W3 pre: Ligand gated anion channels - GABA and gycine receptors
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Give two types of ligand anion channels
GABA receptors
glycine receptors
What do GABA receptors mediate the effects of?
Gamma - Amino Butyric Acid
State the main function of GABA
main inhibitory neurotransmitter in mammal brains
List 3 other agonists for GABA receptors
barbiturates
benzodiazepines
alcohol
What is the main function of glycine
main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the spinal cords of mammals
Give an example of an antagonist for glycine receptors
poison strychnine, which induces seizures
What is the effect of glycine?
motor control - induce hyperpolarisation and reducing neuronal firing
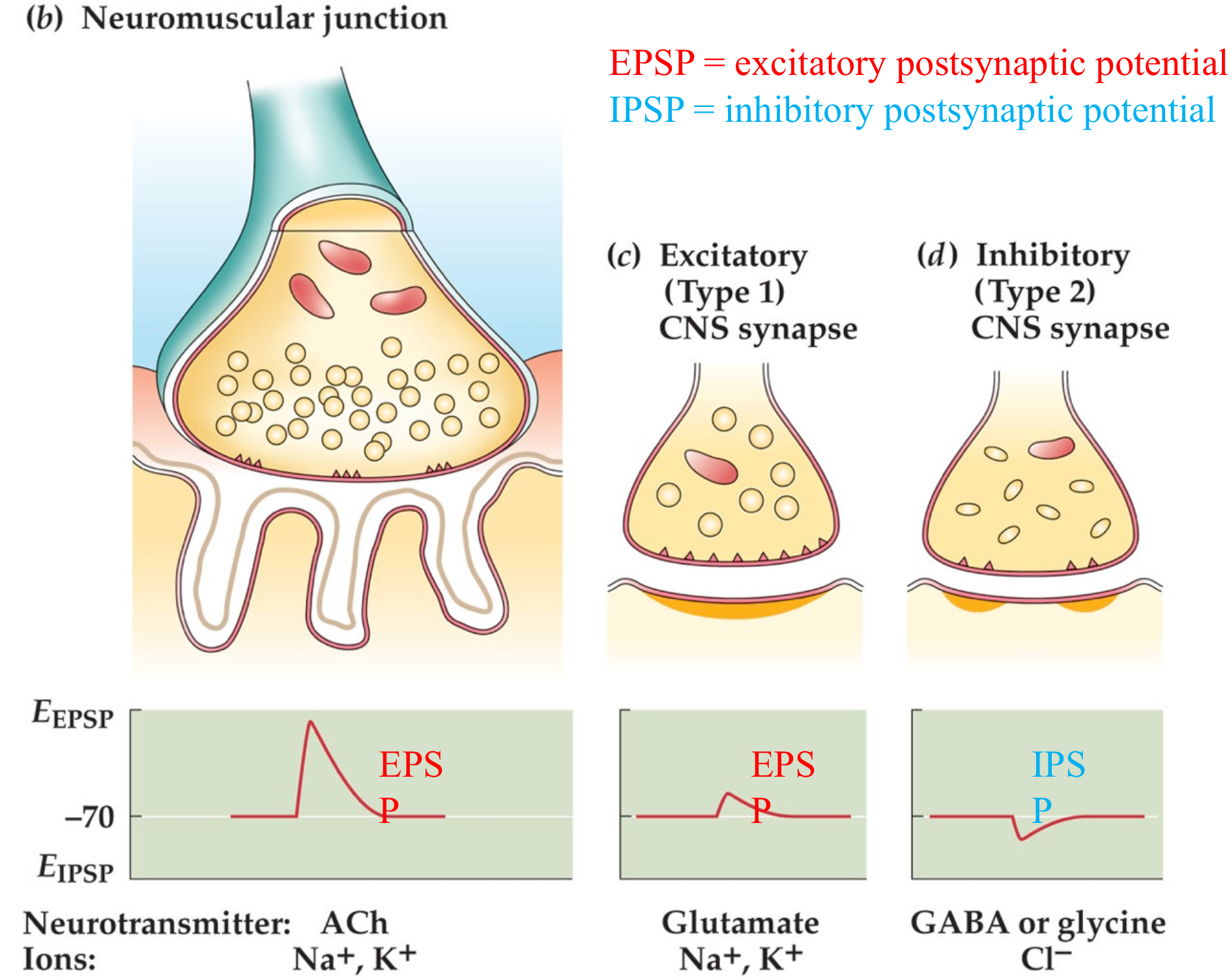
Define ionotropic receptors
binding of a signal to receptor results in change of ion flux into cell
Define metabotropic receptors
binding of a signal to receptor results in a change of enzyme activity within a cell
List 2 types of GABA receptors
A type and B type
GABA-B type receptors
metabotropic (G-protein coupled receptors)
GABA-A type receptors
ionotropic (permeable to Cl- ions)
List the 5 subunits that GABA-A receptors are comprised of and state the structure they form
α
β
γ
δ
ε
form a pentameric structure
What do GABA-A receptors share sequence similarity with?
nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
How many genes encode the α subunit of GABA-A receptors?
1-6
How many genes encode the β subunit of GABA-A receptors?
1-4
How many genes encode the γ subunit of GABA-A receptors?
1-4
How many genes encode the δ subunit of GABA-A receptors?
1
How many genes encode the ε subunit of GABA-A receptors?
1
What facilitates ligand binding in GABA-A receptors?
N terminus tail of all subunits
What subunit of GABA receptors are sensitive to ethanol
δ
What facilitates ligand binding in Glycine receptors?
N terminus tail of α subunits
How many glycine molecules are required for channel opening?
3
List the subunits within glycine receptors
3α
2β
What do phylogenetic analysis of glycine receptors reveal?
that they evolved from GABA-A receptors
How are pores of nAChRs selectively permeable to cations?
negatively charged acidic residues (glutamic acid) are important in conferring selective permeability to cations (sodium)
How are pores of GABA receptors selectively permeable to anions?
positively charged acidic residues (arginine) are important in conferring selective permeability to anions (chlorine)
What is ivermectin?
an anti parasitic agent and insecticide
How does ivermectin exert itself?
by binding and activating glutamate-gated chloride channels in invertebrates
How do inhibitory transmitters cause hyperpolarisation of the post synaptic cell?
triggering an inhibitory post-synaptic potential (IPSP), binding to channels that are permeable to anions
How do excitatory transmitters cause depolarisation of the post synaptic cell?
triggering an excitatory post-synaptic potential (EPSP), binding to channels that are permeable to cations
List two excitatory neurotransmitters
acetylcholine (neuromuscular transmitter in vertebrates)
glutamate (main excitatory transmitter in brain)
List two inhibitory neurotransmitters
GABA
Glycine
Discuss histamines in humans
act as an inflammatory mediator and neuromodulator that acts on G-protein coupled receptors
Discuss histamines in insects
act as an inhibitory neurotransmitter by causing chloride mediated hyperpolarisation