LC CHEMISTRY- FAMILIES AND ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
REBECCA'S LC CHEMSITRY SOME FAMILIES AND ORGANIC COMPOUNDS KNOWT
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
tetrahedral carbon
carbon atom which has tetrahedral geometry
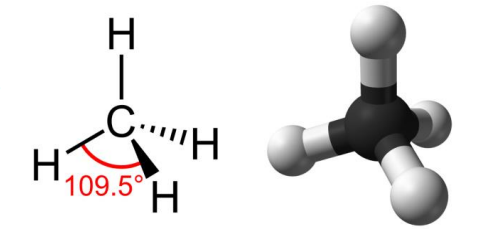
name the two types of tetrahedral carbons
chloroalkanes
alcohols
chloroalkane
compound in which one or more of the hydrogen atoms in an alkane have been replaced by chlorine atoms
chloroalkane examples
chloromethane, trichloromethane
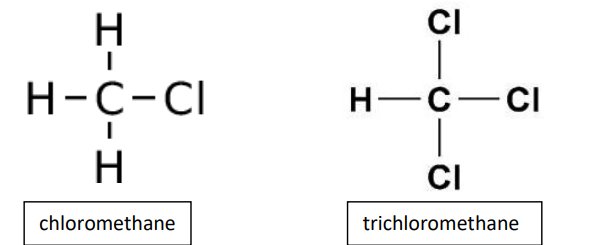
prefix for chlorine group
chloro
use for chloroalkane
industrial solvent, dry cleaning
physical properties of chloroalkane
weakly polar
not soluble in water
soluble in non-polar substances (cyclohexane)
liquids at room temp
functional group
an atom or a group of atoms which are responsible for the characteristic properties of an organic compound or a series of organic compounds
functional group of alchohol
-OH
alcohol ends in
ol
alcohol examples
methanol, propan-2-ol
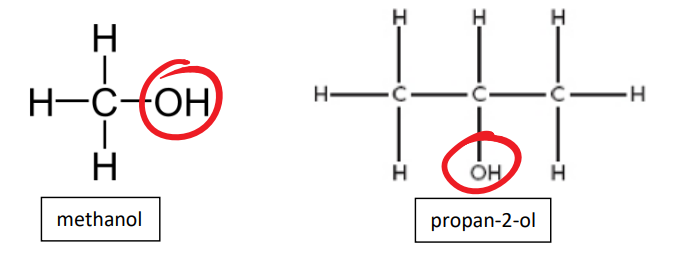
name the 3 types of alcohols
primary alcohols
secondary alcohols
tertiary alcohols
primary alcohols
an alcohol where the carbon atom bonded to the OH group is bonded to only 1 other carbon
secondary alcohols
an alcohol where the carbon atom bonded to the OH group is bonded to only 2 other carbon
teirtary alcohols
an alcohol where the carbon atom bonded to the OH group is bonded to only 3 other carbon
ethanol molecular formula
C2H5OH
what was added to stop the ingestion of ethanol and what happens
methanol, makes it toxic, ethanol is denatured and become methylated spirits
2 physical properties of alcohols
higher boiling points than their corresponding alkanes due to hydrogen bonding between the alcohol molecules
small alcohol molecules are soluble in water due to the hydrogen bonding between the molecules
larger alcohol molecules e.g butanol are not soluble in water as the effect of the hydrogen bonding decreases as the molecule gets bigger
planar carbon
carbon atom which has planar geometry, happens only when the carbon atom is unsaturated (contains a double or triple bond)
ketone functional group
CO-
name the 5 different types of planar carbons
aldehydes
ketones
carboxylic acids
esters
benzene and natural compounds containing benzene rings
aldehyde functional group
-CHO
aldehydes end in
al
aldehydes examples
ethanal propanal
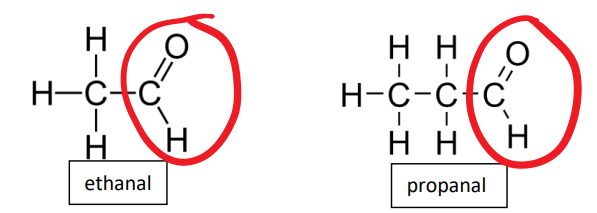
what key functional group in an aldehydes structure
carbonyl group
carbonyl group
highly polar C=O carbonyl group is always located at the end of the carbon chain in an aldehyde
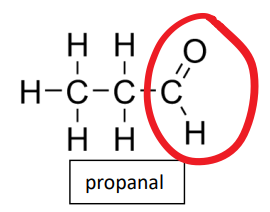
properties of aldehydes and ketones
aldehydes and ketones have higher boiling points than their corresponding alkanes because dipole-dipole forces in aldehydes are stronger than the weak Van der Waals forces in alkane
aldehydes and ketones have lower boiling points than their corresponding alcohols because dipole-dipole forces in aldehydes are weaker than the hydrogen bonds in alcohols
small aldehydes and ketones are water-soluble due to their polar carbonyl group, but as aldehydes get larger, their solubility decreases because the non-polar part of the molecule grows
aromatic
compound containing a benzene ring
aromatic aldehyde example
benzaldehyde
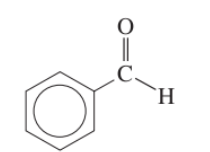
benzaldehyde description
smells like almonds as it is found in almond kernels. It is used as a flavouring agent.
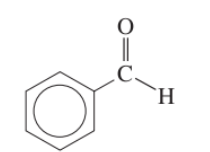
ketone functional group
CO-
ketone functional group ends in
one
ketones example
Propanone, Butan-2-one
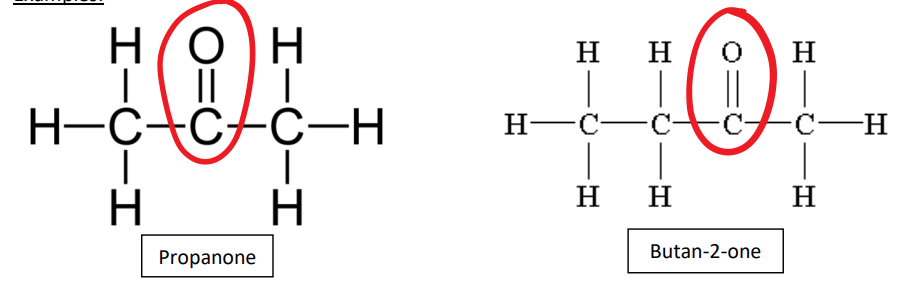
examples of keytones
propanone butan-2-one
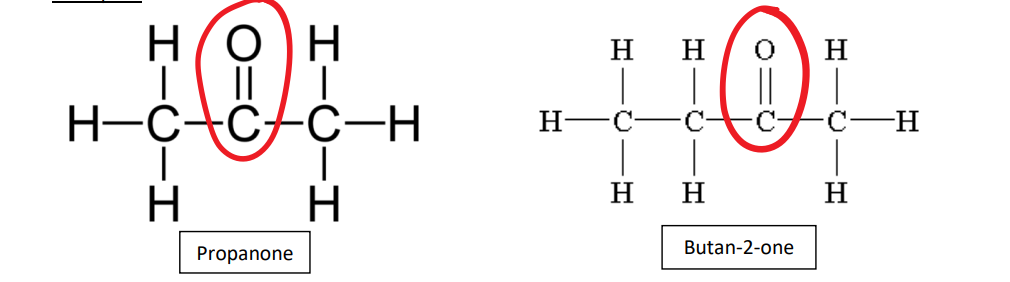
ketone uses
propanone (also called acetone) is used in nail polish remove
what key functional group in a ketone structure
carbonyl group
carbonyl group
carbonyl group in ketone
highly polar C=O carbonyl group is always located on one of the central carbons, and never at the end of the carbon chain in a ketone
carboxylic acids functional group
-COOH
carboxylic acids ending
-oic acids
carboxylic acids examples
methanoic acids, ethanoic acid
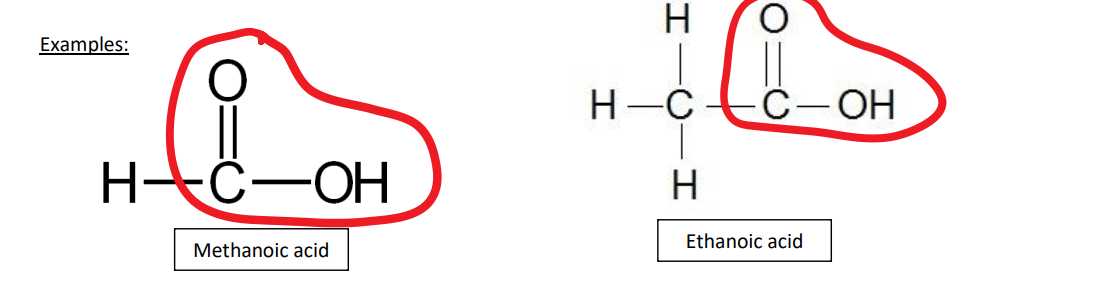
carboxylic acids uses
methanoic acid found in nettle and ant stings
ethanoic acid is used as a flavouring agent in vinegar
used to make cellulose acetate (camera film)
carbonyl group in carboxylic acids
highly polar C=O carbonyl group is always located at the end of the carbon chain in a carboxylic acid
properties of carboxylic acids
carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than alkanes, aldehydes, alcohols, and ketones due to strong hydrogen bonding between molecules.
small carboxylic acids are soluble in water due to hydrogen bonding, but solubility decreases as the carbon chain length increases
ester functional group
COOC
esters name ends in
-yl oate
esters examples
methyl ethanoate, ethyl methanoate
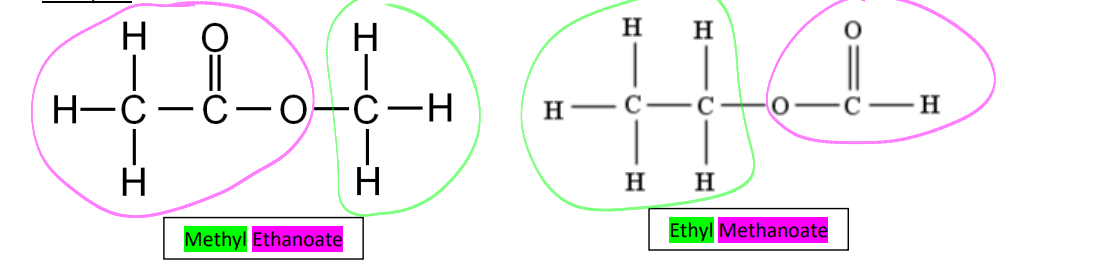
formation of esters
formed by reacting an alcohol with a carboxylic acid, with sulphuric acid being used as a catalyst. this reaction is called a condensation reaction because it results in the loss of a water molecule
uses of esters
used as flavourings and fragrances as they have sweet, fruity scents
fats and oils are naturally occurring esters
physical properties of esters
small esters are soluble in water due to dipole-dipole interactions between the polar C=O group and water molecules
as the carbon chain length increases, solubility decreases because the non-polar hydrocarbon portion outweighs the effect of the polar C=O group
large esters, such as fats and oils, are insoluble in water due to their extensive non-polar hydrocarbon structure