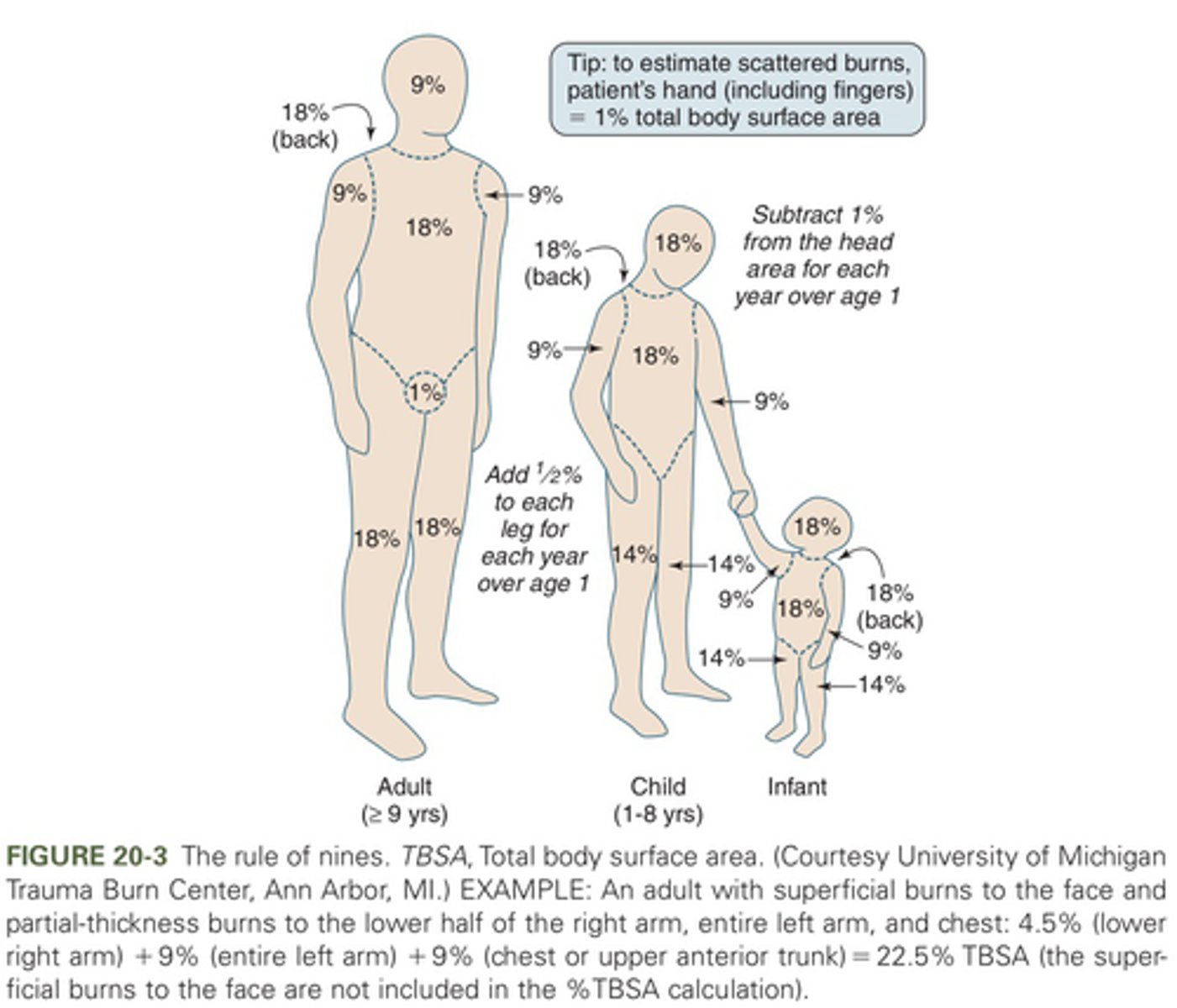
in infants/children, <____% TBSA burn is considered a minor burn but >____% TBSA burn is considered a major burn
minor: <5%
major: >20%
burns are best washed with? cool sterile compresses are used for? chemical burns are cleaned how?
-burns best washed with mild soap and water- disinfectant may inhibit healing
-cool sterile compresses to stop thermal burning but ice NOT recommended
-chemical burns cleaned/irrigated with running water for at least 20 min
what topical antibiotic is used for 2nd-3rd degree burns? superficial burns?
2nd/3rd: silver sulfadiazine unless <2 mos old, burn on face, or sulfa allergy
superficial: aloe vera and Bacitracin ointment
IV fluid resuscitation for children with moderate to severe burns is the same as adults using the Parkland formula which is:
LR 4mL/kg/%TBSA given IV first 24 hrs with 1/2 given first 8 hrs then other 1/2 given over the next 16 hrs
REMEMBER this is on top of the daily fluid requirement
roseola infantum (sixth's disease) is caused by
human herpes virus 6 or 7
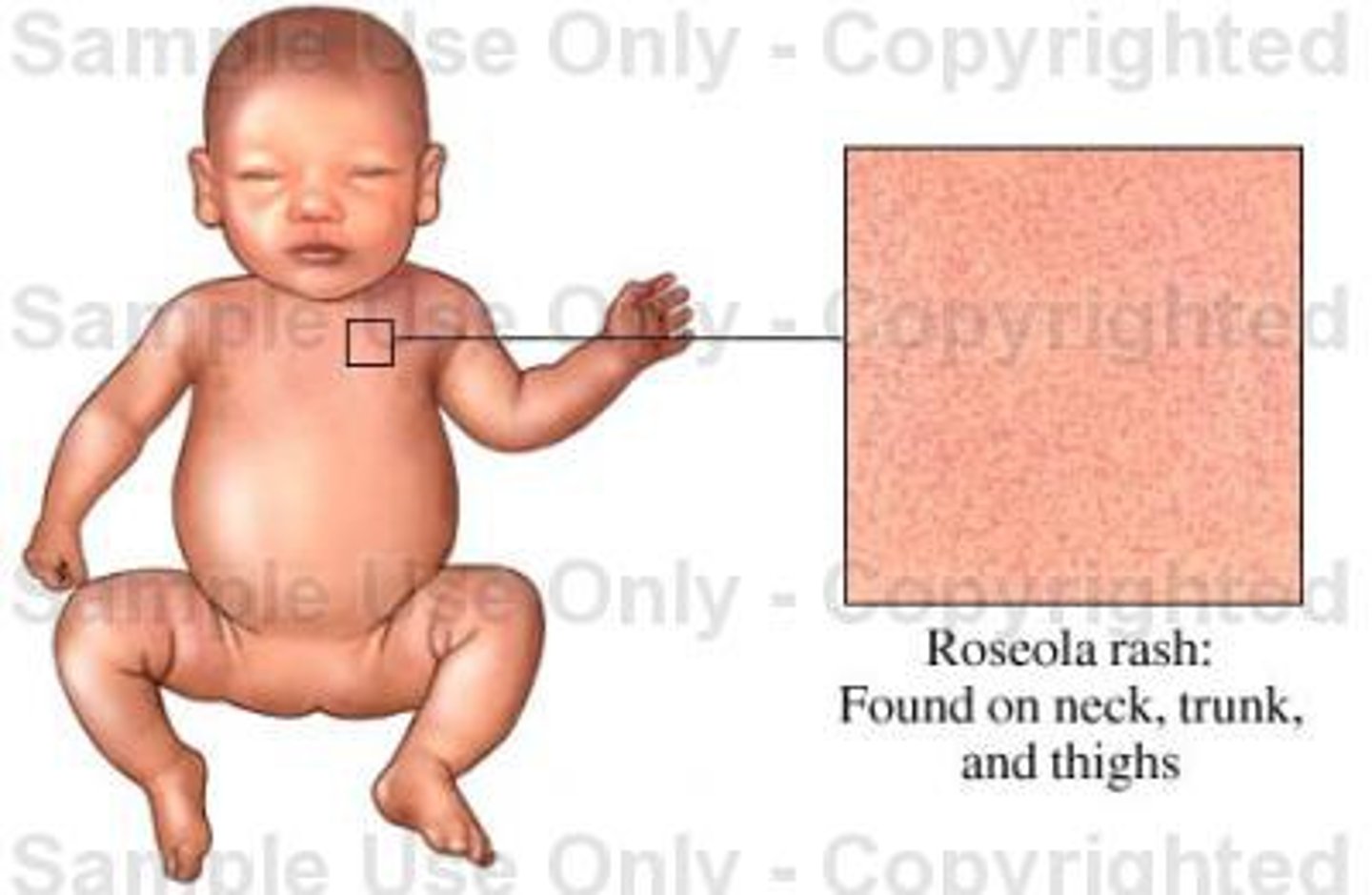
Dx? a 3 year old comes in with a h/o high fever that lasted 4 days and has broken but now has a rash that is rose/pink colored maculopapular and blanchable that started on the trunk/back and has spread to the face; tx?
dx: roseola infantum (sixth's disease) caused by human herpes virus 6 or 7 (this is the ONLY childhood exanthem that starts on trunk and spreads to face!)
tx: supportive, anti-inflammatory, anti-pyretic (to prevent febrile seizures)
coxsackie virus type A vs type B causes what conditions?
A: hand, foot, mouth disease & herpangina
B: pericarditits/myocarditis & pleurodynia
A & B: aseptic meningitis, rashes, common cold sx
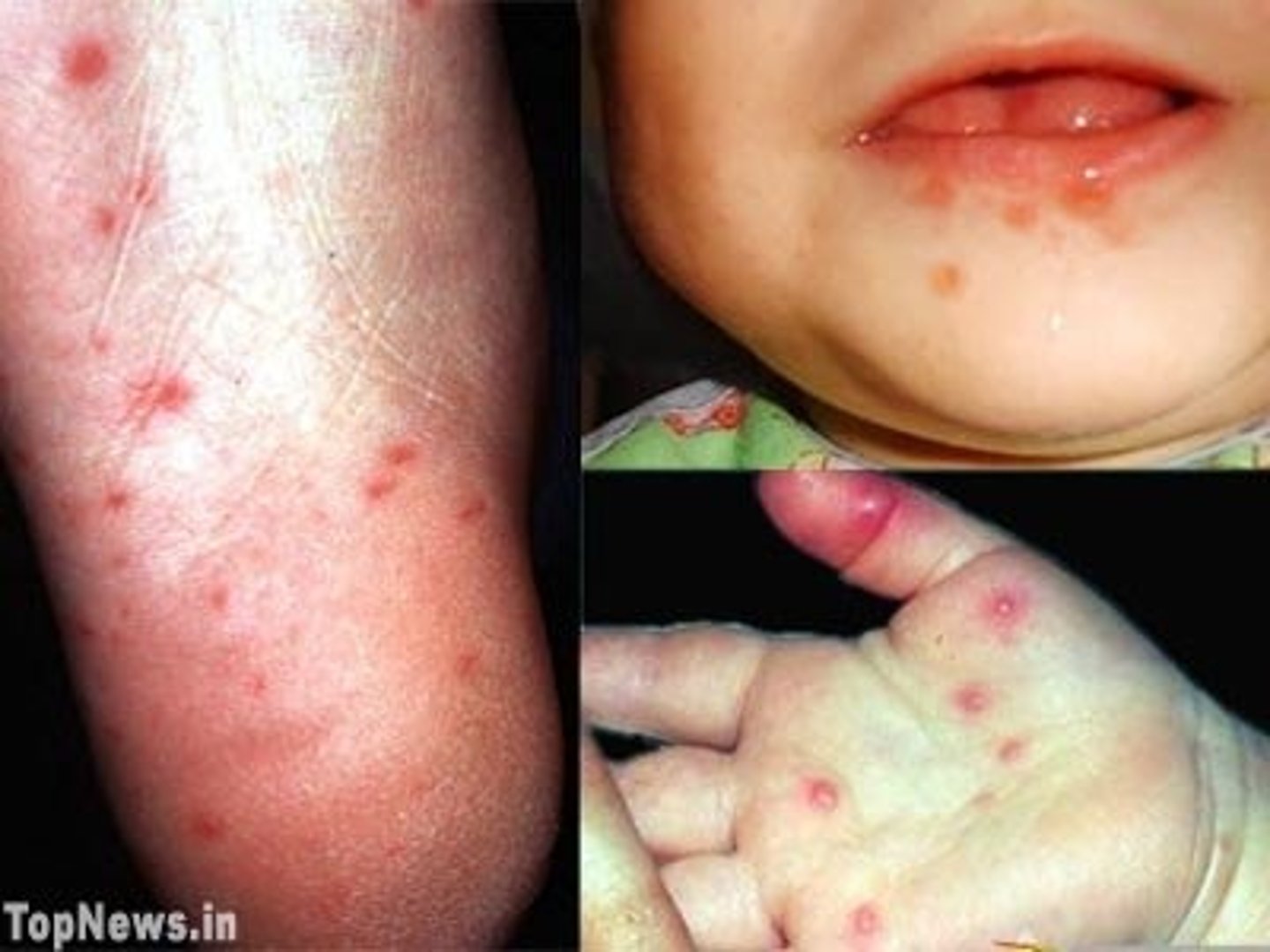
Dx? mild fever, URI sx, dec appetite, vesicular lesions with erythematous halos in oral cavity (esp buccal mucosa and tongue), exanthem 1-2 days later of vesicular, macular, or maculopapular lesions on distal extremitis (often includes palms and soles); tx?
dx: hand, foot, mouth disease (caused by coxsackie A)
tx: supportive (antipyretics, topical lidocaine)
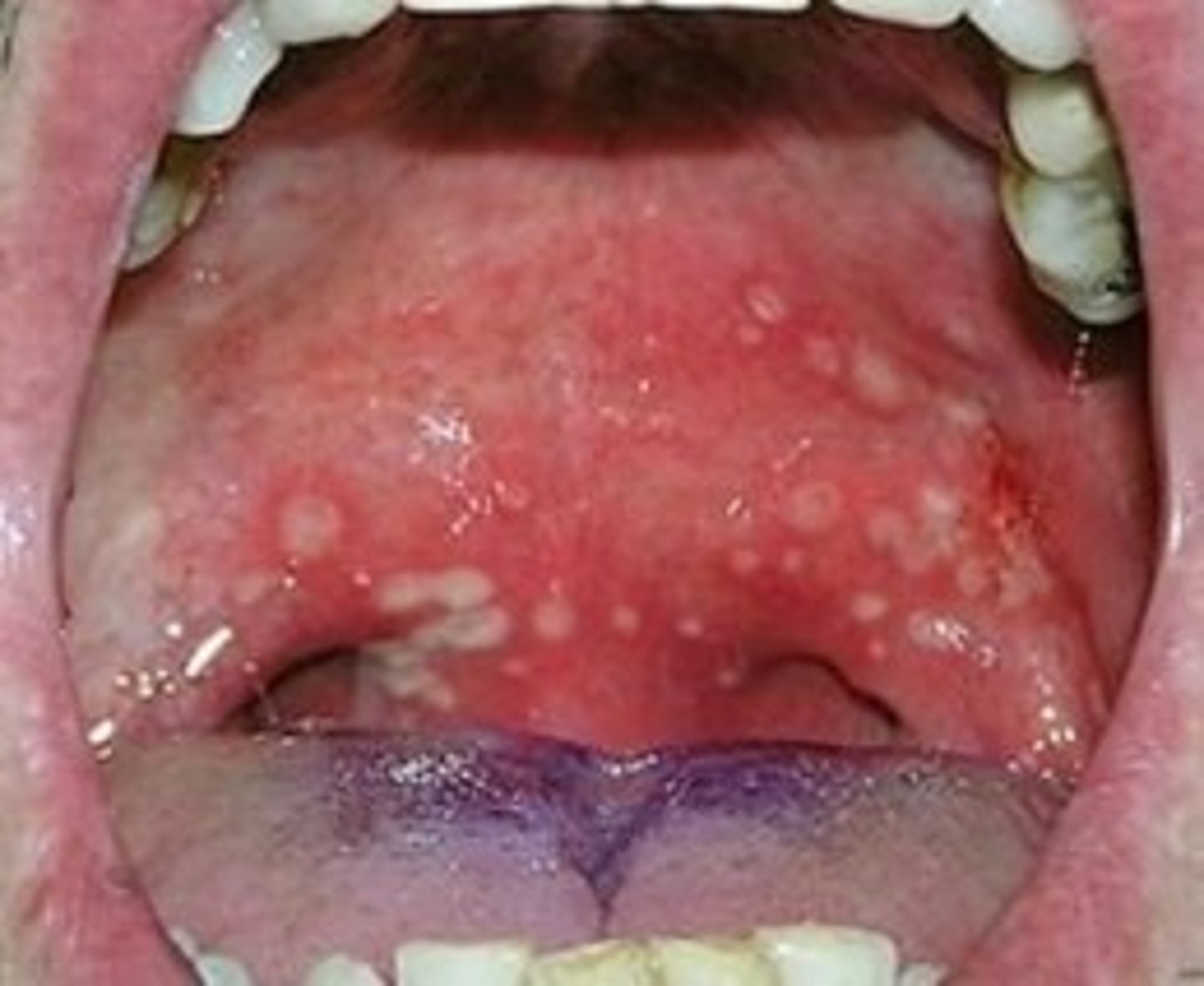
Dx? sudden onset of high fevers, stomatitis (small vesicles on soft palate, uvula & tonsillar pillars that ulcerate before healing), sore throat, lasting 3-5 days; tx?
dx: herpangina (caused by coxsackie A)
tx: supportive (antipyretics, topical lidocaine)
viral pericarditis/myocarditis in infants and children are most commonly caused by
coxsackie B
Dx? fever, severe pleuritic chest pain, paroxysmal spasms of chest/abdominal muscles including diaphragm, and HA; tx?
dx: pleurodynia (caused by coxsackie B)
tx: supportive (anti-pyretics, anti-inflammatories)
Dx? coryza, fever, rash on face/cheeks that appears like slapped cheeks with circumoral pallor 2-4 days, lacy reticular rash on extremities (esp UE) sparing palms/soles that resolves in 2-3 wks, arthralgias, associated fetal loss in pregnancy; tx?
dx: erythema infectiosum (fifth disease/slapped cheek syndrome) caused by parvovirus B19 - do serologies to confirm dx
tx: supportive, anti-inflammatories, anti-pyretics
in pts w/ sickle cell dz or G6PD deficiency, infection w/ parvovirus B19 may precipitate
aplastic crisis
Dx/cause? low grade fever, myalgias, HA, parotid gland pain/swelling; tx? what lab work supports dx? prevention?
dx: mumps (paramyxovirus)
tx: supportive, anti-inflammatories
labs: serologies, inc amylase
prevention: MMR vaccine at 12-15 mos and again at 4-6 y/o
what are some complications of mumps that can appear?
MC in older pts:
orchitis in males (unilateral), oophoritis, encephalitis, aseptic meningitis, MC cause of acute pancreatitis in children, deafness, arthritis, infertility
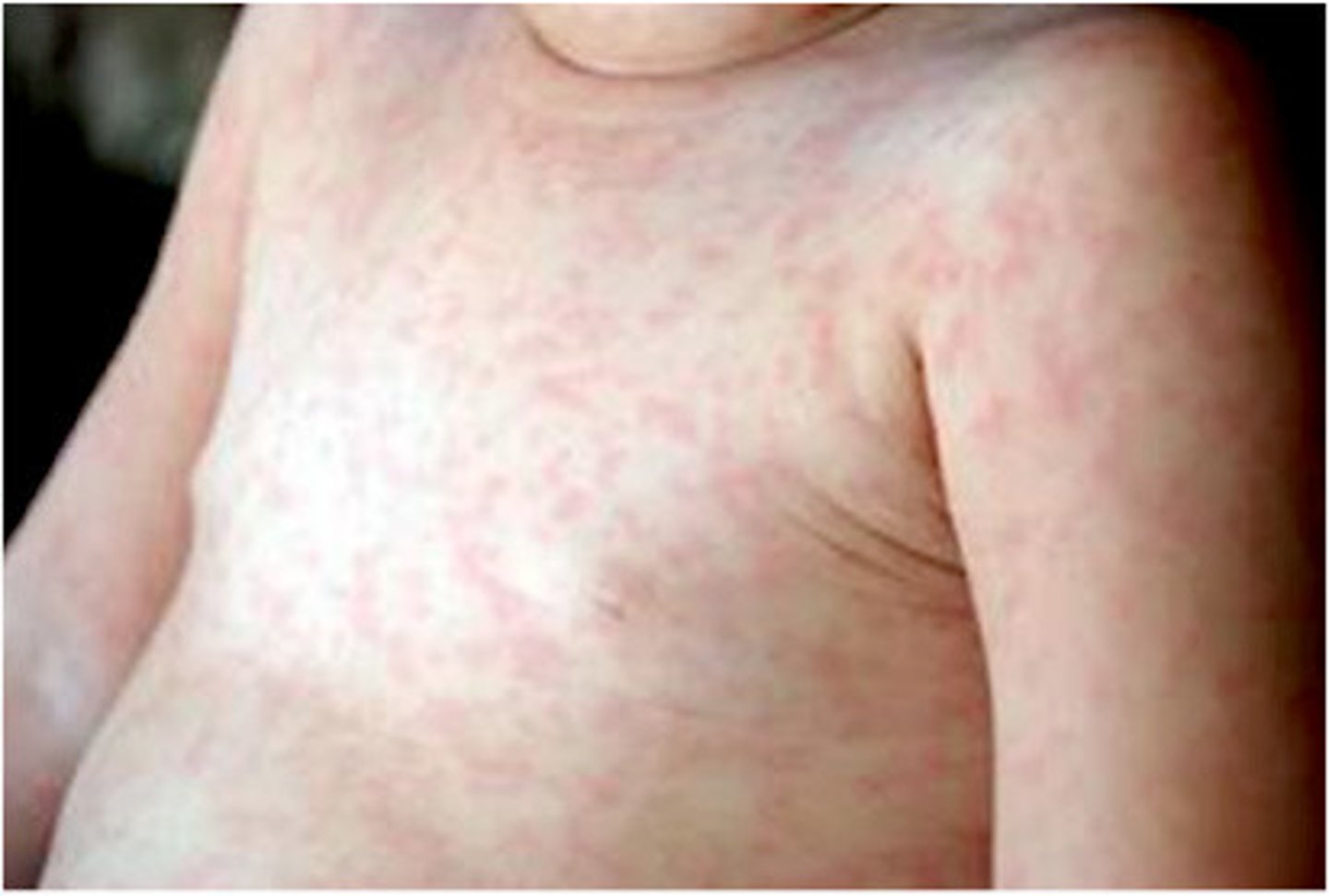
Dx? high fever, cough, coryza, conjunctivitis (3 Cs), koplik spots (small red spots in buccal mucosa w/ pale blue/white center, followed 1-2 days later by maculopapular/morbiliform brick-red rash on face beginning at hairline then moving to extremities lasting ~7 days coalescing and darkening then fading from top to bottom; tx?
dx: rubeola (measles) caused by paramyxovirus (same as mumps)
tx: supportive, anti-inflammatories, vitamin A (reduces mortality)
complications: diarrhea, otitis media, PNA, conjunctivitis, encephalitis
Dx? low grade fever, cough, anorexia, LAD (posterior cervical, posterior auricular), pink/lt red spotted maculopapular rash on face then to extremities that lasts 3 days, small red macules or petechiae on soft palate (Forchheimer spots), in young women +/- transient photosensitivity & joint pains; tx?
dx: rubella (german measles) caused by rubella virus
tx: supportive, anti-inflammatories
generally no complications